|
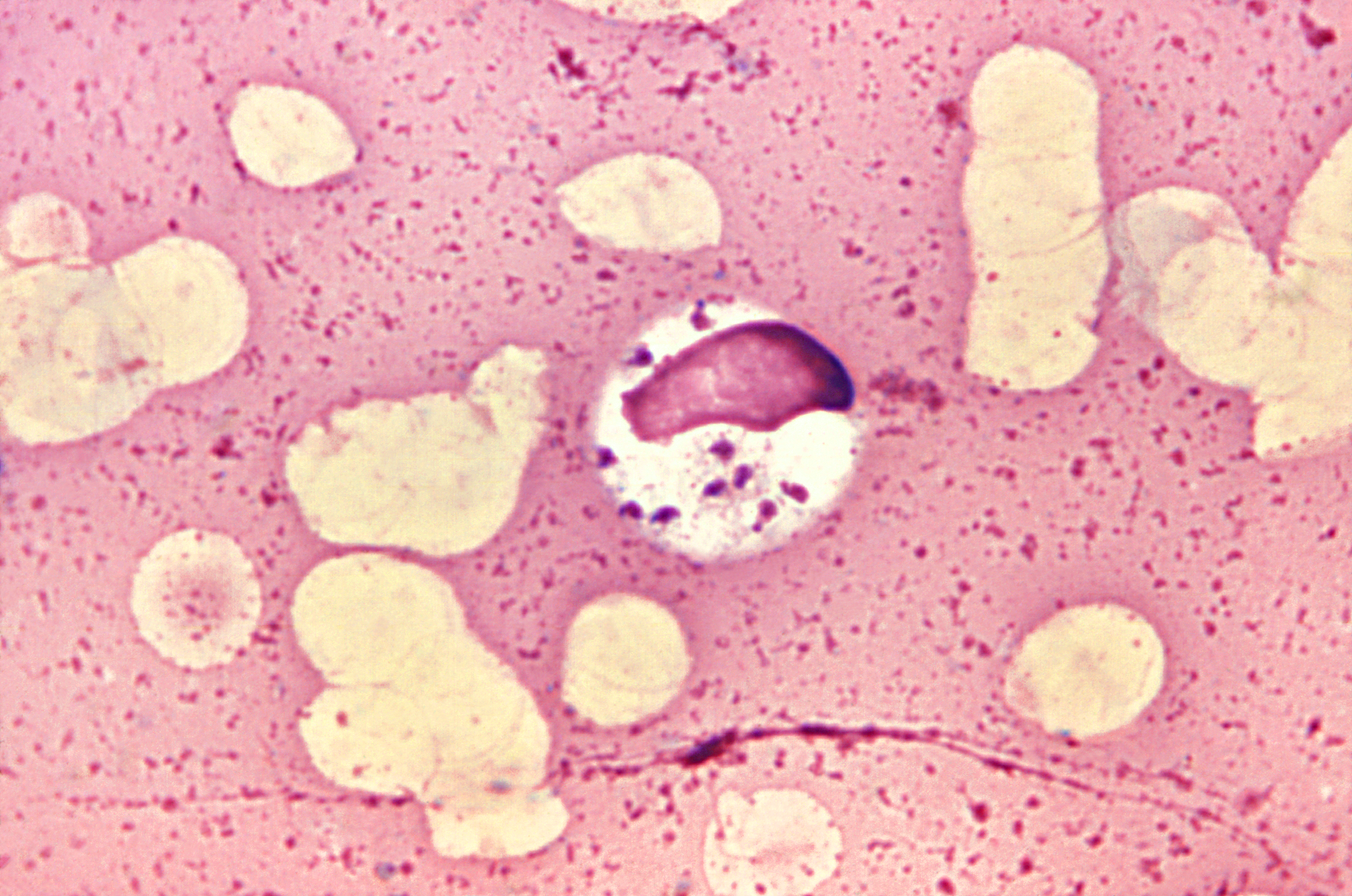
Angomonas
''Angomonas'' is a genus of protists in the order of Trypanosomatida Trypanosomatida is a group of kinetoplastid unicellular organisms distinguished by having only a single flagellum. The name is derived from the Greek ''trypano'' (borer) and ''soma'' (body) because of the corkscrew-like motion of some trypanosom .... Several species of this genus are associated with blow flies. References Trypanosomatida Parasitic excavates Parasites of insects Taxa described in 1991 {{excavata-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Angomonas Deanei
''Angomonas deanei'' is a flagellated trypanosomatid protozoan. As an obligate parasite, it infects the gastrointestinal tract of insects, and is in turn a host to symbiotic bacteria. The bacterial endosymbiont ''Ca.'' "''Kinetoplastibacterium crithidii''" maintains a permanent mutualistic relationship with the protozoan such that it is no longer able to reproduce and survive on its own. The symbiosis, subsequently also discovered in varying degrees in other protists such as '' Strigomonas culicis, Novymonas esmeraldas, Diplonema japonicum'' and ''Diplonema aggregatum'' are considered as good models for the understanding of the evolution of eukaryotes from prokaryotes, and on the origin of cell organelles (i.e. symbiogenesis). The species was first described as ''Crithidia deanei'' in 1973 by a Brazilian parasitologist Aurora L. M. Carvalho. A phylogenetic analysis in 2011 revealed that it belongs to the genus ''Angomonas'', thereby becoming ''Angomonas deanei''. The symbiot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trypanosomatida
Trypanosomatida is a group of kinetoplastid unicellular organisms distinguished by having only a single flagellum. The name is derived from the Greek ''trypano'' (borer) and ''soma'' (body) because of the corkscrew-like motion of some trypanosomatid species. All members are exclusively parasitic, found primarily in insects. A few genera have life-cycles involving a secondary host, which may be a vertebrate, invertebrate or plant. These include several species that cause major diseases in humans. Some trypanosomatida are intracellular parasites, with the important exception of ''Trypanosoma brucei''. Medical importance The three major human diseases caused by trypanosomatids are; African trypanosomiasis (African trypanosomiasis, sleeping sickness, caused by ''Trypanosoma brucei'' and transmitted by Tsetse fly, tsetse flies), South American trypanosomiasis (Chagas disease, caused by ''Trypanosoma cruzi, T. cruzi'' and transmitted by Triatominae, triatomine bugs), and leishmanias ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Angomonas Desouzai
''Angomonas desouzai'' is a parasitic protist from the order Trypanosomatida. Ecology ''Angomonas desouzai'' parasitizes species of the diptera and, like other species of ''Angomonas ''Angomonas'' is a genus of protists in the order of Trypanosomatida Trypanosomatida is a group of kinetoplastid unicellular organisms distinguished by having only a single flagellum. The name is derived from the Greek ''trypano'' (borer) and ...'' harbors endosymbiotic bacteria. References Trypanosomatida Parasitic excavates Parasites of Diptera Protists described in 1989 Euglenozoa species {{Excavata-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Angomonas Ambiguus
''Angomonas ambiguus'' is a parasitic protist from the order Trypanosomatida Trypanosomatida is a group of kinetoplastid unicellular organisms distinguished by having only a single flagellum. The name is derived from the Greek ''trypano'' (borer) and ''soma'' (body) because of the corkscrew-like motion of some trypanosom .... References Trypanosomatida Parasitic excavates Parasites of Diptera Protists described in 2011 Euglenozoa species {{Excavata-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Global Biodiversity Information Facility
The Global Biodiversity Information Facility (GBIF) is an international organisation that focuses on making scientific data on biodiversity available via the Internet using web services. The data are provided by many institutions from around the world; GBIF's information architecture makes these data accessible and searchable through a single portal. Data available through the GBIF portal are primarily distribution data on plants, animals, fungi, and microbes for the world, and scientific names data. The mission of the GBIF is to facilitate free and open access to biodiversity data worldwide to underpin sustainable development. Priorities, with an emphasis on promoting participation and working through partners, include mobilising biodiversity data, developing protocols and standards to ensure scientific integrity and interoperability, building an informatics architecture to allow the interlinking of diverse data types from disparate sources, promoting capacity building and cat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Smithsonian Institution
The Smithsonian Institution ( ), or simply the Smithsonian, is a group of museums, Education center, education and Research institute, research centers, created by the Federal government of the United States, U.S. government "for the increase and diffusion of knowledge". Founded on August 10, 1846, it operates as a trust instrumentality and is not formally a part of any of the Federal government of the United States#branches, three branches of the federal government. The institution is named after its founding donor, British scientist James Smithson. It was originally organized as the United States National Museum, but that name ceased to exist administratively in 1967. The Smithsonian Institution has historical holdings of over 157 million items, 21 museums, 21 libraries, 14 education and research centers, a zoo, and historical and architectural landmarks, mostly located in Washington, D.C. Additional facilities are located in Maryland, New York (state), New York, and Virg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Calliphoridae
The Calliphoridae (commonly known as blowflies, blow flies, blow-flies, carrion flies, bluebottles, or greenbottles) are a family of insects in the order Diptera, with almost 1,900 known species. The maggot larvae, often used as fishing bait, are known as gentles. The family is known to be polyphyletic, but much remains disputed regarding proper treatment of the constituent taxa, some of which are occasionally accorded family status (e.g., Bengaliidae and Helicoboscidae). Description Characteristics Calliphoridae adults are commonly shiny with metallic colouring, often with blue, green, or black thoraces and abdomens. Antennae are three-segmented and aristate. The aristae are plumose their entire length, and the second antennal segment is distinctly grooved. Members of Calliphoridae have branched Rs 2 veins, frontal sutures are present, and calypters are well developed. The characteristics and arrangements of hairlike bristles are used to differentiate among members of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parasitic Excavates
Parasitism is a close relationship between species, where one organism, the parasite, lives (at least some of the time) on or inside another organism, the host, causing it some harm, and is adapted structurally to this way of life. The entomologist E. O. Wilson characterised parasites' way of feeding as "predators that eat prey in units of less than one". Parasites include single-celled protozoans such as the agents of malaria, sleeping sickness, and amoebic dysentery; animals such as hookworms, lice, mosquitoes, and vampire bats; fungi such as honey fungus and the agents of ringworm; and plants such as mistletoe, dodder, and the broomrapes. There are six major parasitic strategies of exploitation of animal hosts, namely parasitic castration, directly transmitted parasitism (by contact), trophicallytransmitted parasitism (by being eaten), vector-transmitted parasitism, parasitoidism, and micropredation. One major axis of classification concerns invasiveness: an endoparas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parasites Of Insects
Parasitism is a Symbiosis, close relationship between species, where one organism, the parasite, lives (at least some of the time) on or inside another organism, the Host (biology), host, causing it some harm, and is Adaptation, adapted structurally to this way of life. The entomologist E. O. Wilson characterised parasites' way of feeding as "predators that eat prey in units of less than one". Parasites include single-celled protozoans such as the agents of malaria, sleeping sickness, and amoebic dysentery; animals such as hookworms, lice, mosquitoes, and vampire bats; fungi such as Armillaria mellea, honey fungus and the agents of ringworm; and plants such as mistletoe, dodder, and the Orobanchaceae, broomrapes. There are six major parasitic Behavioral ecology#Evolutionarily stable strategy, strategies of exploitation of animal hosts, namely parasitic castration, directly transmitted parasitism (by contact), wikt:trophic, trophicallytransmitted parasitism (by being eaten), ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |