|
Anti-collision Device
The anti-collision device (ACD) is a form of automatic train protection used on Indian Railways. Overview The ACD Network is a train-collision prevention system invented by Rajaram Bojji and patented by Konkan Railway Corporation, a public-sector undertaking of the Ministry of Railways, government of India. Anti-collision devices were found to be effective in the Southern Railway zone after a brief trial. Level crossings When Loco ACDs receive 'Gate Open' transmissions from Gate ACDs provided at non-interlocked level crossings, they brake to decelerate to 30 km/h or an alternative predetermined speed. Gate ACDs at manned and unmanned level crossings also warn passengers with the message 'Train Approach'. If a Loco ACD receives a manual 'SOS' message from other train bound ACDs or a station ACD that is within three kilometres of its radial range, it applies brakes automatically to bring the train to a stop. The application of this anti-collision device has been refi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Automatic Train Protection
Automatic train protection (ATP) is the generic term for train protection systems that continually check that the speed of a train is compatible with the permitted speed allowed by signalling, including automatic stop at certain signal aspects. If it is not, ATP activates an Emergency brake (train), emergency brake to stop the train. See also * Advanced Civil Speed Enforcement System * Anti Collision Device * Automatic Warning System * Automatische treinbeïnvloeding (ATB) * Automatic Train Protection (United Kingdom), British Rail's ATP system * Continuous Automatic Warning System (CAWS) * EBICAB * European Train Control System (ETCS) * Kavach_-_Indian_Railways, Kavach * Positive Train Control (PTC) * Punktförmige Zugbeeinflussung (PZB) * Train Protection & Warning System * Train Warning System (India), Train Warning System * Transmission Voie-Machine (TVM) References {{rail-transport-stub Train protection systems ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
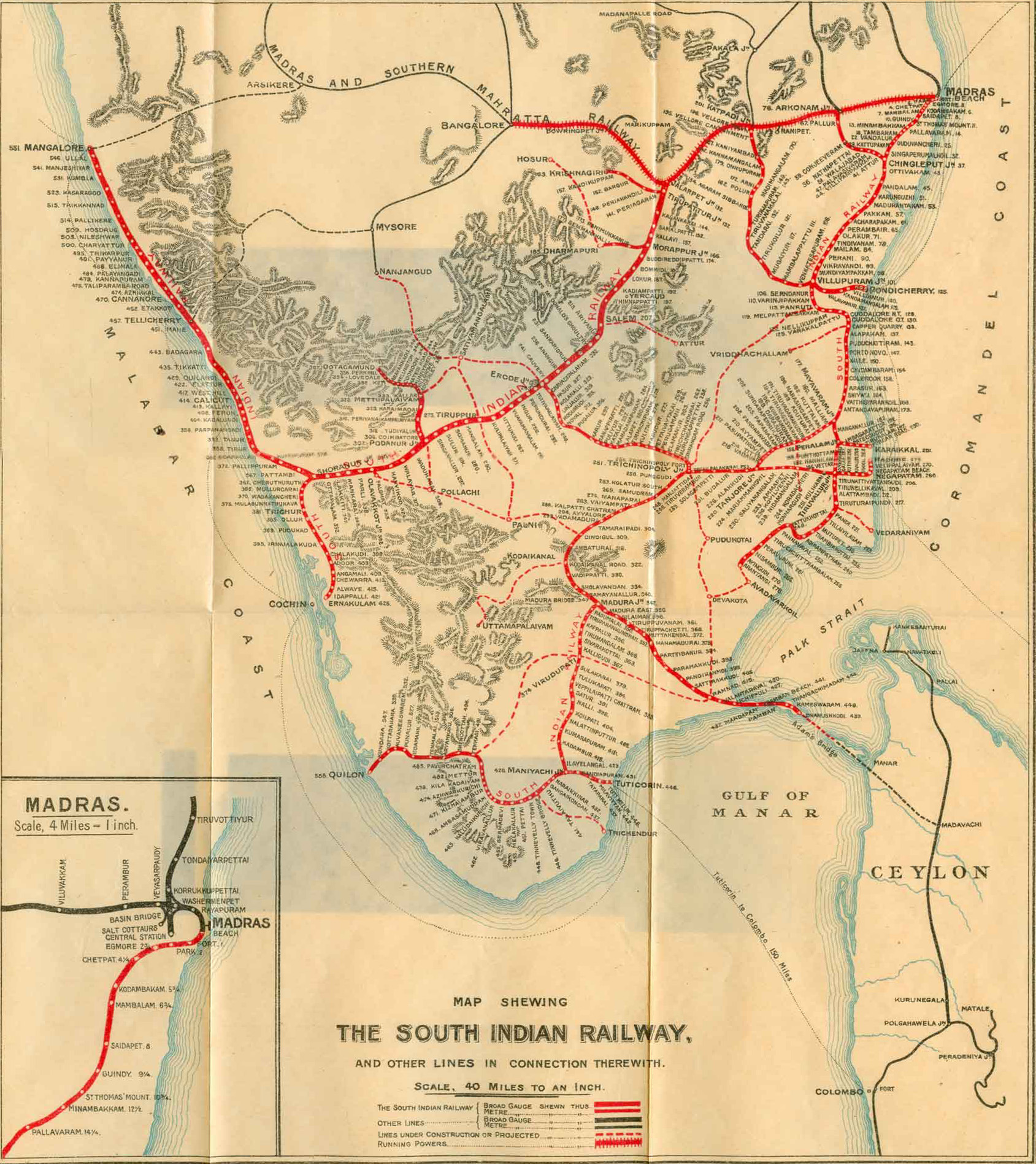
Indian Railways
Indian Railways is a state-owned enterprise that is organised as a departmental undertaking of the Ministry of Railways (India), Ministry of Railways of the Government of India and operates India's national railway system. , it manages the fourth List of countries by rail transport network size, largest national railway system by size with a track length of , running track length of and route length of . , 96.59% of the broad-gauge network is Railway electric traction, electrified. With more than 1.2 million employees, it is the world's List of companies by employees, ninth-largest employer and List of largest employers in India, India's second largest employer. In 1951, the Indian Railways was established by the amalgamation of 42 different railway companies operating in the country, spanning a total of . The railway network across the country was reorganized into six regional zones in 1951–52 for administrative purposes, which was gradually expanded to 18 zones over the ye ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Konkan Railway Corporation
Konkan Railway Corporation Limited (KRCL) is an Indian public sector undertaking which operates Konkan Railway and also undertakes other railway-related projects. It is wholly-owned by the Government of India under the administrative control of the Ministry of Railways and headquartered at CBD Belapur in Navi Mumbai. The railway (railroad) route of KRCL covers the coastal districts of Maharashtra, Goa and Karnataka states of India. The company started its full operations of trains on 26 January 1998. The first passenger train which ran on Konkan railway tracks on 20 March 1993 between Udupi and Mangalore. Konkan Railway Corporation is at the forefront of research and development of new technologies and concepts for Indian railways. During its initial years of operations in the mountainous Konkan region, a spate of accidents prompted Konkan Railway to investigate new technologies. The anti-collision devices, the Sky Bus and RORO are a few of Konkan Railway's innovations.The K ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ministry Of Railways (India)
The Ministry of Railways is a ministry in the Government of India, responsible for the rail transport in India, country's rail transport. The Indian Railways is the rail network operated and administered by the Railway Board constituted by the ministry. The ministry along with the Railway Board is housed inside Rail Bhawan in New Delhi. It is headed by the Minister of Railways (India), Minister of Railways. With more than 1.2 million employees, it is one of the world's List of companies by employees, largest employers. History The first railway track was operational in Chennai, Madras in 1837 and the first passenger train ran in Bombay in 1853. But the earlier railways were operated by private companies with the earliest being the Madras Railway established in 1845 and the Great Indian Peninsular Railway incorporated in 1849. In October 1901, the Secretary of State for India in Council appointed Thomas Robertson as a special commissioner for Indian Railways to prepare a rep ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Government Of India
The Government of India (ISO 15919, ISO: Bhārata Sarakāra, legally the Union Government or Union of India or the Central Government) is the national authority of the Republic of India, located in South Asia, consisting of States and union territories of India, 36 states and union territories. The government is led by the president of India (currently ) who largely exercises the executive powers, and selects the Prime Minister of India, prime minister of India and other ministers for aid and advice. Government has been formed by the The prime minister and their senior ministers belong to the Union Council of Ministers, its executive decision-making committee being the Cabinet (government), cabinet. The government, seated in New Delhi, has three primary branches: the legislature, the executive and the judiciary, whose powers are vested in bicameral Parliament of India, Union Council of Ministers (headed by prime minister), and the Supreme Court of India respectively, with a p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Southern Railway Zone
Southern Railway (SR) is one of the eighteen zones of Indian Railways. It is headquartered at Chennai and operates across the states of Tamil Nadu, Kerala, Andhra Pradesh and the union territory of Puducherry. The origin of the Southern Railway can be traced back to the Madras Railway formed in 1845. Southern Railway was created on 14 April 1951 by merging three state railways, namely, the Madras and Southern Mahratta Railway, the South Indian Railway Company, and the Mysore State Railway and became the first railway zone created in newly formed India. Southern Railway maintains about of railway lines and operates 727 railway stations. It has the distinction of operating the first railway line in India, which opened for traffic from Redhills to Chindadripettai in Madras on 12 September 1836. History The history of the Southern Railway can be traced back to the Madras Railway. In 1832, the proposal to construct the first railway line in India at Madras was made by th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Texas Instruments
Texas Instruments Incorporated (TI) is an American multinational semiconductor company headquartered in Dallas, Texas. It is one of the top 10 semiconductor companies worldwide based on sales volume. The company's focus is on developing analog chips and embedded processors, which account for more than 80% of its revenue. TI also produces digital light processing (DLP) technology and education technology products including calculators, microcontrollers, and multi-core processors. Texas Instruments emerged in 1951 after a reorganization of Geophysical Service Incorporated, a company founded in 1930 that manufactured equipment for use in the seismic industry, as well as defense electronics. TI produced the world's first commercial silicon transistor in 1954, and the same year designed and manufactured the first transistor radio. Jack Kilby invented the integrated circuit in 1958 while working at TI's Central Research Labs. TI also invented the hand-held calculator in 1967, and intr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Open Architecture
Open architecture is a type of computer architecture or software architecture intended to make adding, upgrading, and swapping components with other computers easy. For example, the IBM PC, Amiga 2000 and Apple IIe have an open architecture supporting plug-in cards, whereas the Apple IIc computer has a closed architecture. Open architecture systems may use a standardized system bus such as S-100, PCI or ISA or they may incorporate a proprietary bus standard such as that used on the Apple II, with up to a dozen slots that allow multiple hardware manufacturers to produce add-ons, and for the user to freely install them. By contrast, closed architectures, if they are expandable at all, have one or two "expansion ports" using a proprietary connector design that may require a license fee from the manufacturer, or enhancements may only be installable by technicians with specialized tools or training. Computer platforms may include systems with both open and closed architectures. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kavach (train Protection System)
KAVACH () is an Indian automatic train protection, Automatic Train Protection (ATP) system indigenously developed by Research Design and Standards Organisation, Research Designs & Standards Organisation (RDSO) in collaboration with ''Medha Servo Drives, Kernex Microsystems'' and ''HBL Power Systems''. Initially it was known by the name Train Collision Avoidance System (TCAS). Kavach was adopted by Ministry of Railways (India), Ministry of Railways as the ''National ATP System'' in July 2020. Development of Kavach began in the year 2011 as an open architecture system. In 2014, field trials commenced. First field trial experiments on passenger trains was done in February 2016. Subsequently, Kavach received Safety integrity level, Safety Integrity Level (SIL-4) certification in the year 2019. It is being promoted as one of the cheapest ATP systems available worldwide. The Union budget of India for the FY 2022-23 allocated funds for the rapid implementation of Kavach across 2,000 km ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Train Warning System (India)
The Train Warning System in India is a device that helps prevent trains passing signals at stop. The system is an implementation of Level 1 ERTMS. See also * Anti-collision device * Automatic Train Protection * ETCS The European Train Control System (ETCS) is a train protection system designed to replace the many incompatible systems used by European railways, and railways outside of Europe. ETCS is the signalling and control component of the European ... References External links EFYTimes Railway signalling in India Train protection systems {{India-rail-transport-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |