|
Aksu Basin
The Aksu Basin is a sedimentary basin in southwestern Turkey, around the present-day Aksu River (Turkey), Aksu River. Located at the intersection of several major tectonic systems, in the Isparta Angle, the Aksu Basin covers an area of some 2000 square kilometers. Together with the Köprü Çay Basin and the Manavgat Basin, the Aksu Basin forms part of the broader Antalya Basin. It forms a graben relative to the surrounding Anatolian plateau. The Aksu Basin has been gradually filling up with sediment since Neogene times. General description The Aksu Basin is located at an important intersection of several tectonic systems. To the north, the Anatolian continental plateau is undergoing uplift, while to the south the African Plate, African and Eurasian Plate, Eurasian plates are colliding, producing features like the Mediterranean Ridge and the Hellenic subduction zone. On the west, the Aksu Basin is bounded by the Bey Dağları platform carbonates, where extensional tectonics, the c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sedimentary Basin
Sedimentary basins are region-scale depressions of the Earth's crust where subsidence has occurred and a thick sequence of sediments have accumulated to form a large three-dimensional body of sedimentary rock They form when long-term subsidence creates a regional depression that provides Accommodation (geology), accommodation space for accumulation of sediments. Over millions or tens or hundreds of millions of years the deposition of sediment, primarily gravity-driven transportation of water-borne eroded material, acts to fill the depression. As the sediments are buried, they are subject to increasing pressure and begin the processes of compaction (geology), compaction and lithification that transform them into sedimentary rock. Sedimentary basins are created by deformation of Earth's lithosphere in diverse geological settings, usually as a result of plate tectonics, plate tectonic activity. Mechanisms of crustal deformation that lead to subsidence and sedimentary basin formatio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Basement Rock
In geology, basement and crystalline basement are crystalline rocks lying above the mantle and beneath all other rocks and sediments. They are sometimes exposed at the surface, but often they are buried under miles of rock and sediment. The basement rocks lie below a sedimentary platform or cover, or more generally any rock below sedimentary rocks or sedimentary basins that are metamorphic or igneous in origin. In the same way, the sediments or sedimentary rocks on top of the basement can be called a "cover" or "sedimentary cover". Basement rock consists of continental crustal rock which has been modified several times through tectonic events including deformation, metamorphism, deposition, partial melting and magmatism. Continental crust Basement rock is the thick foundation of ancient, and oldest, metamorphic and igneous rock that forms the crust of continents, often in the form of granite. Basement rock is contrasted to overlying sedimentary rocks which are laid down on top ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Burdigalian
The Burdigalian is, in the geologic timescale, an age (geology), age or stage (stratigraphy), stage in the early Miocene. It spans the time between 20.43 ± 0.05 annum, Ma and 15.97 ± 0.05 Ma (million years ago). Preceded by the Aquitanian (stage), Aquitanian, the Burdigalian was the first and longest warming period of the MioceneEdward Petuch, Ph.D. Florida Atlantic University, Department of Geosciences. and is succeeded by the Langhian. Stratigraphic definition The name Burdigalian comes from ''Burdigala'', the Latin name for the city of Bordeaux, France. The Burdigalian Stage was introduced in scientific literature by Charles Depéret in 1892. The base of the Burdigalian is at the first appearance of foram species ''Globigerinoides altiaperturus'' and the top of magnetic chronozone C6An. , an official GSSP for the Burdigalian had not yet been assigned. The top of the Burdigalian (the base of the Langhian) is defined by the first appearance of foram species ''Praeorbulina gl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
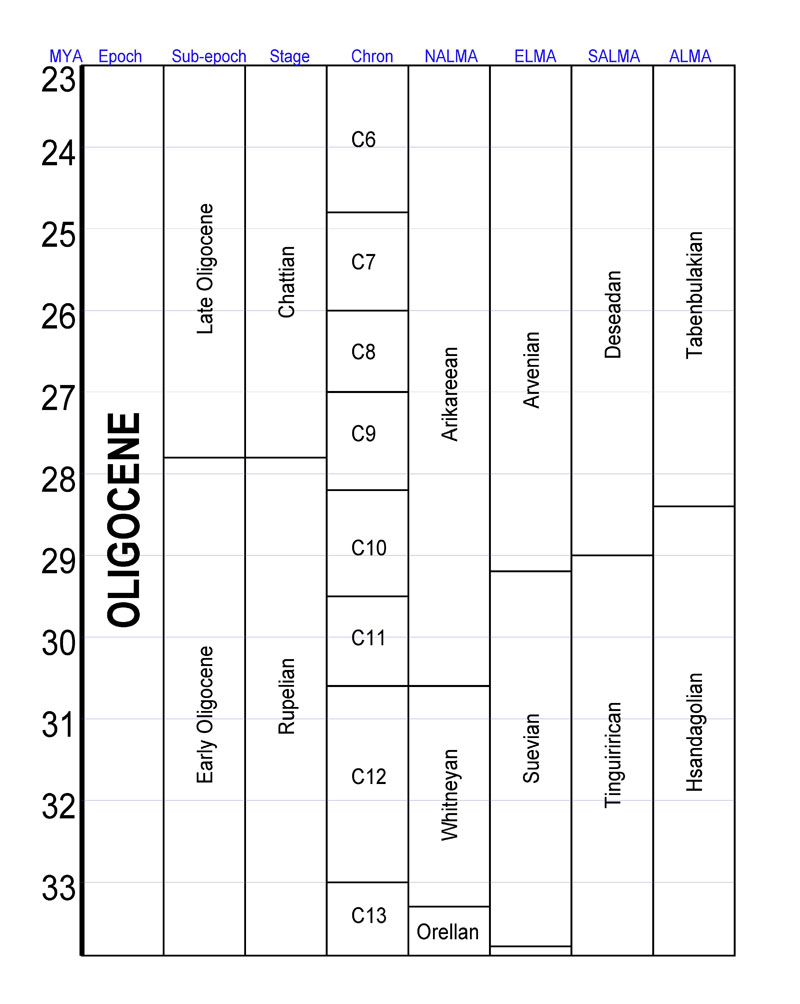
Oligocene
The Oligocene ( ) is a geologic epoch (geology), epoch of the Paleogene Geologic time scale, Period that extends from about 33.9 million to 23 million years before the present ( to ). As with other older geologic periods, the rock beds that define the epoch are well identified but the exact dates of the start and end of the epoch are slightly uncertain. The name Oligocene was coined in 1854 by the German paleontologist Heinrich Ernst Beyrich from his studies of marine beds in Belgium and Germany. The name comes from Ancient Greek (''olígos'') 'few' and (''kainós'') 'new', and refers to the sparsity of Neontology, extant forms of Mollusca, molluscs. The Oligocene is preceded by the Eocene Epoch and is followed by the Miocene Epoch. The Oligocene is the third and final epoch of the Paleogene Period. The Oligocene is often considered an important time of transition, a link between the archaic world of the tropical Eocene and the more modern ecosystems of the Miocene. Major chang ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paleogene
The Paleogene Period ( ; also spelled Palaeogene or Palæogene) is a geologic period and system that spans 43 million years from the end of the Cretaceous Period Ma (million years ago) to the beginning of the Neogene Period Ma. It is the first period of the Cenozoic Era, the tenth period of the Phanerozoic and is divided into the Paleocene, Eocene, and Oligocene epochs. The earlier term Tertiary Period was used to define the time now covered by the Paleogene Period and subsequent Neogene Period; despite no longer being recognized as a formal stratigraphic term, "Tertiary" still sometimes remains in informal use. Paleogene is often abbreviated "Pg", although the United States Geological Survey uses the abbreviation "" for the Paleogene on the Survey's geologic maps. Much of the world's modern vertebrate diversity originated in a rapid surge of diversification in the early Paleogene, as survivors of the Cretaceous–Paleogene extinction event took advantage of empty ecolo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transtension
Transtension is the state in which a rock mass or area of the Earth's crust (geology), crust experiences both ''extensive'' and ''transtensive'' Shear (geology), shear. As such, transtensional regions are characterised by both extensional structures (fault (geology), normal faults, grabens) and wrench structures (strike-slip faults). In general, many tectonic regimes that were previously defined as simple strike-slip shear zones are actually transtensional. It is unlikely that a deforming body will experience 'pure' extension or 'pure' strike-slip. Transtensional shear zones are characterized by the co-existence of different structures, related to both strike-slip shear and extension. End member structures include pure strike-slip faults and purely extensional ("normal") dip-slip faults. Faults which have components of both (termed 'oblique' slip faults) are abundant. Releasing bend ''Releasing bends'' are transtensional structures that form where the orientation of a strike-slip ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crustal Extension
Extensional tectonics is concerned with the structures formed by, and the tectonic processes associated with, the stretching of a planetary body's crust or lithosphere. Deformation styles The types of structure and the geometries formed depend on the amount of stretching involved. Stretching is generally measured using the parameter ''β'', known as the ''beta factor'', where : \beta = \frac \,, ''t''0 is the initial crustal thickness and ''t''1 is the final crustal thickness. It is also the equivalent of the strain parameter ''stretch''. Low beta factor In areas of relatively low crustal stretching, the dominant structures are high to moderate angle normal faults, with associated half grabens and tilted fault blocks. High beta factor In areas of high crustal stretching, individual extensional faults may become rotated to too low a dip to remain active and a new set of faults may be generated. Large displacements may juxtapose syntectonic sediments against metamorphic r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alluvial Fan
An alluvial fan is an accumulation of sediments that fans outwards from a concentrated source of sediments, such as a narrow canyon emerging from an escarpment. They are characteristic of mountainous terrain in arid to Semi-arid climate, semiarid climates, but are also found in more humid environments subject to intense rainfall and in areas of modern glaciation. They range in area from less than to almost . Alluvial fans typically form where a flow of sediment or rocks emerge from a confined channel and are suddenly free to spread out in many directions. For example, many alluvial fans form when steep mountain valleys meet a flat plain. The transition from a narrow channel to a wide open area reduces the carrying capacity of flow and results in Deposition (geology), deposition of sediments. The flow can take the form of infrequent debris flows like in a landslide, or can be carried by an intermittent stream or creek. The reduction of flow is key to the formation of alluvial ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fan Delta
Fan commonly refers to: * Fan (machine), a machine for producing airflow, often used for cooling * Hand fan, an implement held and waved by hand to move air for cooling * Fan (person), short for fanatic; an enthusiast or supporter, especially with regard to entertainment Fan, FAN or fans may also refer to: Arts, entertainment, and media Music * "Fan" (Pascal Obispo song), 2003 * Fan (Offset song), 2023 * ''Fans'' (album), a 1984 album by Malcolm McLaren * "Fans" (song), a 2007 album track on ''Because of the Times'' by the Kings of Leon Other uses in arts, entertainment, and media * ''Fan'' (2007 film), a Uruguayan drama film * ''Fan'' (2016 film), an Indian Hindi film * Fan, a character in the video game ''Yie Ar Kung-Fu'' * Fan, a character in the novella ''A Christmas Carol'' Biology * Free amino nitrogen, in brewing and winemaking, amino acids available for yeast metabolism * Sea fan, a marine animal of the cnidarian phylum Computing and mathematics * Fan (geom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Foreland Basin
A foreland basin is a structural basin that develops adjacent and parallel to a mountain belt. Foreland basins form because the immense mass created by crustal thickening associated with the evolution of a mountain belt causes the lithosphere to bend, by a process known as lithospheric flexure. The width and depth of the foreland basin is determined by the flexural rigidity of the underlying lithosphere, and the characteristics of the mountain belt. The foreland basin receives sediment that is eroded off the adjacent mountain belt, filling with thick sedimentary successions that thin away from the mountain belt. Foreland basins represent an endmember basin type, the other being rift basins. Accommodation (the space available for sediments to be deposited) is provided by loading and downflexure to form foreland basins, in contrast to rift basins, where accommodation space is generated by lithospheric extension. Types of foreland basin Foreland basins can be divided into ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Unconformity
An unconformity is a buried erosional or non-depositional surface separating two rock masses or strata of different ages, indicating that sediment deposition was not continuous. In general, the older layer was exposed to erosion for an interval of time before deposition of the younger layer, but the term is used to describe any break in the sedimentary geologic record. The significance of angular unconformity (see below) was shown by James Hutton, who found examples of Hutton's Unconformity at Jedburgh in 1787 and at Siccar Point in Berwickshire in 1788, both in Scotland. The rocks above an unconformity are younger than the rocks beneath (unless the sequence has been overturned). An unconformity represents time during which no sediments were preserved in a region or were subsequently eroded before the next deposition. The local record for that time interval is missing and geologists must use other clues to discover that part of the geologic history of that area. The interval ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lycian Nappes
Lycian may refer to: * Lycia, a geopolitical region in Anatolia (now Turkey) * Lycian Apollo, a type of ancient Greek statuary * Lycian Way, a hiking trail in southwestern Turkey * Lycian Way Ultramarathon, an annual ultra-marathon in Lycian Way * Lycians, people who lived in Lycia * extinct languages formerly spoken in Lycia, i.e. ** the Lycian language, also known as and ** the Milyan language, formerly known as or, sometimes, * the Lycian alphabet, used to write the Lycian language * Lycian (Unicode block), the Unicode characters comprising the Lycian script See also * Lucian (other) * Lycia (other) Lycia is a former geopolitical region in Anatolia. Lycia may also refer to: Species * ''Lycia'' (moth), a genus of moths in the family Geometridae * ''Lycia'' (butterfly), an invalid name for the butterfly genus ''Lycaena'' People * Lycia Na ... {{disambiguation Language and nationality disambiguation pages ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |