|
Arrubium (castra)
Arrubium was a fort in the Roman province of Moesia (today's Măcin, Romania), (later Scythia Minor) and was part of the defensive frontier system of the Moesian Limes along the Danube. See also *List of castra Castra (Latin, singular castrum) were military forts of various sizes used by the Roman army throughout the Empire in Europe, Asia and Africa. The largest castra were permanent legionary fortresses. Locations The disposition of the castra refl ... References *Oberländer-Târnoveanu, Ernest: Aspecte ale circulaţiei monetare greceşti în Dobrogea de Nord (sec. VI î.e.n - I e.n), Pontica, IX, Constanţa, 1978, p. 59-87. *Florescu, Radu: Limesul dunărean bizantin în vremea dinastiilor isauriană şi macedoneană, Pontica, XIX, Constanţa, 1986, p. 172. Notes External linksRoman castra from Romania - Google MapsEarth Roman auxiliary forts in Romania {{Dacia-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tabula Peutingeriana
' (Latin Language, Latin for 'The Peutinger Map'), also known as Peutinger's Tabula, Peutinger tablesJames Strong (theologian) , James Strong and John McClintock (theologian) , John McClintock (1880)"Eleutheropolis" In: ''The Cyclopedia of Biblical, Theological, and Ecclesiastical Literature''. NY: Haper and Brothers. Accessed 30 August 2024 via biblicalcyclopedia.com. and Peutinger Table, is an illustrated ' (ancient Roman road map) showing the layout of the ''cursus publicus'', the road network of the Roman Empire. The map is a parchment copy, dating from around 1200, of a Late antiquity, Late Antique original. It covers Europe (without the Iberian Peninsula and the British Isles), North Africa, and parts of Asia, including the Middle East, Persia, and the Indian subcontinent. According to one hypothesis, the existing map is based on a document of the 4th or 5th century that contained a copy of the world map originally prepared by Marcus Vipsanius Agrippa, Agrippa during the re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tulcea
Tulcea (; also known by #Names, alternative names) is a city in Northern Dobruja, Romania. It is the administrative center of Tulcea County, and had a population of 65,624 . One village, Tudor Vladimirescu, is administered by the city. It is one of six Romanian county seats List of cities and towns on the river Danube, lying on the river Danube. Names The city is known in Bulgarian, Russian and Ukrainian as Тулча, Romanization of Cyrillic, romanized: ''Tulcha''; in Greek as Αιγισσός, Romanization of Greek, romanized: ''Aigissós''; in Hungarian as ''Tulcsa''; and in Turkish as ''Tulça''. History Iron Age Tulcea was founded in the 7th century BC under the name of ''Aegyssus'', mentioned by Procopius. Ovid recorded a local tradition that ascribed its name to a mythical founder, Aegisos the Caspian. Roman period Aegyssus was built on a high hill, a strategic location for guarding the Danube particularly under the Romans. The amphorae discovered from 1st century ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
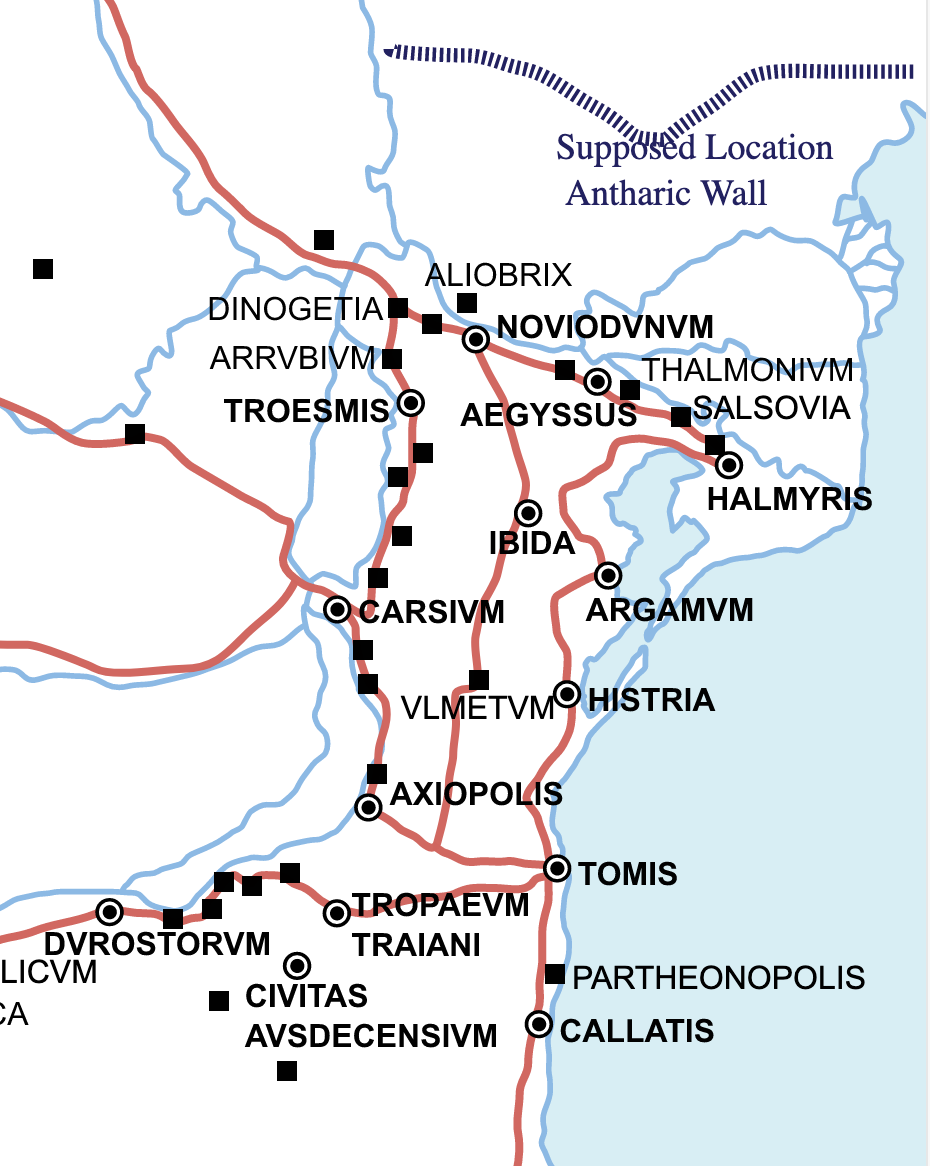
Eastern Moesia Around 100 AD
Eastern or Easterns may refer to: Transportation Airlines *China Eastern Airlines, a current Chinese airline based in Shanghai * Eastern Air, former name of Zambia Skyways *Eastern Air Lines, a defunct American airline that operated from 1926 to 1991 * Eastern Air Lines (2015), an American airline that began operations in 2015 *Eastern Airlines, LLC, previously Dynamic International Airways, a U.S. airline founded in 2010 * Eastern Airways, an English/British regional airline *Eastern Provincial Airways, a defunct Canadian airline that operated from 1949 to 1986 Roads *Eastern Avenue (other), various roads *Eastern Parkway (other), various parkways * Eastern Freeway, Melbourne, Australia * Eastern Freeway Mumbai, Mumbai, India Other *Eastern Railway (other), various railroads *, a cargo liner in service 1946-65 Education *Eastern University (other) *Eastern College (other) Sports * Easterns (cricket team), South African ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moesian Limes
The Moesian Limes () is the modern term given to a linked series of Roman forts on the northern frontier of the Roman province of Moesia along the Danube between the Black Sea shore and Pannonia (present-day Hungary) and dating from the 1st century AD. It was the eastern section of the so-called Danubian Limes and protected the Roman provinces of Upper and Lower Moesia south of the river. The eastern section (today in Romania) is often called the ''limes Scythiae minoris'' as it was located in the late Roman province of Scythia Minor. Characteristics The Moesian Limes includes essentially the linked forts and stations along the Danube from Singidunum (Belgrade) to the mouth of the Danube on the Black Sea. It was not fortified with palisades or a boundary wall but the forts were linked by a road and included eight legionary fortresses, many forts for auxiliary troops and watch/signal towers. Forts along the Danube are 10 to 30 km apart and inter-visibility does not often exis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scythia Minor (Roman Province)
Scythia Minor or Lesser Scythia (Greek: , ) was a Roman province in late Antiquity, occupying the lands between the lower Danube and the Black Sea, the modern-day Dobruja region in Romania and Bulgaria. It was detached from Moesia Inferior by the Emperor Diocletian to form a separate province sometime between 286 and 293 CE. The capital of the province was Tomis (modern-day Constanța). It ceased to exist around 679–681, when the region was overrun by the Bulgars, which the Emperor Constantine IV was forced to recognize in 681. According to the ''Laterculus Veronensis'' of and the ''Notitia Dignitatum'' of , Scythia belonged to the Diocese of Thrace. Its governor held the title of ''praeses'' and its '' dux'' commanded two legions, Legio I Iovia and Legio II Herculia. The office of ''dux'' was replaced by that of '' quaestor exercitus'', covering a wider area, in 536. The indigenous population of Scythia Minor was Dacian and their material culture is apparent archaeol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Romania
Romania is a country located at the crossroads of Central Europe, Central, Eastern Europe, Eastern and Southeast Europe. It borders Ukraine to the north and east, Hungary to the west, Serbia to the southwest, Bulgaria to the south, Moldova to the east, and the Black Sea to the southeast. It has a mainly continental climate, and an area of with a population of 19 million people. Romania is the List of European countries by area, twelfth-largest country in Europe and the List of European Union member states by population, sixth-most populous member state of the European Union. Europe's second-longest river, the Danube, empties into the Danube Delta in the southeast of the country. The Carpathian Mountains cross Romania from the north to the southwest and include Moldoveanu Peak, at an altitude of . Bucharest is the country's Bucharest metropolitan area, largest urban area and Economy of Romania, financial centre. Other major urban centers, urban areas include Cluj-Napoca, Timiș ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roman Province
The Roman provinces (, pl. ) were the administrative regions of Ancient Rome outside Roman Italy that were controlled by the Romans under the Roman Republic and later the Roman Empire. Each province was ruled by a Roman appointed as Roman governor, governor. For centuries, it was the largest administrative unit of the foreign possessions of ancient Rome. With the administrative reform initiated by Diocletian, it became a third level administrative subdivision of the Roman Empire, or rather a subdivision of the Roman diocese, imperial dioceses (in turn subdivisions of the Praetorian prefecture, imperial prefectures). History A province was the basic and, until the Tetrarchy (from AD 293), the largest territorial and administrative unit of the empire's territorial possessions outside Roman Italy. During the republic and early empire, provinces were generally governed by politicians of Roman senate, senatorial rank, usually former Roman consul, consuls or former praetors. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Castra
''Castra'' () is a Latin language, Latin term used during the Roman Republic and Roman Empire for a military 'camp', and ''castrum'' () for a 'Fortification, fort'. Either could refer to a building or plot of land, used as a fortified military base.. Included is a discussion about the typologies of Roman fortifications. In English language, English usage, ''castrum'' commonly translates to "Roman fort", "Roman camp" and "Roman fortress". Scholastic convention tends to translate ''castrum'' as "fort", "camp", "marching camp" or "fortress". Romans used the term ''castrum'' for different sizes of camps – including large Roman legion, legionary fortresses, smaller forts for Cohort (military unit), cohorts or for auxiliary forces, military camp, temporary encampments, and "marching" forts. The diminutive form ''castellum'' was used for fortlets, typically occupied by a detachment of a cohort or a ''centuria''. Etymology ''Castrum'' appears in Oscan language, Oscan and Umbrian ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Măcin
Măcin () is a town in Tulcea County, in the Northern Dobruja region of Romania. Location Măcin is located in the north-western part of the Northern Dobruja region, in Tulcea County. The city is located at the intersection of the DN22 ( E87) and national roads. The DN22 road links it to the Romanian capital, Bucharest (230 km to the West, via Brăila) and to cities of Isaccea and Tulcea (to the East). The DN22D road connects Măcin through a southern route with Tulcea and Constanța. Demographics According to the 2011 census, the town's population numbered 7,666 inhabitants, composed of 91.46% Romanians, 4.8% Roma, 2.92% Turks, and 0.37% Russian Lipovans. At the 2021 census, Măcin had a population of 7,248; of those, 75.95% were Romanians, 5.66% Roma, and 1.93% Turks. History The town is located on an ancient Celtic settlement, named '' Arrubium''. It was included in the Getic polities of Rhemaxos and Zyraxes, then conquered by the Roman Empire, who stationed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Legio V Macedonica
Legio V Macedonica (the Fifth Macedonian Legion) was a Roman legion. It was established in 43 BC by consul Gaius Vibius Pansa Caetronianus and Augustus, Gaius Julius Caesar Octavianus (later known as the Roman Emperor, Emperor Augustus). and based in the Balkan provinces of Macedonia (Roman province), Macedonia, Moesia and Dacia. In the Notitia Dignitatum records from beginning of the fifth century, the legion was still stationed in Dacia, with detachments stationed in the east and Egypt. The last known evidence shows the legion, or detachments from it, stationed in Egypt in the seventh century one or two years before the Islamic conquest of Egypt. It is often assumed that the legion fought in this war and was destroyed, although it is uncertain whether detachments or the whole legion were in Egypt, and there is no further evidence of the legion's eventual fate. Its symbol was the bull, but the eagle was used as well. History 1st century BC: Creation and deployment in Maced ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Troesmis (castra)
Troesmis was an ancient Dacian town and later ancient Roman city and legionary fortress, a major site situated on the Danube and forming a key part of the Limes Moesiae frontier system. Around the fortress the Geto-Dacian town developed. It is situated in what is now Romania near Igliţa-Turcoaia. Between 107 and 163 it was the home of the Roman Legio V Macedonica. The ''Notitia Dignitatum'' shows that in 337–361 it was the headquarters of Legio II Herculia.TOCILESCU 1883a, p. 101 History The ancient Dacian town of Troesmis was conquered by Lucius Pomponius Flaccus in about 15 AD, re-taken from the Getae and given to the Thracian king Rhescuporis II. After the conquest of Dacia in Trajan's Dacian Wars, he transferred the Legio V Macedonica from Oescus to Troesmis. Two settlements grew up near the legionary fortress, the ''canabae'' and the civil settlement called Troesmis. The legio V Macedonica left Troesmis in the 160s to take part in the Parthian war of Lucius Verus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Noviodunum (castra)
Noviodunum ad Istrum was a Roman city that developed around the legionary fortress and naval port near the present town of Isaccea. It was in the Roman province of Moesia and was the headquarters of the Roman Danube fleet ( Classis Flavia Moesica) located on the lower Danube and, from the 4th century AD, the headquarters of the Legio I Iovia (Scythica). From 46 AD the fortress was part of the Moesian Limes frontier defensive system on the Danube. In Late Antiquity the Imperial Road from Marcianopolis ended here. History Noviodunum passed under Roman control with the annexation of Thrace in 46 AD and then being attached to the Roman province of Moesia. The strategic position of the fort allowed the Romans to supervise and control the border of the entire Moesian Limes along this section of the Danube. It became the main port of '' Classis Flavia Moesica'' and a military centre of the region under Domitian, and after the conquest of Dacia by Trajan. Some '' vexillationes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |