|
Alexander Sauli
Alexander (Alessandro) Sauli, C.R.S.P. (15 February 1534 – 11 October 1592) was an Italian priest who is called the "Apostle of Corsica". He is a saint of the Roman Catholic Church. In 1571, he was appointed by Pius V to the ancient see of Aléria, Corsica, where he rebuilt churches, founded colleges and seminaries, and, despite the depredations of corsairs, placed the Church in a flourishing condition. In 1591, he was made Bishop of Pavia, and died at Calosso the following year. He left a number of works, chiefly catechetical. He was beatified by Benedict XIV, 23 April 1742, and canonized by Pope Pius X, 11 December 1904. His feast is celebrated on October 11. Early life Sauli was born in Milan, on February 15, 1534, to an illustrious Lombard family. His parents were Dominic and Tommasina Spinola Sauli. His father was Marquis of Pozzuolo in the territory of Tortona and an assistant to Duke Francesco II Sforza. The marquis was esteemed by the emperor, who was then pre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roman Catholicism
The Catholic Church, also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the largest Christian church, with 1.3 billion baptized Catholics worldwide . It is among the world's oldest and largest international institutions, and has played a prominent role in the history and development of Western civilization. O'Collins, p. v (preface). The church consists of 24 ''sui iuris'' churches, including the Latin Church and 23 Eastern Catholic Churches, which comprise almost 3,500 dioceses and eparchies located around the world. The pope, who is the bishop of Rome, is the chief pastor of the church. The bishopric of Rome, known as the Holy See, is the central governing authority of the church. The administrative body of the Holy See, the Roman Curia, has its principal offices in Vatican City, a small enclave of the Italian city of Rome, of which the pope is head of state. The core beliefs of Catholicism are found in the Nicene Creed. The Catholic Church teaches that it is the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pozzuolo Martesana
Pozzuolo Martesana ( lmo, Pozzoeu or ''Pozzoeul'' ) is a ''comune'' (municipality) in the Metropolitan City of Milan in the Italian region Lombardy, located about east of Milan. Pozzuolo Martesana borders the following municipalities: Inzago, Cassano d'Adda, Gorgonzola, Bellinzago Lombardo, Melzo, Truccazzano. Pozzuolo Martesana is served by Pozzuolo Martesana railway station, the village of Trecella by Trecella railway station Trecella railway station is a railway station in Italy. Located on the Milan–Venice railway, it serves the hamlet of Trecella, in the municipality of Pozzuolo Martesana. Services Trecella is served by lines S5 and S6 of Milan suburban rai .... References External links Official website Cities and towns in Lombardy {{Milan-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Novitiate
The novitiate, also called the noviciate, is the period of training and preparation that a Christian ''novice'' (or ''prospective'') monastic, apostolic, or member of a religious order undergoes prior to taking vows in order to discern whether they are called to vowed religious life. It often includes times of intense study, prayer, living in community, studying the vowed life, deepening one's relationship with God, and deepening one's self-awareness. The canonical time of the novitiate is one year; in case of additional length, it must not be extended over two years. CIC, canon 648 In the Eastern Orthodox Church, the novitiate is officially set at three years before one may be tonsure Tonsure () is the practice of cutting or shaving some or all of the hair on the scalp as a sign of religious devotion or humility. The term originates from the Latin word ' (meaning "clipping" or "shearing") and referred to a specific practice in ...d a monk or nun, though this requirement may ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Religious Habit
A religious habit is a distinctive set of religious clothing worn by members of a religious order. Traditionally some plain garb recognizable as a religious habit has also been worn by those leading the religious eremitic and anchoritic life, although in their case without conformity to a particular uniform style. Uniformity and distinctiveness by order often evolved and changed over time. Interpretation of terms for clothes in religious rules could change over centuries. Furthermore, every time new communities gained importance in a cultural area the need for visual separation increased for new as well as old communities. Thus, modern habits are rooted in historic forms, but do not necessarily resemble them in cut, colour, material, detail or use. In Christian monastic orders of the Catholic, Lutheran and Anglican Churches, the habit often consists of a tunic covered by a scapular and cowl, with a hood for monks or friars and a veil for nuns; in apostolic orders it may ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Assumption Of Mary
The Assumption of Mary is one of the four Marian dogmas of the Catholic Church. Pope Pius XII defined it in 1950 in his apostolic constitution '' Munificentissimus Deus'' as follows: We proclaim and define it to be a dogma revealed by God that the immaculate Mother of God, Mary ever virgin, when the course of her earthly life was finished, was taken up body and soul into the glory of heaven. The declaration was built upon the 1854 dogma of the Immaculate Conception of Mary, which declared that Mary was conceived free from original sin, and both have their foundation in the concept of Mary as the Mother of God. It leaves open the question of whether Mary died or whether she was raised to eternal life without bodily death. The equivalent belief (but not held as dogma) in the Eastern Orthodox Church is the Dormition of the Mother of God or the "Falling Asleep of the Mother of God". The word 'assumption' derives from the Latin word ''assūmptiō'' meaning "taking u ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
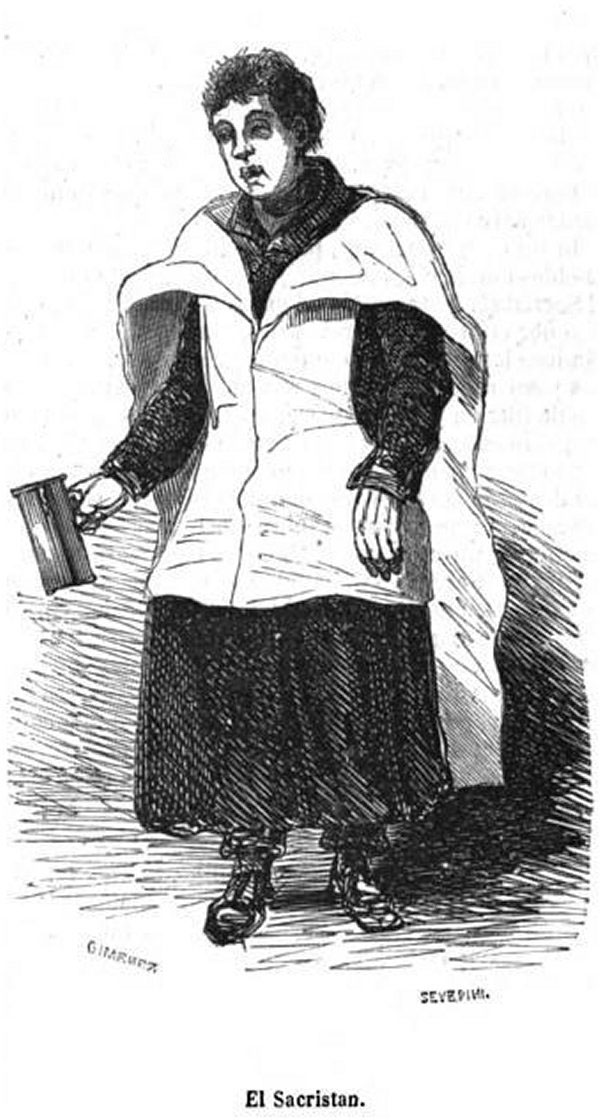
Sacristan
A sacristan is an officer charged with care of the sacristy, the church, and their contents. In ancient times, many duties of the sacrist were performed by the doorkeepers ( ostiarii), and later by the treasurers and mansionarii. The Decretals of Gregory IX speak of the sacristan as if he had an honourable office attached to a certain benefice, and say that his duty was to care for the sacred vessels, vestments, lights, etc. Nowadays the sacristan is elected or appointed. The ''Cæremoniale Episcoporum'' prescribed that in cathedral and collegiate churches the sacristan should be a priest, and describes his duties in regard to the sacristy, the Blessed Eucharist, the baptismal font, the holy oils, the sacred relics, the decoration of the church for the different seasons and feasts, the preparation of what is necessary for the various ceremonies, the pregustation in pontifical Mass, the ringing of the church bells, the preservation of order in the church, and the distrib ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
A Piece Of The Cross Of St Alexander
A, or a, is the first letter and the first vowel of the Latin alphabet, used in the modern English alphabet, the alphabets of other western European languages and others worldwide. Its name in English is ''a'' (pronounced ), plural ''aes''. It is similar in shape to the Ancient Greek letter alpha, from which it derives. The uppercase version consists of the two slanting sides of a triangle, crossed in the middle by a horizontal bar. The lowercase version can be written in two forms: the double-storey a and single-storey ɑ. The latter is commonly used in handwriting and fonts based on it, especially fonts intended to be read by children, and is also found in italic type. In English grammar, " a", and its variant " an", are indefinite articles. History The earliest certain ancestor of "A" is aleph (also written 'aleph), the first letter of the Phoenician alphabet, which consisted entirely of consonants (for that reason, it is also called an abjad to distinguish it fro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Postulant
A postulant (from la, postulare, to ask) was originally one who makes a request or demand; hence, a candidate. The use of the term is now generally restricted to those asking for admission into a Christian monastery or a religious order for the period of time preceding their admission into the novitiate. The term is most commonly used in the Catholic Church, Lutheran Churches, and the Anglican Communion (which includes the Episcopal Church, which uses the term to designate those who are seeking ordination to the diaconate or priesthood. In this respect, postulancy is generally considered the first formal step leading to candidacy and ordination). The Eastern Orthodox Churches uses this term less frequently. Purpose, duration and formation Nuns at a procession in 1915. The postulants in their garbs are walking in front of the professed nuns. The length of time that a prospective candidate remains a postulant may vary depending on the institution, or the postulant's individual ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pentecost
Pentecost (also called Whit Sunday, Whitsunday or Whitsun) is a Christian holiday which takes place on the 50th day (the seventh Sunday) after Easter Sunday. It commemorates the descent of the Holy Spirit upon the Apostles and other followers of Jesus Christ while they were in Jerusalem celebrating the Feast of Weeks, as described in the Acts of the Apostles (Acts 2:1–31). In Western Christianity, Pentecost is celebrated on the 50th day (the seventh Sunday) after Easter Sunday. In the United Kingdom, traditionally the next day, Whit Monday, was (until 1970) also a public holiday. (Since 1971, by statute, the last Monday in May has been a Bank Holiday). The Monday after Pentecost is a legal holiday in many European countries. In Eastern Christianity, Pentecost can also refer to the entire fifty days of Easter through Pentecost inclusive; hence the book containing the liturgical texts is called the "'' Pentecostarion''". Since its date depends on the date of Easter, Pentec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vigil
A vigil, from the Latin ''vigilia'' meaning ''wakefulness'' (Greek: ''pannychis'', or ''agrypnia'' ), is a period of purposeful sleeplessness, an occasion for devotional watching, or an observance. The Italian word ''vigilia'' has become generalized in this sense and means "eve" (as in ''on the eve of the war''). Eves of religious celebrations A vigil may be held on the eve of a major religious festival ( feast days), observed by remaining awake—"watchful"—as a devotional exercise or ritual observance on the eve of a holy day. Such liturgical vigils usually consist of psalms, prayers and hymns, possibly a sermon or readings from the Holy Fathers, and sometimes periods of silent meditation. The term "morning" means that the observance begins on the evening before. In traditional Christianity, the celebration of liturgical feasts begins on the evening before the holy day because the Early Church continued the Jewish practice of beginning the day at sunset rather ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Republic Of Venice
The Republic of Venice ( vec, Repùblega de Venèsia) or Venetian Republic ( vec, Repùblega Vèneta, links=no), traditionally known as La Serenissima ( en, Most Serene Republic of Venice, italics=yes; vec, Serenìsima Repùblega de Venèsia, links=no), was a sovereign state and maritime republic in parts of present-day Italy (mainly northeastern Italy) that existed for 1100 years from AD 697 until AD 1797. Centered on the lagoon communities of the prosperous city of Venice, it incorporated numerous overseas possessions in modern Croatia, Slovenia, Montenegro, Greece, Albania and Cyprus. The republic grew into a trading power during the Middle Ages and strengthened this position during the Renaissance. Citizens spoke the still-surviving Venetian language, although publishing in (Florentine) Italian became the norm during the Renaissance. In its early years, it prospered on the salt trade. In subsequent centuries, the city state established a thalassocracy. It dominat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alexander Sauli Accepts The Cross
Alexander is a male given name. The most prominent bearer of the name is Alexander the Great, the king of the Ancient Greek kingdom of Macedonia who created one of the largest empires in ancient history. Variants listed here are Aleksandar, Aleksander and Aleksandr. Related names and diminutives include Iskandar, Alec, Alek, Alex, Alexandre, Aleks, Aleksa and Sander; feminine forms include Alexandra, Alexandria, and Sasha. Etymology The name ''Alexander'' originates from the (; 'defending men' or 'protector of men'). It is a compound of the verb (; 'to ward off, avert, defend') and the noun (, genitive: , ; meaning 'man'). It is an example of the widespread motif of Greek names expressing "battle-prowess", in this case the ability to withstand or push back an enemy battle line. The earliest attested form of the name, is the Mycenaean Greek feminine anthroponym , , (/ Alexandra/), written in the Linear B syllabic script. Alaksandu, alternatively called ''Alakasandu'' or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)