|
Alkynylation
In organic chemistry, alkynylation is an addition reaction in which a terminal alkyne () is added to a carbonyl group () to form an α-alkynyl alcohol (). When the acetylide is formed from acetylene (), the reaction gives an α-ethynyl alcohol. This process is often referred to as ethynylation. Such processes often involve metal acetylide intermediates. Scope The principal reaction of interest involves the addition of the acetylene () to a ketone () or aldehyde (): :RR'C=O + HC#CR'' -> RR'C(OH)C#CR'' The reaction proceeds with retention of the triple bond. For aldehydes and unsymmetrical ketones, the product is chiral, hence there is interest in asymmetric variants. These reactions invariably involve metal-acetylide intermediates. This reaction was discovered by chemist John Ulric Nef in 1899 while experimenting with reactions of elemental sodium, phenylacetylene, and acetophenone. For this reason, the reaction is sometimes referred to as Nef synthesis. Sometimes this rea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
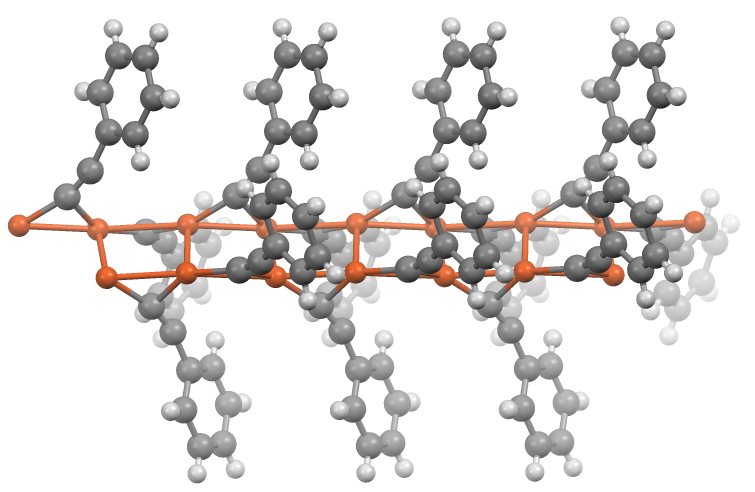
Acetylide
In organometallic chemistry, acetylide refers to chemical compounds with the chemical formulas and , where M is a metal. The term is used loosely and can refer to substituted acetylides having the general structure (where R is an organic side chain). Acetylides are reagents in organic synthesis. The calcium acetylide commonly called calcium carbide is a major compound of commerce. Structure and bonding Alkali metal and alkaline earth metal acetylides of the general formula MC≡CM are salt-like Zintl phase compounds, containing ions. Evidence for this ionic character can be seen in the ready hydrolysis of these compounds to form acetylene and metal oxides, there is also some evidence for the solubility of ions in liquid ammonia. The ion has a closed shell ground state of 1Σ, making it isoelectronic to a neutral molecule N2, which may afford it some stability. Analogous acetylides prepared from other metals, particularly transition metals, show covalent character and are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Terminal Alkyne
\ce \ce Acetylene \ce \ce \ce Propyne \ce \ce \ce \ce 1-Butyne In organic chemistry, an alkyne is an unsaturated hydrocarbon containing at least one carbon—carbon triple bond. The simplest acyclic alkynes with only one triple bond and no other functional groups form a homologous series with the general chemical formula . Alkynes are traditionally known as acetylenes, although the name ''acetylene'' also refers specifically to , known formally as ethyne using IUPAC nomenclature. Like other hydrocarbons, alkynes are generally hydrophobic. Structure and bonding In acetylene, the H–C≡C bond angles are 180°. By virtue of this bond angle, alkynes are rod-like. Correspondingly, cyclic alkynes are rare. Benzyne cannot be isolated. The C≡C bond distance of 121 picometers is much shorter than the C=C distance in alkenes (134 pm) or the C–C bond in alkanes (153 pm). : The triple bond is very strong with a bond strength of 839 kJ/mol. The sigma bond contributes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acetylide Carbonyl Addition
In organometallic chemistry, acetylide refers to chemical compounds with the chemical formulas and , where M is a metal. The term is used loosely and can refer to substituted acetylides having the general structure (where R is an organic side chain). Acetylides are reagents in organic synthesis. The calcium acetylide commonly called calcium carbide is a major compound of commerce. Structure and bonding Alkali metal and alkaline earth metal acetylides of the general formula MC≡CM are salt-like Zintl phase compounds, containing ions. Evidence for this ionic character can be seen in the ready hydrolysis of these compounds to form acetylene and metal oxides, there is also some evidence for the solubility of ions in liquid ammonia. The ion has a closed shell ground state of 1Σ, making it isoelectronic to a neutral molecule N2, which may afford it some stability. Analogous acetylides prepared from other metals, particularly transition metals, show covalent character and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Organic Chemistry
Organic chemistry is a subdiscipline within chemistry involving the science, scientific study of the structure, properties, and reactions of organic compounds and organic materials, i.e., matter in its various forms that contain carbon atoms.Clayden, J.; Greeves, N. and Warren, S. (2012) ''Organic Chemistry''. Oxford University Press. pp. 1–15. . Study of structure determines their structural formula. Study of properties includes Physical property, physical and Chemical property, chemical properties, and evaluation of Reactivity (chemistry), chemical reactivity to understand their behavior. The study of organic reactions includes the organic synthesis, chemical synthesis of natural products, drugs, and polymers, and study of individual organic molecules in the laboratory and via theoretical (in silico) study. The range of chemicals studied in organic chemistry includes hydrocarbons (compounds containing only carbon and hydrogen) as well as compounds based on carbon, but also con ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nef Reaction
In organic chemistry, the Nef reaction is an organic reaction describing the acid hydrolysis of a salt of a primary or secondary nitroalkane () to an aldehyde () or a ketone () and nitrous oxide (). The reaction has been the subject of several literature reviews. The reaction was reported in 1894 by the chemist John Ulric Nef, who treated the sodium salt of nitroethane with sulfuric acid resulting in an 85–89% yield of nitrous oxide and at least 70% yield of acetaldehyde. However, the reaction was pioneered a year earlier in 1893 by Konovalov, who converted the potassium salt of 1-phenylnitroethane with sulfuric acid to acetophenone. Reaction mechanism The reaction mechanism starting from the nitronate salt as the resonance structures 1a and 1b is depicted below: The salt is protonated forming the nitronic acid 2 (in some cases these nitronates have been isolated) and once more to the iminium ion 3. This intermediate is attacked by water in a nucleophilic addition fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lithium Amide
Lithium amide or lithium azanide is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula . It is a white solid with a tetragonal crystal structure. Lithium amide can be made by treating lithium metal with liquid ammonia: : Other lithium amides The conjugate bases of amines are known as amides. Thus, a ''lithium amide'' may also refer to any compound in the class of the lithium salt of an amine. These compounds have the general form , with the chemical lithium amide itself as the parent structure. Common lithium amides include lithium diisopropylamide (LDA), lithium tetramethylpiperidide (LiTMP), and lithium hexamethyldisilazide (LiHMDS). They are produced by the reaction of Li metal with the appropriate amine: : Lithium amides are very reactive compounds. Specifically, they are strong bases. Examples Lithium tetramethylpiperidide has been crystallised as a tetramer. On the other hand, the lithium derivative of bis(1-phenylethyl)amine crystallises as a trimer: It is also pos ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Propargyl Alcohol
Propargyl alcohol, or 2-propyn-1-ol, is an organic compound with the formula C3H4O. It is the simplest stable alcohol containing an alkyne functional group. Propargyl alcohol is a colorless viscous liquid that is miscible with water and most polar organic solvents. Reactions and applications Propargyl alcohol polymerizes with heating or treatment with base. It is used as a corrosion inhibitor, a metal complex solution, a solvent stabilizer and an electroplating brightener additive. It is also used as an intermediate in organic synthesis. Secondary and tertiary substituted propargylic alcohols undergo catalyzed rearrangement reactions to form α,β-unsaturated carbonyl compounds via the Meyer–Schuster rearrangement and others. It can be oxidized to propynal or propargylic acid. As an indication of the electronegativity of an sp carbon, propargyl alcohol is significantly more acidic (p''K''a = 13.6) compared to its sp2-containing analog allyl alcohol (p''K''a = 15.5), which ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grignard Reagent
A Grignard reagent or Grignard compound is a chemical compound with the general formula , where X is a halogen and R is an organic functional group, group, normally an alkyl or aryl. Two typical examples are methylmagnesium chloride and phenylmagnesium bromide . They are a subclass of the organomagnesium compounds. Grignard compounds are popular reagents in organic synthesis for creating new carbon-carbon bonds. For example, when reacted with another halogenated compound in the presence of a suitable catalysis, catalyst, they typically yield and the magnesium halide as a byproduct; and the latter is insoluble in the solvents normally used. In this aspect, they are similar to organolithium reagents. Pure Grignard reagents are extremely reactive solids. They are normally handled as solutions in solvents such as diethyl ether or tetrahydrofuran; which are relatively stable as long as water is excluded. In such a medium, a Grignard reagent is invariably present as a coordinati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arens–van Dorp Synthesis
The Arens–van Dorp synthesis is a name reaction in organic chemistry. It describes the addition of lithiated ethoxyacetylenes to ketones to give propargyl alcohols, which can undergo further reaction to form α,β-unsaturated aldehydes, or esters. There is also a variation of this reaction called the Isler modification, where the acetylide anion is generated in situ from β-chlorovinyl ether using lithium amide Lithium amide or lithium azanide is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula . It is a white solid with a tetragonal crystal structure. Lithium amide can be made by treating lithium metal with liquid ammonia: : Other lithium amides The c .... References {{DEFAULTSORT:Arens-van Dorp synthesis Name reactions Chemistry Organic chemistry ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acetic Acid
Acetic acid , systematically named ethanoic acid , is an acidic, colourless liquid and organic compound with the chemical formula (also written as , , or ). Vinegar is at least 4% acetic acid by volume, making acetic acid the main component of vinegar apart from water and other trace elements. Acetic acid is the second simplest carboxylic acid (after formic acid). It is an important chemical reagent and industrial chemical, used primarily in the production of cellulose acetate for photographic film, polyvinyl acetate for wood glue, and synthetic fibres and fabrics. In households, diluted acetic acid is often used in descaling agents. In the food industry, acetic acid is controlled by the food additive code E260 as an acidity regulator and as a condiment. In biochemistry, the acetyl group, derived from acetic acid, is fundamental to all forms of life. When bound to coenzyme A, it is central to the metabolism of carbohydrates and fats. The global demand for aceti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alkoxy Group
In chemistry, the alkoxy group is an alkyl group which is singularly bonded to oxygen; thus . The range of alkoxy groups is vast, the simplest being methoxy (). An ethoxy group () is found in the organic compound ethyl phenyl ether (, also known as ethoxybenzene). Related to alkoxy groups are aryloxy groups, which have an aryl group singularly bonded to oxygen such as the phenoxy group (). An alkoxy or aryloxy group bonded to an alkyl or aryl () is an ether. If bonded to H it is an alcohol. An alkoxide can refer to salts of alcohols, and they are ionic compounds containing an alkoxide ions ; it is a derivative of an alcohol where the hydrogen of the –OH group is replaced by a metal, for example sodium salt of ethanol () is sodium ethoxide Sodium ethoxide, also referred to as sodium ethylate, is the ionic, organic compound with the formula , or NaOEt (Et = ethane). It is a white solid, although impure samples appear yellow or brown. It dissolves in polar solvents su ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |