|
AREsite
AREsite is a database of AU-rich elements (ARE) in vertebrate mRNA 3'-untranslated regions ( UTRs). AU-rich elements are involved in the control of gene expression. They are the most common determinant of RNA stability in mammalian cells. The most recent version of AREsite is called AREsite 2. It represents an update that allows for more detailed analysis of ARE, GRE, and URE (AU, GU, and U-rich elements). See also * AU-rich element Adenylate-uridylate-rich elements (AU-rich elements; AREs) are found in the 3' untranslated region (UTR) of many messenger RNAs (mRNAs) that code for proto- oncogenes, nuclear transcription factors, and cytokines. AREs are one of the most common d ...s References External links * http://rna.tbi.univie.ac.at/AREsite Biological databases RNA Gene expression Cis-regulatory RNA elements {{Biodatabase-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
AU-rich Element
Adenylate-uridylate-rich elements (AU-rich elements; AREs) are found in the 3' untranslated region (UTR) of many messenger RNAs (mRNAs) that code for proto- oncogenes, nuclear transcription factors, and cytokines. AREs are one of the most common determinants of RNA stability in mammalian cells. AREs are defined as a region with frequent adenine and uridine bases in a mRNA. They usually target the mRNA for rapid degradation. ARE-directed mRNA degradation is influenced by many exogenous factors, including phorbol esters, calcium ionophores, cytokines, and transcription inhibitors. These observations suggest that AREs play a critical role in the regulation of gene transcription during cell growth and differentiation, and the immune response. AREs have been divided into three classes with different sequences. The best characterised adenylate uridylate (AU)-rich Elements have a core sequence of AUUUA within U-rich sequences (for example WWWU(AUUUA)UUUW where W is A or U). This lies ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Database
In computing, a database is an organized collection of data stored and accessed electronically. Small databases can be stored on a file system, while large databases are hosted on computer clusters or cloud storage. The design of databases spans formal techniques and practical considerations, including data modeling, efficient data representation and storage, query languages, security and privacy of sensitive data, and distributed computing issues, including supporting concurrent access and fault tolerance. A database management system (DBMS) is the software that interacts with end users, applications, and the database itself to capture and analyze the data. The DBMS software additionally encompasses the core facilities provided to administer the database. The sum total of the database, the DBMS and the associated applications can be referred to as a database system. Often the term "database" is also used loosely to refer to any of the DBMS, the database system or an appli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
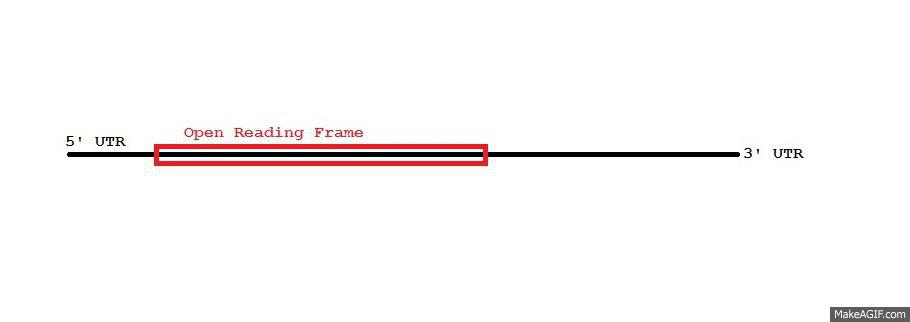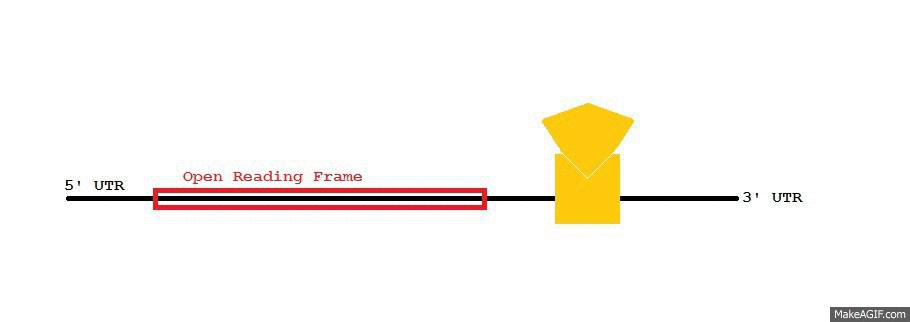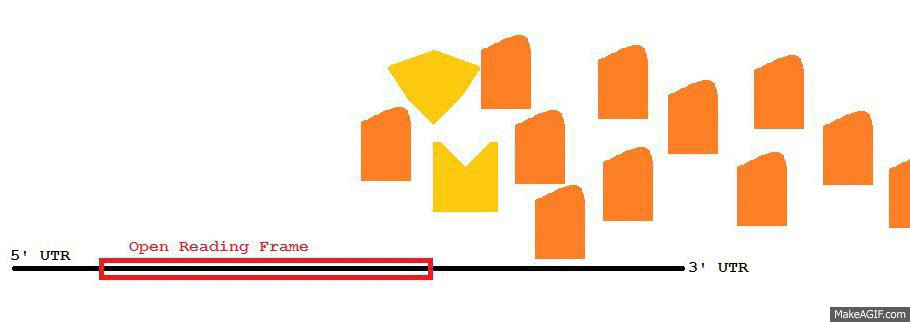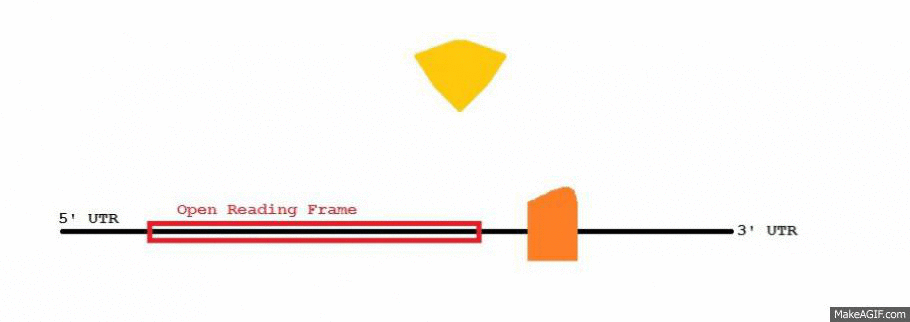
Untranslated Region
In molecular genetics, an untranslated region (or UTR) refers to either of two sections, one on each side of a coding sequence on a strand of mRNA. If it is found on the 5' side, it is called the 5' UTR (or leader sequence), or if it is found on the 3' side, it is called the 3' UTR (or trailer sequence). mRNA is RNA that carries information from DNA to the ribosome, the site of protein synthesis (translation) within a cell. The mRNA is initially transcribed from the corresponding DNA sequence and then translated into protein. However, several regions of the mRNA are usually not translated into protein, including the 5' and 3' UTRs. Although they are called untranslated regions, and do not form the protein-coding region of the gene, uORFs located within the 5' UTR can be translated into peptides. The 5' UTR is upstream from the coding sequence. Within the 5' UTR is a sequence that is recognized by the ribosome which allows the ribosome to bind and initiate translatio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biological Databases
Biological databases are libraries of biological sciences, collected from scientific experiments, published literature, high-throughput experiment technology, and computational analysis. They contain information from research areas including genomics, proteomics, metabolomics, microarray gene expression, and phylogenetics. Information contained in biological databases includes gene function, structure, localization (both cellular and chromosomal), clinical effects of mutations as well as similarities of biological sequences and structures. Biological databases can be classified by the kind of data they collect (see below). Broadly, there are molecular databases (for sequences, molecules, etc.), functional databases (for physiology, enzyme activities, phenotypes, ecology etc), taxonomic databases (for species and other taxonomic ranks), images and other media, or specimens (for museum collections etc.) Databases are important tools in assisting scientists to analyze and explain ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gene Expression
Gene expression is the process by which information from a gene is used in the synthesis of a functional gene product that enables it to produce end products, protein or non-coding RNA, and ultimately affect a phenotype, as the final effect. These products are often proteins, but in non-protein-coding genes such as transfer RNA (tRNA) and small nuclear RNA (snRNA), the product is a functional non-coding RNA. Gene expression is summarized in the central dogma of molecular biology first formulated by Francis Crick in 1958, further developed in his 1970 article, and expanded by the subsequent discoveries of reverse transcription and RNA replication. The process of gene expression is used by all known life— eukaryotes (including multicellular organisms), prokaryotes (bacteria and archaea), and utilized by viruses—to generate the macromolecular machinery for life. In genetics, gene expression is the most fundamental level at which the genotype gives rise to the phen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |