|
Aeromancy
Aeromancy (from Greek ἀήρ ''aḗr'', "air", and ''manteia'', "divination") is divination that is conducted by interpreting atmospheric conditions. Alternate terms include "arologie", "aeriology", and "aërology". Practice Aeromancy uses cloud formations, wind currents, and cosmological events such as comets, to attempt to divine the past, present, or future. There are sub-types of this practice which are as follows: austromancy (wind divination), ceraunoscopy (observing thunder and lightning), chaomancy (aerial vision), meteormancy (meteors, AKA shooting stars), and nephomancy (cloud divination). History Variations on the concept have been used throughout history, the practice is thought to have been used by the ancient Babylonian priests, and is probably alluded to in the bible. Damascius, the last of the Neoplatonists, records an account of nephomancy in the 5th century CE, during the reign of Leo I: Cultural influence The ancient Etruscans produced guides to brontos ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
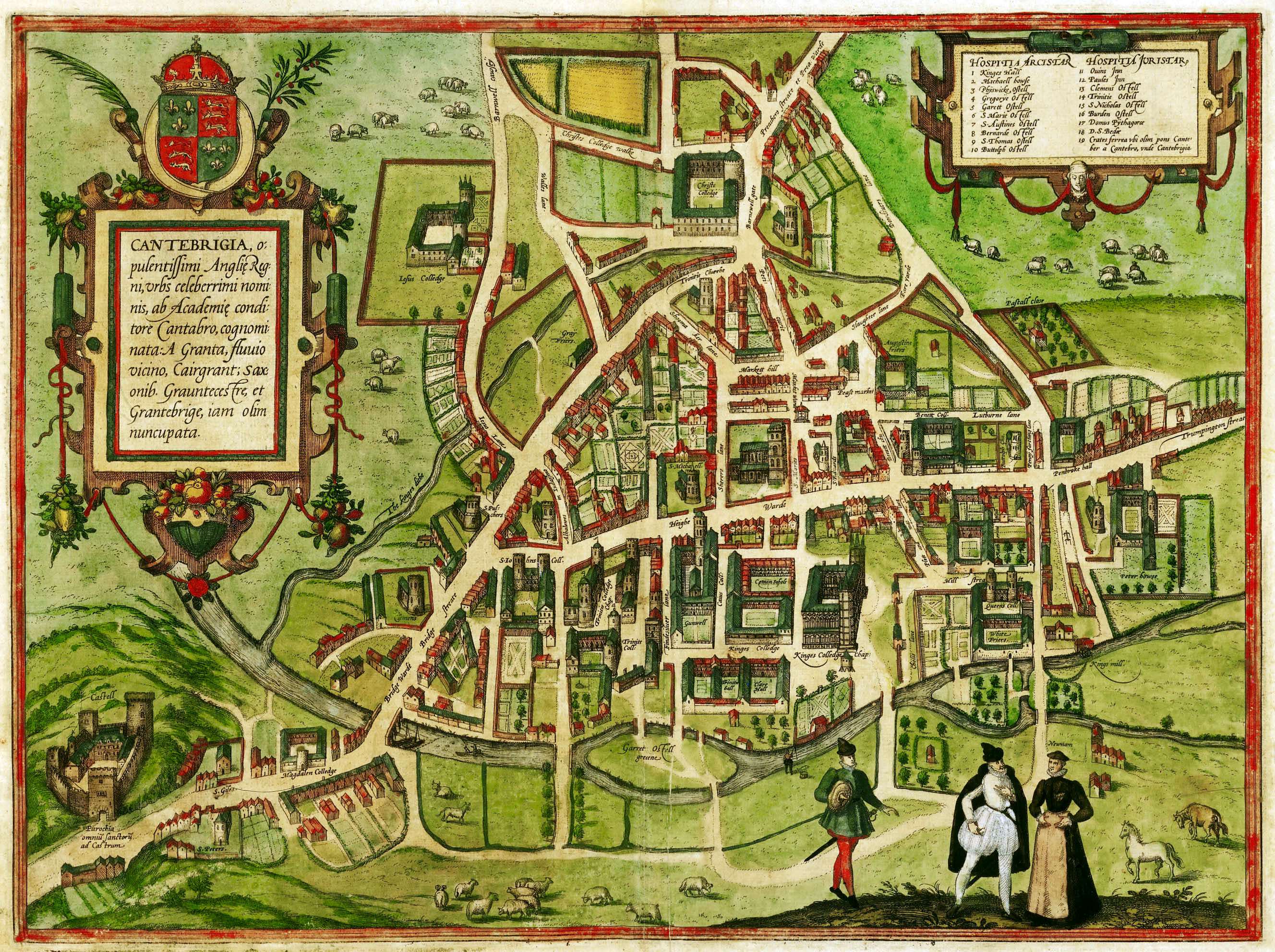
Cambridge, England
Cambridge ( ) is a city and non-metropolitan district in the county of Cambridgeshire, England. It is the county town of Cambridgeshire and is located on the River Cam, north of London. As of the 2021 United Kingdom census, the population of the City of Cambridge was 145,700; the population of the wider built-up area (which extends outside the city council area) was 181,137. (2021 census) There is archaeological evidence of settlement in the area as early as the Bronze Age, and Cambridge became an important trading centre during the Roman and Viking eras. The first town charters were granted in the 12th century, although modern city status was not officially conferred until 1951. The city is well known as the home of the University of Cambridge, which was founded in 1209 and consistently ranks among the best universities in the world. The buildings of the university include King's College Chapel, Cavendish Laboratory, and the Cambridge University Library, one of the large ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Necromancy
Necromancy () is the practice of Magic (paranormal), magic involving communication with the Death, dead by Evocation, summoning their spirits as Ghost, apparitions or Vision (spirituality), visions for the purpose of divination; imparting the means to foretell future events and discover hidden knowledge. Sometimes categorized under ''death magic'', the term is occasionally also used in a more general sense to refer to black magic or witchcraft as a whole. Etymology The word ''necromancy'' is adapted from Late Latin : a loan word from the Koine Greek, post-Classical Greek (, or 'divination through a dead body'), a compound of Ancient Greek (, or 'dead body') and (, or 'divination'). The Koine Greek compound form was first documented in the writings of Origen, Origen of Alexandria in the 3rd century AD. The Classical Greek term was (), from the episode of the ''Odyssey'' in which Odysseus visits the realm of the dead souls, and in Hellenistic Greek; in Classical Latin, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Albertus Magnus
Albertus Magnus ( 1200 – 15 November 1280), also known as Saint Albert the Great, Albert of Swabia, Albert von Bollstadt, or Albert of Cologne, was a German Dominican friar, philosopher, scientist, and bishop, considered one of the greatest medieval philosophers and thinkers. Canonized in 1931, he was known during his lifetime as ''Doctor universalis'' and ''Doctor expertus''; late in his life the sobriquet ''Magnus'' was appended to his name. Scholars such as James A. Weisheipl and Joachim R. Söder have referred to him as the greatest German philosopher and theologian of the Middle Ages. The Catholic Church distinguishes him as one of the Doctors of the Church. Biography It seems likely that Albertus Magnus was born sometime before 1200, given well-attested evidence that he was aged over 80 on his death in 1280. Two later sources say that Albert was about 87 on his death, which has led 1193 to be commonly given as the date of Albert's birth, but this information doe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Johannes Hartlieb
Johannes Hartlieb (c. 1410Hartlieb's year of birth is unknown; his existence is first attested as the author of ''Kunst der Gedächtnüß'', written during 1430–32, and an estimate of his year of birth as either "c. 1400" or "c. 1410" can be found in literature. – 18 May 1468) was a physician of Late Medieval Bavaria, probably of a family from Neuburg an der Donau. He was in the employment of Louis VII of Bavaria and Albert VI of Austria in the 1430s, and of Albert III of Bavaria from 1440, and of the latter's son Sigismund from 1456. In 1444, he married Sibilla, possibly the daughter of Albert and Agnes Bernauer. Hartlieb wrote a compendium on herbs in ca. 1440, and in 1456 the ''puch aller verpoten kunst, ungelaubens und der zaubrey'' (book on all forbidden arts, superstition and sorcery) on the artes magicae, containing the oldest known description of witches' flying ointment. Hartlieb also produced German translations of various classical and medieval authors ( Tr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scapulimancy
Scapulimancy (also spelled scapulomancy and scapulamancy, also termed omoplatoscopy or speal bone reading) is the practice of divination by use of scapulae or speal bones (shoulder blades). It is most widely practiced in China and the Sinosphere as oracle bones, but has also been independently developed in other traditions including the West. Historically, scapulimancy has taken two major forms. In the first, "apyromantic", the scapula of an animal was simply examined after its slaughter. This form was widespread in Europe, Northern Africa and the Near East. However, the second form, " pyromantic" scapulimancy, involving the heating or burning of the bone and interpretation of the results, was practiced in East Asia and North America. Americas The belief amongst the Mistassini Cree and Naskapi Innu peoples was that all animal remains were to be treated in accordance with taboos. This can blur the distinction between ritually or religiously significant remains and secular uses o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Palmistry
Palmistry is the pseudoscientific practice of fortune-telling through the study of the palm. Also known as palm reading, chiromancy, chirology or cheirology, the practice is found all over the world, with numerous cultural variations. Those who practice palmistry are generally called ''palmists'', ''hand readers'', ''hand analysts'', or ''chirologists''. There are many—and often conflicting—interpretations of various lines and palmar features across various teachings of palmistry. Palmistry is widely viewed as a pseudoscience due to various contradictions between different interpretations and the lack of evidence for palmistry's predictions. History Ancient palmistry Palmistry is a practice common to many different places on the Eurasian landmass; it has been practiced in the cultures of Sumer, Babylonia, Arabia, Canaan, Persia, India, Nepal, Tibet and China. The acupuncturist Yoshiaki Omura describes its roots in Hindu astrology (known in Sanskrit as '' jyotish''), ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pyromancy
Pyromancy (Ancient Greek ἐμπυρία (empyria), ''divination by fire'')Liddell, H.G. & Scott, R. (1940). ''A Greek-English Lexicon. revised and augmented throughout by Sir Henry Stuart Jones. with the assistance of. Roderick McKenzie.'' Oxford: Clarendon Press. is the art of divination by means of fire or flames. The word ''pyromancy'' is adapted from the Greek word ''pyromanteia'', from pyr (πῦρ, ''fire)'' ''and'' ''manteia'' (μαντεία, ''divination by means of''). Its first known use was in the 1300s, and it evolved into the Late Latin word ''piromantia'' and Old French word ''piromance.''“Pyromancy.” Merriam-Webster.com Dictionary, Merriam-Webster, https://www.merriam-webster.com/dictionary/pyromancy . Accessed 26 Jan. 2023. History of pyromancy Due to the importance of fire in society in prehistory and its continued importance within civilizations, it is quite likely that pyromancy was one of the earlier forms of divination, arising independently in many c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydromancy
Hydromancy (Ancient Greek ὑδρομαντεία, ''water-divination'',Liddell, H.G. & Scott, R. (1940). ''A Greek-English Lexicon. revised and augmented throughout by Sir Henry Stuart Jones. with the assistance of. Roderick McKenzie.'' Oxford: Clarendon Press. from ὕδωρ, ''water'', and μαντεία, ''divination'') is a method of divination by means of water, including the color, ebb and flow, or ripples produced by pebbles dropped in a pool. It also refers to the entering of a trance by staring at a chosen form of water, which is a form of scrying. Methods of hydromancy There are various methods of hydromancy. Hydromancy with rain water was termed "hydatoscopy", and hydromancy with water from a spring was termed "pegomancy". The Jesuit M. A. Del Rio (1551–1608) described several methods of hydromancy. The first method described depicts a ring hanging by a string that is dipped into a vessel of water which was shaken. A judgment or prediction is made by the number ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geomancy
Geomancy, a compound of Greek roots denoting "earth divination", was originally used to mean methods of divination that interpret geographic features, markings on the ground, or the patterns formed by soil, rock (geology), rocks, or sand. Its definition has expanded over time (along with the recognized definition of the suffix ''-mancy''), to include any spiritual, metaphysical, or pseudoscientific practice that is related to the Earth. In recent times the term has been applied to a wide range of other occult and fringe activities, including Earth mysteries and the introduction of ley lines and . Geomancy was one of the forms of divination throughout Africa and Europe in premodern times, but was considered a forbidden practice by Christians in medieval Europe.Johannes Hartlieb (Munich, 1456) ''The Book of All Forbidden Arts''; quoted in In other regions and cultures, geomancy practices include ''Sikidy'' and ''Ifá'' (found in Africa), I Ching and Feng shui (found in China), Ku ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Renaissance Magic
Renaissance magic was a resurgence in Hermeticism and Neoplatonic varieties of the magical arts which arose along with Renaissance humanism in the 15th and 16th centuries CE. During the Renaissance period, magic and occult practices underwent significant changes that reflected shifts in cultural, intellectual, and religious perspectives. C. S. Lewis, in his work on English literature, highlighted the transformation in how magic was perceived and portrayed. In medieval stories, magic had a fantastical and fairy-like quality, while in the Renaissance, it became more complex and tied to the idea of hidden knowledge that could be explored through books and rituals. This change is evident in the works of authors like Spenser, Marlowe, Chapman, and Shakespeare, who treated magic as a serious and potentially dangerous pursuit. Heinrich Cornelius Agrippa, a scholar, physician, and astrologer, popularized the Hermetic and Cabalistic magic of Marsilio Ficino and Giovanni Pico della ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hebrew Bible
The Hebrew Bible or Tanakh (;"Tanach" . '' Random House Webster's Unabridged Dictionary''. ; ; or ), also known in Hebrew as (; ), is the canonical collection of scriptures, comprising the Torah (the five Books of Moses), the Nevi'im (the Books of the Prophets), and the [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |