|
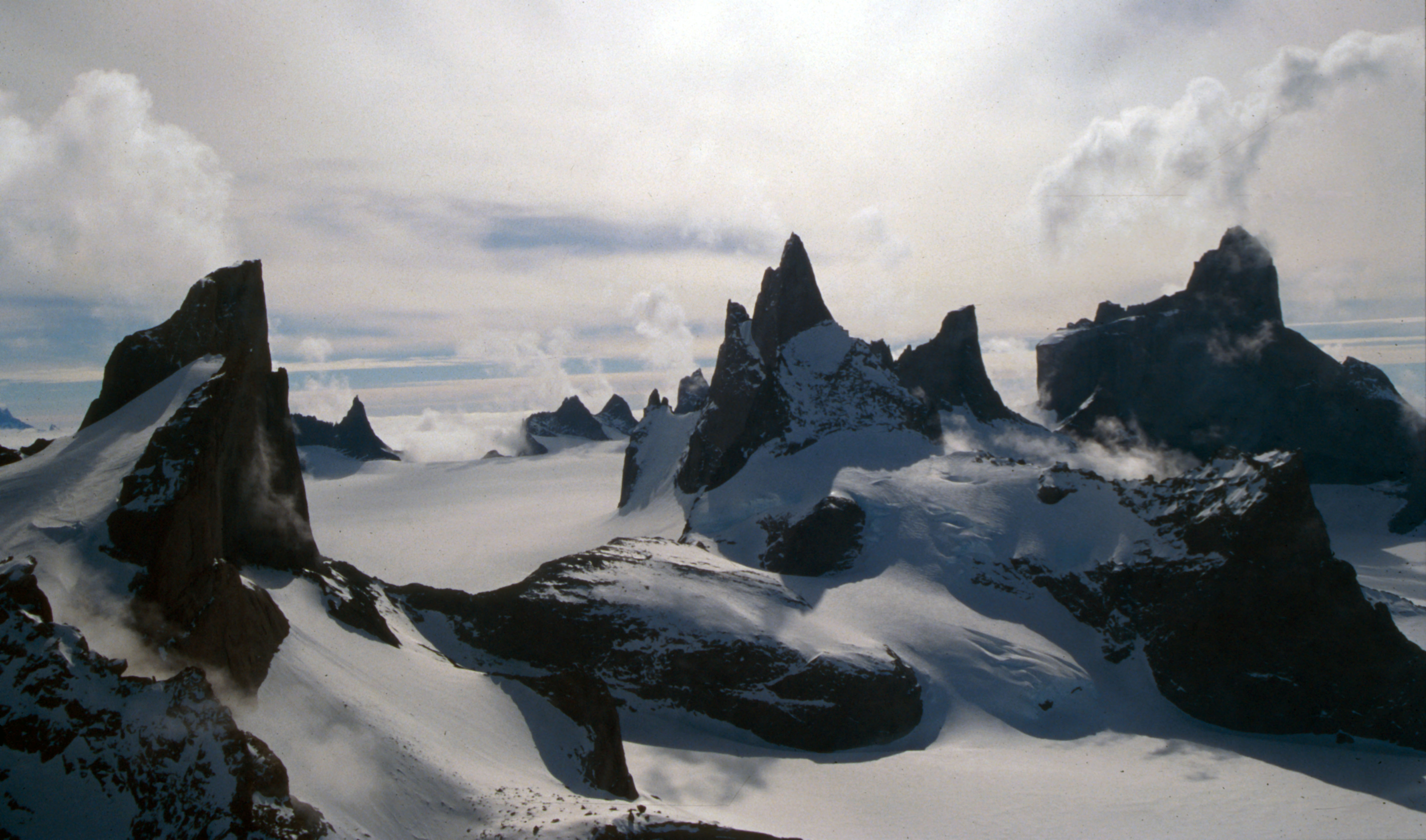
Annandags Peaks
The Annandags Peaks () are a group of small, isolated peaks about southwest of the Jule Peaks (Christmas Peaks) in Queen Maud Land. They were mapped by Norwegian cartographers from surveys and from air photos by the Norwegian–British–Swedish Antarctic Expedition (1949–52) and named "Annandagstoppane" (Boxing Day's Peaks). The Annadagstoppane granite is the only exposed part of the Archaean basement of the Grunehogna Craton and the only Archaean fragment of West Gondwana (Africa and South America) left in Antarctica. U-Pb dating of the youngest detrital zircons from Annandagstoppane returned an age of 3067±8 Ma and a tectonic-magmatic history identical to that of the Kaapvaal craton in southern Africa. This suggests that the Kaapvaal-Grunehogna Craton remained stable for 2.5 billion years before it was split by the Pan-African orogeny. Hafnium dating of phenocrystic and detrital zircons in the granite revealed several crustal sources up to 3.9 billion years old. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jule Peaks
The Jule Peaks () are a small group of isolated peaks located about west-northwest of Borg Mountain in Queen Maud Land, Antarctica. They were mapped by Norwegian cartographers from surveys and air photos by the Norwegian–British–Swedish Antarctic Expedition (1949–1952), and named Juletoppane (the Christmas peaks). The Annandags Peaks The Annandags Peaks () are a group of small, isolated peaks about southwest of the Jule Peaks (Christmas Peaks) in Queen Maud Land. They were mapped by Norwegian cartographers from surveys and from air photos by the Norwegian–British–Swedish ... sit about 15 nautical miles (30 km) southwest. References Mountains of Queen Maud Land Princess Martha Coast {{PrincessMarthaCoast-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Detrital Zircon Geochronology
Detrital zircon geochronology is the science of geochronology, analyzing the age of zircons deposited within a specific sedimentary rock, sedimentary unit by examining their inherent radioisotopes, most commonly the uranium–lead dating, uranium–lead ratio. Zircon is a common Accessory mineral, accessory or trace mineral constituent of most granite and felsic igneous rocks. Due to its hardness, durability and chemical inertness, zircon persists in sedimentary deposits and is a common constituent of most sands. Zircons contain trace amounts of uranium and thorium and can be dated using several modern analytical techniques. Detrital zircon geochronology has become increasingly popular in geological studies from the 2000s mainly due to the advancement in radiometric dating techniques. Detrital zircon age data can be used to constrain the maximum depositional age, determine provenance (geology), provenance, and reconstruct the tectonic setting on a regional scale. Detrital zirco ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
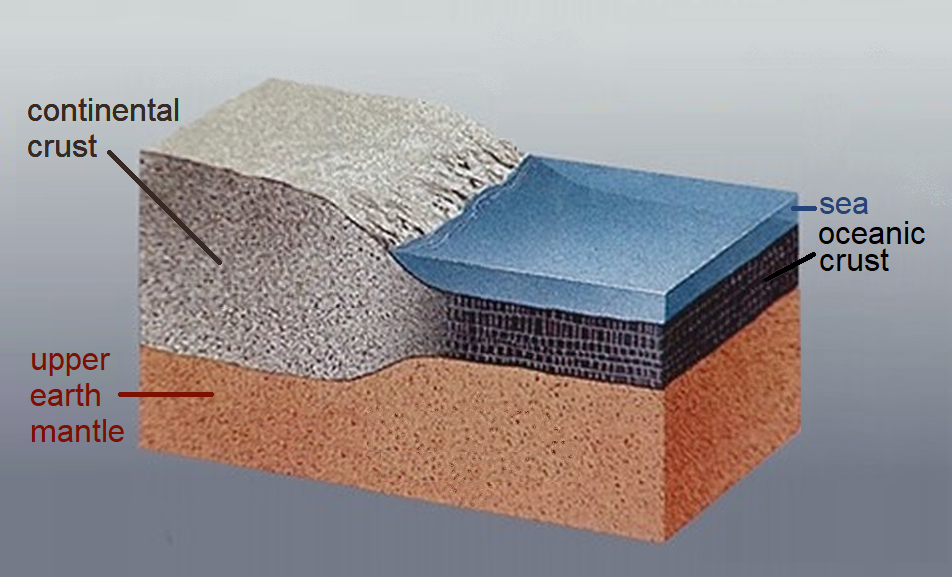
Craton
A craton ( , , or ; from "strength") is an old and stable part of the continental lithosphere, which consists of Earth's two topmost layers, the crust and the uppermost mantle. Having often survived cycles of merging and rifting of continents, cratons are generally found in the interiors of tectonic plates; the exceptions occur where geologically recent rifting events have separated cratons and created passive margins along their edges. Cratons are characteristically composed of ancient crystalline basement rock, which may be covered by younger sedimentary rock. They have a thick crust and deep lithospheric roots extending several hundred kilometres into Earth's mantle. Terminology The term ''craton'' is used to distinguish the stable portion of the continental crust from regions that are more geologically active and unstable. Cratons are composed of two layers: a continental '' shield'', in which the basement rock crops out at the surface, and a '' platform'' which o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Continental Crust
Continental crust is the layer of igneous, metamorphic, and sedimentary rocks that forms the geological continents and the areas of shallow seabed close to their shores, known as '' continental shelves''. This layer is sometimes called '' sial'' because its bulk composition is richer in aluminium silicates (Al-Si) and has a lower density compared to the oceanic crust, called '' sima'' which is richer in magnesium silicate (Mg-Si) minerals. Changes in seismic wave velocities have shown that at a certain depth (the Conrad discontinuity), there is a reasonably sharp contrast between the more felsic upper continental crust and the lower continental crust, which is more mafic in character. Most continental crust is dry land above sea level. However, 94% of the Zealandia continental crust region is submerged beneath the Pacific Ocean, with New Zealand constituting 93% of the above-water portion. Thickness and density The continental crust consists of various layers, with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phenocryst
image:montblanc granite phenocrysts.JPG, 300px, Granites often have large feldspar, feldspathic phenocrysts. This granite, from the Switzerland, Swiss side of the Mont Blanc massif, has large white phenocrysts of plagioclase (that have trapezoid shapes when cut through). 1 euro coin (diameter 2.3 cm) for scale. A phenocryst is an early forming, relatively large and usually conspicuous crystal distinctly larger than the grains of the rock Matrix (geology), groundmass of an igneous rock. Such rocks that have a distinct difference in the size of the crystals are called Porphyry (geology), porphyries, and the adjective porphyritic is used to describe them. Phenocrysts often have euhedral forms, either due to early growth within a magma, or by post-emplacement recrystallization (geology), recrystallization. Normally the term ''phenocryst'' is not used unless the crystals are directly observable, which is sometimes stated as greater than in diameter. Phenocrysts below this level, but s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hafnium
Hafnium is a chemical element; it has symbol Hf and atomic number 72. A lustrous, silvery gray, tetravalent transition metal, hafnium chemically resembles zirconium and is found in many zirconium minerals. Its existence was predicted by Dmitri Mendeleev in 1869, though it was not identified until 1922, by Dirk Coster and George de Hevesy. Hafnium is named after , the Latin name for Copenhagen, where it was discovered. Hafnium is used in filaments and electrodes. Some semiconductor fabrication processes use its oxide for integrated circuits at 45 nanometers and smaller feature lengths. Some superalloys used for special applications contain hafnium in combination with niobium, titanium, or tungsten. Hafnium's large neutron capture cross section makes it a good material for neutron absorption in control rods in nuclear power plants, but at the same time requires that it be removed from the neutron-transparent corrosion-resistant zirconium alloys used in nuclear r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pan-African Orogeny
The Pan-African orogeny was a series of major Neoproterozoic orogenic events which related to the formation of the supercontinents Gondwana and Pannotia about 600 million years ago. This orogeny is also known as the Pan-Gondwanan or Saldanian Orogeny. The Pan-African orogeny and the Grenville orogeny are the largest known systems of orogenies on Earth. The sum of the continental crust formed in the Pan-African orogeny and the Grenville orogeny makes the Neoproterozoic the period of Earth's history that has produced most continental crust. History and terminology The term ''Pan-African'' was coined by for a tectono-thermal event at about 500 Ma when a series of mobile belts in Africa formed between much older African cratons. At the time, other terms were used for similar orogenic events on other continents, i.e. '' Brasiliano'' in South America; ''Adelaidean'' in Australia; and ''Beardmore'' in Antarctica. Later, when plate tectonics became generally accepted, the term ''Pan-A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Detritus (geology)
Detritus (; adj. ''detrital'' ) is particles of rock derived from pre-existing rock through weathering and erosion.Essentials of Geology, 3rd Ed, Stephen Marshak, p G-7 A fragment of detritus is called a clast.Essentials of Geology, 3rd Ed, Stephen Marshak, p G-5 Detrital particles can consist of lithic fragments (particles of recognisable rock), or of monomineralic fragments (mineral grains). These particles are often transported through sedimentary processes into depositional systems such as riverbeds, lakes or the ocean, forming sedimentary successions. Diagenetic processes can transform these sediments into rock through cementation and lithification Lithification (from the Ancient Greek word ''lithos'' meaning 'rock' and the Latin-derived suffix ''-ific'') is the process in which sediments compact under pressure, expel connate fluids, and gradually become solid rock. Essentially, lithificati ..., forming sedimentary rocks such as sandstone. These rocks can then in turn ag ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Queen Maud Land
Queen Maud Land () is a roughly region of Antarctica Territorial claims in Antarctica, claimed by Norway as a dependent territory. It borders the claimed British Antarctic Territory 20th meridian west, 20° west, specifically the Caird Coast, Coats Land on the West, and the Australian Antarctic Territory 45th meridian east, 45° east, specifically Enderby Land on the East. In addition, a small unclaimed area from 1939 was annexed in June 2015. Positioned in East Antarctica, it makes out about one-fifth of the continent, and is named after the Norwegian Maud of Wales, Queen Maud (1869–1938). In 1930, the Norwegian Hjalmar Riiser-Larsen was the first person known to have set foot in the territory. On 14 January 1939, the territory was claimed by Norway. On 23 June 1961, Queen Maud Land became part of the Antarctic Treaty System, making it a demilitarised zone. It is one of dependencies of Norway, two Antarctic claims made by Norway, the other being Peter I Island. They are adm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Uranium–lead Dating
Uranium–lead dating, abbreviated U–Pb dating, is one of the oldest and most refined of the radiometric dating schemes. It can be used to date rocks that formed and crystallised from about 1 million years to over 4.5 billion years ago with routine precisions in the 0.1–1 percent range. The method is usually applied to zircon. This mineral incorporates uranium and thorium atoms into its crystal structure, but strongly rejects lead when forming. As a result, newly-formed zircon crystals will contain no lead, meaning that any lead found in the mineral is radiogenic. Since the exact rate at which uranium decays into lead is known, the current ratio of lead to uranium in a sample of the mineral can be used to reliably determine its age. The method relies on two separate decay chains, the uranium series from 238U to 206Pb, with a half-life of 4.47 billion years and the actinium series from 235U to 207Pb, with a half-life of 710 million years. Decay routes Uranium decays to l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gondwana
Gondwana ( ; ) was a large landmass, sometimes referred to as a supercontinent. The remnants of Gondwana make up around two-thirds of today's continental area, including South America, Africa, Antarctica, Australia (continent), Australia, Zealandia, Arabian Peninsula, Arabia, and the Indian subcontinent. Gondwana was formed by the Accretion (geology), accretion of several cratons (large stable blocks of the Earth's crust), beginning with the East African Orogeny, the collision of India and Geography of Madagascar, Madagascar with East Africa, and culminating in with the overlapping Brasiliano orogeny, Brasiliano and Kuunga orogeny, Kuunga orogenies, the collision of South America with Africa, and the addition of Australia and Antarctica, respectively. Eventually, Gondwana became the largest piece of continental crust of the Paleozoic Era, covering an area of some , about one-fifth of the Earth's surface. It fused with Laurasia during the Carboniferous to form Pan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |