|
Anartes
The Anartes (or Anarti, Anartii or Anartoi)Jan Czarnecki (1975) 120 were Celtic tribes, or, in the case of those sub-groups of Anartes which penetrated the ancient region of Dacia (roughly modern Romania), Celts culturally assimilated by the Dacians.Oltean Ioana A (2007) 47 Ptolemy's ''Geographia'' locates the ''Anartoi'' in the north of Dacia.Jan Czarnecki (1975) 119 Some groups of Anartes occupied parts of modern Slovakia and southeastern Poland. The Dacian town of '' Docidava'' was situated in the territory of the Anartes, according to Pârvan. The ''Anartophracti'' (or ''Anartofraktoi'') are mentioned by Ptolemy. This tribe's name appears to be compound Latin-Greek name and may be related to the ''Anartoi'' resident in Dacia, Czarnecki argues.Jan Czarnecki (1975) 119 The ''Anartofraktoi'' were a northern Dacian tribe, according to Braune or mixed Dacian-Celtic, according to Pârvan. In ancient sources, the earliest mention of the Anartes is in the Elogium of Tusculum (10 BC ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Púchov Culture
The Púchov culture was an archaeological culture named after site of Púchov-Skalka in Slovakia. Its probable bearer was the Celtic Cotini and/or Anartes tribes. It existed in northern and central Slovakia (although it also plausibly spread to the surrounding regions) between the 2nd century BCE and the 1st century CE. Characteristics The Púchov culture developed from the Lusatian culture and it was influenced later by the Illyrian culture, the Celts, and by the beginning of the Christian era, the Dacians. Settlements were situated on moderate hill sides and near streams. The largest known religious, economic, and political center of the Púchov culture was the hill-fort of Havránok, famous for its traces of human sacrifice. Disappearance As a result of the Dacian and Germanic tribal expansions at the beginning of the Common Era Common Era (CE) and Before the Common Era (BCE) are year notations for the Gregorian calendar (and its predecessor, the Julian calendar) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dacians
The Dacians (; ; ) were the ancient Indo-European inhabitants of the cultural region of Dacia, located in the area near the Carpathian Mountains and west of the Black Sea. They are often considered a subgroup of the Thracians. This area includes mainly the present-day countries of Romania and Moldova, as well as parts of Ukraine, Moravian Banovina, Eastern Serbia, Northern Bulgaria, Slovakia, Hungary and Southern Poland. The Dacians and the related Getae spoke the Dacian language, which has a debated relationship with the neighbouring Thracian language and may be a subgroup of it. Dacians were somewhat culturally influenced by the neighbouring Scythians and by the Celtic invasion of the Balkans, Celtic invaders of the 4th century BC. Name and etymology Name The Dacians were known as ''Geta'' (plural ''Getae'') in Ancient Greek writings, and as ''Dacus'' (plural ''Daci'') or ''Getae'' in Roman Empire, Roman documents, but also as ''Dagae'' and ''Gaete'' as depicted on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
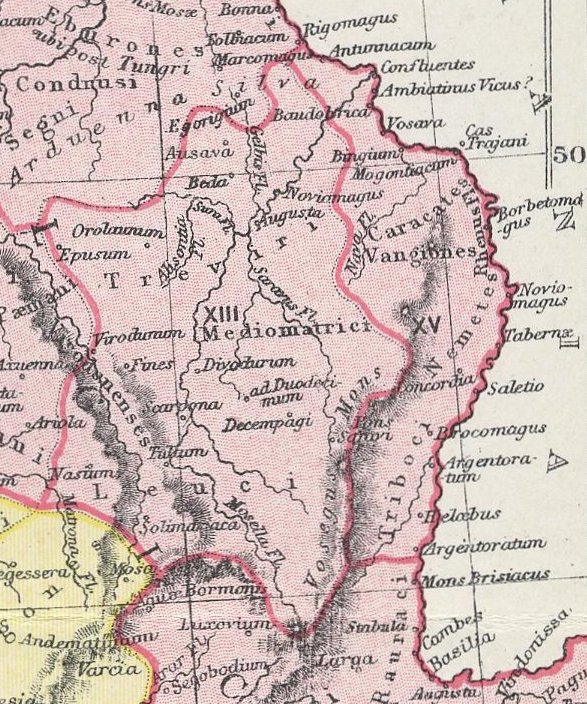
Nemetes
The Nemetes or Nemeti were a tribe settled along the Upper Rhine by Ariovistus in the 1st century BC. Their area of settlement was the contact zone between Celtic (Gaulish) and Germanic peoples. According to Tacitus, the Nemetes were "unquestionably Germanic". The name of the tribe, however, is Celtic as the name of its main town ''Noviomagus'' meaning ''novios'' 'new' and ''magos'' 'plain', 'market' (cf. Welsh ''maes'' 'field', Old Irish ''mag'' 'plain'), as are those of several gods worshipped in their territory, including Nemetona, who is thought to have been their eponymous deity.John T. Koch (2006). ''Celtic Culture: A Historical Encyclopedia.'' ABC-CLIO, p. 1351. Both of these names are taken to be derivations from the Celtic stem '' nemeto-'' "sacred grove".Xavier Delamarre (2003). ''Dictionnaire de la langue gauloise.'' Éditions Errance, p. 233. In '' De Bello Gallico'', Caesar writes that the Hercynian Forest "begins at the frontiers of the Helvetii, and Rauraci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
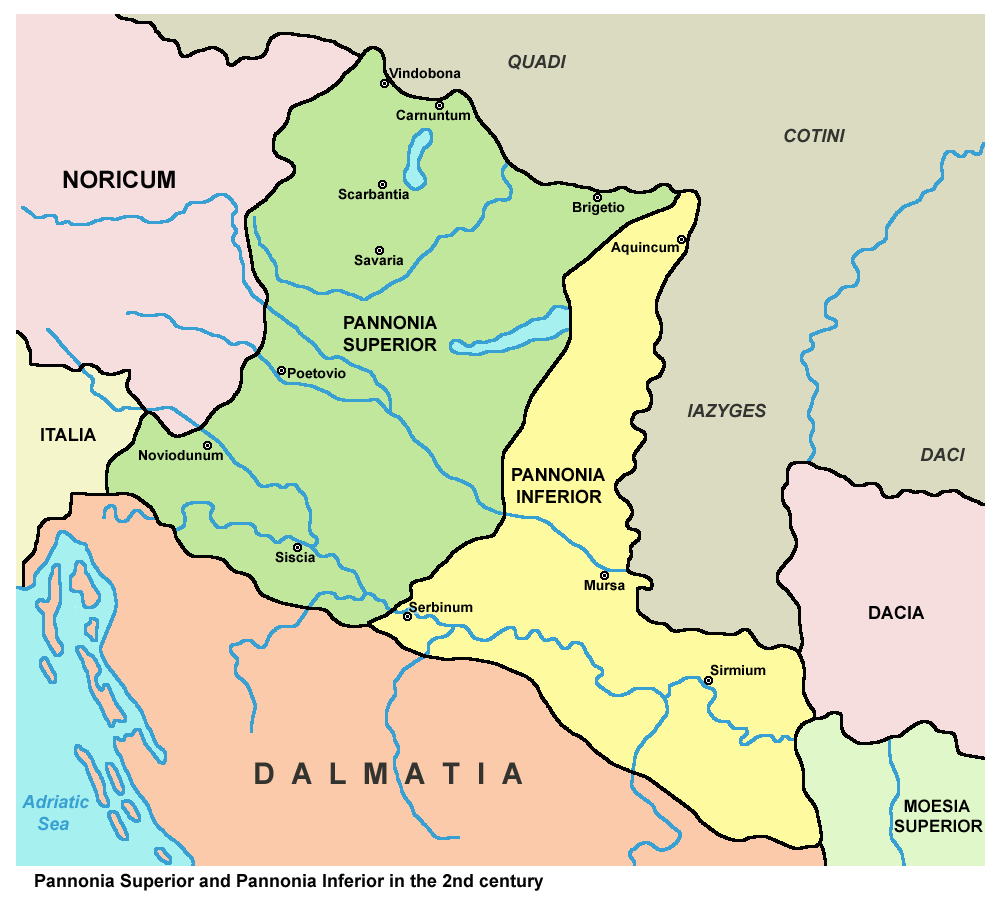
Pannonia Popolazioni Png
Pannonia (, ) was a province of the Roman Empire bounded on the north and east by the Danube, on the west by Noricum and upper Italy, and on the southward by Dalmatia and upper Moesia. It included the modern regions western Hungary, western Slovakia, eastern Austria, northern Croatia, north-western Serbia, northern Slovenia, and northern Bosnia and Herzegovina. Background In the Early Iron Age, Transdanubia was inhabited by the Pannonians or Pannonii, a collection of Illyrian tribes. The Celts invaded in the Late Iron Age and Gallo-Roman historian Pompeius Trogus writes that the Celts were met with heavy resistance from the locals and were not able to overrun the southern part of Transdanubia. Some tribes advanced as far as Delphi, with the Scordisci settling in Syrmia (279 BC) upon being forced to withdraw. The arrival of the Celts in Transdanubia disrupted the flow of amber from the Baltic Sea region, through the Amber Road, to the Illyrians. They founded many villages. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
De Bello Gallico
''Commentarii de Bello Gallico'' (; ), also ''Bellum Gallicum'' (), is Julius Caesar's first-hand account of the Gallic Wars, written as a third-person narrative. In it, Caesar describes the battles and intrigues that took place in the nine years he spent fighting the Celtic and Germanic peoples in Gaul who opposed Roman conquest. The "Gaul" to which Caesar refers is ambiguous, as the term had various connotations in Roman writing and discourse during Caesar's time. Generally, Gaul included all of the regions primarily inhabited by Celts, aside from the province of Gallia Narbonensis (modern-day Provence and Languedoc-Roussillon), which had already been conquered in Caesar's time, therefore encompassing the rest of modern France, Belgium, Western Germany, and parts of Switzerland. As the Roman Republic made inroads deeper into Celtic territory and conquered more land, the definition of "Gaul" shifted. Concurrently, "Gaul" was also used in common parlance as a synonym for "uncout ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pannonia Inferior
Pannonia Inferior, lit. Lower Pannonia, was a province of the Roman Empire. Its capital was Sirmium. It was one of the border provinces on the Danube. It was formed in the year 103 AD by Emperor Trajan who divided the former province of Pannonia into two parts: Pannonia Superior and Pannonia Inferior. The province included parts of present-day states of Hungary, Serbia, Croatia, and Bosnia and Herzegovina. The province was bordered to the east (across the Danube) by a Sarmatian tribe—the Iazyges. Later, the Vandals appeared to the north-east. Settlements Major settlements in Pannonia Inferior included: * ''Sirmium'' (Sremska Mitrovica) which several times served as an imperial residence for several emperors. * '' Aquincum'' (Buda), the provincial capital. * ''Cuccium'' ( Ilok) * ''Cibalae'' (Vinkovci) * ''Mursa'' ( Osijek) * ''Certissa'' ( Đakovo) * ''Marsonia'' (Slavonski Brod) * ''Sopianae'' (Pécs) Aftermath and legacy The province was yet again split during the reign of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roman Province
The Roman provinces (, pl. ) were the administrative regions of Ancient Rome outside Roman Italy that were controlled by the Romans under the Roman Republic and later the Roman Empire. Each province was ruled by a Roman appointed as Roman governor, governor. For centuries, it was the largest administrative unit of the foreign possessions of ancient Rome. With the administrative reform initiated by Diocletian, it became a third level administrative subdivision of the Roman Empire, or rather a subdivision of the Roman diocese, imperial dioceses (in turn subdivisions of the Praetorian prefecture, imperial prefectures). History A province was the basic and, until the Tetrarchy (from AD 293), the largest territorial and administrative unit of the empire's territorial possessions outside Roman Italy. During the republic and early empire, provinces were generally governed by politicians of Roman senate, senatorial rank, usually former Roman consul, consuls or former praetors. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marcus Aurelius
Marcus Aurelius Antoninus ( ; ; 26 April 121 – 17 March 180) was Roman emperor from 161 to 180 and a Stoicism, Stoic philosopher. He was a member of the Nerva–Antonine dynasty, the last of the rulers later known as the Five Good Emperors and the last emperor of the Pax Romana, an age of relative peace, calm, and stability for the Roman Empire lasting from 27 BC to 180 AD. He served as Roman consul in 140, 145, and 161. Marcus Aurelius was the son of the praetor Marcus Annius Verus (father of Marcus Aurelius), Marcus Annius Verus and his wife, Domitia Calvilla. He was related through marriage to the emperors Trajan and Hadrian. Marcus was three when his father died, and was raised by his mother and Marcus Annius Verus (II), paternal grandfather. After Hadrian's Adoption in ancient Rome, adoptive son, Aelius Caesar, died in 138, Hadrian adopted Marcus's uncle Antoninus Pius as his new heir. In turn, Antoninus adopted Marcus and Lucius Verus, Lucius, the son of Aelius. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marcomanni
The Marcomanni were a Germanic people who lived close to the border of the Roman Empire, north of the River Danube, and are mentioned in Roman records from approximately 60 BC until about 400 AD. They were one of the most important members of the powerful cluster of allied Suebian peoples in this region, which also included the Hermunduri, Varisti, and Quadi along the Danube, and the Semnones and Langobardi to their north. After a major defeat to the Romans in about 9 BC, the Marcomanni somehow received a new king named Maroboduus, who had grown up in Rome. He subsequently led his people and several others into a region surrounded by forests and mountains in the present day Czech Republic. Before 9 BC the homeland of the Marcomanni is not known, but archaeological evidence suggests that they lived near the central Elbe river and Saale, or possibly to the southwest of this region in Franconia. The Marcomanni were first reported by Julius Caesar among the Germanic peoples ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roman Empire
The Roman Empire ruled the Mediterranean and much of Europe, Western Asia and North Africa. The Roman people, Romans conquered most of this during the Roman Republic, Republic, and it was ruled by emperors following Octavian's assumption of effective sole rule in 27 BC. The Western Roman Empire, western empire collapsed in 476 AD, but the Byzantine Empire, eastern empire lasted until the fall of Constantinople in 1453. By 100 BC, the city of Rome had expanded its rule from the Italian peninsula to most of the Mediterranean Sea, Mediterranean and beyond. However, it was severely destabilised by List of Roman civil wars and revolts, civil wars and political conflicts, which culminated in the Wars of Augustus, victory of Octavian over Mark Antony and Cleopatra at the Battle of Actium in 31 BC, and the subsequent conquest of the Ptolemaic Kingdom in Egypt. In 27 BC, the Roman Senate granted Octavian overarching military power () and the new title of ''Augustus (title), Augustus'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rauraci
The Rauraci or Raurici were a small Gallic tribe dwelling in the Upper Rhine region, around the present-day city of Basel, during the Iron Age and the Roman period. Name They are mentioned as ''Rauracis'' and ''Rauracorum'' by Caesar (mid-1st c. BC), ''Raurici'' (var. -''aci'') by Pliny (1st c. AD), and as ''Rauracense'' in the ''Notitia Dignitatum'' (5th c. AD)., s.v. ''Rauraci'' and ''Col. Augusta Raurica''. The ethnonym ''Rauraci'' derives from the ancient Celtic name of the river Ruhr, ''Raura''. The city of Augst, attested in the 2nd century AD as ''Augoústa Rhauríkōn'' (Αὐγούστα Ῥαυρίκων), is indirectly named after the tribe. Geography Territory Their name seems to indicate an original homeland near the river Ruhr, further north of their attested territory. After their failed migration towards southwestern Gaul was repelled by the Romans in 58 BC, the Rauraci settled in the Upper Rhine area, with a territory stretching from the foothills of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |