|
Apollo 5
Apollo 5 (launched January 22, 1968), also known as AS-204, was the uncrewed first flight of the Apollo Lunar Module (LM) that would later carry astronauts to the surface of the Moon. The Saturn IB rocket bearing the LM lifted off from Cape Kennedy on January 22, 1968. The mission was successful, though due to programming problems an alternate mission to that originally planned was executed. Like Apollo 4, this flight was long delayed, due in part to setbacks in development of the LM, manufactured by Grumman Aircraft. The original Saturn IB rocket that was to take the first LM (LM-1) to space was taken down during the delays and replaced with the one that would have launched Apollo 1 if the spacecraft fire that killed three astronauts had not occurred. LM-1 arrived at the Kennedy Space Center in June 1967; the following months were occupied in testing and placing the LM atop the Saturn IB. After final delays due to equipment trouble, the countdown began on Janua ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
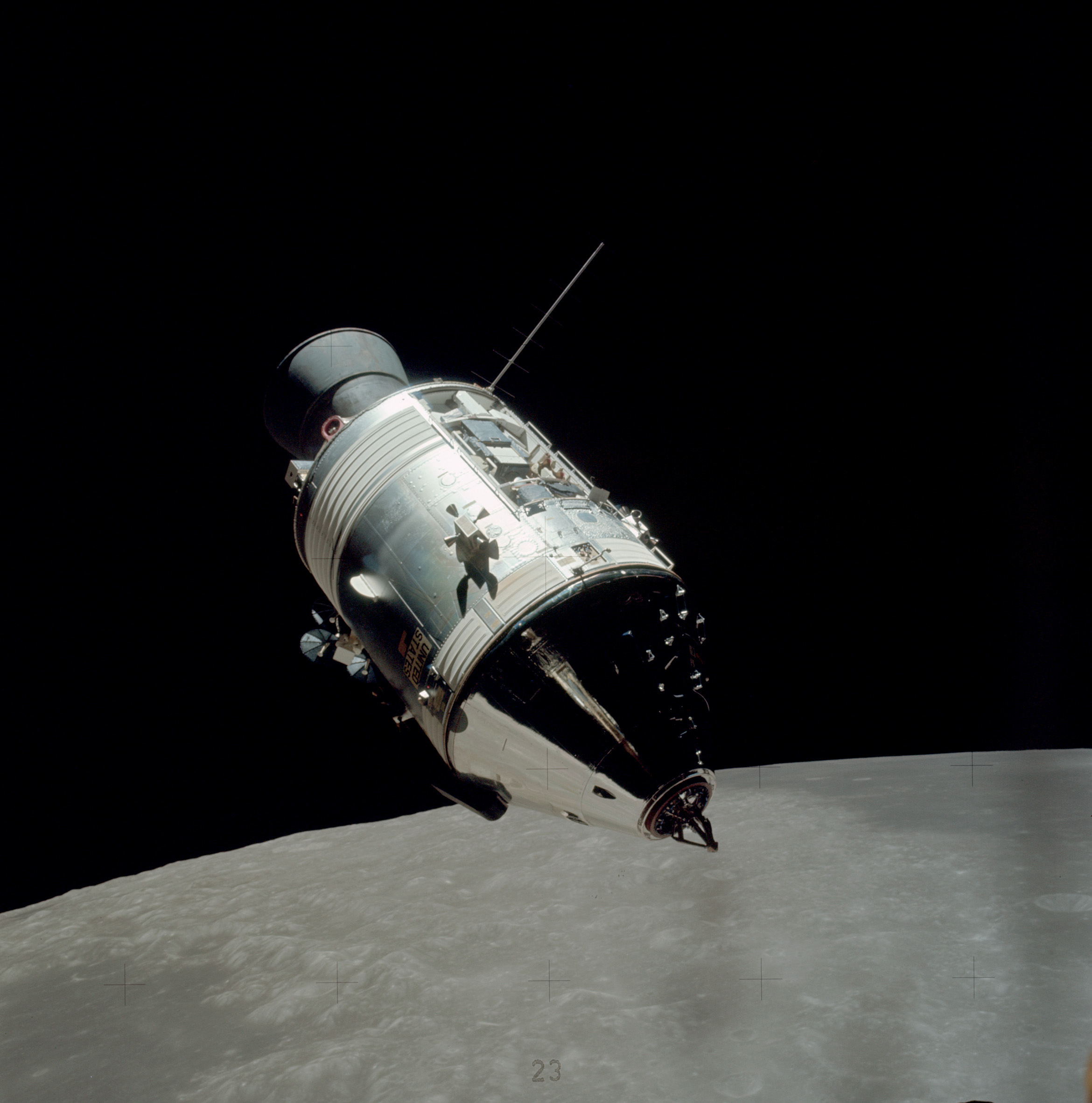
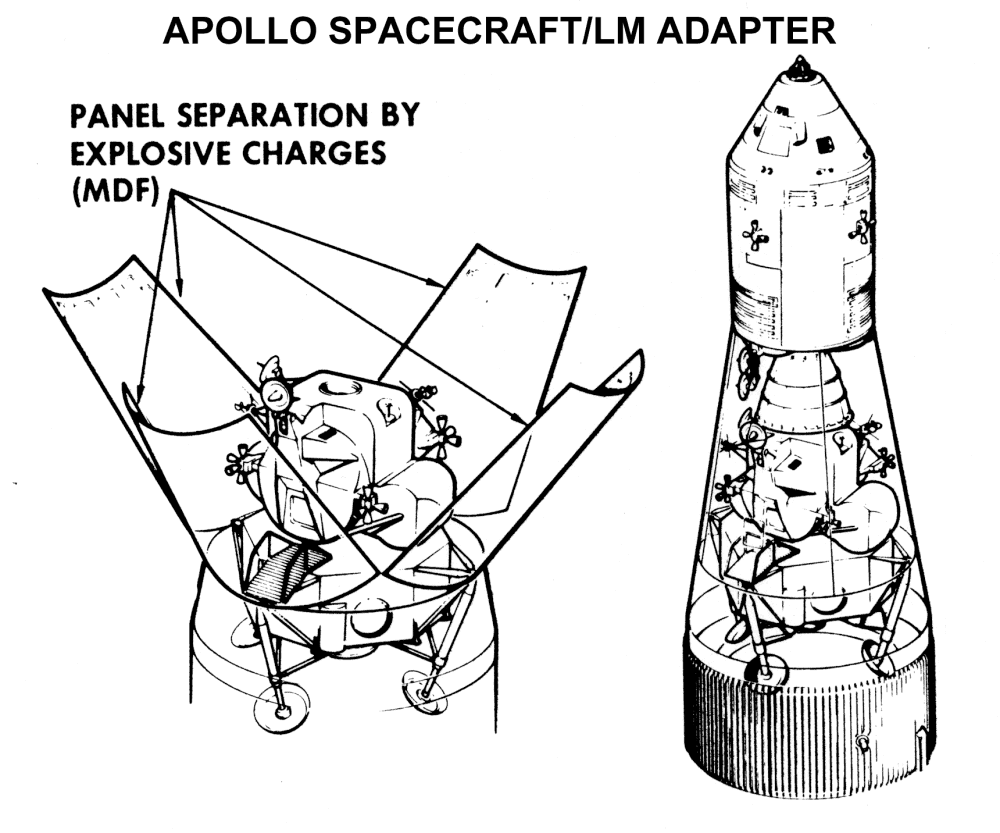
Apollo (spacecraft)
The Apollo spacecraft was composed of three parts designed to accomplish the American Apollo program's goal of landing astronauts on the Moon by the end of the 1960s and returning them safely to Earth. The expendable (single-use) spacecraft consisted of a combined command and service module (CSM) and an Apollo Lunar Module (LM). Two additional components complemented the spacecraft stack for space vehicle assembly: a spacecraft–LM adapter (SLA) designed to shield the LM from the aerodynamic stress of launch and to connect the CSM to the Saturn launch vehicle and a launch escape system (LES) to carry the crew in the command module safely away from the launch vehicle in the event of a launch emergency. The design was based on the lunar orbit rendezvous approach: two docked spacecraft were sent to the Moon and went into lunar orbit. While the LM separated and landed, the CSM remained in orbit. After the lunar excursion, the two craft rendezvoused and docked in lunar orbit, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Apollo Guidance Computer
The Apollo Guidance Computer (AGC) was a digital computer produced for the Apollo program that was installed on board each Apollo command module (CM) and Apollo Lunar Module (LM). The AGC provided computation and electronic interfaces for guidance, navigation, and control of the spacecraft. The AGC was among the first computers based on silicon integrated circuits (ICs). The computer's performance was comparable to the first generation of home computers from the late 1970s, such as the Apple II, TRS-80, and Commodore PET. At around 2 cubic feet in size, AGC held 4,100 IC packages. The AGC has a 16-bit Word (computer architecture), word length, with 15 data bits and one [ arity bit. Most of the software on the AGC is stored in a special read-only memory known as core rope memory, fashioned by weaving wires through and around magnetic cores, though a small amount of read/write core memory is available. Astronauts communicated with the AGC using a numeric display and keyboard call ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cape Canaveral Space Launch Complex 37
Space Launch Complex 37 (SLC-37), previously Launch Complex 37 (LC-37), is a launch complex on Cape Canaveral Space Force Station, Florida. Originally built to support the Apollo program, the complex consists of two launch pads: LC-37A and SLC-37B. Pad 37A has never been used, while 37B hosted Saturn I and Saturn IB launches in the 1960s as well as Delta IV and Delta IV Heavy launches from 2002 to 2024. Currently, the pad is not officially leased to anyone. However, SpaceX is expected to become the next tenant of SLC-37 for use as a launch site for Starship, so far possessing a limited right of entry and a draft environmental impact statement. History Saturn I and IB (1964–1968) Launch Complex 37 began construction in 1959, being envisioned to be a second site to launch the experimental heavy-lift Saturn rockets, joining Launch Complex 34 (LC-34) to the south. Originally, it was planned to be the launch site for an Earth orbit rendezvous (EOR) strategy to potentially ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Samuel C
Samuel is a figure who, in the narratives of the Hebrew Bible, plays a key role in the transition from the biblical judges to the Kingdom of Israel (united monarchy), United Kingdom of Israel under Saul, and again in the monarchy's transition from Saul to David. He is Veneration, venerated as a prophet in Judaism, Christianity, and Islam. In addition to his role in the Bible, Samuel is mentioned in Jewish rabbinic literature, rabbinical literature, in the Christian New Testament, and in the second chapter of the Quran (although the text does not mention him by name). He is also treated in the fifth through seventh books of ''Antiquities of the Jews'', written by the Jewish scholar Josephus in the first century. He is first called "the Seer" in Books of Samuel, 1 Samuel 9:9. Biblical account Family Samuel's mother was Hannah (biblical figure), Hannah and his father was Elkanah. Elkanah lived at Ramathaim-Zophim, Ramathaim in the district of Zuph. His genealogy is also found in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Major General (United States)
In the United States Armed Forces, a major general is a two-star rank, two-star general officer in the United States United States Army, Army, United States Marine Corps, Marine Corps, United States Air Force, Air Force, and United States Space Force, Space Force. A major general ranks above a Brigadier general (United States), brigadier general and below a Lieutenant general (United States), lieutenant general. The U.S. uniformed services pay grades, pay grade of major general is O-8. It is equivalent to the rank of Rear admiral (United States)#Rear admiral, rear admiral in the other United States Uniformed services of the United States, uniformed services which use Naval officer ranks, naval ranks. It is abbreviated as MG in the Army, MajGen in the Marine Corps, and in the Air Force and Space Force. Major general is the highest permanent peacetime rank that can be conferred upon a commissioned officer in the uniformed services (except when General of the Army (United States ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bethpage, New York
Bethpage (formerly known as Central Park) is a Hamlet (New York), hamlet and census-designated place (CDP) located within the Oyster Bay (town), New York, Town of Oyster Bay in Nassau County, New York, Nassau County, on the South Shore (Long Island), South Shore of Long Island, in New York (state), New York, United States. The population was 16,658 at the 2020 United States census. History The name ''Bethpage'' comes from the Quakers, Quaker Thomas Powell (1641–1722), Thomas Powell, who named the area after the Biblical town Bethphage, which was between Jericho and Jerusalem in the Holy Land. Present-day Bethpage was part of the 1695 Bethpage Purchase. An early name for the northern section of present-day Bethpage was ''Bedelltown'', a name that appeared on maps at least as late as 1906. On maps just before the arrival of the Long Island Rail Road (LIRR), the name ''Bethpage'' appears for a community now included in both the post office district and school district of the ad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saturn V
The Saturn V is a retired American super heavy-lift launch vehicle developed by NASA under the Apollo program for human exploration of the Moon. The rocket was human-rated, had multistage rocket, three stages, and was powered by liquid-propellant rocket, liquid fuel. Flown from 1967 to 1973, it was used for nine crewed flights to the Moon, and to launch Skylab, the first American space station. the Saturn V remains the only launch vehicle to have carried humans beyond low Earth orbit (LEO). The Saturn V holds the record for the largest payload capacity to low Earth orbit, , which included unburned propellant needed to send the Apollo command and service module and Apollo Lunar Module, Lunar Module to the Moon. The largest production model of the Saturn (rocket family), Saturn family of rockets, the Saturn V was designed under the direction of Wernher von Braun at the Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama; the lead contractors for construction of the rocket were ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Apollo Spacecraft
The Apollo spacecraft was composed of three parts designed to accomplish the American Apollo program's goal of landing astronauts on the Moon by the end of the 1960s and returning them safely to Earth. The expendable (single-use) spacecraft consisted of a Apollo command and service module, combined command and service module (CSM) and an Apollo Lunar Module (LM). Two additional components complemented the spacecraft stack for space vehicle assembly: a spacecraft–LM adapter (SLA) designed to shield the LM from the aerodynamic stress of launch and to connect the CSM to the Saturn (rocket family), Saturn launch vehicle and a launch escape system (LES) to carry the crew in the command module safely away from the launch vehicle in the event of a launch emergency. The design was based on the lunar orbit rendezvous approach: two docked spacecraft were sent to the Moon and went into lunar orbit. While the LM separated and landed, the CSM remained in orbit. After the lunar excursion ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lunar Orbit Rendezvous
Lunar orbit rendezvous (LOR) is a process for landing humans on the Moon and returning them to Earth. It was utilized for the Apollo program missions in the 1960s and 1970s. In a LOR mission, a main spacecraft and a lunar lander travel to lunar orbit. The lunar lander then independently descends to the surface of the Moon, while the main spacecraft remains in lunar orbit. After completion of the mission there, the lander returns to lunar orbit to space rendezvous, rendezvous and re-docking and berthing of spacecraft, dock with the main spacecraft, then is discarded after transfer of crew and payload. Only the main spacecraft returns to Earth. Lunar orbit rendezvous was first proposed in 1919 by Russian engineer Yuri Kondratyuk, as the most economical way of sending a human on a round-trip journey to the Moon. The most famous example involved Project Apollo's command and service module (CSM) and lunar module (LM), where they were both sent to a translunar flight in a single rocket ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
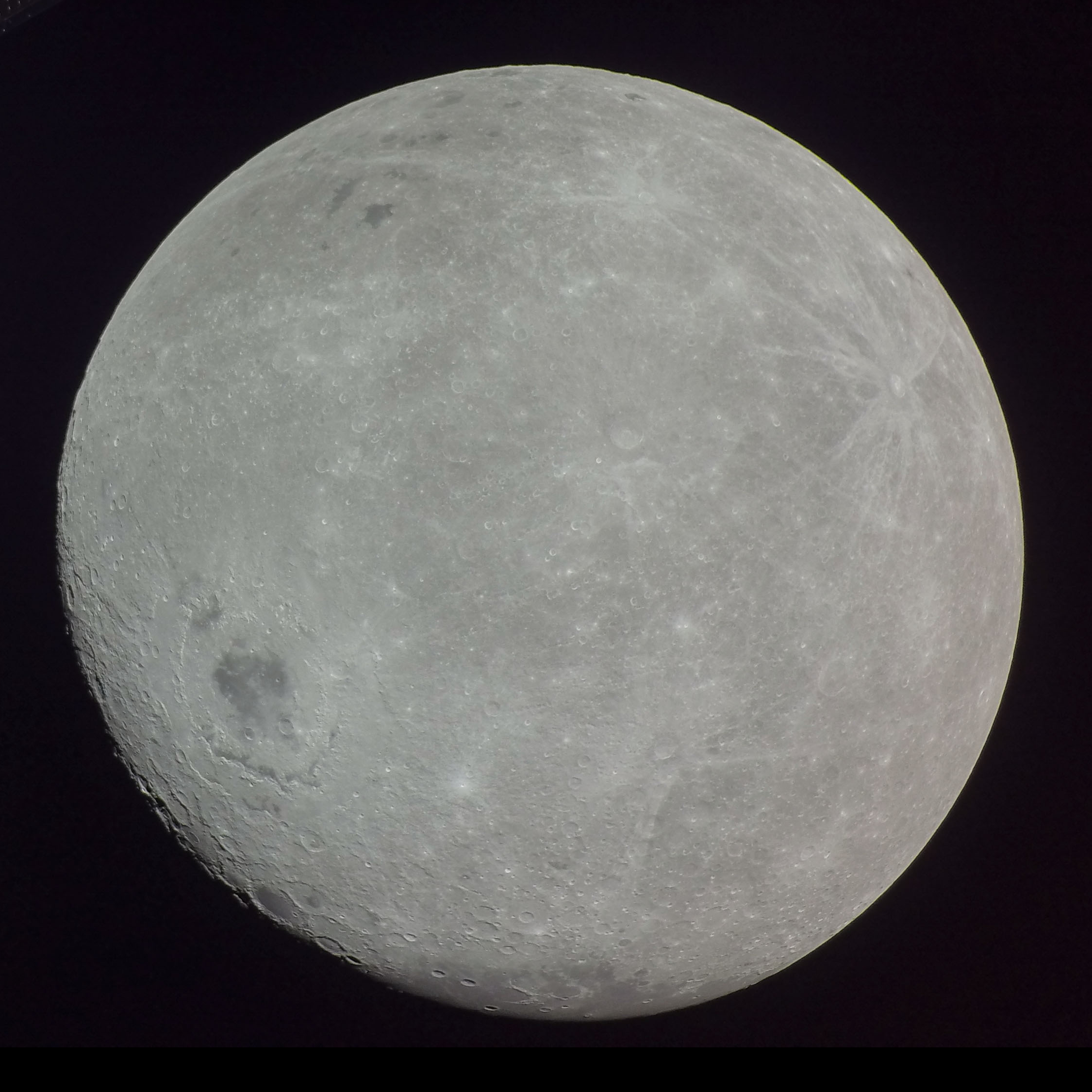
Moon
The Moon is Earth's only natural satellite. It Orbit of the Moon, orbits around Earth at Lunar distance, an average distance of (; about 30 times Earth diameter, Earth's diameter). The Moon rotation, rotates, with a rotation period (lunar day) that is synchronized to its orbital period (Lunar month#Synodic month, lunar month) of 29.5 Earth days. This is the product of Earth's gravitation having tidal forces, tidally pulled on the Moon until one part of it stopped rotating away from the near side of the Moon, near side, making always the same lunar surface face Earth. Conversley, the gravitational pull of the Moon, on Earth, is the main driver of Earth's tides. In geophysical definition of planet, geophysical terms, the Moon is a planetary-mass object or satellite planet. Its mass is 1.2% that of the Earth, and its diameter is , roughly one-quarter of Earth's (about as wide as the contiguous United States). Within the Solar System, it is the List of Solar System objects by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
We Choose To Go To The Moon
Address at Rice University on the Nation's Space Effort, commonly known by the sentence in the middle of the speech "We choose to go to the Moon", was a speech on September 12, 1962, by John F. Kennedy, the President of the United States. The aim was to bolster public support for his proposal to land a man on the Moon before the end of the decade and bring him safely back to Earth. Kennedy gave the speech, largely written by presidential advisor and speechwriter Ted Sorensen, to a large crowd at Rice University Stadium in Houston, Texas. In his speech, Kennedy characterized space as a new frontier, invoking the pioneer spirit that dominated American folklore. He infused the speech with a sense of urgency and destiny, and emphasized the freedom enjoyed by Americans to choose their destiny rather than have it chosen for them. Although he called for competition with the Soviet Union, Kennedy also proposed making the Moon landing a joint project. The speech resonated widely, al ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John F
John is a common English name and surname: * John (given name) * John (surname) John may also refer to: New Testament Works * Gospel of John, a title often shortened to John * First Epistle of John, often shortened to 1 John * Second Epistle of John, often shortened to 2 John * Third Epistle of John, often shortened to 3 John People * John the Baptist (died ), regarded as a prophet and the forerunner of Jesus Christ * John the Apostle (died ), one of the twelve apostles of Jesus Christ * John the Evangelist, assigned author of the Fourth Gospel, once identified with the Apostle * John of Patmos, also known as John the Divine or John the Revelator, the author of the Book of Revelation, once identified with the Apostle * John the Presbyter, a figure either identified with or distinguished from the Apostle, the Evangelist and John of Patmos Other people with the given name Religious figures * John, father of Andrew the Apostle and Saint Peter * Pope Jo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |