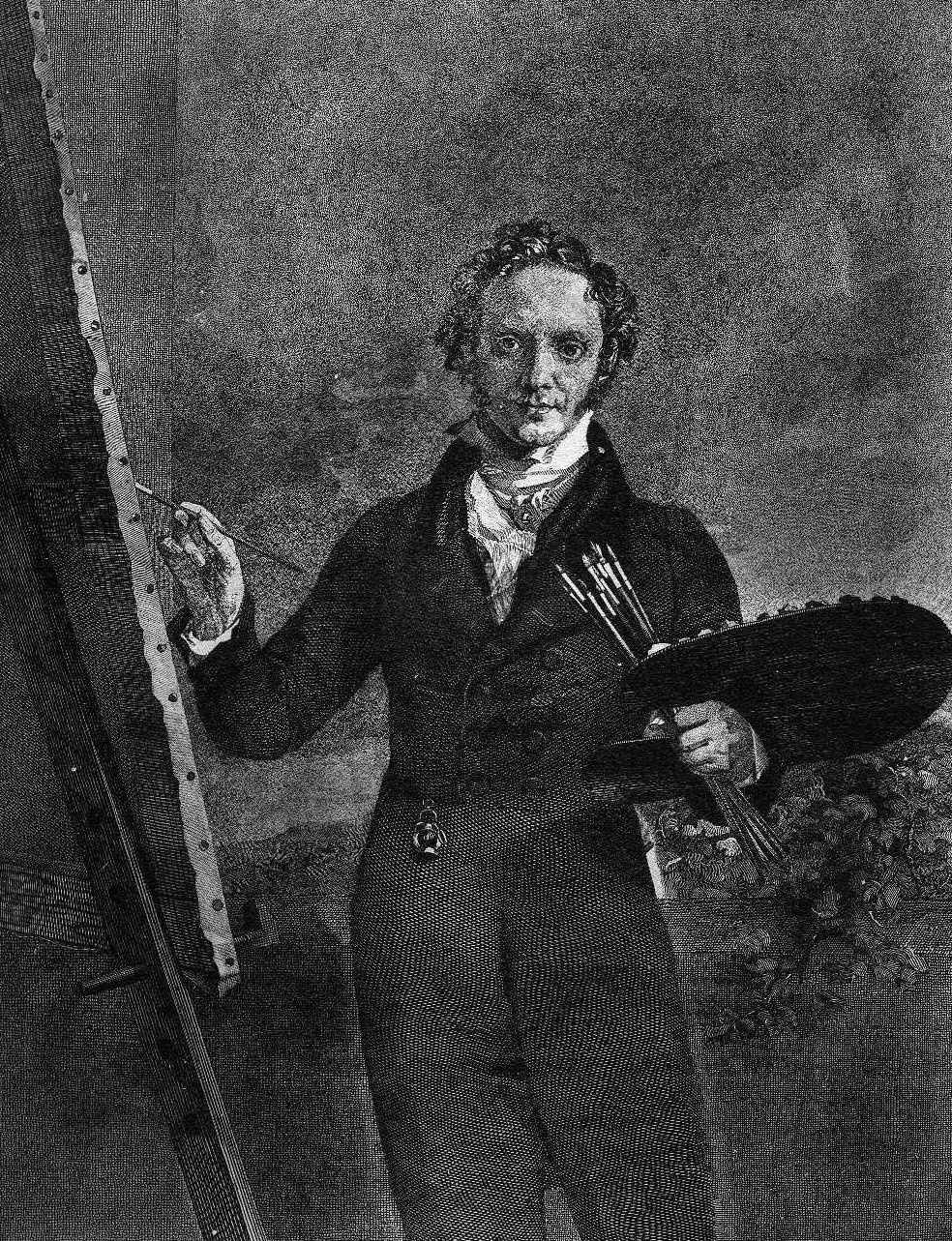|
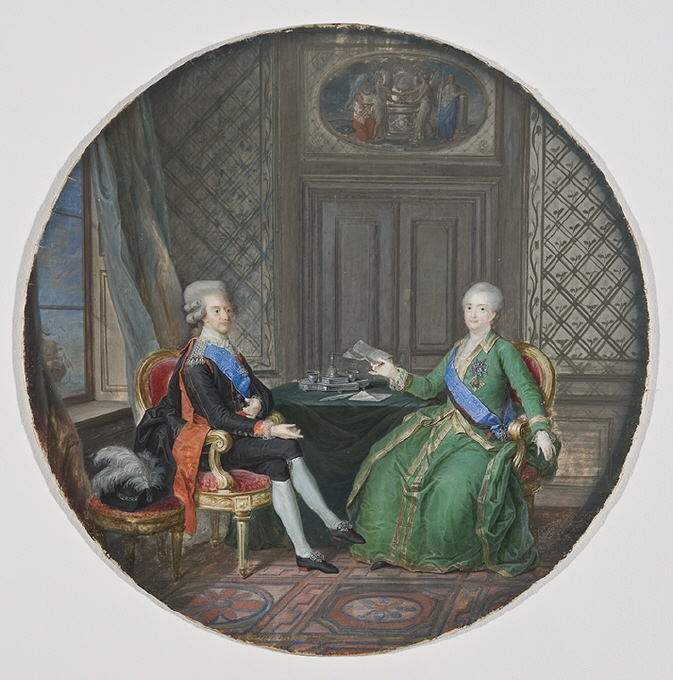
Aleksey Arakcheyev
Count Alexey Andreyevich Arakcheyev or Arakcheev (; b. in Garusovo – d. in Gruzino) was an Imperial Russian general and statesman during the reign of Tsar Alexander I. He served under Tsars Paul I and Alexander I as an army commander and Inspector of Artillery. He had a violent temper, but was a competent artillerist, and is known for his reforms of Russian artillery known as the "System of 1805". When Alexander was succeeded by Nicholas I, he lost all his offices. Early years Count Arakcheyev was born on his father's estate in Garusovo, in Vyshnevolotsky Uyezd (at the time a part of Novgorod Governorate, from 1796 part of Tver Governorate). He was educated in arithmetic by a priest, and though he shone at arithmetic, he never mastered writing and grammar. In 1783, with the help of General Peter Ivanovich Melissino, Arakcheyev enrolled in the Shlyakhetny artillery school in Saint-Petersburg. By 1787 he had become a lieutenant instructor, and gave artillery and fort ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
George Dawe
George Dawe (6 February 1781 – 15 October 1829) was an English portraitist who painted 329 portraits of Russian generals active during Napoleon's invasion of Russia for the Military Gallery of the Winter Palace. He relocated to Saint Petersburg in 1819, where he won acclaim for his work from the artistic establishment and complimentary verses by Pushkin. He was the son of Philip Dawe, a successful mezzotint engraver who also produced political cartoons relating to the events of the Boston Tea Party. One of his brothers was Henry Edward Dawe, also a portraitist. He died on 15 October 1829 in Kentish Town, United Kingdom. Life and career Early life and studies George Dawe was born on 6 February 1781 to Philip Dawe and Jane in Brewer Street, in the parish of St James's in Westminster. Philip was an artist and engraver in mezzotint who had worked with Hogarth and Joseph Mallord William Turner and who also produced satirical political cartoons about life in America w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Catherine The Great
Catherine II. (born Princess Sophie of Anhalt-Zerbst; 2 May 172917 November 1796), most commonly known as Catherine the Great, was the reigning empress of Russia from 1762 to 1796. She came to power after overthrowing her husband, Peter III. Under her long reign, inspired by the ideas of the Enlightenment, Russia experienced a renaissance of culture and sciences, which led to the founding of many new cities, universities, and theatres, along with large-scale immigration from the rest of Europe and the recognition of Russia as one of the great powers of Europe. In her accession to power and her rule of the empire, Catherine often relied on her noble favourites, most notably Count Grigory Orlov and Grigory Potemkin. Assisted by highly successful generals such as Alexander Suvorov and Pyotr Rumyantsev, and admirals such as Samuel Greig and Fyodor Ushakov, she governed at a time when the Russian Empire was expanding rapidly by conquest and diplomacy. In the south, the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Military Settlements
Military settlements () represented a special organization of the Russian military forces in 1810–1857, which allowed the combination of military service and agricultural employment. The beginning of the reform The Emperor Alexander I of Russia (reigned 1801-1825) introduced military settlements in order to set up an inexpensive reserve of trained military forces. Count Alexei Arakcheyev, who had held senior military and political appointments, established the first military settlement (1810-1812) in the Klimovichskiy Uyezd of the Mogilev Governorate (in present-day Belarus). The organization of military settlements got under way on a large scale from 1816. In 1817 Count Arakcheyev officially became the head of all the military settlements () in Russia. Internal organization The quartered military forces were being formed from among married soldiers, who had already served in the army for no less than six years, and local men (mainly, peasants) between 18 and 45 years of a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Patriotic War Of 1812
The French invasion of Russia, also known as the Russian campaign (), the Second Polish War, and in Russia as the Patriotic War of 1812 (), was initiated by Napoleon with the aim of compelling the Russian Empire to comply with the continental blockade of the United Kingdom. Widely studied, Napoleon's incursion into Russia stands as a focal point in military history, recognized as among the most devastating military endeavors globally. In a span of fewer than six months, the campaign exacted a staggering toll, claiming the lives of nearly a million soldiers and civilians. On 24 June 1812 and subsequent days, the initial wave of the multinational Grande Armée crossed the Neman River, marking the entry from the Duchy of Warsaw into Russia. Employing extensive forced marches, Napoleon rapidly advanced his army of nearly half a million individuals through Western Russia, encompassing present-day Belarus, in a bid to dismantle the disparate Russian forces led by Barclay de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
State Council Of Imperial Russia
The State Council ( rus, Госуда́рственный сове́т, p=ɡəsʊˈdarstvʲɪn(ː)ɨj sɐˈvʲet) was the supreme state advisory body to the tsar in the Russian Empire. From 1906, it was the upper house of the parliament under the Russian Constitution of 1906. 18th century Early tsars' councils were small and dealt primarily with external politics. Peter I of Russia introduced the Privy Council. Catherine I of Russia introduced the Supreme Privy Council. Its role varied during different reigns. Peter III of Russia created the Imperial Council on 20 May 1762 ("Императорский Совет"), or, formally "The Council at the Highest Court" ("Совет при высочайшем дворе"). It was dismissed shortly after the succession of Catherine II of Russia. 1810–1906 The State Council was established by Alexander I of Russia in 1810 as part of Speransky's reforms. Although envisaged by Speransky as the upper chamber of the Russian parliame ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Gulf Of Bothnia
The Gulf of Bothnia (; ; ) is divided into the Bothnian Bay and the Bothnian Sea, and it is the northernmost arm of the Baltic Sea, between Finland's west coast ( East Bothnia) and the northern part of Sweden's east coast ( West Bothnia and North Bothnia). In the south of the gulf lies Åland, between the Sea of Åland and the Archipelago Sea. Name Bothnia is a latinization. The Swedish name was originally just , with being Old Norse for "gulf" or "bay", which is also the meaning of the second element . The name was applied to the Gulf of Bothnia as in Old Norse, after , which at the time referred to the coastland west of the gulf. Later, was applied to the regions of on the western side and on the eastern side ('West Bottom' and 'East Bottom'). The Finnish name of Österbotten, (, meaning 'land'), hint as to the meaning in both languages: the meaning of includes both 'bottom' and 'north'. is the base word for north, , with an adjectival suffix added. / is c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Finnish War
The Finnish War (; ; ) was fought between the Gustavian era, Kingdom of Sweden and the Russian Empire from 21 February 1808 to 17 September 1809 as part of the Napoleonic Wars. As a result of the war, the eastern third of Sweden was established as the autonomous Grand Duchy of Finland within the Russian Empire. Other notable effects were the Riksdag of the Estates, Swedish parliament's adoption of a Instrument of Government (1809), new constitution and the establishment of the House of Bernadotte, the new Swedish Act of Succession, Swedish royal house, in 1818. Background After the Russian Emperor Alexander I of Russia, Alexander I concluded the 1807 Treaty of Tilsit with Napoleon, Alexander, in his letter on 24 September 1807 to the Swedish King Gustav IV Adolf, informed the king that the peaceful relations between Russia and Sweden depended on Swedish agreement to abide by the limitations of the Treaty of Tilsit which in practice meant that Sweden would have been required ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Horse Artillery
Horse artillery was a type of light, fast-moving, and fast-firing field artillery that consisted of light cannons or howitzers attached to light but sturdy two-wheeled carriages called caissons or limbers, with the individual crewmen riding on horses. This was in contrast to other forms of field artillery which may also be horse-drawn but were heavier and whose gunners either marched on foot or were transported seated on the gun carriage, wagons or limbers. Horse artillery units provided highly mobile fire support especially to cavalry units, and existed in armies in Europe, the Americas, and Asia, from the early 17th to the mid-20th century. Tactics Once in position, horse artillery crews were trained to quickly dismount, deploy or unlimber their guns (detach them from their caissons), then rapidly fire grapeshot, shells or round shot at the enemy. They could then just as rapidly limber-up (reattach the guns to the caissons), remount, and be ready to move to a new position, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Licorne
Licorne (, ''Yedinorog'', 'unicorn') is the French name of an 18th- and 19th-century Russian cannon, a type of muzzle-loading howitzer, devised in 1757 by M.W. Danilov and S.A. Martynov and accepted by artillery commander, general Peter Ivanovich Shuvalov. The licorne was a hybrid between the howitzers and guns of the era (a gun-howitzer), with a longer barrel than contemporary howitzers, giving projectiles a flatter trajectory, but longer range. Similar to the howitzers, they had a powder chamber of smaller diameter than the gun caliber, but whereas a howitzer's chamber was cylindrical, a licorne's was conical, with its base diameter the same as the gun bore. The conical chamber was easier to load and facilitated the placement of the projectile perfectly in the center of the barrel. Licornes were able to fire both the solid shot used for cannons and howitzer shells, as well as grapeshot and canister. The length of the barrel was 9 or 10 calibres, and the weight of the pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Battle Of Austerlitz
The Battle of Austerlitz (2 December 1805/11 Frimaire An XIV French Republican calendar, FRC), also known as the Battle of the Three Emperors, was one of the most important military engagements of the Napoleonic Wars. The battle occurred near the town of Slavkov u Brna, Austerlitz in the Austrian Empire (now Slavkov u Brna in the Czech Republic). Around 158,000 troops were involved, of which around 24,000 were killed or wounded. The battle is often cited by military historians as one of Napoleon's tactical masterpieces, in the same league as other historic engagements like Hannibal's Battle of Cannae, Cannae (216 BC) or Alexander the Great's Battle of Gaugamela, Gaugamela (331 BC).Byron Farwell, Farwell p. 64. "Austerlitz is generally regarded as one of Napoleon's tactical masterpieces and has been ranked as the equal of Arbela, Cannae, and Leuthen."Trevor N. Dupuy, Dupuy p. 102 Note: Dupuy was not afraid of expressing an opinion, and he classified some of his subjects as Great ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Count
Count (feminine: countess) is a historical title of nobility in certain European countries, varying in relative status, generally of middling rank in the hierarchy of nobility. Pine, L. G. ''Titles: How the King Became His Majesty''. New York: Barnes & Noble, 1992. p. 73. . Especially in earlier medieval periods the term often implied not only a certain status, but also that the ''count'' had specific responsibilities or offices. The etymologically related English term " county" denoted the territories associated with some countships, but not all. The title of ''count'' is typically not used in England or English-speaking countries, and the term ''earl'' is used instead. A female holder of the title is still referred to as a ''countess'', however. Origin of the term The word ''count'' came into English from the French ', itself from Latin '—in its accusative form ''comitem''. It meant "companion" or "attendant", and as a title it indicated that someone was delegated to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Lieutenant-general
Lieutenant general (Lt Gen, LTG and similar) is a military rank used in many countries. The rank traces its origins to the Middle Ages, where the title of lieutenant general was held by the second-in-command on the battlefield, who was normally subordinate to a captain general. In modern armies, lieutenant general normally ranks immediately below general (or colonel general) and above major general; it is equivalent to the navy rank of vice admiral, and in air forces with a separate rank structure, it is equivalent to air marshal. In the United States, a lieutenant general has a three star insignia and commands an army corps, typically made up of three Division (military), army divisions, and consisting of around 60,000 to 70,000 soldiers. The seeming incongruity that a lieutenant general outranks a major general (whereas a Major (rank), major outranks a lieutenant) is due to the derivation of major general from sergeant major general, which was a rank subordinate to lieutenan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |