|
ASHRAE
The American Society of Heating, Refrigerating and Air-Conditioning Engineers (ASHRAE ) is an American professional association seeking to advance heating, ventilation, air conditioning and refrigeration (HVAC&R) systems design and construction. ASHRAE has over 50,000 members in more than 130 countries worldwide. ASHRAE's members comprise building services engineers, architects, mechanical contractors, building owners, equipment manufacturers' employees, and others concerned with the design and construction of HVAC&R systems in buildings. The society funds research projects, offers continuing education programs, and develops and publishes technical standards to improve building services engineering, energy efficiency, indoor air quality, and sustainable development. History ASHRAE was founded in 1894 at a meeting of engineers in New York City, formerly headquartered at 345 East 47th Street (the United Engineering Center), and has held an annual meeting since 1895. Until ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thermal Comfort
Thermal comfort is the condition of mind that expresses subjective satisfaction with the thermal environment.ANSI/ASHRAE Standard 55-2017, Thermal Environmental Conditions for Human Occupancy The human body can be viewed as a heat engine where food is the input energy. The human body will release excess heat into the environment, so the body can continue to operate. The heat transfer is proportional to temperature difference. In cold environments, the body loses more heat to the environment and in hot environments the body does not release enough heat. Both the hot and cold scenarios lead to discomfort. Maintaining this standard of thermal comfort for occupants of buildings or other enclosures is one of the important goals of HVAC ( heating, ventilation, and air conditioning) design engineers. Thermal neutrality is maintained when the heat generated by human metabolism is allowed to dissipate, thus maintaining thermal equilibrium with the surroundings. The main factors that in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ASHRAE 90
The American Society of Heating, Refrigerating and Air-Conditioning Engineers (ASHRAE ) is an American professional association seeking to advance heating, ventilation, air conditioning and refrigeration (HVAC&R) systems design and construction. ASHRAE has over 50,000 members in more than 130 countries worldwide. ASHRAE's members comprise building services engineers, architects, mechanical contractors, building owners, equipment manufacturers' employees, and others concerned with the design and construction of HVAC&R systems in buildings. The society funds research projects, offers continuing education programs, and develops and publishes technical standards to improve building services engineering, energy efficiency, indoor air quality, and sustainable development. History ASHRAE was founded in 1894 at a meeting of engineers in New York City, formerly headquartered at 345 East 47th Street (the United Engineering Center), and has held an annual meeting since 1895. Until 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ASHRAE 55
''ANSI/ASHRAE Standard 55: Thermal Environmental Conditions for Human Occupancy'' is an American National Standard published by ASHRAE that establishes the ranges of indoor environmental conditions to achieve acceptable thermal comfort for occupants of buildings. It was first published in 1966, and since 2004 has been updated every three to six years. The most recent version of the standard was published in 2023. Organization of standard The body of the standard consists of a foreword (describing changes made in the current version), eight sections and several normative appendices: # Purpose # Scope # Definitions # General requirements # Conditions that provide thermal comfort # Design compliance # Evaluation of comfort in existing buildings # References : Normative Appendix A: Methods for determining operative temperature : Normative Appendix B: Computer program for calculation of PMV/PPD :Normative Appendix C: Procedure for Calculating Comfort Impact of Solar Gain on Occupants ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ASHRAE Handbook
The ASHRAE Handbook is the four-volume flagship publication of the nonprofit technical organization ASHRAE (American Society of Heating, Refrigerating and Air-Conditioning Engineers). This Handbook is considered the most comprehensive and authoritative repository of practical knowledge on the various topics that form the field of heating, ventilation, air-conditioning, and refrigeration ( HVAC&R). The four volumes are ''Fundamentals'', ''Refrigeration'', ''HVAC Applications'' ("Applications"), and ''HVAC Systems and Equipment'' ("Systems and Equipment"). Members of ASHRAE receive the current volume, in both print and CD-ROM form, each year as a basic membership benefit. An enhanced electronic version, known as ''ASHRAE Handbook Online'' is a web-based version updated annually that contains the four latest volumes as well as extra content such as calculations, demonstration videos, and spreadsheets. The various versions of the Handbook are typically available to the public v ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
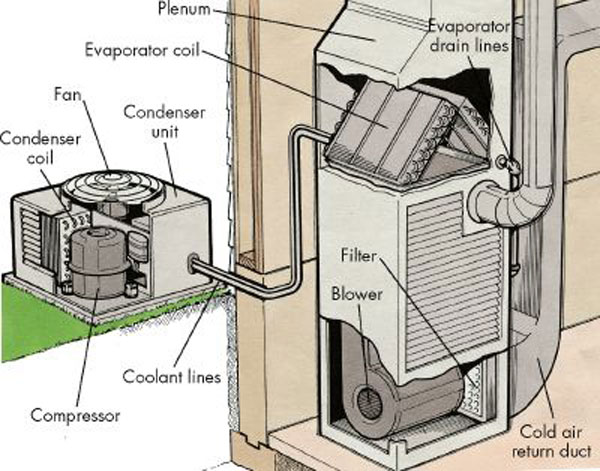
Heating, Ventilation, And Air Conditioning
Heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC ) is the use of various technologies to control the temperature, humidity, and purity of the air in an enclosed space. Its goal is to provide thermal comfort and acceptable indoor air quality. HVAC system design is a subdiscipline of mechanical engineering, based on the principles of thermodynamics, fluid mechanics, and heat transfer. "Refrigeration" is sometimes added to the field's abbreviation as HVAC&R or HVACR, or "ventilation" is dropped, as in HACR (as in the designation of HACR-rated circuit breakers). HVAC is an important part of residential structures such as single family homes, apartment buildings, hotels, and senior living facilities; medium to large industrial and office buildings such as skyscrapers and hospitals; vehicles such as cars, trains, airplanes, ships and submarines; and in marine environments, where safe and Sick building syndrome, healthy building conditions are regulated with respect to temperature and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
BACnet
BACnet is a communication protocol for building automation and control (BAC) networks. It is defined by ANSI/ASHRAE 135 and ISO 16484-5. BACnet was designed to allow communication of building automation and control systems for applications such as heating, ventilating, and air-conditioning control (HVAC), lighting control, access control, and fire detection systems and their associated equipment. The BACnet protocol provides mechanisms for computerized building automation devices to exchange information, regardless of the particular building service they perform. History Protocol and standards The development of the BACnet protocol began in June, 1987, in Nashville, Tennessee, at the inaugural meeting of the ASHRAE BACnet committee, known at that time as SPC 135P, "EMCS Message Protocol". The committee worked at reaching consensus using working groups to divide up the task of creating a standard. The working groups focused on specific areas and provided information and recommen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Refrigerant
A refrigerant is a working fluid used in the cooling, heating, or reverse cooling/heating cycles of air conditioning systems and heat pumps, where they undergo a repeated phase transition from a liquid to a gas and back again. Refrigerants are heavily regulated because of their toxicity and flammability, as well as the contribution of CFC and HCFC refrigerants to ozone depletion and the contribution of HFC refrigerants to climate change. Refrigerants are used in a direct expansion (DX) circulating system to transfer energy from one environment to another, typically from inside a building to outside or vice versa. These can be air conditioner cooling only systems, cooling & heating reverse DX systems, or heat pump and heating only DX cycles. Refrigerants are controlled substances that are classified by several international safety regulations and, depending on their classification, may only be handled by qualified engineers due to extreme pressure, temperature, flammability, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Refrigeration
Refrigeration is any of various types of cooling of a space, substance, or system to lower and/or maintain its temperature below the ambient one (while the removed heat is ejected to a place of higher temperature).IIR International Dictionary of Refrigeration, http://dictionary.iifiir.org/search.php ASHRAE Terminology, https://www.ashrae.org/technical-resources/free-resources/ashrae-terminology Refrigeration is an artificial, or human-made, cooling method. Refrigeration refers to the process by which energy, in the form of heat, is removed from a low-temperature medium and transferred to a high-temperature medium. This work of energy transfer is traditionally driven by work (physics), mechanical means (whether ice or electromechanics, electromechanical machines), but it can also be driven by heat, magnetism, electricity, laser cooling, laser, or other means. Refrigeration has many applications, including household refrigerators, industrial freezers, cryogenics, and air conditioni ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Building Services Engineering
Building services engineering (BSE), service engineering or facilities and services planning engineering is a Regulation and licensure in engineering, professional engineering discipline that strives to achieve a safe and comfortable Indoor air quality, indoor environment while minimizing the environmental impact of a building. Building services engineering can be considered a subdiscipline of ''utility engineering'', ''supply engineering'' and ''architectural engineering (building engineering)'', which are all subsets of ''civil engineering''. Building services engineering encompasses the professional disciplines ''mechanical, electrical and plumbing (MEP)'' and ''technical building services'', specifically the fields of * HVAC and building related sanitary engineering * electrical engineering including building automation and building related telecommunications engineering * mechanical engineering insofar it is building related, e.g. in the construction of elevators Building ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indoor Air Quality
Indoor air quality (IAQ) is the air quality within buildings and Nonbuilding structure, structures. Poor indoor air quality due to indoor air pollution is known to affect the health, comfort, and well-being of building occupants. It has also been linked to Sick Building Syndrome, sick building syndrome, respiratory issues, reduced productivity, and impaired learning in schools. Common pollutants of indoor air include: Passive smoking, secondhand tobacco smoke, Household air pollution, air pollutants from indoor combustion, radon, Mold health issues, molds and other allergens, carbon monoxide, volatile organic compounds, legionella and other bacteria, Asbestos, asbestos fibers, carbon dioxide, ozone and Atmospheric particulate matter, particulates. Source control, filtration, and the use of ventilation (architecture), ventilation to dilute contaminants are the primary methods for improving indoor air quality. Although ventilation is an integral component of maintaining good indoo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Streamlining Energy Efficiency For Schools Act Of 2014 (H
The Streamlining Energy Efficiency for Schools Act of 2014 () is a bill that would require the United States Department of Energy to establish a centralized clearinghouse to disseminate information on federal programs, incentives, and mechanisms for financing energy-efficient retrofits and upgrades at schools. The bill would require the DOE to collect the data from all federal agencies and store it in one place online. The bill was introduced into the United States House of Representatives during the 113th United States Congress. Provisions of the bill ''This summary is based largely on the summary provided by the Congressional Research Service, a public domain source.'' The Streamlining Energy Efficiency for Schools Act of 2014 would amend the Energy Policy and Conservation Act to direct the United States Secretary of Energy ( DOE), acting through the Office of Energy Efficiency and Renewable Energy, to act as the lead federal agency for coordinating and disseminating informa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |