|
Acer Laboratories Incorporated
ALi Corporation (formerly Acer Laboratories Incorporated or Acer Labs Inc., and commonly known as ALi) is a major designer and manufacturer of Embedded system, embedded systems Integrated circuit, integrated circuits, and a former manufacturer of personal computer integrated circuits. It is based in Taiwan, and is a subsidiary of the Acer (company), Acer group. The company was founded in 1987, its president is Teddy Lu. Part of ALi including the personal computer integrated circuits business was spun off as ULi Electronics Inc. in June 2003. ULi was acquired by Nvidia in 2006 for $52 million. Products Chipsets 80X86 Chipsets Pentium and Socket 7 Chipsets Slot 1 and Socket 370 Chipsets Slot A and Socket A Chipsets Socket 478 Chipsets Socket 754/Socket 939, 939/Socket 940, 940 Chipsets Southbridge Chips Gigabyte GA-5AX rev. 3.0 20081118.jpg, ALi M1541-based motherboard with AMD K6-2 300 MHz processor Ali M1535.jpg, ALi M1535 Southbridge (computing), southbridge c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Semiconductor Industry
The semiconductor industry is the aggregate of companies engaged in the design and fabrication of semiconductors and semiconductor devices, such as transistors and integrated circuits. Its roots can be traced to the invention of the transistor by Shockley, Brattain, and Bardeen at Bell Labs in 1948. Bell Labs licensed the technology for $25,000, and soon many companies, including Motorola (1952), Schockley Semiconductor (1955), Sylvania, Centralab, Fairchild Semiconductor and Texas Instruments were making transistors. In 1958 Jack Kilby of Texas Instruments and Robert Noyce of Fairchild independently invented the Integrated Circuit, a method of producing multiple transistors on a single "chip" of Semiconductor material. This kicked off a number of rapid advances in fabrication technology leading to the exponential growth in semiconductor device production, known as Moore's law that has persisted over the past six or so decades. The industry's annual semiconductor sale ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Socket 3
Socket 3 was a series of CPU sockets for various x86 microprocessors. It was sometimes found alongside a secondary socket designed for a math coprocessor chip, such as the 487. Socket 3 resulted from Intel's creation of lower voltage microprocessors. An upgrade to Socket 2, it rearranged the pin layout. Socket 3 is compatible with 168-pin socket CPUs. Socket 3 was a 237-pin zero insertion force (ZIF) 19×19 pin grid array (PGA) socket suitable for the 3.3 V and 5 V, 25–50 MHz Intel 486 SX, 486 DX, 486 DX2, 486 DX4, 486 OverDrive and Pentium OverDrive processors as well as AMD Am486, Am5x86 and Cyrix Cx5x86 processors. See also * List of Intel microprocessors * List of AMD microprocessors A list is a set of discrete items of information collected and set forth in some format for utility, entertainment, or other purposes. A list may be memorialized in any number of ways, including existing only in the mind of the list-maker, but ... References Soc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pentium II
The Pentium II is a brand of sixth-generation Intel x86 microprocessors based on the P6 (microarchitecture), P6 microarchitecture, introduced on May 7, 1997. It combined the ''P6'' microarchitecture seen on the Pentium Pro with the MMX (instruction set), MMX instruction set of the Pentium MMX, and is the second processor using the Pentium (brand), Pentium brand. Containing 7.5 million transistors (27.4 million in the case of the mobile Dixon with 256 Kilobyte, KB on-die CPU Cache, L2 cache), the Pentium II featured an improved version of the first ''P6''-generation core of the Pentium Pro, which contained 5.5 million transistors. However, its L2 cache subsystem was a downgrade when compared to the Pentium Pro's. In 1998, Intel stratified the Pentium II family by releasing the Pentium II-based Celeron line of processors for low-end computers and the Intel Pentium II Xeon line for servers and workstations. The Celeron was characterized by a reduced or omitted (in some cases p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Socket 370
Socket 370, also known as PGA370, is a CPU socket first used by Intel for Pentium III and Celeron processors to first complement and later replace the older Slot 1 CPU interface on personal computers. The "370" refers to the number of pin holes in the socket for CPU pins. Socket 370 was replaced by Socket 423 in 2000. Overview Socket 370 started out as a budget-oriented platform for 66 MHz Front-side bus, FSB PPGA Mendocino Celeron CPUs in late 1998, as the move to on-die L2 cache eliminated the need for a Printed circuit board, PCB design as seen on Slot 1. Socket 370 then became Intel's main desktop socket from late 1999 to late 2000 for 100/133 MHz FSB FC-PGA Coppermine (microprocessor), Coppermine Pentium IIIs. In 2001, the FC-PGA2 Pentium III#Tualatin, Tualatin Pentium III processors brought changes to the infrastructure which required dedicated Tualatin-compatible motherboards; some manufacturers would indicate this with a blue (instead of white) socket. These late socket ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Slot 1
Slot 1 refers to the physical and electrical specification for the connector used by some of Intel's microprocessors, including the Pentium Pro, Celeron, Pentium II and the Pentium III. Both single and dual processor configurations were implemented. Intel reverted to the traditional socket interface with the release of Socket 370 in 1999. General With the introduction of the Pentium II CPU, the need for greater access for testing had made the transition from socket to slot necessary. Previously with the Pentium Pro, Intel had combined processor and cache dies in the same Socket 8 package. These were connected by a full-speed bus, resulting in significant performance benefits. Unfortunately, this method required that the two components be bonded together early in the production process, before testing was possible. As a result, a single, tiny flaw in either die made it necessary to discard the entire assembly, causing low production yield and high cost. Intel subseq ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Super Socket 7
Super Socket 7, also referred to as Super 7, is a hardware-level extension of the Socket 7 Zero insertion force, ZIF socket specification for x86 processors. It was released in May 1998. Compatible motherboards and chipsets use a standard Socket 7 connection for the CPU, while adding certain features including a maximum 100 Megahertz, MHz front-side bus and support for Accelerated Graphics Port, AGP graphics cards. Super Socket 7 was used by Advanced Micro Devices, AMD AMD K6-2, K6-2 and AMD K6-III, K6-III processors, some of the final Cyrix M-II processors, some of the final Integrated Device Technology, IDT WinChip, WinChip 2 processors, and Rise Technology, Rise mP6 processors. It is backward compatibility, backward compatible with Socket 7 CPUs, meaning a Socket 7 CPU can be used with a Super Socket 7 motherboard, but a Super Socket 7 CPU cannot operate at full speed in a Socket 7 motherboard. Socket 5 CPUs are pin-compatible with Super Socket 7, but not all motherboards d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
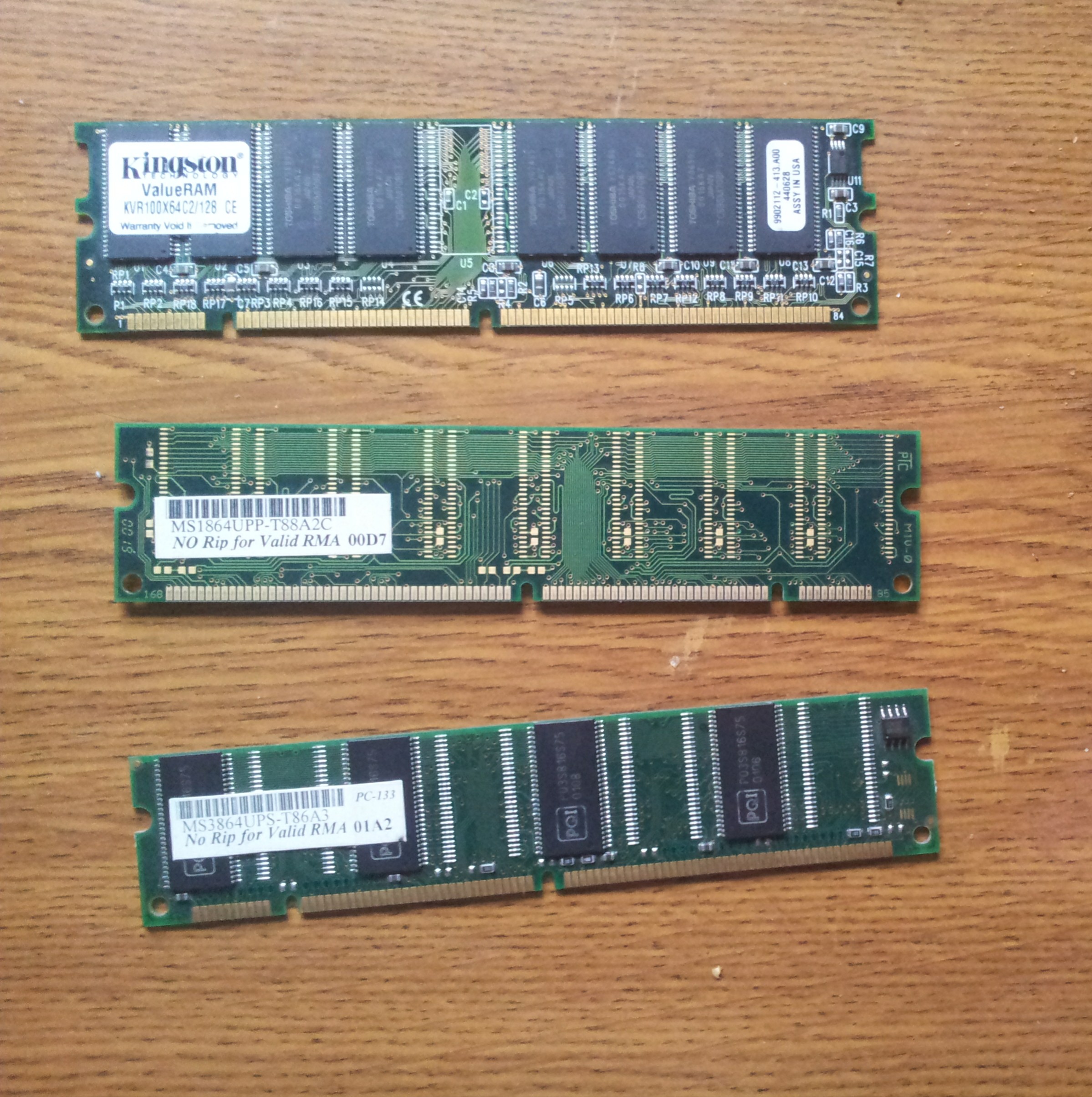
SDRAM
Synchronous dynamic random-access memory (synchronous dynamic RAM or SDRAM) is any DRAM where the operation of its external pin interface is coordinated by an externally supplied clock signal. DRAM integrated circuits (ICs) produced from the early 1970s to the early 1990s used an ''asynchronous'' interface, in which input control signals have a direct effect on internal functions delayed only by the trip across its semiconductor pathways. SDRAM has a ''synchronous'' interface, whereby changes on control inputs are recognised after a rising edge of its clock input. In SDRAM families standardized by JEDEC, the clock signal controls the stepping of an internal finite-state machine that responds to incoming commands. These commands can be pipelined to improve performance, with previously started operations completing while new commands are received. The memory is divided into several equally sized but independent sections called ''banks'', allowing the device to operate on a memor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
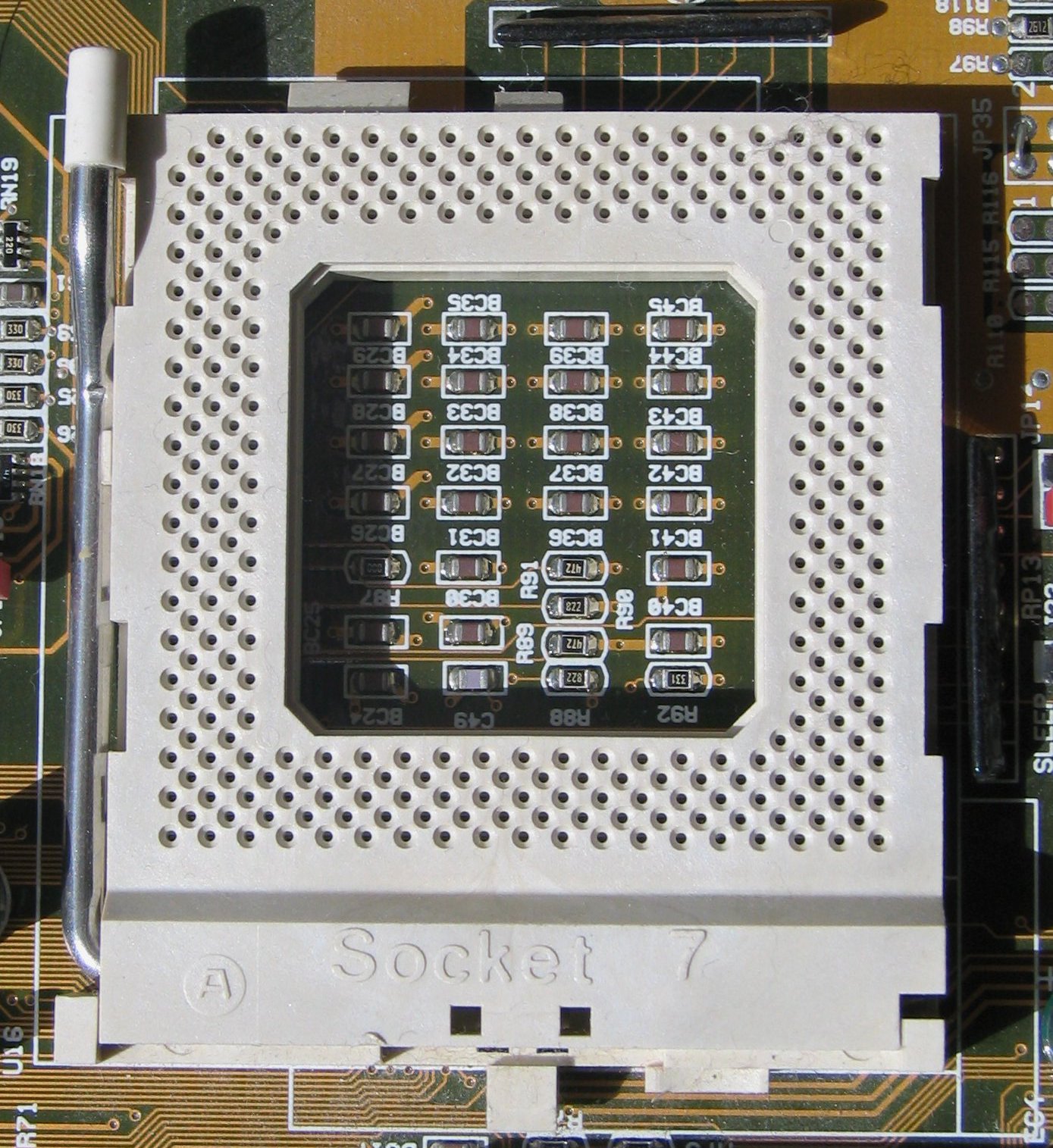
Socket 7
Socket 7 is a physical and electrical specification for an x86-style CPU socket on a personal computer motherboard. It was released in June 1995. The socket supersedes the earlier Socket 5, and accepts P5 Pentium microprocessors manufactured by Intel, as well as compatibles made by Cyrix/IBM, AMD, IDT and others. Socket 7 was the only socket that supported a wide range of CPUs from different manufacturers and a wide range of speeds. Differences between Socket 5 and Socket 7 are that Socket 7 has an extra pin and is designed to provide dual split rail voltage, as opposed to Socket 5's single voltage. However, not all motherboard manufacturers supported the dual voltage on their boards initially. Socket 7 is backwards compatible; a Socket 5 CPU can be inserted and used on a Socket 7 motherboard. Processors that used Socket 7 are the AMD K5 and K6, the Cyrix 6x86 and 6x86MX, the IDT WinChip, the Intel P5 Pentium (2.5–3.5 V, 75–200 MHz), the Pentium MMX (166–233 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Socket 5
Socket 5 was created for the second generation of Intel P5 (microarchitecture), P5 Pentium (brand), Pentium processors operating at speeds from 75 to 133 MHz as well as certain Pentium OverDrive and Pentium MMX processors with core voltage 3.3 V. It superseded the earlier Socket 4. It was released in March 1994. Consisting of 320 pins, this was the first socket to use a staggered pin grid array, or SPGA, which allowed the chip's pins to be spaced closer together than earlier sockets. Socket 5 was replaced by Socket 7 in 1995. External linksDifferences between Socket 5 and Socket 7(archived) See also * List of Intel microprocessors * List of AMD microprocessors References {{earlysock CPU sockets, Socket 005 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Socket 4
Socket 4, presented in 1993, was the first CPU socket designed for the early P5 Pentium microprocessors. Socket 4 was the only 5-volt socket for the Pentium. Socket 4 does support a special Pentium OverDrive, which allows running at 120 MHz (for the 60 MHz Pentium) or 133 MHz (for the 66 MHz Pentium). Socket 4 was superseded by the 3.3-volt-powered Socket 5 in 1994. See also * List of Intel microprocessors This generational list of Intel processors attempts to present all of Intel's processors from the 4-bit 4004 (1971) to the present high-end offerings. Concise technical data is given for each product. Latest 15th generation Core Deskto ... References {{earlysock Socket 004 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Accelerated Graphics Port
Accelerated Graphics Port (AGP) is a parallel expansion card standard, designed for attaching a video card to a computer system to assist in the acceleration of 3D computer graphics. It was originally designed as a successor to PCI-type connections for video cards. Since 2004, AGP was progressively phased out in favor of PCI Express (PCIe), which is serial, as opposed to parallel; by mid-2008, PCI Express cards dominated the market and only a few AGP models were available, with GPU manufacturers and add-in board partners eventually dropping support for the interface in favor of PCI Express. Advantages over PCI AGP is a superset of the PCI standard, designed to overcome PCI's limitations in serving the requirements of the era's high-performance graphics cards. The primary advantage of AGP is that it doesn't share the PCI bus, providing a dedicated, point-to-point pathway between the expansion slot(s) and the motherboard chipset. The direct connection also allows higher clock ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Error Detection And Correction
In information theory and coding theory with applications in computer science and telecommunications, error detection and correction (EDAC) or error control are techniques that enable reliable delivery of digital data over unreliable communication channels. Many communication channels are subject to channel noise, and thus errors may be introduced during transmission from the source to a receiver. Error detection techniques allow detecting such errors, while error correction enables reconstruction of the original data in many cases. Definitions ''Error detection'' is the detection of errors caused by noise or other impairments during transmission from the transmitter to the receiver. ''Error correction'' is the detection of errors and reconstruction of the original, error-free data. History In classical antiquity, copyists of the Hebrew Bible were paid for their work according to the number of stichs (lines of verse). As the prose books of the Bible were hardly ever w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |