|
Amanasaurus
''Amanasaurus'' (meaning "rain lizard") is a genus of silesaurid dinosauriforms from the Late Triassic Santa Maria Supersequence of Rio Grande do Sul, Brazil. The genus contains a single species, ''A. nesbitti'', known from two partial femora. Discovery and naming The ''Amanasaurus'' holotype specimen, CAPPA/UFSM 0374, was discovered in the ''Hyperodapedon'' Assemblage Zone of the Santa Maria Supersequence (Candelária Sequence) of the Paraná Basin, dated to the late Carnian stage of the Late Triassic. It consists of a proximal right femur. CAPPA/UFSM 0375, a distal left femur belonging to a larger individual from the same locality, was also referred to ''Amanasaurus''. In 2023, Müller & Garcia announced ''Amanasaurus nesbitti'' as a new genus and species of silesaurid based on these remains. The Genus#Use, generic name, "''Amanasaurus''", combines the Tupi language, Tupi word "amana", meaning "rain", with the Greek language, Greek "saurus", meaning "lizard", in reference ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Silesaurid
Silesauridae is an extinct family of Triassic dinosauriforms. It is most commonly considered to be a clade of non-dinosaur dinosauriforms, and the sister group of dinosaurs. Some studies have instead suggested that most or all silesaurids comprised an early diverging clade or a paraphyletic grade within ornithischian dinosaurs. Silesaurids have a consistent general body plan, with a fairly long neck and legs and possibly quadrupedal habits, but most silesaurids are heavily fragmentary nonetheless. Furthermore, they occupied a variety of ecological niches, with early silesaurids (such as '' Lewisuchus'') being carnivorous and later taxa (such as ''Kwanasaurus'') having adaptations for specialized herbivory. As indicated by the contents of referred coprolites, ''Silesaurus'' may have been insectivorous, feeding selectively on small beetles and other arthropods. Classification Silesauridae is typically considered the sister group to Dinosauria. The group was named in 2010 by Max ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2024 In Archosaur Paleontology
This article records new taxa of every kind of fossil archosaur that are scheduled to be Species description, described during 2024, as well as other significant discoveries and events related to the paleontology of archosaurs published in 2024. Pseudosuchians New pseudosuchian taxa General pseudosuchian research * Evidence of the impact of function on the evolution of the lower jaw morphology in crocodile-line archosaurs is presented by Rawson ''et al.'' (2024). * A review of studies on the thermometabolism of crocodile-line archosaurs from the preceding 20 years is published by Faure-Brac (2024). * Sennikov (2024) interprets Ornithosuchidae, ornithosuchids as macrophagous predators with specialized jaw apparatus, and notes analogs between them and saber-toothed therapsids (including mammals). * A study on the locomotion of ''Riojasuchus, Riojasuchus tenuisceps'' is published by von Baczko ''et al.'' (2024), who reconstruct ''R. tenuisceps'' as having an erect posture ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
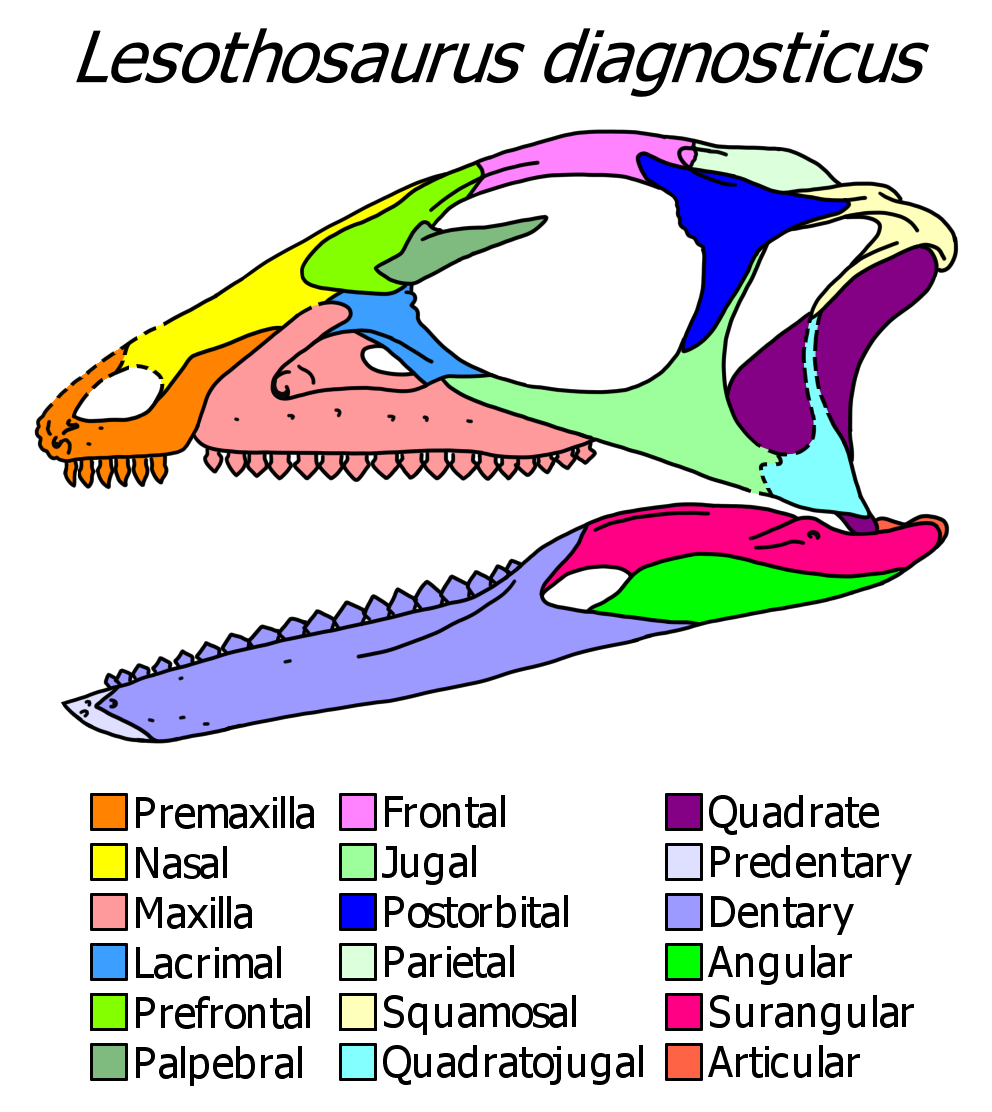
Ornithischia
Ornithischia () is an extinct clade of mainly herbivorous dinosaurs characterized by a pelvic structure superficially similar to that of birds. The name ''Ornithischia'', or "bird-hipped", reflects this similarity and is derived from the Greek stem ' (), meaning "bird", and ' (), meaning "hip". However, as theropod dinosaurs, birds are only distantly related to this group. Ornithischians with well known anatomical adaptations include the ceratopsians or "horn-faced" dinosaurs (e.g. ''Triceratops''), the pachycephalosaurs or "thick-headed" dinosaurs, the armored dinosaurs ( Thyreophora) such as stegosaurs and ankylosaurs, and the ornithopods. There is strong evidence that certain groups of ornithischians lived in herds, often segregated by age group, with juveniles forming their own flocks separate from adults. Some were at least partially covered in filamentous (hair- or feather- like) pelts, and there is much debate over whether these filaments found in specimens of '' Ti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Santa Maria Supersequence
The Santa Maria Formation is a sedimentary geological formation, rock formation found in Rio Grande do Sul, Brazil. It is primarily Carnian in age (Late Triassic), and is notable for its fossils of cynodonts, "rauisuchian" pseudosuchians, and early dinosaurs and other Dinosauromorpha, dinosauromorphs, including the herrerasaurid ''Staurikosaurus'', the Basal (phylogenetics), basal sauropodomorpha, sauropodomorphs ''Buriolestes'' and ''Saturnalia (genus), Saturnalia,'' and the Lagerpetidae, lagerpetid ''Ixalerpeton''. The formation is named after the city of Santa Maria (Rio Grande do Sul), Santa Maria in the central region of Rio Grande do Sul, where outcrops were first studied. The Santa Maria Formation makes up the majority of the Santa Maria Supersequence, which extends through the entire Late Triassic. The Santa Maria Supersequence is divided into four geological Sequence (geology), sequences, separated from each other by short Unconformity, unconformities. The first two of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Late Triassic
The Late Triassic is the third and final epoch (geology), epoch of the Triassic geologic time scale, Period in the geologic time scale, spanning the time between annum, Ma and Ma (million years ago). It is preceded by the Middle Triassic Epoch and followed by the Early Jurassic Epoch. The corresponding series (stratigraphy), series of rock beds is known as the Upper Triassic. The Late Triassic is divided into the Carnian, Norian and Rhaetian Geologic time scale, ages. Many of the first dinosaurs evolved during the Late Triassic, including ''Plateosaurus'', ''Coelophysis'', ''Herrerasaurus'', and ''Eoraptor''. The Triassic–Jurassic extinction event began during this epoch and is one of the five major mass extinction events of the Earth. Etymology The Triassic was named in 1834 by Friedrich August von Namoh, Friedrich von Alberti, after a succession of three distinct rock layers (Greek meaning 'triad') that are widespread in southern Germany: the lower Buntsandstein (colourful ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ignotosaurus
''Ignotosaurus'' is an extinct genus of silesaurid dinosauriform known from the Late Triassic (Carnian) Cancha de Bochas Member of the Ischigualasto Formation in the Ischigualasto-Villa Unión Basin in northwestern Argentina.Martínez et al., 2013 It was therefore contemporary with early dinosaurs such as ''Herrerasaurus,'' and lived in the same place. Etymology The name, meaning 'unknown lizard' from the Latin 'ignotus' 'unknown' and the Greek '' 'lizard', is quite apt as there is only one specimen known and this specimen is only known from the right ilium. This ilium is approximately long, but it is difficult to say accurately how large ''Ignotosaurus'' was. Description The ilium is slender, and its blade has an extremely thin central portion (only thick), hence the specific name 'fragilis'. It has the saddle-shaped lateral profile of most silesaurids, and is longer than it is deep. The acetabulum has a back wall created by a ventral flange and this closes a socket ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ICZN
The International Code of Zoological Nomenclature (ICZN) is a widely accepted convention in zoology that rules the formal scientific naming of organisms treated as animals. It is also informally known as the ICZN Code, for its formal author, the International Commission on Zoological Nomenclature (which shares the acronym "ICZN"). The rules principally regulate: * How names are correctly established in the frame of binominal nomenclature * How to determine whether a given name is available * Which available name must be used in case of name conflicts ( valid name) * How scientific literature must cite names Zoological nomenclature is independent of other systems of nomenclature, for example botanical nomenclature. This implies that animals can have the same generic names as plants (e.g. there is a genus '' Abronia'' in both animals and plants). The rules and recommendations have one fundamental aim: to provide the maximum universality and continuity in the naming of all anima ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scientific Reports
''Scientific Reports'' is a peer-reviewed open-access scientific mega journal published by Nature Portfolio, covering all areas of the natural sciences. The journal was established in 2011. The journal states that their aim is to assess solely the scientific validity of a submitted paper, rather than its perceived importance, significance, or impact. In September 2016, the journal became the largest in the world by number of articles, overtaking '' PLOS ONE''. Abstracting and indexing The journal is abstracted and indexed in the Chemical Abstracts Service, the Science Citation Index Expanded, and selectively in Index Medicus/MEDLINE/PubMed. According to the ''Journal Citation Reports'', the journal has a 2023 impact factor 3.8. Reviewing policy The ''Guide to Referees'' states that to be published, "a paper must be scientifically valid and technically sound in methodology and analysis", and reviewers have to ensure manuscripts "are not assessed based on their perceived impor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sister Taxon
In phylogenetics, a sister group or sister taxon, also called an adelphotaxon, comprises the closest relative(s) of another given unit in an evolutionary tree. Definition The expression is most easily illustrated by a cladogram: Taxon A and taxon B are sister groups to each other. Taxa A and B, together with any other extant or extinct descendants of their most recent common ancestor (MRCA), form a monophyletic group, the clade AB. Clade AB and taxon C are also sister groups. Taxa A, B, and C, together with all other descendants of their MRCA form the clade ABC. The whole clade ABC is itself a subtree of a larger tree which offers yet more sister group relationships, both among the leaves and among larger, more deeply rooted clades. The tree structure shown connects through its root to the rest of the universal tree of life. In cladistic standards, taxa A, B, and C may represent specimens, species, genera, or any other taxonomic units. If A and B are at the same taxonomic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cladogram
A cladogram (from Greek language, Greek ''clados'' "branch" and ''gramma'' "character") is a diagram used in cladistics to show relations among organisms. A cladogram is not, however, an Phylogenetic tree, evolutionary tree because it does not show how ancestors are related to descendants, nor does it show how much they have changed, so many differing evolutionary trees can be consistent with the same cladogram. A cladogram uses lines that branch off in different directions ending at a clade, a group of organisms with a last common ancestor. There are many shapes of cladograms but they all have lines that branch off from other lines. The lines can be traced back to where they branch off. These branching off points represent a hypothetical ancestor (not an actual entity) which can be inferred to exhibit the traits shared among the terminal taxa above it. This hypothetical ancestor might then provide clues about the order of evolution of various features, adaptation, and other e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Silesaurus
''Silesaurus'' is a genus of silesaurid dinosauriform from the Late Triassic, of what is now Poland. Discovery and naming The Krasiejów claypit near Opole, Poland, was first discovered as a fossil locality in the 1980s after quarrying for a nearby cement plant reached the fossil layer, though scientific excavations began in 1993 with the discovery of an almost complete phytosaur skull by Polish paleontologist Jerzy Dzik. Preliminary investigations identified Krasiejów as a diverse vertebrate assemblage, named the "'' Paleorhinus'' fauna", preserving partially articulated skeletons of amphibians and reptiles, including possible early dinosaurs from the middle to late Carnian. Following these preliminary reports, extensive excavations of Krasiejów were undertaken from 2000 to 2002, collecting numerous skulls, partially articulated skeletons, and isolated remains. An area with dense skeletons was left intact to construct a museum exhibit of the University of Opole around, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |