|
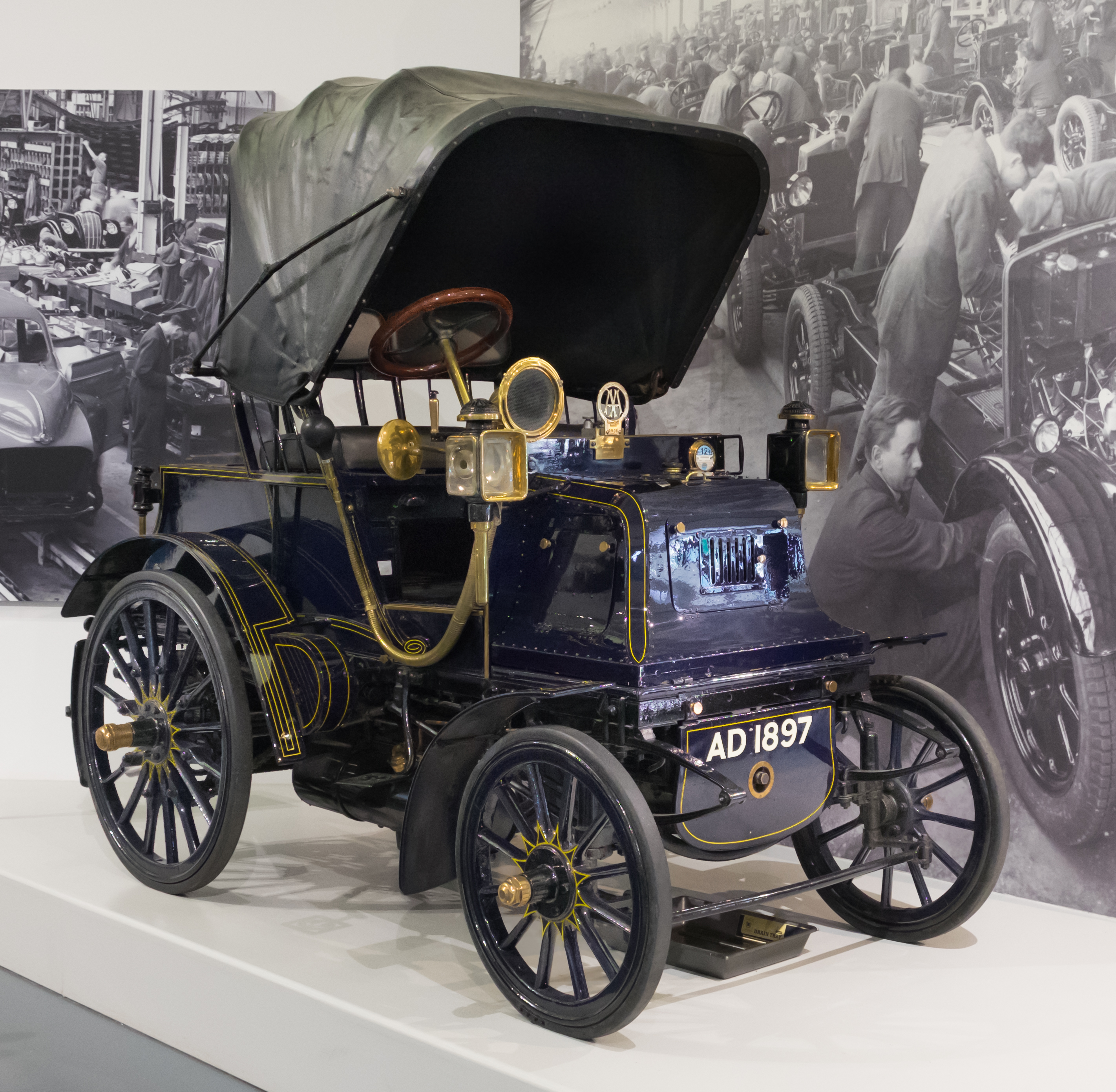
Apperson Six Sport Sedan
The Apperson Six Sport Sedan was a car manufactured by the Apperson Company of Kokomo, Indiana. Apperson Six Sport Sedan specifications (1926 data) * Color – Imperial blue, maroon, and gray-green * Seating Capacity – Five * Wheelbase – 120 inches * Wheels - Disc * 'Tires'' - 32” x 5.77” balloon * Service Brakes – Mechanical four wheel brakes * Engine - Six cylinder, vertical, cast en bloc, 3-3/16 x 4-1/4 inches; head removable; valves in head; H.P. 24.4 N.A.C.C. rating * Lubrication – Force feed * Crankshaft - Four bearing * Radiator – Tubular * Cooling – Thermo-syphon * Ignition system – Storage Battery * Starting System – Two Unit * Voltage – Six to eight * Wiring System – Single * Gasoline System – Vacuum * Clutch – Disc * Transmission – Selective sliding * Gear Changes – 3 forward, 1 reverse, mechanically operated * Drive – Spiral bevel * Rear Springs – Three-quarter elliptic * Rear Axle – Semi-floating * Steering Gear – Wor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Apperson
The Apperson was a brand of American automobile manufactured from 1901 to 1926 in Kokomo, Indiana. Company history The company was founded by the brothers Edgar and Elmer Apperson shortly after they left Haynes-Apperson; for a time they continued to use a FR layout-mounted flat-twin engine, following it with a horizontal four. Apperson cars In 1904, Apperson offered vertical fours in two models. The 1904 ''Apperson Touring Car'' was a touring car model. Equipped with a tonneau, it could seat 6 passengers and sold for US$6000. The vertical-mounted straight-4, situated at the front of the car, produced 40 hp (29.8 kW). A 4-speed transmission was fitted. The steel-framed car weighed 2800 lb (1270 kg). The wheel base was 96 inches. The Apperson offered electric lights, a novelty for the time, and used a modern cellular radiator. The 25 hp (18.6 kW) version weighed 1800 lb (816 kg) and sold for US$3500. In 1906 the company catalo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
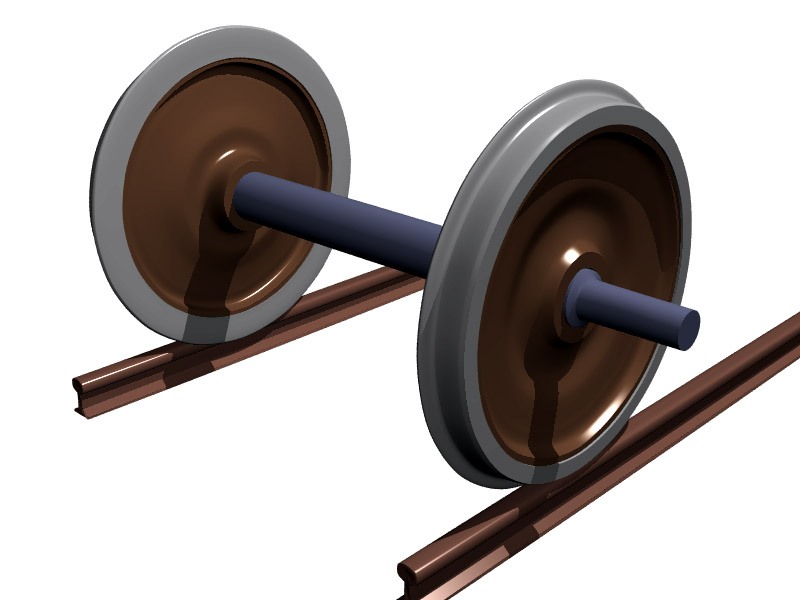
Axle
An axle or axletree is a central shaft for a rotation, rotating wheel and axle, wheel or gear. On wheeled vehicles, the axle may be fixed to the wheels, rotating with them, or fixed to the vehicle, with the wheels rotating around the axle. In the former case, bearing (mechanical), bearings or Bushing (bearing), bushings are provided at the mounting points where the axle is supported. In the latter case, a bearing or bushing sits inside a central hole in the wheel to allow the wheel or gear to rotate around the axle. Sometimes, especially on bicycles, the latter type of axle is referred to as a ''spindle (tool), spindle''. Terminology On cars and trucks, several senses of the word ''axle'' occur in casual usage, referring to the shaft itself, its housing, or simply any transverse pair of wheels. Strictly speaking, a shaft that rotates with the wheel, being either Bolt (fastener), bolted or rotating spline, splined in fixed relation to it, is called an ''axle'' or ''axle shaft ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brougham (car Body)
A brougham () was originally a car body style where the driver sat outside and passengers seated within an enclosed cabin, — deriving the configuration from the earlier brougham (carriage), ''brougham'' horse-drawn carriage. Similar in style to the later Coupe de Ville, town car, the brougham style was used on chauffeur-driven petrol and electric cars. In later years, several manufacturers (mostly in the United States) have used the term brougham as a prestigious Car model, model name or luxurious Automotive trim nomenclature, trim level on cars where the driver is in the cabin with the passengers (i.e. cars that do not use the brougham body style). Early broughams As a car body style, a brougham was initially a vehicle similar to a limousine but with an outside seat in front for the chauffeur and an enclosed cabin behind for the passengers. As such, it was a version of the town car but, in its earliest incarnation, with the sharply squared rear end of the roof and the forw ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phaeton Body
A phaeton is a style of open automobile without any fixed weather protection, which was popular from the 1900s until the 1930s. It is an automotive equivalent of the horse-drawn fast, lightweight phaeton carriage. A popular style in the US from the mid–1920s and continuing into the first half of the 1930s was the dual cowl phaeton, with a cowl separating the rear passengers from the driver and front passenger. Phaetons fell from favour when closed cars and convertible body styles became widely available during the 1930s. Eventually, the term "phaeton" became so widely and loosely applied that almost any vehicle with two axles and a row or rows of seats across the body could be called a phaeton. Convertibles and pillarless hardtops were sometimes marketed as "phaetons" after actual phaetons were phased out. History The term ''phaeton'' had historically described a light, open four-wheeled carriage. When automobiles arrived it was applied to a light two-seater with m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
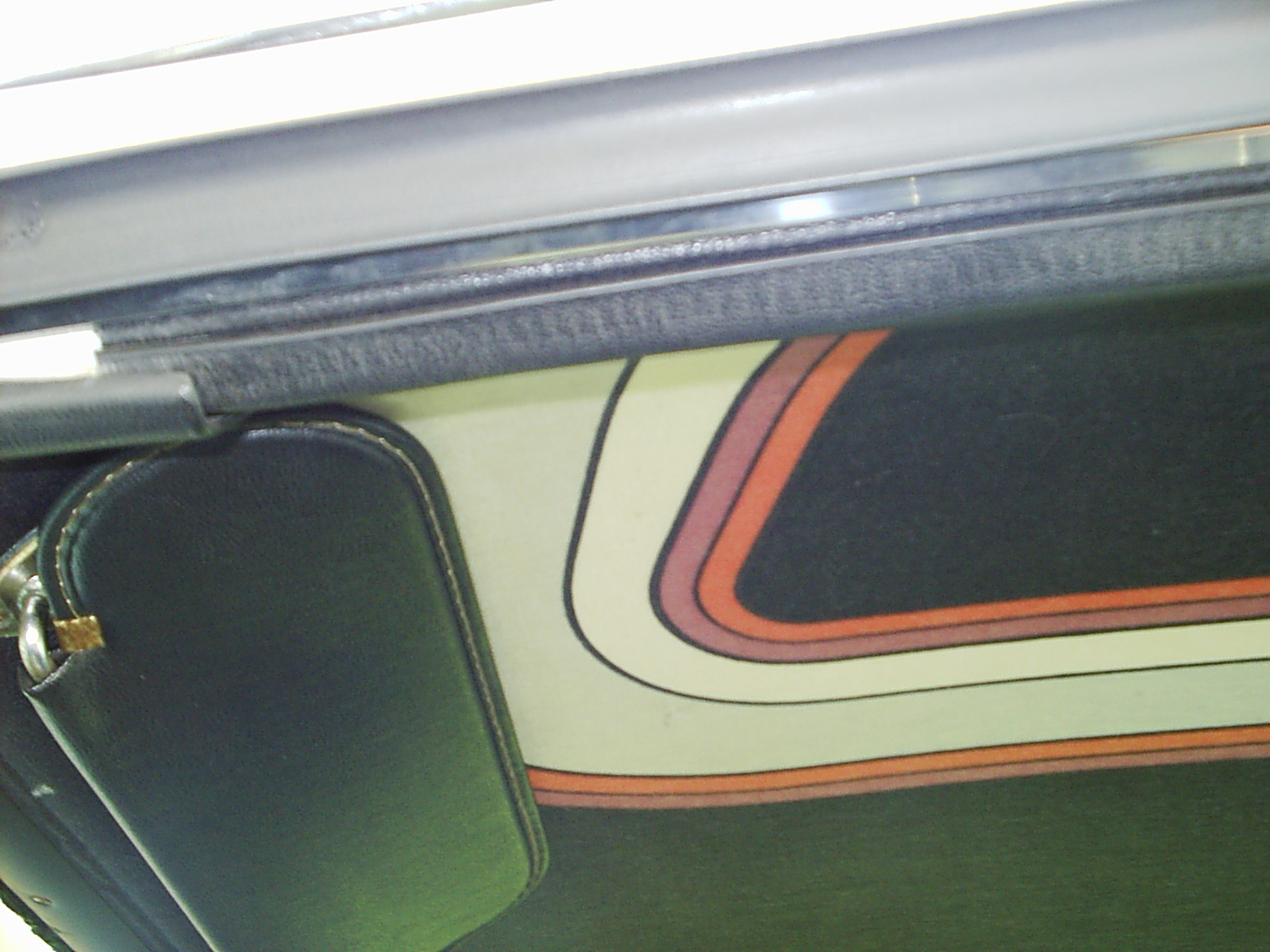
Sun Visor
A sun visor is a component of an automobile located on the interior just above the windshield (also known as the shield). They are designed with a hinged flap that is adjustable to help shade the eyes of drivers and passengers from the glare of sunlight. Design Starting in 1924, automobiles such as the Ford Model T began to include an exterior sun visor on its closed body versions. Other early automobiles also had externally attached sun visors to their windshields until 1931, when interior mounts were introduced. As automobile design advanced with windshields mounted on an angle to lessen wind resistance, the outside or "cadet-type" sun visors were no longer seen on cars starting from 1932. Henceforth, sun visors were mounted inside the vehicle, making the hinged flap easier to reach and adjust. Most modern cars have two sun visors, one for the driver's side and a second for the passenger's side, with the rear-view mirror often mounted in between the two sun visors. Each vis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cowl
A cowl is an item of clothing consisting of a long, hooded garment with wide sleeves, often worn by monks. It was developed during the Early Middle Ages. The term may have originally referred to the hooded portion of a cloak, though contemporary usage refers to an entire closed garment. A cowl is traditionally bestowed upon the monk at the time of making solemn, or lifetime, profession. Today, it is worn primarily by most Catholic and Anglican monks when participating in liturgical services. Description Developed during the Early Middle Ages, the cowl became the formal garment for those in monastic life. Both St. Jerome and John Cassian refer to it as part of a monk's dress. In modern times, it is worn over the habit during liturgical services. Originally, ''cowl'' may have referred simply to the hooded portion of a cloak. In contemporary usage, however, it is distinguished from a cloak or cape (''cappa'') by the fact that it refers to an entire closed garment consist ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Snubber
A snubber is a device used to suppress ("wiktionary:snub, snub") a phenomenon such as voltage transients in electronics, electrical systems, pressure transients in fluid systems (caused by for example water hammer) or excess force or rapid movement in mechanics, mechanical systems. Electrical systems Snubbers are frequently used in electrical systems with an electromagnetic induction, inductive load where the sudden interruption of electric current, current flow leads to a large counter-electromotive force: a rise in voltage across the current switching device that opposes the change in current, in accordance with Faraday's law of induction, Faraday's law. This transient can be a source of electromagnetic interference (EMI) in other circuits. Additionally, if the voltage generated across the device is beyond what the device is intended to tolerate, it may damage or destroy it. The snubber provides a short-term alternative current path around the current switching device so that th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Armrest
An armrest (or arm-rest) is a part of a chair, where a person can rest their arms on. Armrests are built into a large variety of chairs such as automotive chairs, armchairs, airline seats, sofas, and more. Adjustable armrests are commonly found in ergonomic office chairs and gaming chairs. In automobiles Armrest is also a feature found in most modern automobiles on which the occupants can rest their arms. Armrests are commonly placed between the front car seats on the driver and passenger side of the vehicle. Sometimes one or two armrests may also be attached to each individual seat, a feature commonly found in minivans (MPVs) and some SUVs. Many larger cars also have a broad arm-rest between the back seats, which may be folded out when the central (third) seating place is not required. In some designs where occupant safety is emphasised, including some Volvo models, the armrest doubles as a child seat, complete with specially adjustable seatbelt. Armrests in some veh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ammeter
An ammeter (abbreviation of ''ampere meter'') is an measuring instrument, instrument used to measure the electric current, current in a Electrical circuit, circuit. Electric currents are measured in amperes (A), hence the name. For direct measurement, the ammeter is connected in series with the circuit in which the current is to be measured. An ammeter usually has low Electrical resistance and conductance, resistance so that it does not cause a significant voltage drop in the circuit being measured. Instruments used to measure smaller currents, in the milliampere or microampere range, are designated as ''milliammeters'' or ''microammeters''. Early ammeters were laboratory instruments that relied on the Earth's magnetic field for operation. By the late 19th century, improved instruments were designed which could be mounted in any position and allowed accurate measurements in electric power systems. It is generally represented by letter 'A' in a circuit. History The relatio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Speedometer
A speedometer or speed meter is a gauge (instrument), gauge that measures and displays the instantaneous speed of a vehicle. Now universally fitted to motor vehicles, they started to be available as options in the early 20th century, and as standard equipment from about 1910 onwards. Other vehicles may use devices analogous to the speedometer with different means of sensing speed, eg. boats use a pit log, while aircraft use an airspeed indicator. Charles Babbage is credited with creating an early type of a speedometer, which was usually fitted to locomotives. The electric speedometer was invented by the Croats, Croat Josip Belušić in 1888 and was originally called a velocimeter. History The speedometer was originally patented by Josip Belušić (Giuseppe Bellussich) in 1888. He presented his invention at the Exposition Universelle (1889), 1889 Exposition Universelle in Paris. His invention had a pointer and a magnet, using eddy current, electricity to work. German inven ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rearview Mirror
A rearview mirror (or rear-view mirror) is a, usually flat, mirror in automobiles and other vehicles, designed to allow the driver to see rearward through the vehicle's rear window (rear windshield). In cars, the rearview mirror is usually affixed to the top of the windshield on a double-swivel mount allowing it to be adjusted to suit the height and viewing angle of any driver and to swing harmlessly out of the way if impacted by a vehicle occupant in a collision. The rearview mirror is augmented by one or more side-view mirrors, which serve as the only rear-vision mirrors on trucks, motorcycles and bicycles. History Early use of fixed mirrors was described as early as 1906, with a trade magazine noting mirrors for showing what is coming behind were now popular on closed bodied automobiles, and were likely to be widely adopted in a short time. The same year, a Mr. Bilal Ghanty from France patented a "''Warning mirror for automobiles''". The Argus Dash Mirror, adjustabl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |