|
Analytical Performance Modeling
Analytical Performance Modeling is a method to model the behaviour of a system in a spreadsheet. It is used in Software performance testing. It allows evaluation of design options and system sizing based on actual or anticipated business usage. It is therefore much faster and cheaper than performance testing, though it requires thorough understanding of the hardware platforms. The Model The model is fed with measurements of transaction resource demands (CPU, disk I/O, LAN, WAN), weighted by the transaction-mix (business transactions per unit of time). The weighted transaction resource demands are added-up to obtain the resource demands and divided by the resource capacity to obtain the resource loads. Changes in response time can also be predicted by the model. For example, in a simple case with a single resource, the response time formula: R=S/(1-U) where R=response_time, S=service_time, U=utilization, will calculate the response time as the utilization of that resource varies betw ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
Software Performance Testing
In software quality assurance, performance testing is in general a testing practice performed to determine how a system performs in terms of responsiveness and stability under a particular workload. It can also serve to investigate, measure, validate or verify other quality attributes of the system, such as scalability, reliability and resource usage. Performance testing, a subset of performance engineering, is a computer science practice which strives to build performance standards into the implementation, design and architecture of a system. Testing types Load testing Software load testing, Load testing is the simplest form of performance testing. A load test is usually conducted to understand the behavior of the system under a specific expected load. This load can be the expected concurrent number of users on the application software, application performing a specific number of Transaction processing, transactions within the set duration. This test will give out the respo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
CreateSpace
On-Demand Publishing, LLC, doing business as CreateSpace, was a self-publishing service owned by Amazon. The company was founded in 2000 in South Carolina South Carolina ( ) is a U.S. state, state in the Southeastern United States, Southeastern region of the United States. It borders North Carolina to the north and northeast, the Atlantic Ocean to the southeast, and Georgia (U.S. state), Georg ... as BookSurge and was acquired by Amazon in 2005. CreateSpace published books containing any content at all, other than just placeholder text. It neither edited nor verified. Books were printed on demand, meaning each volume was produced in response to an actual purchase on Amazon. CreateSpace continued its publishing services for 8 years until its transfer to Amazon's Media on Demand. By 2018, it had published 1,416,384 books for over 15,000 authors. In July 2018, CreateSpace announced it would be transferring media to Amazon's Media on Demand services in the following m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
Wide Area Network
A wide area network (WAN) is a telecommunications network that extends over a large geographic area. Wide area networks are often established with leased telecommunication circuits. Businesses, as well as schools and government entities, use wide area networks to relay data to staff, students, clients, buyers and suppliers from various locations around the world. In essence, this mode of telecommunication allows a business to effectively carry out its daily function regardless of location. The Internet may be considered a WAN. Many WANs are, however, built for one particular organization and are private. WANs can be separated from local area networks (LANs) in that the latter refers to physically proximal networks. Design options The textbook definition of a WAN is a computer network spanning regions, countries, or even the world. However, in terms of the application of communication protocols and concepts, it may be best to view WANs as computer networking technologies used ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
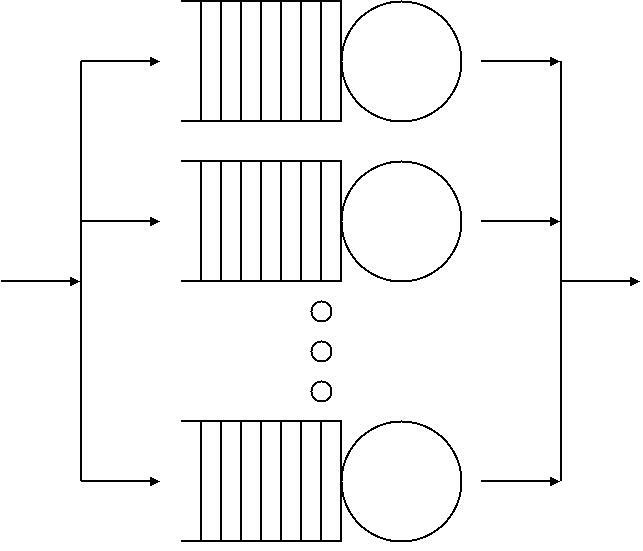 |
Queueing Theory
Queueing theory is the mathematical study of waiting lines, or queues. A queueing model is constructed so that queue lengths and waiting time can be predicted. Queueing theory is generally considered a branch of operations research because the results are often used when making business decisions about the resources needed to provide a service. Queueing theory has its origins in research by Agner Krarup Erlang, who created models to describe the system of incoming calls at the Copenhagen Telephone Exchange Company. These ideas were seminal to the field of teletraffic engineering and have since seen applications in telecommunications, traffic engineering, computing, project management, and particularly industrial engineering, where they are applied in the design of factories, shops, offices, and hospitals. Spelling The spelling "queueing" over "queuing" is typically encountered in the academic research field. In fact, one of the flagship journals of the field is '' Queue ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
 |
Software Testing
Software testing is the act of checking whether software satisfies expectations. Software testing can provide objective, independent information about the Quality (business), quality of software and the risk of its failure to a User (computing), user or sponsor. Software testing can determine the Correctness (computer science), correctness of software for specific Scenario (computing), scenarios but cannot determine correctness for all scenarios. It cannot find all software bug, bugs. Based on the criteria for measuring correctness from an test oracle, oracle, software testing employs principles and mechanisms that might recognize a problem. Examples of oracles include specifications, Design by Contract, contracts, comparable products, past versions of the same product, inferences about intended or expected purpose, user or customer expectations, relevant standards, and applicable laws. Software testing is often dynamic in nature; running the software to verify actual output ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |