|
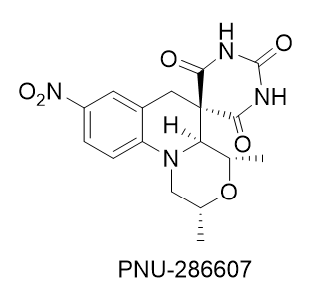
AZD0914
Zoliflodacin (development codes AZD0914 and ETX0914) is an experimental antibiotic that is being studied for the treatment of antibiotic resistant bacteria, antibiotic resistant ''Neisseria gonorrhoeae'' (gonorrhea). It has a novel mechanism of action which involves Enzyme inhibitor, inhibition of bacterial type II topoisomerases. Zoliflodacin is being drug development, developed as part of a public-private partnership between Innoviva Specialty Therapeutics and the Global Antibiotic Research & Development Partnership (GARDP), and the drug has demonstrated clinical efficacy equivalent to ceftriaxone in Phase III clinical trials. Susceptible bacteria Zoliflodacin has shown in vitro activity against the following species of bacteria: * Staphylococcus aureus * Staphylococcus pyogenes * Streptococcus agalactiae * Streptococcus pneumoniae * Haemophilus influenzae * Moraxella catarrhalis * Mycoplasma pneumoniae * Neisseria gonorrhoeae * Chlamydia trachomatis * Mycoplasma genitalium ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hepatic
The liver is a major metabolic organ (anatomy), organ exclusively found in vertebrates, which performs many essential biological Function (biology), functions such as detoxification of the organism, and the Protein biosynthesis, synthesis of various proteins and various other Biochemistry, biochemicals necessary for digestion and growth. In humans, it is located in the quadrants and regions of abdomen, right upper quadrant of the abdomen, below the thoracic diaphragm, diaphragm and mostly shielded by the lower right rib cage. Its other metabolic roles include carbohydrate metabolism, the production of a number of hormones, conversion and storage of nutrients such as glucose and glycogen, and the decomposition of red blood cells. Anatomical and medical terminology often use the prefix List of medical roots, suffixes and prefixes#H, ''hepat-'' from ἡπατο-, from the Greek language, Greek word for liver, such as hepatology, and hepatitis The liver is also an accessory digestive ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Staphylococcus Aureus
''Staphylococcus aureus'' is a Gram-positive spherically shaped bacterium, a member of the Bacillota, and is a usual member of the microbiota of the body, frequently found in the upper respiratory tract and on the skin. It is often positive for catalase and nitrate reduction and is a facultative anaerobe, meaning that it can grow without oxygen. Although ''S. aureus'' usually acts as a commensal of the human microbiota, it can also become an opportunistic pathogen, being a common cause of skin infections including abscesses, respiratory infections such as sinusitis, and food poisoning. Pathogenic strains often promote infections by producing virulence factors such as potent protein toxins, and the expression of a cell-surface protein that binds and inactivates antibodies. ''S. aureus'' is one of the leading pathogens for deaths associated with antimicrobial resistance and the emergence of antibiotic-resistant strains, such as methicillin-resistant ''S. aur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pharmacia & Upjohn
Pharmacia & Upjohn was a global pharmaceutical company formed by the merger of Sweden-based Pharmacia AB and the American company Upjohn in 1995. Today the remainder of the company is owned by Pfizer. In 1997, Pharmacia & Upjohn sold several brands to Johnson & Johnson, including Motrin and Cortaid. History Amersham In 1997, the biotechnology division of the company Pharmacia Biotech merged with Amersham Life Science with the new merged entity being known as Amersham Pharmacia Biotech. In 2001, the company was renamed Amersham Biotech. In 2002, Pharmacia sold its share of the company to Amersham plc. In 2004, Amersham Biosciences was acquired by GE Healthcare. In 1998, the nutrition division of the company was sold to Fresenius. Monsanto Monsanto acquired the pharmaceutical company G. D. Searle & Company in 1985. In 1998, Searle and the Monsanto Pharma Sector partnered with Pfizer to develop and promote celecoxib, an anti-inflammatory drug used to treat arthritis. Brande ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
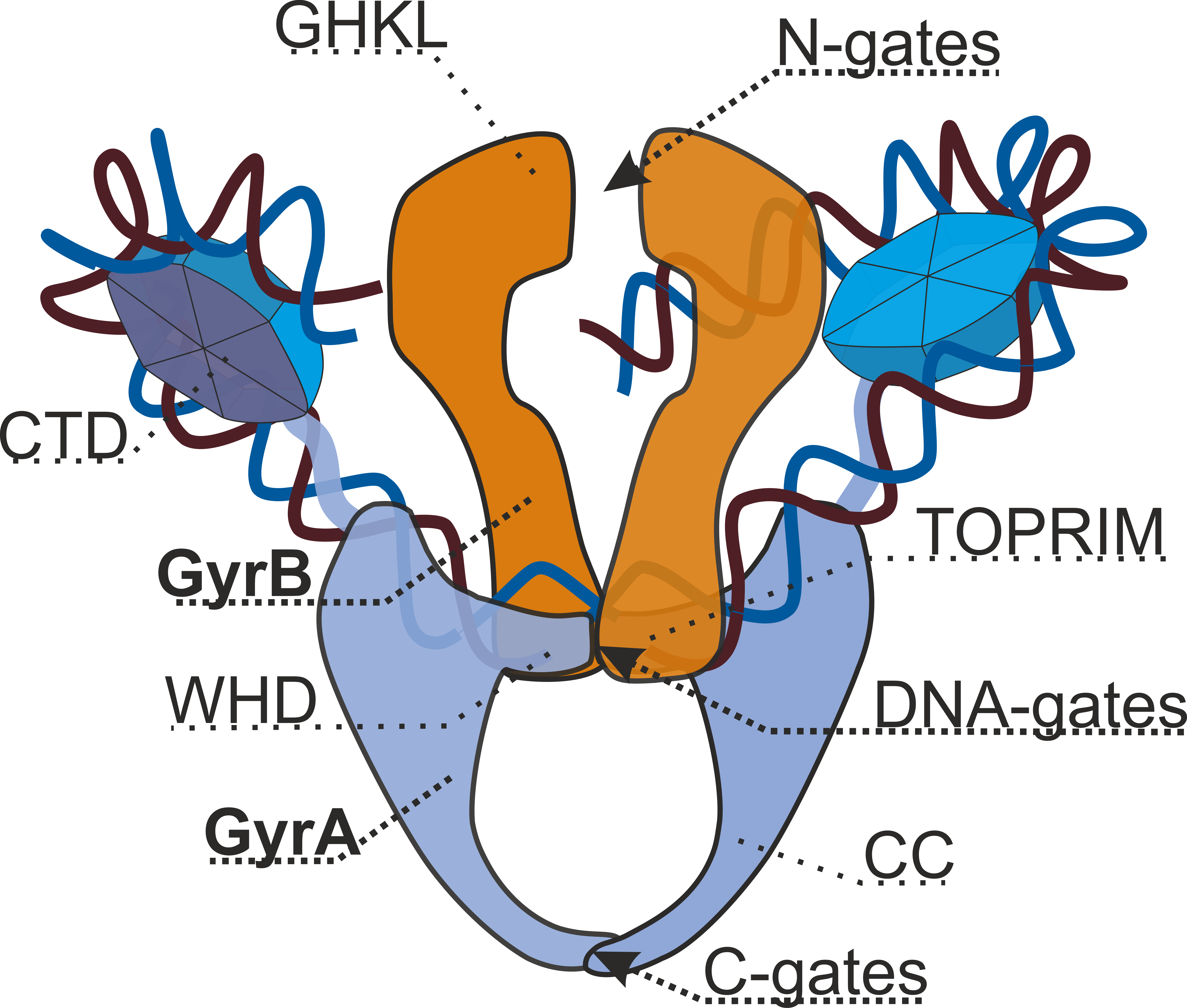
DNA Gyrase
DNA gyrase, or simply gyrase, is an enzyme within the class of topoisomerase and is a subclass of Type II topoisomerases that reduces topological strain in an ATP dependent manner while double-stranded DNA is being unwound by elongating RNA-polymerase or by helicase in front of the progressing replication fork. It is the only known enzyme to actively contribute negative supercoiling to DNA, while it also is capable of relaxing positive supercoils. It does so by looping the template to form a crossing, then cutting one of the double helices and passing the other through it before releasing the break, changing the linking number by two in each enzymatic step. This process occurs in bacteria, whose single circular DNA is cut by DNA gyrase and the two ends are then twisted around each other to form supercoils. Gyrase is also found in eukaryotic plastids: it has been found in the apicoplast of the malarial parasite ''Plasmodium falciparum'' and in chloroplasts of several plants. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gram-negative
Gram-negative bacteria are bacteria that, unlike gram-positive bacteria, do not retain the crystal violet stain used in the Gram staining method of bacterial differentiation. Their defining characteristic is that their cell envelope consists of a thin peptidoglycan cell wall sandwiched between an inner ( cytoplasmic) membrane and an outer membrane. These bacteria are found in all environments that support life on Earth. Within this category, notable species include the model organism '' Escherichia coli'', along with various pathogenic bacteria, such as '' Pseudomonas aeruginosa'', '' Chlamydia trachomatis'', and '' Yersinia pestis''. They pose significant challenges in the medical field due to their outer membrane, which acts as a protective barrier against numerous antibiotics (including penicillin), detergents that would normally damage the inner cell membrane, and the antimicrobial enzyme lysozyme produced by animals as part of their innate immune system. Furthe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fastidious Organism
A fastidious organism is any organism that has complex or particular nutritional requirements. In other words, a fastidious organism will only grow when specific nutrients are included in its medium. The more restrictive term fastidious microorganism is used in microbiology to describe microorganisms that will grow only if special nutrients are present in their culture medium. Thus fastidiousness is often practically defined as being difficult to culture, by any method yet tried. Examples An example of a fastidious bacterium is '' Neisseria gonorrhoeae'', which requires blood or hemoglobin and several amino acids and vitamins to grow.Todar, Kenneth''Neisseria gonorrhoeae'', the Gonococcus, and Gonorrhea. Lectures in Microbiology. 2009. Retrieved 2013-03-05. Other examples include ''Campylobacter'' spp. and ''Helicobacter'' spp., which are capnophilic – require elevated CO2 – among other requirements. Fastidious organisms are not inherently "weak"—they can flourish an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gram-positive
In bacteriology, gram-positive bacteria are bacteria that give a positive result in the Gram stain test, which is traditionally used to quickly classify bacteria into two broad categories according to their type of cell wall. The Gram stain is used by microbiologists to place bacteria into two main categories, gram-positive (+) and gram-negative bacteria, gram-negative (−). Gram-positive bacteria have a thick layer of peptidoglycan within the cell wall, and gram-negative bacteria have a thin layer of peptidoglycan. Gram-positive bacteria retain the crystal violet stain used in the test, resulting in a purple color when observed through an optical microscope. The thick layer of peptidoglycan in the bacterial cell wall retains the Stain (biology), stain after it has been fixed in place by iodine. During the decolorization step, the decolorizer removes crystal violet from all other cells. Conversely, gram-negative bacteria cannot retain the violet stain after the decolorization ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mycoplasma Genitalium
''Mycoplasma genitalium'' (also known as ''MG','' Mgen, or since 2018, ''Mycoplasmoides genitalium'') is a sexually transmitted, small and pathogenic bacterium that lives on the mucous epithelial cells of the urinary and genital tracts in humans. Medical reports published in 2007 and 2015 state that Mgen is becoming increasingly common. Resistance to multiple antibiotics, including the macrolide azithromycin, which until recently was the most reliable treatment, is becoming prevalent. The bacterium was first isolated from the urogenital tract of humans in 1981, and was eventually identified as a new species of '' Mycoplasma'' in 1983. It can cause negative health effects in men and women. It also increases the risk for HIV spread with higher occurrences in those previously treated with the azithromycin antibiotics. Symptoms of infection Mgen is a bacterium recognized for causing urethritis in both men and women along with cervicitis and pelvic inflammation in women ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chlamydia Trachomatis
''Chlamydia trachomatis'' () is a Gram-negative, Anaerobic organism, anaerobic bacterium responsible for Chlamydia infection, chlamydia and trachoma. ''C. trachomatis'' exists in two forms, an extracellular infectious elementary body (EB) and an intracellular non-infectious reticulate body (RB). The EB attaches to host cells and enter the cell using Effector (biology), effector proteins, where it transforms into the metabolically active RB. Inside the cell, RBs rapidly replicate before transitioning back to EBs, which are then released to infect new host cells. The earliest description of ''C. trachomatis'' was in 1907 by Stanislaus von Prowazek and Ludwig Halberstädter as a protozoan. It was later thought to be a virus due to its small size and inability to grow in laboratories. It was not until 1966 when it was discovered as a bacterium by Electron microscope, electron microscopy after its internal structures were visually observed. There are currently 18 Serotype, serovars of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mycoplasma Pneumoniae
''Mycoplasma pneumoniae'' is a species of very small-cell bacteria that lack a cell wall, in the class Mollicutes. ''M. pneumoniae'' is a human pathogen that causes the disease Mycoplasma pneumonia, a form of atypical bacterial pneumonia related to cold agglutinin disease. It is one of the smallest self-replicating organisms and its discovery traces back to 1898 when Nocard and Roux isolated a microorganism linked to cattle pneumonia. This microbe shared characteristics with pleuropneumonia-like organisms (PPLOs), which were soon linked to pneumonias and arthritis in several animals. A significant development occurred in 1944 when Monroe Eaton cultivated an agent thought responsible for human pneumonia in embryonated chicken eggs, referred to as the "Eaton agent." This agent was classified as a bacteria due to its cultivation method and because antibiotics were effective in treating the infection, questioning its viral nature. In 1961, a researcher named Robert Chanock, collabo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moraxella Catarrhalis
''Moraxella catarrhalis'' is a fastidious, nonmotile, Gram-negative, aerobic, oxidase-positive diplococcus that can cause infections of the respiratory system, middle ear, eye, central nervous system, and joints of humans. It causes the infection of the host cell by sticking to the host cell using trimeric autotransporter adhesins. Epidemiology ''Moraxella catarrhalis'' is a human pathogen with an affinity for the human upper respiratory tract and the middle ear. Other primates, such as macaques, might become infected by this bacterium. Rodents including rats, mice, and chinchillas have been used to study ''Moraxella catarrhalis'' with varying degrees of success. History The taxonomy of ''Moraxella catarrhalis'' is a topic that has caused confusion in the past. The bacteria was initially placed in the genus '' Neisseria'', before being moved into a separate genus named '' Branhamella'' in honor of Dr. Sara Branham in 1970. In 1984 this bacterium once again had a c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |