|
Aper (praetorian Prefect)
Aper (also known as Lucius Flavius Aper and Arrius Aper, died 284) was a Roman citizen of the third century AD. First known to history as a professional soldier, he went on to serve as an acting provincial governor and finally became Praetorian prefect, under the Emperor Carus - in effect "vice principis" (a term best understood as 'the emperor's deputy'). This rendered him hugely influential in the government of the empire - not excepting in matters of peace and war. Aper's career coincided with and benefited from the momentous changes in the structure of the Roman army and the Roman state introduced in the middle years of the third century that brought men such as himself - i.e. members of the Roman equestrian order with a strong military background - to the fore in the public administration. Almost certainly he would have been a man of considerable ability. However, as was almost invariably the case with those who rose to the highest levels in the Imperial Service, the main el ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Routledge
Routledge ( ) is a British multinational corporation, multinational publisher. It was founded in 1836 by George Routledge, and specialises in providing academic books, academic journals, journals and online resources in the fields of the humanities, behavioral science, behavioural science, education, law, and social science. The company publishes approximately 1,800 journals and 5,000 new books each year and their backlist encompasses over 140,000 titles. Routledge is claimed to be the largest global academic publisher within humanities and social sciences. In 1998, Routledge became a subdivision and Imprint (trade name), imprint of its former rival, Taylor & Francis, Taylor & Francis Group (T&F), as a result of a £90-million acquisition deal from Cinven, a venture capital group which had purchased it two years previously for £25 million. Following the merger of Informa and T&F in 2004, Routledge became a publishing unit and major imprint within the Informa "academic publishing ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
V Macedonica
Legio V Macedonica (the Fifth Macedonian Legion) was a Roman legion. It was established in 43 BC by consul Gaius Vibius Pansa Caetronianus and Gaius Julius Caesar Octavianus (later known as the Emperor Augustus). and based in the Balkan provinces of Macedonia, Moesia and Dacia. In the Notitia Dignitatum records from beginning of the fifth century, the legion was still stationed in Dacia, with detachments stationed in the east and Egypt. The last known evidence shows the legion, or detachments from it, stationed in Egypt in the seventh century one or two years before the Islamic conquest of Egypt. It is often assumed that the legion fought in this war and was destroyed, although it is uncertain whether detachments or the whole legion were in Egypt, and there is no further evidence of the legion's eventual fate. Its symbol was the bull, but the eagle was used as well. History 1st century BC: Creation and deployment in Macedonia The Legio V was one of the original twenty-eig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hungary
Hungary is a landlocked country in Central Europe. Spanning much of the Pannonian Basin, Carpathian Basin, it is bordered by Slovakia to the north, Ukraine to the northeast, Romania to the east and southeast, Serbia to the south, Croatia and Slovenia to the southwest, and Austria to the west. Hungary lies within the drainage basin of the Danube, Danube River and is dominated by great lowland plains. It has a population of 9.6 million, consisting mostly of ethnic Hungarians, Hungarians (Magyars) and a significant Romani people in Hungary, Romani minority. Hungarian language, Hungarian is the Languages of Hungary, official language, and among Languages of Europe, the few in Europe outside the Indo-European languages, Indo-European family. Budapest is the country's capital and List of cities and towns of Hungary, largest city, and the dominant cultural and economic centre. Prior to the foundation of the Hungarian state, various peoples settled in the territory of present-day Hun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Budapest
Budapest is the Capital city, capital and List of cities and towns of Hungary, most populous city of Hungary. It is the List of cities in the European Union by population within city limits, tenth-largest city in the European Union by population within city limits and the List of cities and towns on the river Danube, second-largest city on the river Danube. The estimated population of the city in 2025 is 1,782,240. This includes the city's population and surrounding suburban areas, over a land area of about . Budapest, which is both a List of cities and towns of Hungary, city and Counties of Hungary, municipality, forms the centre of the Budapest metropolitan area, which has an area of and a population of 3,019,479. It is a primate city, constituting 33% of the population of Hungary. The history of Budapest began when an early Celts, Celtic settlement transformed into the Ancient Rome, Roman town of Aquincum, the capital of Pannonia Inferior, Lower Pannonia. The Hungarian p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
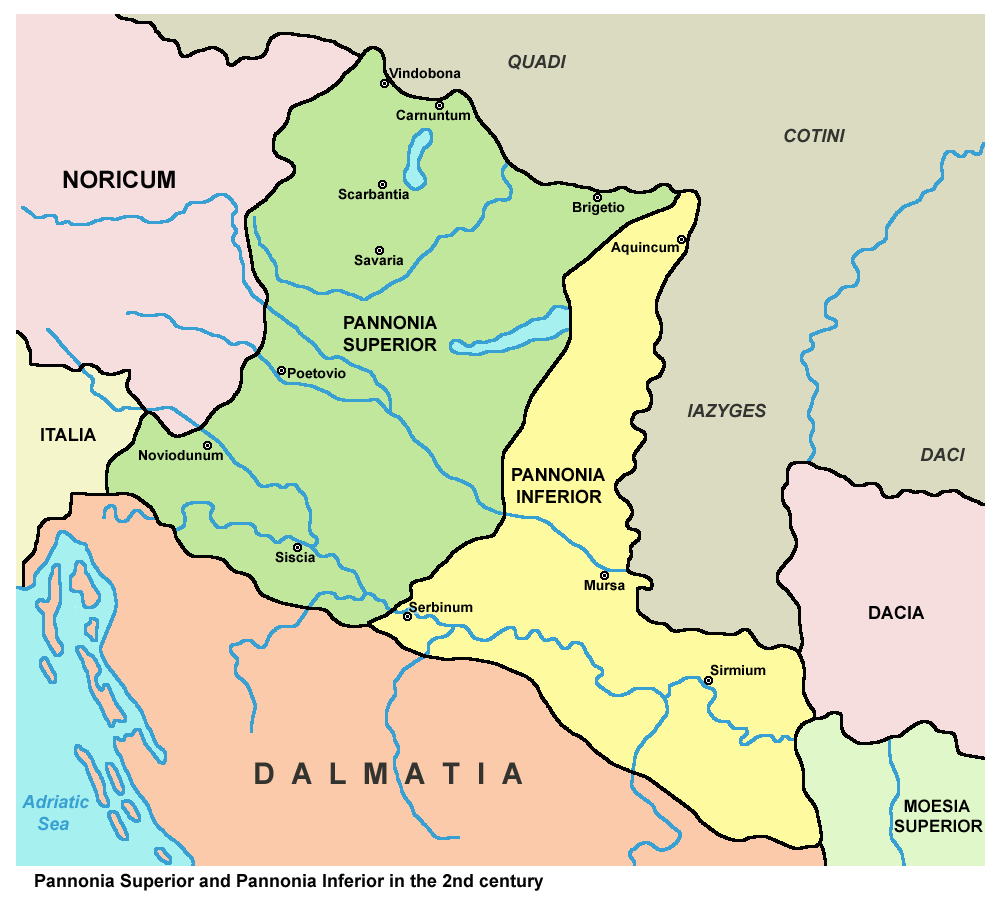
Pannonia Inferior
Pannonia Inferior, lit. Lower Pannonia, was a province of the Roman Empire. Its capital was Sirmium. It was one of the border provinces on the Danube. It was formed in the year 103 AD by Emperor Trajan who divided the former province of Pannonia into two parts: Pannonia Superior and Pannonia Inferior. The province included parts of present-day states of Hungary, Serbia, Croatia, and Bosnia and Herzegovina. The province was bordered to the east (across the Danube) by a Sarmatian tribe—the Iazyges. Later, the Vandals appeared to the north-east. Settlements Major settlements in Pannonia Inferior included: * ''Sirmium'' (Sremska Mitrovica) which several times served as an imperial residence for several emperors. * '' Aquincum'' (Buda), the provincial capital. * ''Cuccium'' ( Ilok) * ''Cibalae'' (Vinkovci) * ''Mursa'' ( Osijek) * ''Certissa'' ( Đakovo) * ''Marsonia'' (Slavonski Brod) * ''Sopianae'' (Pécs) Aftermath and legacy The province was yet again split during the reign of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aquincum
Aquincum (, ) was an ancient city, situated on the northeastern borders of the province of Pannonia within the Roman Empire. The ruins of the city can be found in Budapest, the capital city of Hungary. It is believed that Marcus Aurelius wrote at least part of his book ''Meditations'' at Aquincum. History Aquincum was originally settled by the Eravisci, a Celtic tribe. Aquincum served as a military base ('' castrum''), having been part of the Roman border protection system called '' limes''. Around AD 41–54, a 500-strong cavalry unit arrived, and a Roman legion of 6,000 men ( Legio II Adiutrix) was stationed there by AD 89. The city gradually grew around the fortress, and after Pannonia was reorganised by the Romans in AD 103, Aquincum became the capital city of the Roman province of Pannonia Inferior until the administrative reform of Diocletian more than a century later. Under Hadrian, the city obtained municipal status, while under Septimius Severus, Aquincum became a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sasanian Empire
The Sasanian Empire (), officially Eranshahr ( , "Empire of the Iranian peoples, Iranians"), was an List of monarchs of Iran, Iranian empire that was founded and ruled by the House of Sasan from 224 to 651. Enduring for over four centuries, the length of the Sasanian dynasty's reign over ancient Iran was second only to the directly preceding Arsacid dynasty of Parthia. Founded by Ardashir I, whose rise coincided with the decline of Arsacid influence in the face of both internal and external strife, the House of Sasan was highly determined to restore the legacy of the Achaemenid Empire by expanding and consolidating the Iranian nation's dominions. Most notably, after defeating Artabanus IV of Parthia during the Battle of Hormozdgan in 224, it began competing far more zealously with the neighbouring Roman Empire than the Arsacids had, thus sparking a new phase of the Roman–Iranian Wars. This effort by Ardashir's dynasty ultimately re-established Iran as a major power of late an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roman Syria
Roman Syria was an early Roman province annexed to the Roman Republic in 64 BC by Pompey in the Third Mithridatic War following the defeat of King of Armenia Tigranes the Great, who had become the protector of the Hellenistic kingdom of Syria. Following the partition of the Herodian Kingdom of Judea into a tetrarchy in 4 BC, it was gradually absorbed into Roman provinces, with Roman Syria annexing Iturea and Trachonitis. By the late 2nd century AD, the province was divided into Coele Syria and Syria Phoenice. Provincia Syria Syria was annexed to the Roman Republic in 64 BC, when Pompey the Great had the Seleucid king Antiochus XIII Asiaticus executed and deposed his successor Philip II Philoromaeus. Pompey appointed Marcus Aemilius Scaurus to the post of governor of Syria. Following the fall of the Roman Republic and its transformation into the Roman Empire, Syria became a Roman imperial province, governed by a Legate. During the early empire, the Roman army in Sy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mesopotamia (Roman Province)
Mesopotamia was the name of a Roman province, initially a short-lived creation of the Roman emperor Trajan in 116–117 and then re-established by Emperor Septimius Severus in c. 198. Control of the province was subsequently fought over between the Roman and the Sassanian Empire, Sassanian empires until the Early Muslim conquests, Muslim conquests of the 7th century. Trajan's province In 113, the Roman emperor Trajan (r. 98–117) Trajan's Parthian campaign, launched a war against Rome's long-time eastern rival, the Parthian Empire. In 114, he conquered Roman Armenia, Armenia, which was made into a province, and by the end of 115, he had conquered northern Mesopotamia. This too was organized as a province in early 116, when coins were minted to celebrate the fact. Later in the same year, Trajan marched into central and southern Mesopotamia (enlarging and completing the province of Mesopotamia) and across the river Tigris to Adiabene, which he annexed into another Roman provin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Publius Aelius Aelianus
Publius Aelius Aelianus was a senior officer in the Imperial Roman army in the mid-3rd century AD who rose from lowly origins to become the prefect of a legion under Emperor Gallienus. He was one of the earliest beneficiaries of Gallienus's policy that effectively excluded senators from army commands in favour of career-soldiers of equestrian rank. His later life is obscure. He was possibly ''procurator'' (i.e. Chief Financial Officer) of Epirus in the late-260s, but the foremost authorities query this identification. However, there are stronger grounds for believing that he was appointed a ''praeses'' (provincial governor of equestrian rank) in ''Africa'', most likely under the Emperor Probus. Sources The sum total of our knowledge of this man derives from five epigraph inscriptions from: (a) A fragment of an epigraphic inscription from ''Poetovio'' (now Ptuj in Slovenia) that indicates that one ''AEL...I'' (a '' Vir Egregius'', presumed to be Aelianus) commanded ''vexillationes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lucius Petronius Taurus Volusianus
Lucius Petronius Taurus Volusianus (died c.286 AD) was a Roman citizen, apparently of equestrian origins, whose career in the Imperial Service in the mid-Third Century AD carried him from a relatively modest station in life to the highest public offices and senatorial status in a very few years. He may have secured his first appointments before the Licinian Dynasty – ( Valerian and his son Gallienus) – acceded to the Empire in 253 AD, but it was in the course of their reign that his upward progress achieved an almost unprecedented momentum and the second factor seems to have been a consequence of the first. The nature of his relationship to the Licinii is uncertain, but it seems likely that a common origin in the Etruscan region of central Italy at least predisposed Gallienus in his favour and he seems to have been that emperor's most trusted servant and adviser during the period of his sole reign - 260(?)-268 AD. Contemporary sources Almost all that is known of Volusianus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dacia
Dacia (, ; ) was the land inhabited by the Dacians, its core in Transylvania, stretching to the Danube in the south, the Black Sea in the east, and the Tisza in the west. The Carpathian Mountains were located in the middle of Dacia. It thus roughly corresponds to present-day Romania, as well as parts of Moldova, Bulgaria, Serbia, Hungary, Slovakia, Czech Republic, Poland and Ukraine. A Dacian kingdom that united the Dacians and the Getae was formed under the rule of Burebista in 82 BC and lasted until the Roman conquest in AD 106. As a result of the Trajan's Dacian Wars, wars with the Roman Empire, after the conquest of Dacia, the population was dispersed, and the capital city, Sarmizegetusa Regia, was destroyed by the Romans. However, the Romans built a settlement bearing the same name, Ulpia Traiana Sarmizegetusa, Ulpia Traiana Sarmizegetuza, 40 km away, to serve as the capital of the newly established Roman Dacia, Roman province of Dacia. A group of "Free Dacians" may ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |