|
APEP FC Players
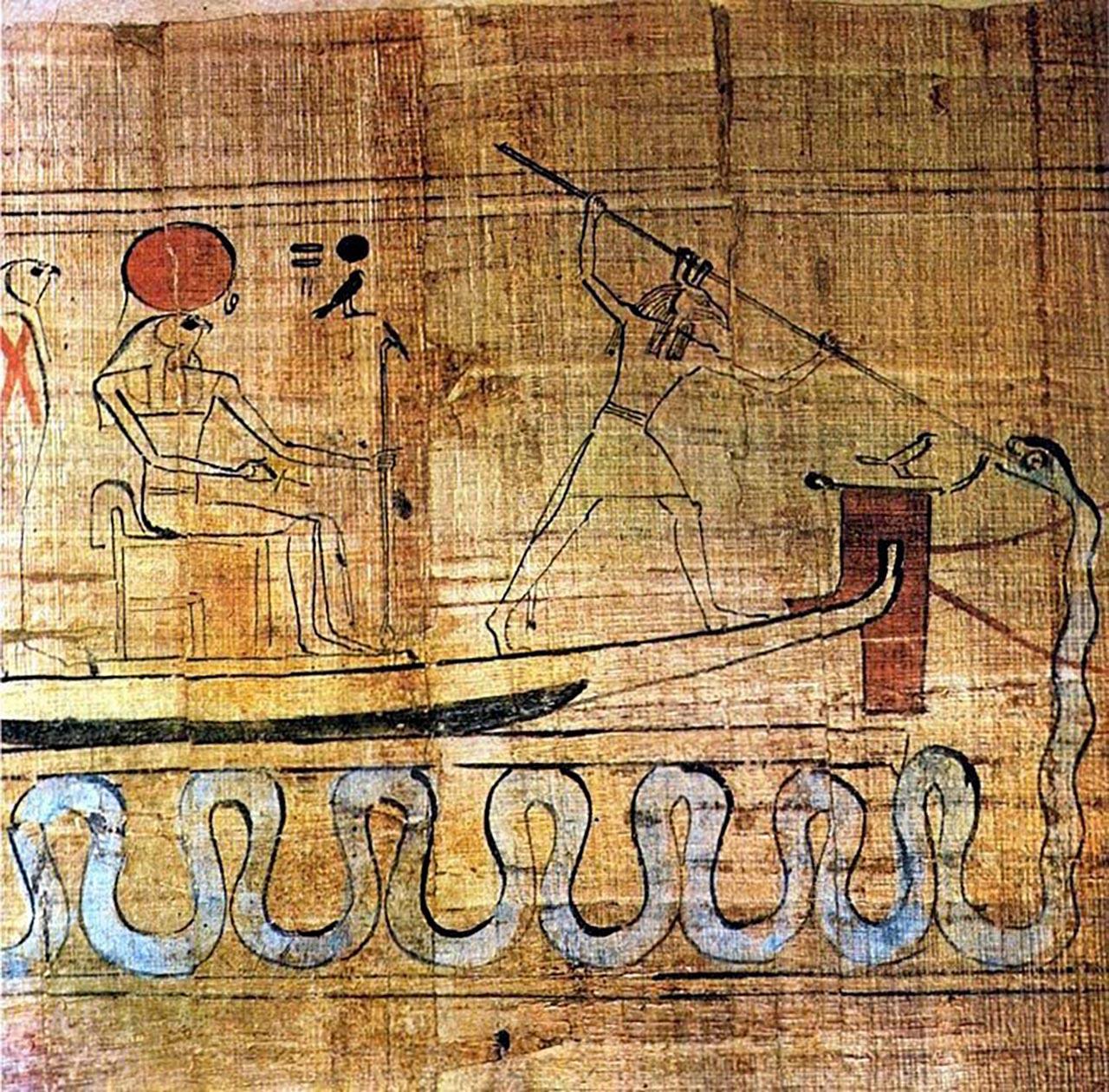
Apophis (; ), also known as Apep () or Aphoph (, ) Erman, Adolf, and Hermann Grapow, eds. 1926–1953. ''Wörterbuch der aegyptischen Sprache im Auftrage der deutschen Akademien''. 6 vols. Leipzig: J. C. Hinrichs'schen Buchhandlungen. (Reprinted Berlin: Akademie-Verlag GmbH, 1971). is the ancient Egyptian deity who embodied darkness and disorder, and was thus the opponent of light and Maat (order/truth). Ra was the bringer of light and hence the biggest opposer of Apophis. Features Because Ra was the solar deity, bringer of light, and thus the upholder of Maat, Apophis was viewed as the greatest enemy of Ra, and thus was given the title ''Enemy of Ra'', and also "the Lord of Chaos". "The Lord of Chaos" was seen as a giant snake or serpent leading to such titles as ''Serpent from the Nile'' and ''Evil Dragon''. Some elaborations said that he stretched 16 yards in length and had a head made of flint. Presented on a Naqada I (c. 4000–3550 BCE) C-ware bowl (now in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
KV16
Tomb KV16 is located in the Valley of the Kings in Egypt. It was used for the burial of Pharaoh Ramesses I of the Nineteenth dynasty of Egypt, Nineteenth Dynasty. The burial place was discovered by Giovanni Battista Belzoni, Giovanni Belzoni in October 1817. As Ramesses I ruled for less than two years, his sepulchre is rather truncated, being only twenty-nine metres long. It consists of two descending staircases, linking a sloping corridor and leading to the burial chamber. Like the tomb of Horemheb (KV57), the grave is decorated with the ''Book of Gates.'' The sarcophagus, still in place in the final chamber, is constructed of red quartzite. References * Reeves, N & Wilkinson, R.H. The Complete Valley of the Kings, 1996, Thames and Hudson, London. * Siliotti, A. Guide to the Valley of the Kings and to the Theban Necropolises and Temples, 1996, A.A. Gaddis, Cairo. Gallery File:Tumba de Ramsés I, Valle de las Reyes, Luxor, Egipto, 2022-04-03, DD 103.jpg, File:Tumba de Ramsés ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amratian Culture
The Amratian culture, also called Naqada I, was an archaeological culture of prehistoric Upper Egypt. It lasted approximately from 4000 to 3500 BC. Overview The Amratian culture is named after the archaeological site of el-Amrah, located around south of Badari in Upper Egypt. El-Amrah was the first site where this culture group was found without being mingled with the later Gerzeh culture (Naqada II). However, this period is better attested at the Nagada site, thus it also is referred to as the Naqada I culture. Black-topped pottery continued to be produced, but white cross-line pottery, a type which has been decorated with close parallel white lines being crossed by another set of close parallel white lines, begins to be produced during this time. The Amratian falls between S.D. 30 and 39 in Flinders Petrie's sequence dating system. Trade between the Amratian culture bearers in Upper Egypt and populations of Lower Egypt is attested during this time through new excavated obj ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Priest
A priest is a religious leader authorized to perform the sacred rituals of a religion, especially as a mediatory agent between humans and one or more deity, deities. They also have the authority or power to administer religious rites; in particular, rites of sacrifice to, and propitiation of, a deity or deities. Their office or position is the "priesthood", a term which also may apply to such persons collectively. A priest may have the duty to hear confessions periodically, give marriage counseling, provide prenuptial counseling, give spiritual direction, teach catechism, or visit those confined indoors, such as the sick in hospitals and nursing homes. Description According to the trifunctional hypothesis of prehistoric Proto-Indo-European society, priests have existed since the earliest of times and in the simplest societies, most likely as a result of agricultural surplus#Neolithic, agricultural surplus and consequent social stratification. The necessity to read sacred text ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ancient Egypt
Ancient Egypt () was a cradle of civilization concentrated along the lower reaches of the Nile River in Northeast Africa. It emerged from prehistoric Egypt around 3150BC (according to conventional Egyptian chronology), when Upper and Lower Egypt were amalgamated by Menes, who is believed by the majority of List of Egyptologists, Egyptologists to have been the same person as Narmer. The history of ancient Egypt unfolded as a series of stable kingdoms interspersed by the "Periodization of ancient Egypt, Intermediate Periods" of relative instability. These stable kingdoms existed in one of three periods: the Old Kingdom of Egypt, Old Kingdom of the Early Bronze Age; the Middle Kingdom of Egypt, Middle Kingdom of the Middle Bronze Age; or the New Kingdom of Egypt, New Kingdom of the Late Bronze Age. The pinnacle of ancient Egyptian power was achieved during the New Kingdom, which extended its rule to much of Nubia and a considerable portion of the Levant. After this period, Egypt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cats In Ancient Egypt
In ancient Egypt, cats were represented in social and religious scenes dating as early as 1980 BC. Several ancient Egyptian deities were depicted and sculptured with cat-like heads such as Mafdet, Bastet and Sekhmet, representing justice, fertility, and power, respectively. The deity Mut was also depicted as a cat and in the company of a cat. Cats were praised for killing venomous snakes, rodents and birds that damaged crops, and protecting the Pharaoh since at least the First Dynasty of Egypt. Skeletal remains of cats were found among funerary goods dating to the Twelfth Dynasty of Egypt, 12th Dynasty. The protective function of cats is indicated in the ''Book of the Dead'', where a cat represents Ra and the benefits of the sun for life on Earth. Cat-shaped decorations used during the New Kingdom of Egypt indicate that the domesticated cat became more popular in daily life. Cats were depicted in association with the name of Bastet. Cat cemeteries at the archaeological sites Speo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eye Of Ra
The Eye of Ra or Eye of Re, usually depicted as sun disk or right ''wedjat''-eye (paired with the Eye of Horus, left ''wedjat''-eye), is an entity in ancient Egyptian mythology that functions as an extension of the sun god Ra's power, equated with the disk of the sun, but it often behaves as an independent goddess, a feminine counterpart to Ra and a violent force that subdues his enemies. This goddess, also known with the theonym Wedjat, can be equated with several particular deities, including Hathor, Sekhmet, Bastet, Raet-Tawy, Menhit, Tefnut, and Mut. The eye goddess acts as mother, sibling, consort, and daughter of the sun god. She is his partner in the creative cycle in which he begets the renewed form of himself that is born at dawn. The eye's violent aspect defends Ra against the agents of disorder that threaten his rule. This dangerous aspect of the eye goddess is often represented by a lioness or by the uraeus, or cobra, a symbol of protection and royal authority. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Set (god)
Set (; Egyptian language#Egyptological pronunciation, Egyptological: ''Sutekh - swtẖ ~ stẖ'' or: Seth ) is a deity, god of deserts, storms, disorder, violence, and foreigners in ancient Egyptian religion. In Ancient Greek, the god's name is given as (). Set had a positive role where he accompanied Ra on his solar barque, barque to repel Apep (Apophis), the serpent of Chaos. Set had a vital role as a reconciled combatant. He was lord of the Red Land (desert), where he was the balance to Horus' role as lord of the Black Land (fertile land). In the Osiris myth, the most important Egyptian mythology, Egyptian myth, Set is portrayed as the usurper who murdered and mutilated his own brother, Osiris. Osiris's sister-wife, Isis, reassembled his corpse and resurrection, resurrected her dead brother-husband with the help of the goddess Nephthys. The resurrection lasted long enough to conceive his son and heir, Horus. Horus sought revenge upon Set, and many of the ancient Egyptian myt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Joris Borghouts
Joris Frans Borghouts (17 June 1939 – 7 September 2018) was a Dutch Egyptologist. He was Professor of Egyptology at Leiden University from 1985 to 2004. Career Borghouts was born in on 17 June 1939. He obtained his doctorate at Leiden University in 1971 with a dissertation titled: ''The magical texts of Papyrus Leiden I 348''. From 1969 to 1976 he worked as a scientific employee at the Egyptological Seminar of the University of Amsterdam. He returned to Leiden University in 1976. Borghouts succeeded Jac. J. Janssen as professor and head of the Egyptology department in 1985. Under Borghouts the department reached its maximum size. Around the year 2000 the department became threatened by budget cuts. Borghouts defended the needs of the department and stated that he would see the department become academically irrelevant otherwise. Borghouts retired in 2004. However, he remained attached to Leiden University and The Netherlands Institute for the Near East. Borghouts was elected a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coffin Texts
The Coffin Texts are a collection of ancient Egyptian funerary spells written on coffins beginning in the First Intermediate Period. They are partially derived from the earlier Pyramid Texts, reserved for royal use only, but contain substantial new material related to everyday desires, indicating a new target audience of common people. Coffin texts are dated back to 2100 BCE. Ordinary Egyptians who could afford a coffin had access to these funerary spells and the pharaoh no longer had exclusive rights to an afterlife. As the modern name of this collection of some 1,185 spells implies, they were mostly inscribed on Middle Kingdom coffins. They were also sometimes written on tomb walls, stelae, canopic chests, papyri and mummy masks. Due to the limited writing surfaces of some of these objects, the spells were often abbreviated, giving rise to long and short versions, some of which were later copied in the Book of the Dead. Content In contrast to the Pyramid Texts which focus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Duat
The Duat or Tuat (Ancient Egyptian: Hieroglyph: 𓇽 romanized: dwꜣt) is a concept in ancient Egyptian mythology involving death. It is most often seen as a realm where people go after they die. Due to linguistic shifts within Ancient Egypt, the ''Duat'' has also been called Te () and Amenthes (). What is known of the ''Duat'' derives principally from funerary texts such as the '' Book of Gates'', the ''Book of Caverns'', the '' Coffin Texts'', the '' Amduat'', and the ''Book of the Dead,'' among many other sources. It is generally known best as a dark subterranean realm that not only houses the deceased, but a variety of deities. Common deities depicted in these texts are Osiris, Anubis, Thoth, Horus, and Maat in various forms. While all of these documents involve the ''Duat'', each of them fulfilled a different purpose and depict the ''Duat'' in a variety of unique ways. Overview This realm is most often depicted as a setting for a variety of rituals and mythological e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New Kingdom Of Egypt
The New Kingdom, also called the Egyptian Empire, refers to ancient Egypt between the 16th century BC and the 11th century BC. This period of History of ancient Egypt, ancient Egyptian history covers the Eighteenth Dynasty of Egypt, Eighteenth, Nineteenth Dynasty of Egypt, Nineteenth, and Twentieth Dynasty of Egypt, Twentieth dynasties. Through radiocarbon dating, the establishment of the New Kingdom has been placed between 1570 and 1544 BC. The New Kingdom followed the Second Intermediate Period of Egypt, Second Intermediate Period and was succeeded by the Third Intermediate Period of Egypt, Third Intermediate Period. It was the most prosperous time for the Egyptians#History, Egyptian people and marked the peak of Egypt's power. In 1845, the concept of a "New Kingdom" as Periodization of ancient Egypt, one of three "golden ages" was coined by German scholar Christian Charles Josias von Bunsen; the original definition would evolve significantly throughout the 19th and 20th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Apep 2
Apophis (; ), also known as Apep () or Aphoph (, ) Erman, Adolf, and Hermann Grapow, eds. 1926–1953. ''Wörterbuch der aegyptischen Sprache im Auftrage der deutschen Akademien''. 6 vols. Leipzig: J. C. Hinrichs'schen Buchhandlungen. (Reprinted Berlin: Akademie-Verlag GmbH, 1971). is the ancient Egyptian deity who embodied darkness and disorder, and was thus the opponent of light and Maat (order/truth). Ra was the bringer of light and hence the biggest opposer of Apophis. Features Because Ra was the solar deity, bringer of light, and thus the upholder of Maat, Apophis was viewed as the greatest enemy of Ra, and thus was given the title ''Enemy of Ra'', and also "the Lord of Chaos". "The Lord of Chaos" was seen as a giant snake or serpent leading to such titles as ''Serpent from the Nile'' and ''Evil Dragon''. Some elaborations said that he stretched 16 yards in length and had a head made of flint. Presented on a Naqada I (c. 4000–3550 BCE) C-ware bowl (now in C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |