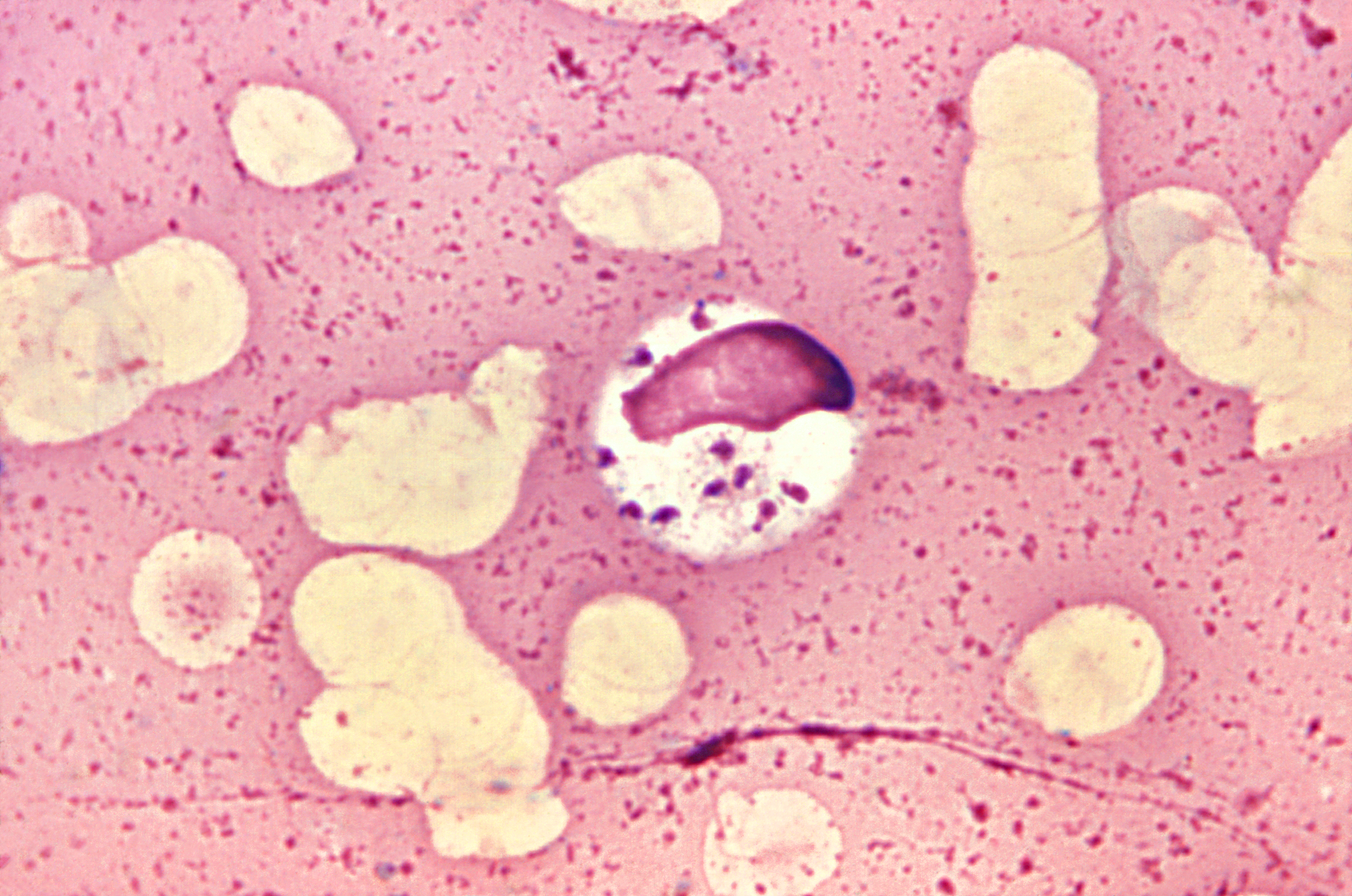
|
Angomonas Ambiguus
''Angomonas ambiguus'' is a parasitic protist from the order Trypanosomatida Trypanosomatida is a group of kinetoplastid unicellular organisms distinguished by having only a single flagellum. The name is derived from the Greek ''trypano'' (borer) and ''soma'' (body) because of the corkscrew-like motion of some trypanosom .... References Trypanosomatida Parasitic excavates Parasites of Diptera Protists described in 2011 Euglenozoa species {{Excavata-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trypanosomatida
Trypanosomatida is a group of kinetoplastid unicellular organisms distinguished by having only a single flagellum. The name is derived from the Greek ''trypano'' (borer) and ''soma'' (body) because of the corkscrew-like motion of some trypanosomatid species. All members are exclusively parasitic, found primarily in insects. A few genera have life-cycles involving a secondary host, which may be a vertebrate, invertebrate or plant. These include several species that cause major diseases in humans. Some trypanosomatida are intracellular parasites, with the important exception of ''Trypanosoma brucei''. Medical importance The three major human diseases caused by trypanosomatids are; African trypanosomiasis (African trypanosomiasis, sleeping sickness, caused by ''Trypanosoma brucei'' and transmitted by Tsetse fly, tsetse flies), South American trypanosomiasis (Chagas disease, caused by ''Trypanosoma cruzi, T. cruzi'' and transmitted by Triatominae, triatomine bugs), and leishmanias ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parasitic Excavates
Parasitism is a close relationship between species, where one organism, the parasite, lives (at least some of the time) on or inside another organism, the host, causing it some harm, and is adapted structurally to this way of life. The entomologist E. O. Wilson characterised parasites' way of feeding as "predators that eat prey in units of less than one". Parasites include single-celled protozoans such as the agents of malaria, sleeping sickness, and amoebic dysentery; animals such as hookworms, lice, mosquitoes, and vampire bats; fungi such as honey fungus and the agents of ringworm; and plants such as mistletoe, dodder, and the broomrapes. There are six major parasitic strategies of exploitation of animal hosts, namely parasitic castration, directly transmitted parasitism (by contact), trophicallytransmitted parasitism (by being eaten), vector-transmitted parasitism, parasitoidism, and micropredation. One major axis of classification concerns invasiveness: an endoparas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protists Described In 2011
A protist ( ) or protoctist is any eukaryotic organism that is not an animal, land plant, or fungus. Protists do not form a natural group, or clade, but are a paraphyletic grouping of all descendants of the last eukaryotic common ancestor excluding land plants, animals, and fungi. Protists were historically regarded as a separate taxonomic kingdom known as Protista or Protoctista. With the advent of phylogenetic analysis and electron microscopy studies, the use of Protista as a formal taxon was gradually abandoned. In modern classifications, protists are spread across several eukaryotic clades called supergroups, such as Archaeplastida (photoautotrophs that includes land plants), SAR, Obazoa (which includes fungi and animals), Amoebozoa and "Excavata". Protists represent an extremely large genetic and ecological diversity in all environments, including extreme habitats. Their diversity, larger than for all other eukaryotes, has only been discovered in recent decades thro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |