|
Acidic Oxides
An acidic oxide is an oxide that either produces an acidic solution upon addition to water, or acts as an acceptor of hydroxide ions effectively functioning as a Lewis acid. Acidic oxides will typically have a low pKa and may be inorganic or organic. A commonly encountered acidic oxide, carbon dioxide produces an acidic solution (and the generation of carbonic acid) when dissolved. Generally non-metallic oxides are acidic. The acidity of an oxide can be reasonably assumed by its accompanying constituents. Less electronegative elements tend to form basic oxides such as sodium oxide and magnesium oxide, whereas more electronegative elements tend to produce acidic oxides as seen with carbon dioxide and phosphorus pentoxide. Some oxides like aluminium oxides are amphoteric while some oxides may be neutral. Acidic oxides are of environmental concern. Sulfur and nitrogen oxides are considered air pollutants as they react with atmospheric water vapour to produce acid rain. Examp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydroxide
Hydroxide is a diatomic anion with chemical formula OH−. It consists of an oxygen and hydrogen atom held together by a single covalent bond, and carries a negative electric charge. It is an important but usually minor constituent of water. It functions as a base, a ligand, a nucleophile, and a catalyst. The hydroxide ion forms salts, some of which dissociate in aqueous solution, liberating solvated hydroxide ions. Sodium hydroxide is a multi-million-ton per annum commodity chemical. The corresponding electrically neutral compound HO• is the hydroxyl radical. The corresponding covalently bound group of atoms is the hydroxy group. Both the hydroxide ion and hydroxy group are nucleophiles and can act as catalysts in organic chemistry. Many inorganic substances which bear the word ''hydroxide'' in their names are not ionic compounds of the hydroxide ion, but covalent compounds which contain hydroxy groups. Hydroxide ion The hydroxide ion is naturally produced ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chromium Trioxide
Chromium trioxide (also known as chromium(VI) oxide or chromic anhydride) is an inorganic compound with the formula . It is the acidic anhydride of chromic acid, and is sometimes marketed under the same name. This compound is a dark-purple solid under anhydrous conditions and bright orange when wet. The substance dissolves in water accompanied by hydrolysis. Millions of kilograms are produced annually, mainly for electroplating. Chromium trioxide is a powerful oxidiser, a mutagen, and a carcinogen. Production, structure, and basic reactions Chromium trioxide is generated by treating sodium dichromate with sulfuric acid: : Approximately 100,000 tonnes are produced annually by this or similar routes. The solid consists of chains of tetrahedrally coordinated chromium atoms that share vertices. Each chromium center therefore shares two oxygen centers with neighbors. Two oxygen atoms are not shared, giving an overall stoichiometry of 1:3. The structure of monomeric has been ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phosphorus(V) Oxide
Phosphorus pentoxide is a chemical compound with molecular formula P4 O10 (with its common name derived from its empirical formula, P2O5). This white crystalline solid is the anhydride of phosphoric acid. It is a powerful desiccant and dehydrating agent. Structure Phosphorus pentoxide crystallizes in at least four forms or polymorphs. The most familiar one, a metastable form (shown in the figure), comprises molecules of P4O10. Weak van der Waals forces hold these molecules together in a hexagonal lattice (However, in spite of the high symmetry of the molecules, the crystal packing is not a close packing). The structure of the P4O10 cage is reminiscent of adamantane with ''T''d symmetry point group. It is closely related to the corresponding anhydride of phosphorous acid, P4O6. The latter lacks terminal oxo groups. Its density is 2.30 g/cm3. It boils at 423 °C under atmospheric pressure; if heated more rapidly it can sublimate. This form can be made by condensing the vap ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phosphorous Acid
Phosphorous acid (or phosphonic acid) is the Compound (chemistry), compound described by the chemical formula, formula . It is diprotic (readily ionizes two protons), not triprotic as might be suggested by its formula. Phosphorous acid is an intermediate in the preparation of other phosphorus compounds. Organic derivatives of phosphorous acid, compounds with the formula , are called phosphonic acids. Nomenclature and tautomerism Solid has tetrahedral geometry about the central phosphorus atom, with a bond of 132 picometer, pm, one double bond of 148 pm and two longer single bonds of 154 pm. In common with other phosphorus oxides with bonds (e.g.hypophosphorous acid and dialkyl phosphites), it exists in equilibrium with an extremely minor tautomer . (In contrast, arsenous acid's major tautomer is the trihydroxy form.) IUPAC recommends that the trihydroxy form be called phosphorous acid, and the dihydroxy form phosphonic acid.. Only the reduced phosphorus c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phosphorus(III) Oxide
Phosphorus trioxide is the chemical compound with the molecular formula P4O6. Although the molecular formula suggests the name tetraphosphorus hexoxide, the name phosphorus trioxide preceded the knowledge of the compound's molecular structure, and its usage continues today. This colorless solid is structurally related to adamantane. It is formally the anhydride of phosphorous acid, H3PO3, but cannot be obtained by the dehydration of the acid. A white solid that melts at room temperature, it is waxy, crystalline and highly toxic, with garlic odor. Preparation It is obtained by the combustion of phosphorus in a limited supply of air at low temperatures. :P4 + 3 O2 → P4O6 By-products include red phosphorus suboxide. Chemical properties Phosphorus trioxide reacts with water to form phosphorous acid, reflecting the fact that it is the anhydride of that acid. : P4O6 + 6 H2O → 4 H3PO3 It reacts with hydrogen chloride to form H3PO3 and phosphorus trichloride. : P4O6 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
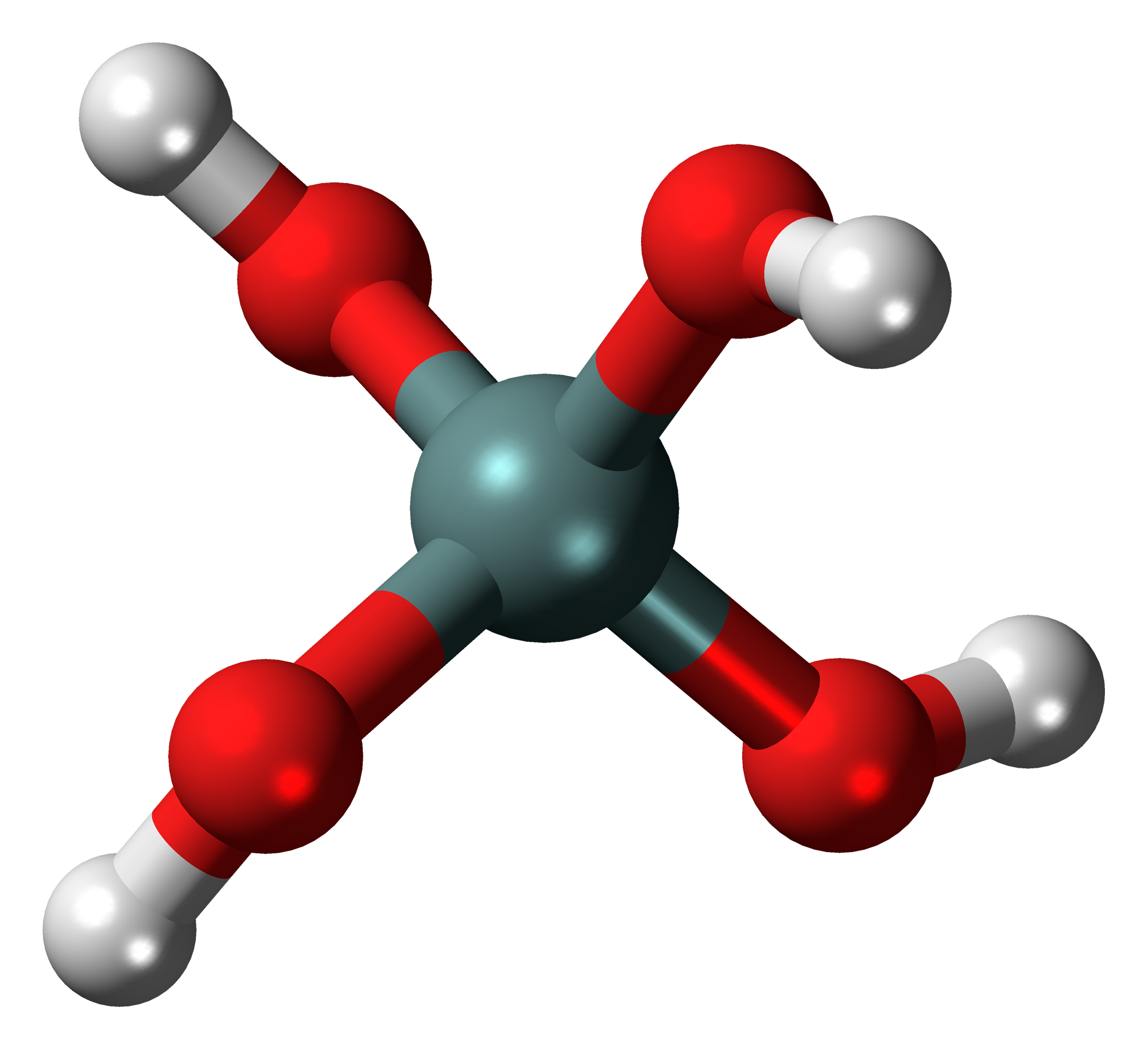
Silicic Acid
In chemistry, a silicic acid () is any chemical compound containing the element silicon attached to oxide () and hydroxyl () groups, with the general formula or, equivalently, . Orthosilicic acid is a representative example. Silicic acids are rarely observed in isolation, but are thought to exist in aqueous solutions, including seawater, and play a role in biomineralization. They are typically colorless weak acids that are sparingly soluble in water. Like the silicate anions, which are their better known conjugate bases, silicic acids are proposed to be oligomeric or polymeric. No Monomer, simple silicic acid has ever been identified, since these species are primarily of theoretical interest. Depending on the number of silicon atoms present, there are mono- and polysilicic (di-, tri-, tetrasilicic, etc.) acids. Well defined silicic acids have not been obtained in a form that has been characterized by X-ray crystallography. Examples Reactions Silicic acids can be seen as hy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
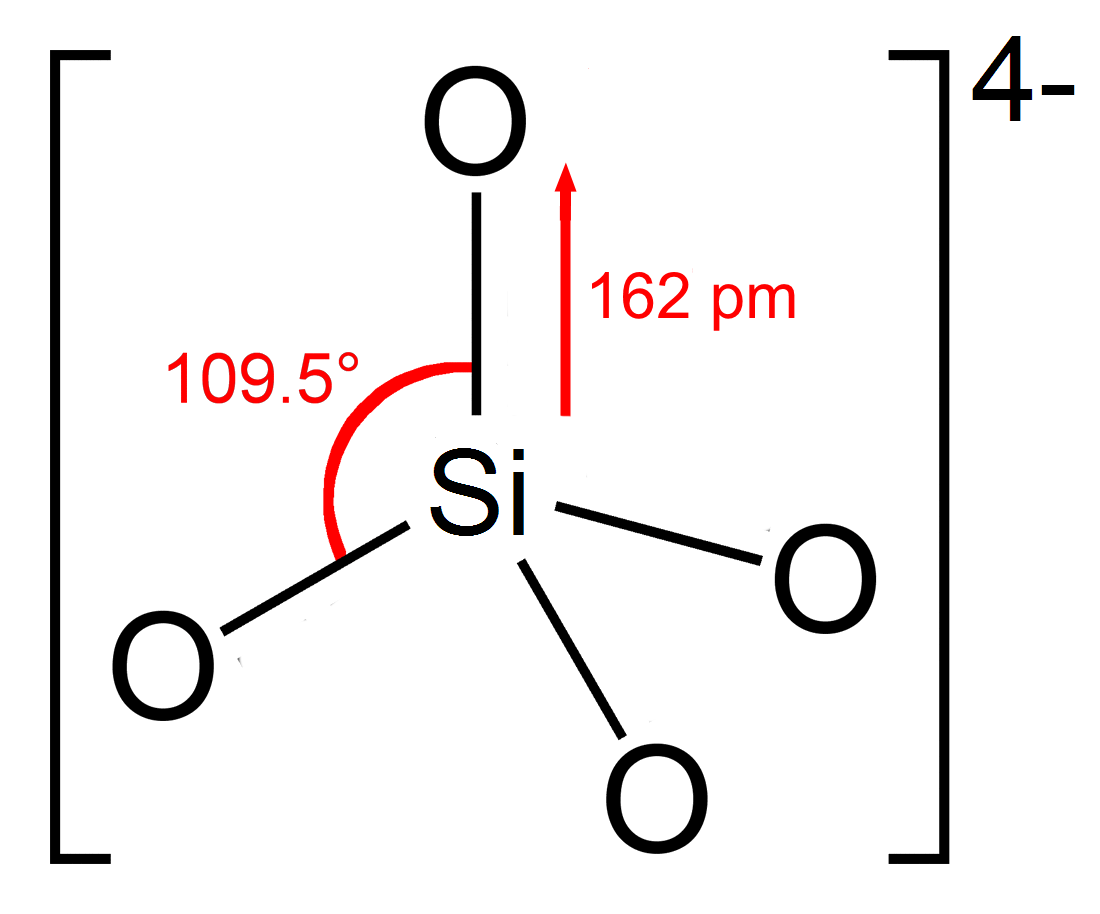
Silicate
A silicate is any member of a family of polyatomic anions consisting of silicon and oxygen, usually with the general formula , where . The family includes orthosilicate (), metasilicate (), and pyrosilicate (, ). The name is also used for any salt of such anions, such as sodium metasilicate; or any ester containing the corresponding chemical group, such as tetramethyl orthosilicate. The name "silicate" is sometimes extended to any anions containing silicon, even if they do not fit the general formula or contain other atoms besides oxygen; such as hexafluorosilicate . Most commonly, silicates are encountered as silicate minerals. For diverse manufacturing, technological, and artistic needs, silicates are versatile materials, both natural (such as granite, gravel, and garnet) and artificial (such as Portland cement, ceramics, glass, and waterglass). Structural principles In most silicates, a silicon atom occupies the center of an idealized tetrahedron whose cor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Silicon Dioxide
Silicon dioxide, also known as silica, is an oxide of silicon with the chemical formula , commonly found in nature as quartz. In many parts of the world, silica is the major constituent of sand. Silica is one of the most complex and abundant families of materials, existing as a compound of several minerals and as a synthetic product. Examples include fused quartz, fumed silica, opal, and aerogels. It is used in structural materials, microelectronics, and as components in the food and pharmaceutical industries. All forms are white or colorless, although impure samples can be colored. Silicon dioxide is a common fundamental constituent of glass. Structure In the majority of silicon dioxides, the silicon atom shows tetrahedral coordination, with four oxygen atoms surrounding a central Si atomsee 3-D Unit Cell. Thus, SiO2 forms 3-dimensional network solids in which each silicon atom is covalently bonded in a tetrahedral manner to 4 oxygen atoms. In contrast, CO2 is a li ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aluminate
In chemistry, an aluminate is a compound containing an oxyanion of aluminium, such as sodium aluminate. In the naming of inorganic compounds, it is a suffix that indicates a polyatomic anion with a central aluminium atom. Aluminate oxyanions Aluminium oxide (alumina) is amphoteric: it dissolves in both bases and acids. When dissolved in bases it forms hydroxyaluminate ions in the same way as aluminium hydroxide or aluminium salts. The hydroxyaluminate or hydrated aluminate can be precipitated and then calcined to produce anhydrous aluminates. Aluminates are often formulated as a combination of basic oxide and aluminium oxide, for example the formula of anhydrous sodium aluminate NaAlO2 would be shown as Na2O·Al2O3. A number of aluminate oxyanions are known: * The simplest is the approximately tetrahedral found in the compound Na5AlO4, * framework ions in anhydrous sodium aluminate NaAlO2 and monocalcium aluminate, CaAl2O4 made up of corner-sharing tetrahedra. * A ring ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aluminium Oxide
Aluminium oxide (or aluminium(III) oxide) is a chemical compound of aluminium and oxygen with the chemical formula . It is the most commonly occurring of several Aluminium oxide (compounds), aluminium oxides, and specifically identified as aluminium oxide. It is commonly called alumina and may also be called aloxide, aloxite, ALOX or alundum in various forms and applications and alumina is refined from bauxite. It occurs naturally in its crystalline Polymorphism (materials science), polymorphic phase (matter), phase α-Al2O3 as the mineral corundum, varieties of which form the precious gemstones ruby and sapphire,which have an alumina content approaching 100%. Al2O3 is used as feedstock to produce aluminium metal, as an abrasive owing to its hardness, and as a refractory material owing to its high melting point. Natural occurrence Corundum is the most common naturally occurring crystallinity, crystalline form of aluminium oxide. ruby, Rubies and sapphires are gem-quality forms o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Permanganic Acid
Permanganic acid (or manganic(VII) acid) is the inorganic compound with the formula H MnO4 and various hydrates. This strong oxoacid has been isolated as its dihydrate. It is the conjugate acid of permanganate salts. It is the subject of few publications and its characterization as well as its uses are very limited. Preparation and structure Permanganic acid is most often prepared by the reaction of dilute sulfuric acid with a solution of barium permanganate, the insoluble barium sulfate byproduct being removed by filtering: :Ba(MnO4)2 + H2SO4 → 2 HMnO4 + BaSO4↓ The sulfuric acid used must be dilute; reactions of permanganates with concentrated sulfuric acid yield the anhydride, manganese heptoxide. Permanganic acid has also been prepared through the reaction of hydrofluorosilicic acid with potassium permanganate, through electrolysis, and through hydrolysis of manganese heptoxide, though the last route often results in explosions. Crystalline permanganic acid has bee ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Manganese Heptoxide
Manganese(VII) oxide (manganese heptoxide) is an inorganic compound with the formula . Manganese heptoxide is a volatile liquid with an oily consistency. It is a highly reactive and powerful oxidizer that reacts explosively with nearly any organic compound. It was first described in 1860. It is the acid anhydride of permanganic acid. Properties The crystalline form of this chemical compound is dark green. The liquid is green by reflected light and red by transmitted light. It is soluble in carbon tetrachloride, and decomposes when in contact with water. Structure Its solubility properties indicate a nonpolar molecular species, which is confirmed by its structure. The molecules consist of a pair of tetrahedra that share a common vertex. The vertices are occupied by oxygen atoms and at the centers of the tetrahedra are the Mn(VII) centers. The connectivity is indicated by the formula O3Mn−O−MnO3. The terminal Mn−O distances are 1.585 Å and the bridging oxygen is 1.77 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |