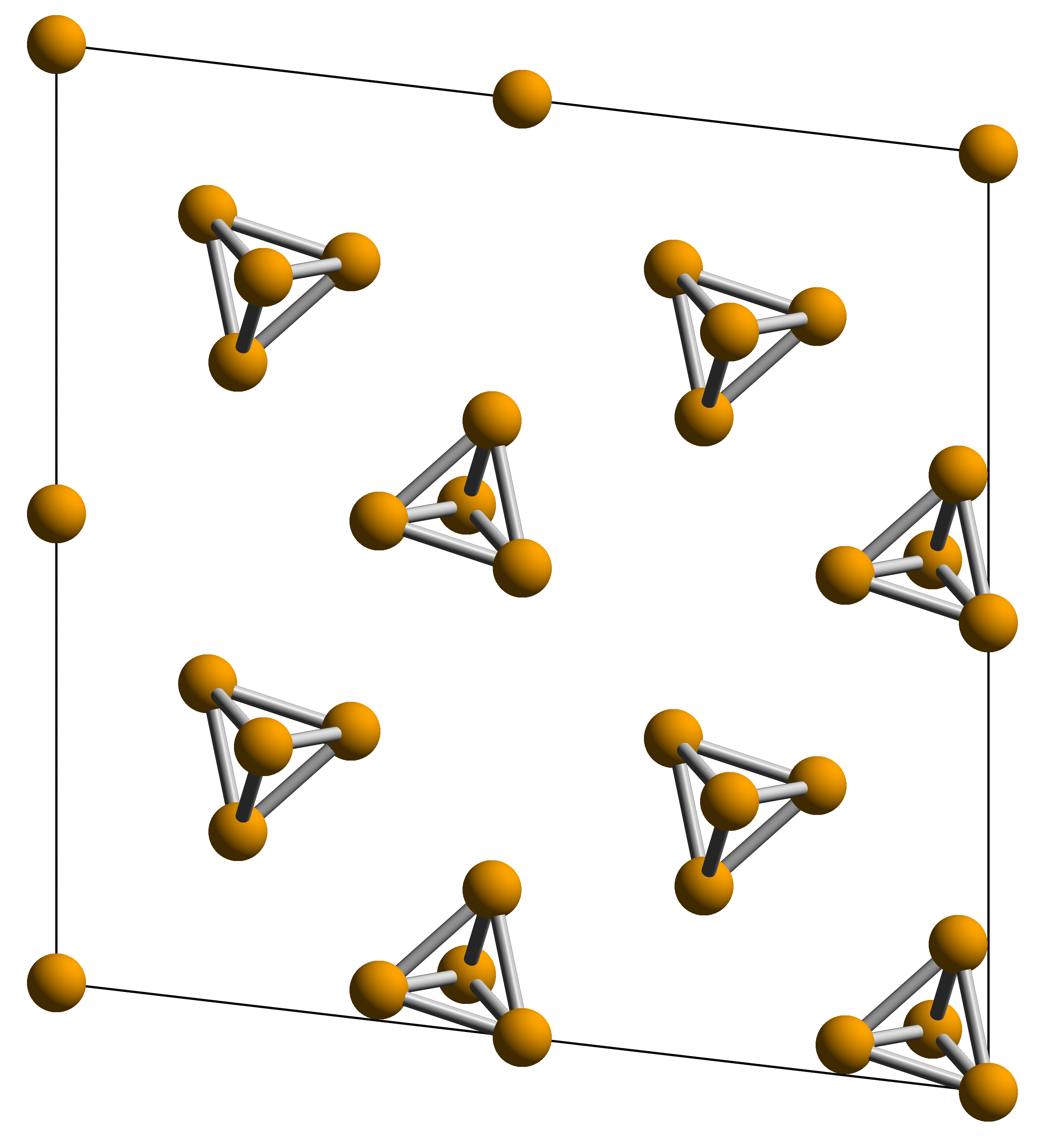|
Allotropes Of Arsenic
Arsenic in the solid state can be found as gray, black, or yellow Allotropy, allotropes. These various forms feature diverse structural motifs, with yellow arsenic enabling the widest range of reactivity. In particular, reaction of yellow arsenic with main group and transition metal elements results in compounds with wide-ranging structural motifs, with Butterfly cluster compound, butterfly, Sandwich compound, sandwich and realgar-type moieties featuring most prominently. Gray arsenic Gray arsenic, also called grey arsenic or metallic arsenic, is the most stable allotrope of the element at room temperature, and as such is its most common form. This soft, brittle allotrope of arsenic has a steel gray, metallic color, and is a good conductor. The rhombohedral form of this allotrope is analogous to the Allotropes of phosphorus, phosphorus allotrope black phosphorus. In its α-form, As6 rings in chair confirmations are condensed into packed layers lying perpendicular to the crystallo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arsenic Allotropes And Their Molecular Structures
Arsenic is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol As and atomic number 33. It is a metalloid and one of the pnictogens, and therefore shares many properties with its group 15 neighbors phosphorus and antimony. Arsenic is notoriously toxic. It occurs naturally in many minerals, usually in combination with sulfur and metals, but also as a pure elemental crystal. It has various Allotropes of arsenic, allotropes, but only the grey form, which has a metallic appearance, is important to industry. The primary use of arsenic is in alloys of lead (for example, in car batteries and ammunition). Arsenic is also a common n-type dopant in semiconductor electronic devices, and a component of the III–V compound semiconductor gallium arsenide. Arsenic and its compounds, especially the trioxide, are used in the production of pesticides, treated wood products, herbicides, and insecticides. These applications are declining with the increasing recognition of the persistent tox ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chile
Chile, officially the Republic of Chile, is a country in western South America. It is the southernmost country in the world and the closest to Antarctica, stretching along a narrow strip of land between the Andes, Andes Mountains and the Pacific Ocean. Chile had a population of 17.5 million as of the latest census in 2017 and has a territorial area of , sharing borders with Peru to the north, Bolivia to the northeast, Argentina to the east, and the Drake Passage to the south. The country also controls several Pacific islands, including Juan Fernández Islands, Juan Fernández, Isla Salas y Gómez, Desventuradas Islands, Desventuradas, and Easter Island, and claims about of Antarctica as the Chilean Antarctic Territory. The capital and largest city of Chile is Santiago, and the national language is Spanish language, Spanish. Conquest of Chile, Spain conquered and colonized the region in the mid-16th century, replacing Incas in Central Chile, Inca rule; however, they Arauco War ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Butterfly Complexes Of Iron Formed Via Reaction With Yellow Arsenic
Butterflies are winged insects from the lepidopteran superfamily Papilionoidea, characterized by large, often brightly coloured wings that often fold together when at rest, and a conspicuous, fluttering flight. The oldest butterfly fossils have been dated to the Paleocene, about 56 million years ago, though molecular evidence suggests that they likely originated in the Cretaceous. Butterflies have a four-stage life cycle, and like other holometabolous insects they undergo complete metamorphosis. Winged adults lay eggs on the food plant on which their larvae, known as caterpillars, will feed. The caterpillars grow, sometimes very rapidly, and when fully developed, pupate in a chrysalis. When metamorphosis is complete, the pupal skin splits, the adult insect climbs out, expands its wings to dry, and flies off. Some butterflies, especially in the tropics, have several generations in a year, while others have a single generation, and a few in cold locations may take several y ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chromium And Molybdenum Triple-decker Sandwich Complexes Of Arsenic
Chromium is a chemical element; it has symbol Cr and atomic number 24. It is the first element in group 6. It is a steely-grey, lustrous, hard, and brittle transition metal. Chromium is valued for its high corrosion resistance and hardness. A major development in steel production was the discovery that steel could be made highly resistant to corrosion and discoloration by adding metallic chromium to form stainless steel. Stainless steel and chrome plating (electroplating with chromium) together comprise 85% of the commercial use. Chromium is also greatly valued as a metal that is able to be highly polished while resisting tarnishing. Polished chromium reflects almost 70% of the visible spectrum, and almost 90% of infrared light. The name of the element is derived from the Greek word χρῶμα, ''chrōma'', meaning color, because many chromium compounds are intensely colored. Industrial production of chromium proceeds from chromite ore (mostly FeCr2O4) to produce ferrochrom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electron Density Topology In A Niobium-arsenic-phosphorus Complex
The electron (, or in nuclear reactions) is a subatomic particle with a negative one elementary electric charge. It is a fundamental particle that comprises the ordinary matter that makes up the universe, along with up and down quarks. Electrons are extremely lightweight particles that orbit the positively charged nucleus of atoms. Their negative charge is balanced by the positive charge of protons in the nucleus, giving atoms their overall neutral charge. Ordinary matter is composed of atoms, each consisting of a positively charged nucleus surrounded by a number of orbiting electrons equal to the number of protons. The configuration and energy levels of these orbiting electrons determine the chemical properties of an atom. Electrons are bound to the nucleus to different degrees. The outermost or valence electrons are the least tightly bound and are responsible for the formation of chemical bonds between atoms to create molecules and crystals. These valence electrons also f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Silylene
Silylene is a chemical compound with the formula SiR2. It is the silicon analog of carbene. Silylene rapidly when condensed. Silylenes are formal derivatives of silylene with its hydrogens replaced by other substituents. Most examples feature amido (NR2) or alkyl/aryl groups. Silylenes have been proposed as reactive intermediates. They are carbene analogs. Synthesis and properties Silylenes have been generated by thermolysis or photolysis of polysilanes, by silicon atom reactions ( insertion, addition or abstraction), by pyrolysis of silanes, or by reduction of 1,1-dihalosilane. It has long been assumed that the conversion of metallic Si to tetravalent silicon compounds proceeds via silylene intermediates: :Si + Cl2 → SiCl2 :SiCl2 + Cl2 → SiCl4 Similar considerations apply to the direct process, the reaction of methyl chloride and bulk silicon. Early observations of silylenes involved generation of dimethylsilylene by dechlorination of dimethyldichlorosilane: ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Butterfly Compounds Of Arsenic With Main Group Elements
Butterflies are winged insects from the lepidopteran superfamily Papilionoidea, characterized by large, often brightly coloured wings that often fold together when at rest, and a conspicuous, fluttering flight. The oldest butterfly fossils have been dated to the Paleocene, about 56 million years ago, though molecular evidence suggests that they likely originated in the Cretaceous. Butterflies have a four-stage life cycle, and like other holometabolous insects they undergo complete metamorphosis. Winged adults lay eggs on the food plant on which their larvae, known as caterpillars, will feed. The caterpillars grow, sometimes very rapidly, and when fully developed, pupate in a chrysalis. When metamorphosis is complete, the pupal skin splits, the adult insect climbs out, expands its wings to dry, and flies off. Some butterflies, especially in the tropics, have several generations in a year, while others have a single generation, and a few in cold locations may take several yea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phosphorus
Phosphorus is a chemical element; it has Chemical symbol, symbol P and atomic number 15. All elemental forms of phosphorus are highly Reactivity (chemistry), reactive and are therefore never found in nature. They can nevertheless be prepared artificially, the two most common allotropes being white phosphorus and red phosphorus. With as its only stable isotope, phosphorus has an occurrence in Earth's crust of about 0.1%, generally as phosphate rock. A member of the pnictogen family, phosphorus readily forms a wide variety of organic compound, organic and inorganic compound, inorganic compounds, with as its main oxidation states +5, +3 and −3. The isolation of white phosphorus in 1669 by Hennig Brand marked the scientific community's first discovery since Antiquity of an element. The name phosphorus is a reference to the Phosphorus (morning star), god of the Morning star in Greek mythology, inspired by the faint glow of white phosphorus when exposed to oxygen. This property is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metastability
In chemistry and physics, metastability is an intermediate energetic state within a dynamical system other than the system's state of least energy. A ball resting in a hollow on a slope is a simple example of metastability. If the ball is only slightly pushed, it will settle back into its hollow, but a stronger push may start the ball rolling down the slope. Bowling pins show similar metastability by either merely wobbling for a moment or tipping over completely. A common example of metastability in science is isomerisation. Higher energy isomers are long lived because they are prevented from rearranging to their preferred ground state by (possibly large) barriers in the potential energy. During a metastable state of finite lifetime, all state-describing parameters reach and hold stationary values. In isolation: *the state of least energy is the only one the system will inhabit for an indefinite length of time, until more external energy is added to the system (unique "absolu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
White Phosphorus
White phosphorus, yellow phosphorus, or simply tetraphosphorus (P4) is an allotrope of phosphorus. It is a translucent waxy solid that quickly yellows in light (due to its photochemical conversion into red phosphorus), and impure white phosphorus is for this reason called yellow phosphorus. White phosphorus is the first allotrope of phosphorus, and in fact the first elementary substance to be discovered that was not known since ancient times. It glows greenish in the dark (when exposed to oxygen) and is highly flammable and pyrophoric (self-igniting) upon contact with air. It is toxic, causing severe liver damage on ingestion and phossy jaw from chronic ingestion or inhalation. The odour of combustion of this form has a characteristic garlic odor, and samples are commonly coated with white " diphosphorus pentoxide", which consists of tetrahedra with oxygen inserted between the phosphorus atoms and at their vertices. White phosphorus is only slightly soluble in water and can ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
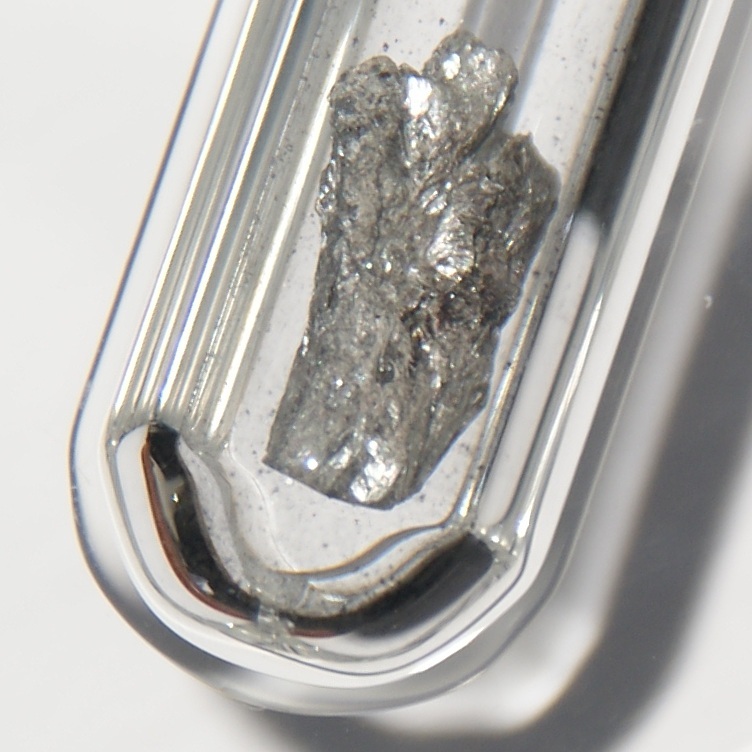
Yellow Arsenic
Arsenic in the solid state can be found as gray, black, or yellow allotropes. These various forms feature diverse structural motifs, with yellow arsenic enabling the widest range of reactivity. In particular, reaction of yellow arsenic with main group and transition metal elements results in compounds with wide-ranging structural motifs, with butterfly, sandwich and realgar-type moieties featuring most prominently. Gray arsenic Gray arsenic, also called grey arsenic or metallic arsenic, is the most stable allotrope of the element at room temperature, and as such is its most common form. This soft, brittle allotrope of arsenic has a steel gray, metallic color, and is a good conductor. The rhombohedral form of this allotrope is analogous to the phosphorus allotrope black phosphorus. In its α-form, As6 rings in chair confirmations are condensed into packed layers lying perpendicular to the crystallographic ''c'' axis. Within each layer, the vicinal As-As bond distances are 2.517 � ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Copiapó Province
Copiapó Province () is one of three provinces of the northern Chilean region of Atacama (III). Its capital is the city of Copiapó. Geography and demography According to the 2012 census by the National Statistics Institute (''INE''), the province spans an area of and had a population of 183,973 inhabitants, giving it a population density of . It is the tenth largest province in the country. Between the 1992 and 2002 censuses, the population grew by 24.9% (31,021 persons). Administration As a province, Copiapó is a second-level administrative division of Chile, which is further divided into three communes (''comunas''). The province is administered by a presidentially appointed regional delegate. Communes #Copiapó #Caldera A caldera ( ) is a large cauldron-like hollow that forms shortly after the emptying of a magma chamber in a volcanic eruption. An eruption that ejects large volumes of magma over a short period of time can cause significant detriment to the str ... # ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |