AU-rich Element on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Adenylate-uridylate-rich elements (AU-rich elements; AREs) are found in the 3' untranslated region (UTR) of many
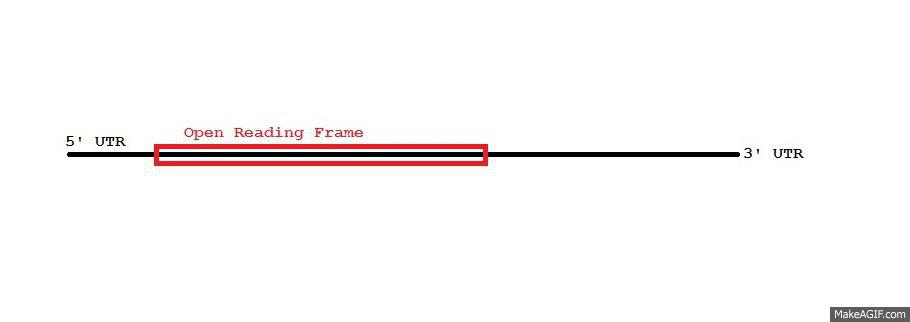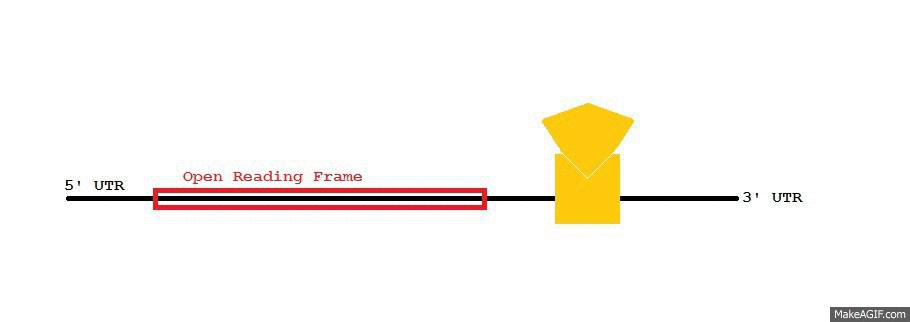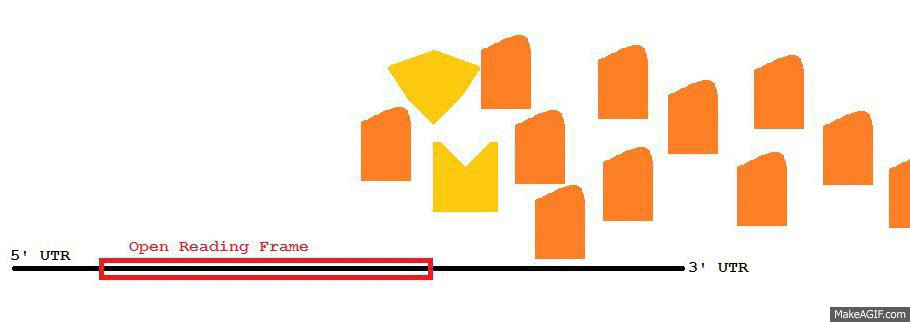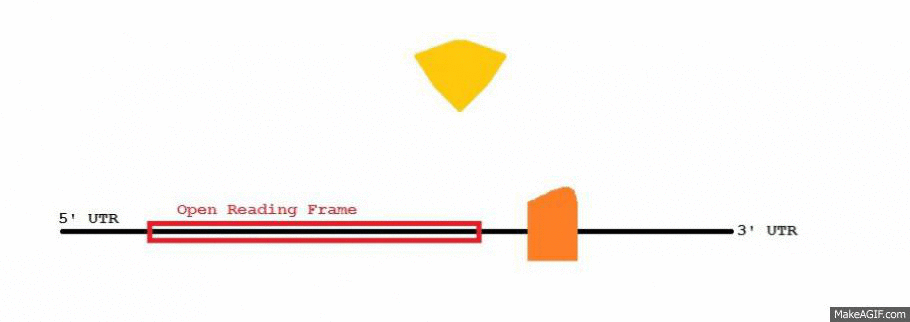 TTP's (ZFP36's) expression is rapidly induced by insulin. Immunoprecipitation experiments have shown that TTP co-precipitates with an exosome, suggesting that it helps recruit exosomes to the
TTP's (ZFP36's) expression is rapidly induced by insulin. Immunoprecipitation experiments have shown that TTP co-precipitates with an exosome, suggesting that it helps recruit exosomes to the
Review of original publication discovering AU-rich elementsPillars link to original 1986 Cell publication discovering AU-rich elementsmRNA Translational blockade by AU-rich elementsARED: AU-rich element databaseTransterm page for AU-Rich ElementAREsite: An online resource for the analysis of AREs
{{DEFAULTSORT:Au-Rich Element RNA Gene expression Cis-regulatory RNA elements
messenger RNA
In molecular biology, messenger ribonucleic acid (mRNA) is a single-stranded molecule of RNA that corresponds to the genetic sequence of a gene, and is read by a ribosome in the process of synthesizing a protein.
mRNA is created during the ...
s (mRNA
In molecular biology, messenger ribonucleic acid (mRNA) is a single-stranded molecule of RNA that corresponds to the genetic sequence of a gene, and is read by a ribosome in the process of Protein biosynthesis, synthesizing a protein.
mRNA is ...
s) that code for proto-oncogene
An oncogene is a gene that has the potential to cause cancer. In tumor cells, these genes are often mutated, or expressed at high levels.
s, nuclear transcription factor
In molecular biology, a transcription factor (TF) (or sequence-specific DNA-binding factor) is a protein that controls the rate of transcription (genetics), transcription of genetics, genetic information from DNA to messenger RNA, by binding t ...
s, and cytokine
Cytokines () are a broad and loose category of small proteins (~5–25 kDa) important in cell signaling.
Cytokines are produced by a broad range of cells, including immune cells like macrophages, B cell, B lymphocytes, T cell, T lymphocytes ...
s. AREs are one of the most common determinants of RNA stability in mammalian cells and can also modulate mRNA translation. The function of AREs was originally discovered by Shaw and Kamen in 1985, when Gray Shaw transferred the ARE from the 3' UTR of the human GM-CSF gene into the 3' UTR of a rabbit beta-globin gene. Shaw postulated that the conserved GM-CSF sequences must have a function as they were very similar to the conserved 3' UTR sequences that he had previously observed in mouse IFN-alpha genes.
A comparison of the mouse and human cDNAs encoding TNF (aka cachectin) in 1986 revealed that the TNF genes also shared an unusual conserved TTATTTAT sequence in their 3'UTRs, leading to speculation of a regulatory function that might be acting either at the DNA transcription level or at the mRNA level. After the discovery and publication by Shaw that AREs actually function at the mRNA level, ribonucleotide sequences with frequent adenine
Adenine (, ) (nucleoside#List of nucleosides and corresponding nucleobases, symbol A or Ade) is a purine nucleotide base that is found in DNA, RNA, and Adenosine triphosphate, ATP. Usually a white crystalline subtance. The shape of adenine is ...
and uridine
Uridine (symbol U or Urd) is a glycosylated pyrimidine analog containing uracil attached to a ribose ring (or more specifically, a ribofuranose) via a β-N1- glycosidic bond. The analog is one of the five standard nucleosides which make up nuc ...
bases in 3' UTR of an mRNA
In molecular biology, messenger ribonucleic acid (mRNA) is a single-stranded molecule of RNA that corresponds to the genetic sequence of a gene, and is read by a ribosome in the process of Protein biosynthesis, synthesizing a protein.
mRNA is ...
were eventually classified (see description below). AREs often target the mRNA for rapid degradation. However, ARE-directed mRNA degradation is influenced by many exogenous factors, including phorbol esters, calcium ionophores, cytokines, and transcription inhibitors. In 1989, it was reported that AREs could sometimes function to block the translation of mRNAs. Further research revealed that AREs could sometimes also function to increase translation of mRNAs by recruiting the microRNP-related proteins FXR1 and AGO2 during conditions of cell cycle arrest. In 2025 it was reported that a synthetic ARE, with a certain configuration of AUUUA repeats that enhance HuR binding, can increase protein expression up to 5-fold. This finding may be useful for many mRNA-based therapeutics. Collectively, all of these observations suggest that it is the changing dynamic conditions within a cell that dictates how the ARE of an mRNA will function.
All of these data observations strongly suggest that AREs play a critical role in the regulation of gene expression during cell growth and differentiation, as well as the immune response
An immune response is a physiological reaction which occurs within an organism in the context of inflammation for the purpose of defending against exogenous factors. These include a wide variety of different toxins, viruses, intra- and extracellula ...
. As evidence of its critical role, deletion of the AREs from the 3' UTR in either the TNF gene or GM-CSF gene in mice leads to over expression of each respective gene product, causing dramatic disease phenotypes.
AREs have been divided into three classes with different sequences. The best characterized adenylate uridylate (AU)-rich Elements have a core sequence of AUUUA within U-rich sequences (for example WWWU(AUUUA)UUUW where W is A or U). This lies within a 50–150 base sequence, repeats of the core AUUUA element are often required for function. A single AUUUA shows very little mRNA destabilizing function, whereas AUUUAUUUAUUUA shows some mRNA destabilizing function when inserted into the 3'UTR of a rabbit beta-globin gene.
A number of different protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residue (biochemistry), residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including Enzyme catalysis, catalysing metab ...
s (e.g. HuA, HuB, HuC, HuD, HuR) bind to these elements and stabilise the mRNA. The sequence AUUUAUUUA is the minimal sequence required for HuR binding and multiple AUUUA sequences can be inserted at the beginning of the 3' UTR to maximize HuR binding. Other ARE binding proteins (AUF1, TTP, BRF1, TIA-1, TIAR, and KSRP) destabilize the mRNA, miRNA
Micro ribonucleic acid (microRNA, miRNA, μRNA) are small, single-stranded, non-coding RNA molecules containing 21–23 nucleotides. Found in plants, animals, and even some viruses, miRNAs are involved in RNA silencing and post-transcri ...
s may also bind to some of them. For example, the human microRNA, miR16, contains an UAAAUAUU sequence that is complementary to the ARE sequence and appears to be required for ARE-mRNA turnover. HuD (also called ELAVL4) binds to AREs and increases the half-life of ARE-bearing mRNAs in neurons during brain development and plasticity.
AREsite—a database for ARE containing genes—has recently been developed with the aim to provide detailed bioinformatic characterization of AU-rich elements.
Classifications
*Class I ARE elements, like the c-fos gene, have dispersed AUUUA motifs within or near U-rich regions. *Class II elements, like the GM-CSF gene, have overlapping AUUUA motifs within or near U-rich regions. *Class III elements, like the c-jun gene, are a much less well-defined class—they have a U-rich region but no AUUUA repeats. No real ARE consensus sequence has been determined yet, and these categories are based neither on the same biological functions, nor on the homologous proteins.Mechanism of ARE-mediated decay
AREs are recognized by RNA binding proteins such as tristetraprolin (TTP), AUF1, and Hu Antigen R ( HuR). Although the exact mechanism is not very well understood, recent publications have attempted to propose the action of some of these proteins. AUF1, also known as hnRNP D, binds AREs through RNA recognition motifs (RRMs). AUF1 is also known to interact with the translation initiation factor eIF4G and with poly(A)-binding protein, indicating that AUF1 senses the translational status of mRNA and decays accordingly through the excision of the poly(A) tail. TTP's (ZFP36's) expression is rapidly induced by insulin. Immunoprecipitation experiments have shown that TTP co-precipitates with an exosome, suggesting that it helps recruit exosomes to the
TTP's (ZFP36's) expression is rapidly induced by insulin. Immunoprecipitation experiments have shown that TTP co-precipitates with an exosome, suggesting that it helps recruit exosomes to the mRNA
In molecular biology, messenger ribonucleic acid (mRNA) is a single-stranded molecule of RNA that corresponds to the genetic sequence of a gene, and is read by a ribosome in the process of Protein biosynthesis, synthesizing a protein.
mRNA is ...
containing AREs. Alternatively, HuR proteins have a stabilizing effect—their binding to AREs increases the half-life of mRNA
In molecular biology, messenger ribonucleic acid (mRNA) is a single-stranded molecule of RNA that corresponds to the genetic sequence of a gene, and is read by a ribosome in the process of Protein biosynthesis, synthesizing a protein.
mRNA is ...
s. Similar to other RNA-binding proteins, this class of proteins contain three RRMs, two of which are specific to ARE elements. A likely mechanism for HuR action relies on the idea that these proteins compete with other proteins that normally have a destabilizing effect on mRNA
In molecular biology, messenger ribonucleic acid (mRNA) is a single-stranded molecule of RNA that corresponds to the genetic sequence of a gene, and is read by a ribosome in the process of Protein biosynthesis, synthesizing a protein.
mRNA is ...
s. HuRs are involved in genotoxic response—they accumulate in the cytoplasm in response to UV exposure and stabilize mRNA
In molecular biology, messenger ribonucleic acid (mRNA) is a single-stranded molecule of RNA that corresponds to the genetic sequence of a gene, and is read by a ribosome in the process of Protein biosynthesis, synthesizing a protein.
mRNA is ...
s that encode proteins involved in DNA repair.
Disease
Problems with mRNA stability have been identified in viral genomes, cancer cells, and various diseases. Research shows that many of these problems arise because of faulty ARE function. Deficiency of the ZFP36 family show that ZFP36 ARE binding proteins are critical regulators of T cell homeostasis and autoimmunity. Some of these problems have been listed below: * The c-fos gene produces a transcription factor that is activated in several cancers, the ARE present in c-fos plays a role in its post-transcriptional regulation. * c-myc gene, also responsible for producing transcription factors found in several cancers, the ARE present in c-myc plays a role in its post-transcriptional regulation. * The Cox-2 gene catalyses the production of prostaglandins—it overexpresses in several cancers, and is stabilized by the binding of CUGBP2 RNA-binding protein to AREReferences
External links
Review of original publication discovering AU-rich elements
{{DEFAULTSORT:Au-Rich Element RNA Gene expression Cis-regulatory RNA elements