|
Anurogryllus Arboreus
''Anurogryllus arboreus'', the common short-tailed cricket or arboreal short-tailed cricket, is a species of cricket in the family Gryllidae. It is native to the southern and south-eastern United States where it lives in a burrow that it digs. Description Like other short-tail crickets in its genus, the adult ''A. arboreus'' is a pale brown cricket with a vestigial ovipositor. When it first matures, the adult insect has wings, but it soon sheds these and is afterwards flightless. Taxonomy and distribution At one time, nearly all the short-tailed crickets in the United States were considered to belong to the species ''Anurogryllus muticus'', the range of which extended from Canada to much of South America. In a revision of the genus made by T. J. Walker in 1973, ''Anurogryllus arboreus'' was split off on the basis of the behavior of the male when calling, and on certain morphological differences. ''A. arboreus'' occurs primarily along the Atlantic Coast from New Jersey to Florida ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thomas J
Clarence Thomas (born June 23, 1948) is an American jurist who serves as an associate justice of the Supreme Court of the United States. He was nominated by President George H. W. Bush to succeed Thurgood Marshall and has served since 1991. After Marshall, Thomas is the second African American to serve on the Court and its longest-serving member since Anthony Kennedy's retirement in 2018. Thomas was born in Pin Point, Georgia. After his father abandoned the family, he was raised by his grandfather in a poor Gullah community near Savannah. Growing up as a devout Catholic, Thomas originally intended to be a priest in the Catholic Church but was frustrated over the church's insufficient attempts to combat racism. He abandoned his aspiration of becoming a clergyman to attend the College of the Holy Cross and, later, Yale Law School, where he was influenced by a number of conservative authors, notably Thomas Sowell, who dramatically shifted his worldview from progressiv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Species
In biology, a species is the basic unit of Taxonomy (biology), classification and a taxonomic rank of an organism, as well as a unit of biodiversity. A species is often defined as the largest group of organisms in which any two individuals of the appropriate sexes or mating types can reproduction, produce Fertility, fertile offspring, typically by sexual reproduction. Other ways of defining species include their karyotype, DNA sequence, morphology (biology), morphology, behaviour or ecological niche. In addition, paleontologists use the concept of the chronospecies since fossil reproduction cannot be examined. The most recent rigorous estimate for the total number of species of eukaryotes is between 8 and 8.7 million. However, only about 14% of these had been described by 2011. All species (except viruses) are given a binomial nomenclature, two-part name, a "binomial". The first part of a binomial is the genus to which the species belongs. The second part is called the specifi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
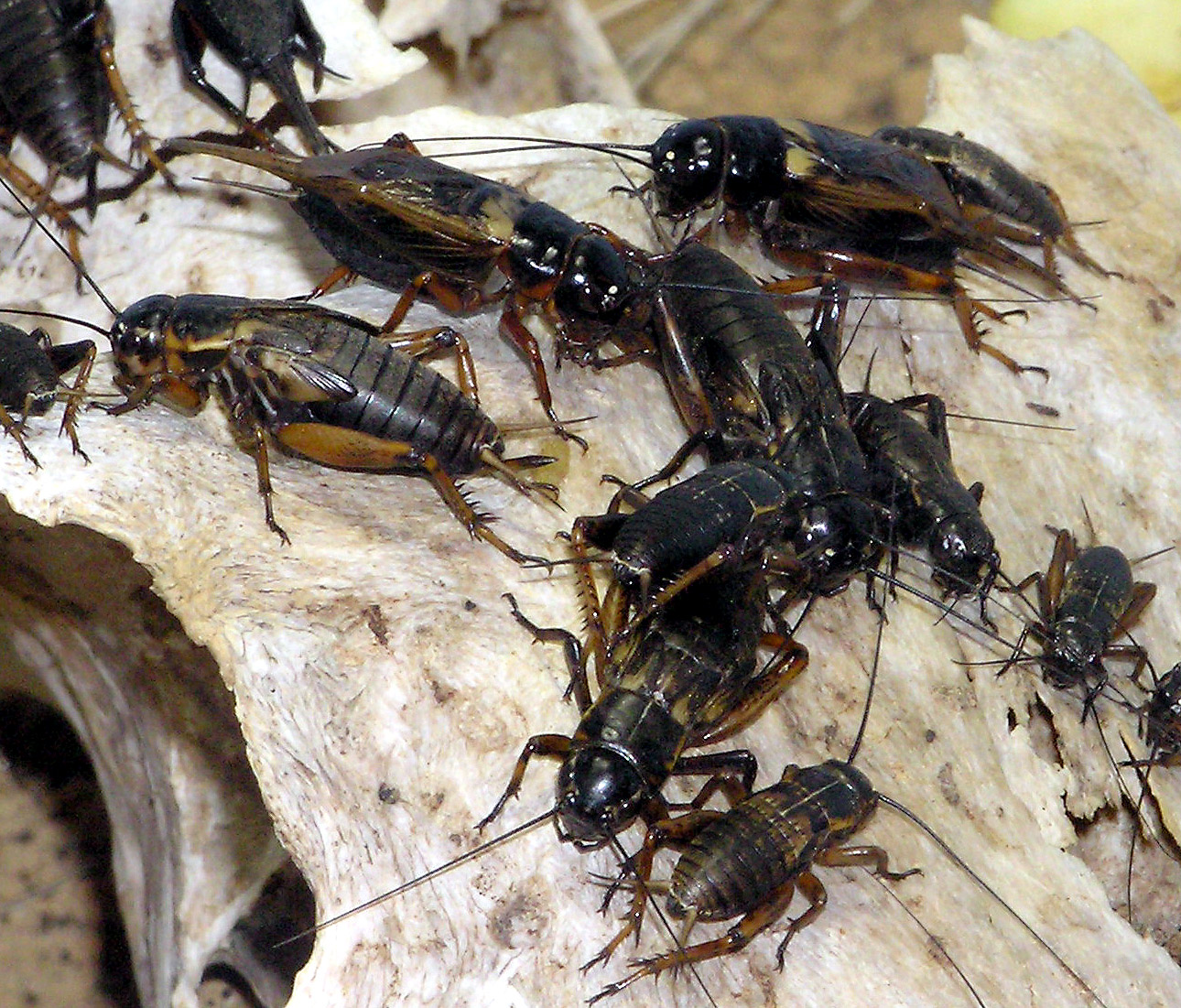
Cricket (insect)
Crickets are orthopteran insects which are related to bush crickets, and, more distantly, to grasshoppers. In older literature, such as Imms,Imms AD, rev. Richards OW & Davies RG (1970) ''A General Textbook of Entomology'' 9th Ed. Methuen 886 pp. "crickets" were placed at the family level (''i.e.'' Gryllidae), but contemporary authorities including Otte now place them in the superfamily Grylloidea. The word has been used in combination to describe more distantly related taxa in the suborder Ensifera, such as king crickets and mole crickets. Crickets have mainly cylindrically-shaped bodies, round heads, and long antennae. Behind the head is a smooth, robust pronotum. The abdomen ends in a pair of long cerci; females have a long, cylindrical ovipositor. Diagnostic features include legs with 3-segmented tarsi; as with many Orthoptera, the hind legs have enlarged femora, providing power for jumping. The front wings are adapted as tough, leathery elytra, and some cricke ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gryllidae
The family ''Gryllidae'' contains the subfamilies and genera which entomologists now term true crickets. Having long, whip-like antennae, they belong to the Orthopteran suborder Ensifera, which has been greatly reduced in the last 100 years (''e.g.'' ImmsImms AD, rev. Richards OW & Davies RG (1970) ''A General Textbook of Entomology'' 9th Ed. Methuen 886 pp.): taxa such as the spider-crickets and allies, sword-tail crickets, wood or ground crickets and scaly crickets have been elevated to family level. The type genus is '' Gryllus'' and the first use of the family name "Gryllidae" was by Walker. They have a worldwide distribution (except Antarctica). The largest members of the family are the -long bull crickets ('' Brachytrupes'') which excavate burrows a metre or more deep. The tree crickets ( Oecanthinae) are delicate white or pale green insects with transparent fore wings, while the field crickets ( Gryllinae) are robust brown or black insects. Subfamilies The fami ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ovipositor
The ovipositor is a tube-like organ used by some animals, especially insects, for the laying of eggs. In insects, an ovipositor consists of a maximum of three pairs of appendages. The details and morphology of the ovipositor vary, but typically its form is adapted to functions such as preparing a place for the egg, transmitting the egg, and then placing it properly. For most insects, the organ is used merely to attach the egg to some surface, but for many parasitic species (primarily in wasps and other Hymenoptera), it is a piercing organ as well. Some ovipositors only retract partly when not in use, and the basal part that sticks out is known as the scape, or more specifically oviscape, the word ''scape'' deriving from the Latin word '' scāpus'', meaning "stalk" or "shaft". In insects Grasshoppers use their ovipositors to force a burrow into the earth to receive the eggs. Cicadas pierce the wood of twigs with their ovipositors to insert the eggs. Sawflies slit t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anurogryllus Muticus
''Anurogryllus muticus'', also known as De Geer's short-tailed cricket or simply short-tailed cricket (a name common to many ''Anurogryllus'' species) is a species of Cricket (insect), cricket in the family Gryllidae. It is native to Bermuda, the West Indies, Central and South America. It is Nocturnality, nocturnal and hides in a burrow by day. Taxonomy At one time, nearly all the short-tailed crickets in the United States were considered to belong to the species ''Anurogryllus muticus'', the range of which extended from Canada to much of South America. In a revision of the genus made by T. Walker in 1973, ''Anurogryllus arboreus'' was split off on the basis of the calling behavior of the male, and on certain Morphology (biology), morphological differences. The range of ''A. muticus'' is now considered to include Bermuda, the West Indies, Central and South America as far south as southern Brazil while that of ''A. arboreus'' covers much of the continental United States. There a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Morphology (biology)
Morphology is a branch of biology dealing with the study of the form and structure of organisms and their specific structural features. This includes aspects of the outward appearance ( shape, structure, colour, pattern, size), i.e. external morphology (or eidonomy), as well as the form and structure of the internal parts like bones and organs, i.e. internal morphology (or anatomy). This is in contrast to physiology, which deals primarily with function. Morphology is a branch of life science dealing with the study of gross structure of an organism or taxon and its component parts. History The etymology of the word "morphology" is from the Ancient Greek (), meaning "form", and (), meaning "word, study, research". While the concept of form in biology, opposed to function, dates back to Aristotle (see Aristotle's biology), the field of morphology was developed by Johann Wolfgang von Goethe (1790) and independently by the German anatomist and physiologist Karl Fr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anurogryllus
''Anurogryllus'', commonly known as short-tailed crickets, is a genus of crickets in the tribe Gryllini; species are recorded from the Americas. The common and scientific names derive from the vestigial, poorly developed ovipositors of females. Species The Orthoptera Species File database lists the following species: *'' Anurogryllus abortivus'' (Saussure, 1874) *'' Anurogryllus amolgos'' Otte & Perez-Gelabert, 2009 *'' Anurogryllus annae'' Otte & Perez-Gelabert, 2009 *'' Anurogryllus antillarum'' (Saussure, 1874) *'' Anurogryllus arboreus'' Walker, 1973 *'' Anurogryllus beebei'' Otte & Perez-Gelabert, 2009 *'' Anurogryllus brevicaudatus'' Saussure, 1877 *'' Anurogryllus celerinictus'' Walker, 1973 *'' Anurogryllus cubensis'' (Rehn, 1937) *'' Anurogryllus ecphylos'' Otte, 2006 *'' Anurogryllus ellops'' Otte & Perez-Gelabert, 2009 *'' Anurogryllus forcipatus'' (Saussure, 1897) *'' Anurogryllus fulvaster'' (Chopard, 1956) *'' Anurogryllus fuscus'' Caudell, 1913 *'' Anurogryllus gn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anurogryllus Celerinictus
''Anurogryllus celerinictus'', the Indies short-tailed cricket, is a species of cricket Cricket is a bat-and-ball game played between two teams of eleven players on a field at the centre of which is a pitch with a wicket at each end, each comprising two bails balanced on three stumps. The batting side scores runs by striki ... in the family Gryllidae. It was described in 1973 by Thomas J. Walker. In January 2019, the noise from its song was proposed as the cause of the Havana syndrome. A JASON report from November 2018 (declassified in September 2021) concluded that sounds recorded during investigations of Havana syndrome most likely came from ''A. celerinictus''. References {{Taxonbar, from=Q10413906 Gryllinae Insects of the United States Insects of Cuba Insects described in 1973 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Florida Keys
The Florida Keys are a coral island, coral cay archipelago located off the southern coast of Florida, forming the southernmost part of the continental United States. They begin at the southeastern coast of the Florida peninsula, about south of Miami, and extend in a gentle arc south-southwest and then westward to Key West, Florida, Key West, the westernmost of the inhabited islands, and on to the uninhabited Dry Tortugas. The islands lie along the Florida Straits, dividing the Atlantic Ocean to the east from the Gulf of Mexico to the northwest, and defining one edge of Florida Bay. At the nearest point, the southern part of Key West is just from Cuba. The Florida Keys are between about 24.3 and 25.5 degrees North latitude. More than 95 percent of the land area lies in Monroe County, Florida, Monroe County, but a small portion extends northeast into Miami-Dade County, Florida, Miami-Dade County, such as Totten Key. The total land area is . As of the United States Census, 2010, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
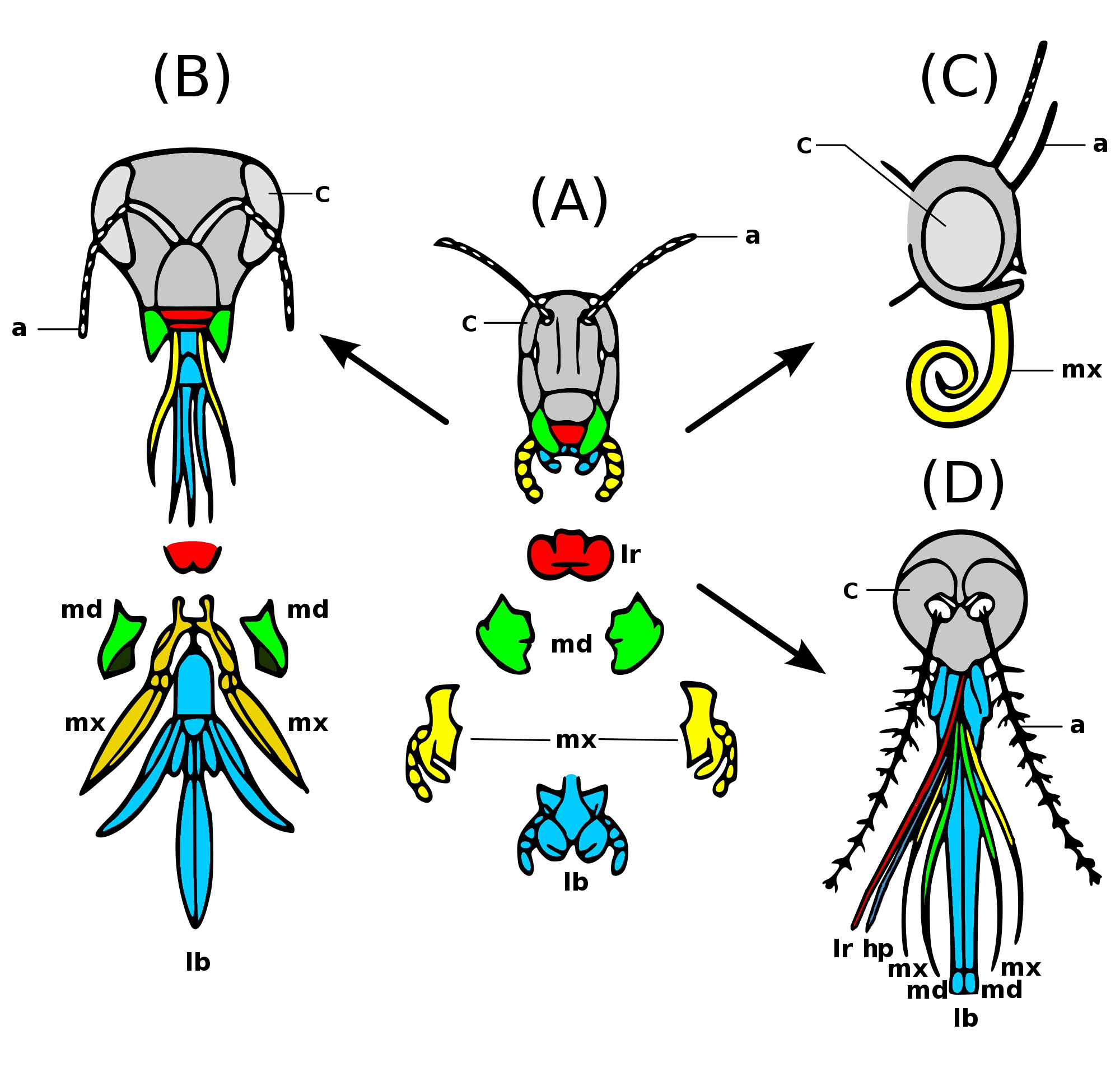
Insect Mouthparts
Insects have mouthparts that may vary greatly across insect species, as they are adapted to particular modes of feeding. The earliest insects had chewing mouthparts. Most specialisation of mouthparts are for piercing and sucking, and this mode of feeding has evolved a number of times idependently. For example, mosquitoes and aphids (which are true bugs) both pierce and suck, however female mosquitoes feed on animal blood whereas aphids feed on plant fluids. Evolution Like most external features of arthropods, the mouthparts of Hexapoda are highly derived. Insect mouthparts show a multitude of different functional mechanisms across the wide diversity of insect species. It is common for significant homology to be conserved, with matching structures forming from matching primordia, and having the same evolutionary origin. However, even if structures are almost physically and functionally identical, they may not be homologous; their analogous functions and appearance might be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nymph (biology)
In biology, a nymph is the immature form of some invertebrates, particularly insects, which undergoes gradual metamorphosis ( hemimetabolism) before reaching its adult stage. Unlike a typical larva, a nymph's overall form already resembles that of the adult, except for a lack of wings (in winged species). In addition, while a nymph moults, it never enters a pupal stage. Instead, the final moult results in an adult insect. Nymphs undergo multiple stages of development called instars. This is the case, for example, in Orthoptera ( crickets, grasshoppers and locusts), Hemiptera (cicadas, shield bugs, whiteflies, aphids, leafhoppers, froghoppers, treehoppers etc.), mayflies, termites, cockroaches, mantises, stoneflies and Odonata ( dragonflies and damselflies). Nymphs of aquatic insects, as in the Odonata, Ephemeroptera, and Plecoptera, are also called naiads, an Ancient Greek name for mythological water nymphs. Usage of the term 'naiad' is no longer popular among en ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |






.jpg)