|
KV16
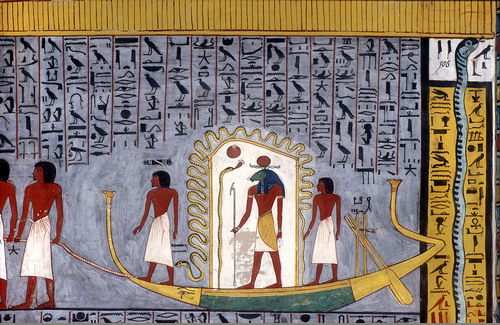
Tomb KV16 is located in the Valley of the Kings in Egypt. It was used for the burial of Pharaoh Ramesses I of the Nineteenth dynasty of Egypt, Nineteenth Dynasty. The burial place was discovered by Giovanni Battista Belzoni, Giovanni Belzoni in October 1817. As Ramesses I ruled for less than two years, his sepulchre is rather truncated, being only twenty-nine metres long. It consists of two descending staircases, linking a sloping corridor and leading to the burial chamber. Like the tomb of Horemheb (KV57), the grave is decorated with the ''Book of Gates.'' The sarcophagus, still in place in the final chamber, is constructed of red quartzite. References * Reeves, N & Wilkinson, R.H. The Complete Valley of the Kings, 1996, Thames and Hudson, London. * Siliotti, A. Guide to the Valley of the Kings and to the Theban Necropolises and Temples, 1996, A.A. Gaddis, Cairo. Gallery File:Tumba de Ramsés I, Valle de las Reyes, Luxor, Egipto, 2022-04-03, DD 103.jpg, File:Tumba de Ramsés ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ramesses I
Menpehtyre Ramesses I (or Ramses) was the founding pharaoh of ancient Egypt's Nineteenth Dynasty of Egypt, 19th Dynasty. The dates for his short reign are not completely known but the timeline of late 1290s BC, 1292–1290 BC is frequently cited as well as 1290s BC, 1295–1294 BC. While Ramesses I was the founder of the 19th Dynasty, his brief reign mainly serves to mark the transition between the reign of Horemheb, who had stabilized Egypt in the late 18th Dynasty, and the rule of the powerful pharaohs of his own dynasty, in particular his son Seti I, and grandson Ramesses II. Origins Originally called Paramessu, Ramesses I was of non-royal birth, being born into a noble military family from the Nile Delta region, perhaps near the former Hyksos capital of Avaris. He was a son of a troop commander called Seti (commander), Seti. His uncle Khaemwaset, an army officer, married Tamwadjesy, the matron of Tutankhamun's Harem of Amun, who was a relative of Amenhotep called Huy, Huy, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Book Of Gates
The Book of Gates is an ancient Egyptian funerary text dating from the New Kingdom. The ''Book of Gates'' is long and detailed, consisting of one hundred scenes. It narrates the passage of a newly deceased soul into the next world journeying with the sun god, Ra, through the underworld during the hours of the night towards his resurrection. The soul is required to pass through a series of 'gates' at each hour of the journey. Each gate is guarded by a different serpent deity that is associated with a different goddess. It is important that the deceased knows the names of each guardian. Depictions of the judgment of the dead are shown in the last three hours. The text implies that some people will pass through unharmed, but others will suffer torment in a lake of fire. At the end of Ra's journey through the underworld, he emerges anew to take his place back in the sky. History The text was not named by the Egyptians. It was named by French Egyptologist Gaston Maspero who ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Burials In The Valley Of The Kings
The following is a list of burials in the Valley of the Kings, in Thebes (modern Luxor, Egypt) and nearby areas. The numbering system was established by John Gardner Wilkinson in 1821. Wilkinson numbered the 21 tombs known to him (some of which had been open since antiquity) according to their location, starting at the entrance to the valley and then moving south and west. Tombs that have been discovered since then have been allocated a sequential KV number (those in the Western Valley are known by the WV equivalent) in the order of their discovery. Since the mid 20th century, Egyptologists have used the acronym An acronym is a type of abbreviation consisting of a phrase whose only pronounced elements are the initial letters or initial sounds of words inside that phrase. Acronyms are often spelled with the initial Letter (alphabet), letter of each wor ... "KV" (standing for Kings' Valley) to designate tombs located in the Valley of the Kings. Additionally, the acronym "WV ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Valley Of The Kings
The Valley of the Kings, also known as the Valley of the Gates of the Kings, is an area in Egypt where, for a period of nearly 500 years from the Eighteenth Dynasty to the Twentieth Dynasty, rock-cut tombs were excavated for pharaohs and powerful nobles under the New Kingdom of ancient Egypt. It is a wadi sitting on the west bank of the Nile, opposite Thebes (modern-day Luxor) and within the heart of the Theban Necropolis.Siliotti (1997), p. 13 There are two main sections: the East Valley, where the majority of the royal tombs are situated; and the West Valley, otherwise known as the Valley of the Monkeys. With the 2005 discovery of a new chamber and the 2008 discovery of two further tomb entrances, the Valley of the Kings is known to contain 65 tombs and chambers, ranging in size from the simple pit that is KV54 to the complex tomb that is KV5, which alone has over 120 chambers for the sons of Ramesses II. It was the principal burial place for the New Kingdom's major roya ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nineteenth Dynasty Of Egypt
The Nineteenth Dynasty of Egypt (notated Dynasty XIX), also known as the Ramessid dynasty, is classified as the second Dynasty of the Ancient Egyptian New Kingdom of Egypt, New Kingdom period, lasting from 1292 BC to 1189 BC. The 19th Dynasty and the 20th Dynasty furthermore together constitute an era known as the ''Ramesside period''. This Dynasty was founded by Vizier (Ancient Egypt), Vizier Ramesses I, whom Pharaoh Horemheb chose as his successor to the throne. History Background The warrior kings of the early Eighteenth Dynasty of Egypt, 18th Dynasty had encountered only little resistance from neighbouring kingdoms, allowing them to expand their realm of influence easily, but the international situation had changed radically towards the end of the dynasty. The Hittites had gradually extended their influence into Syria and Canaan to become a major power in international politics, a power that both Seti I and his son Ramesses II would confront in the future. 19th Dynasty ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Giovanni Battista Belzoni
Giovanni Battista Belzoni (; 5 November 1778 – 3 December 1823), sometimes known as The Great Belzoni, was a prolific Italian explorer and pioneer archaeologist of Egyptian antiquities. He is known for his removal to England of the seven-tonne bust of Ramesses II, the clearing of sand from the entrance of the great temple at Abu Simbel, the discovery and documentation of the tomb of Seti I (still sometimes known as "Belzoni's Tomb"), including the sarcophagus of Seti I, and the first to penetrate into the Pyramid of Khafre, the second pyramid of the Giza complex. Early life Belzoni was born in Padua. His father was a barber who sired fourteen children. His family was from Rome and when Belzoni was 16 he went to work there, saying that he studied hydraulics. He intended on taking monastic vows, but in 1798 the occupation of the city by French troops drove him from Rome and changed his proposed career. In 1800 he moved to the Batavian Republic (now Netherlands) where he ear ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Egypt
Egypt ( , ), officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, is a country spanning the Northeast Africa, northeast corner of Africa and Western Asia, southwest corner of Asia via the Sinai Peninsula. It is bordered by the Mediterranean Sea to northern coast of Egypt, the north, the Gaza Strip of Palestine and Israel to Egypt–Israel barrier, the northeast, the Red Sea to the east, Sudan to Egypt–Sudan border, the south, and Libya to Egypt–Libya border, the west; the Gulf of Aqaba in the northeast separates Egypt from Jordan and Saudi Arabia. Cairo is the capital, list of cities and towns in Egypt, largest city, and leading cultural center, while Alexandria is the second-largest city and an important hub of industry and tourism. With over 109 million inhabitants, Egypt is the List of African countries by population, third-most populous country in Africa and List of countries and dependencies by population, 15th-most populated in the world. Egypt has one of the longest histories o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pharaoh
Pharaoh (, ; Egyptian language, Egyptian: ''wikt:pr ꜥꜣ, pr ꜥꜣ''; Meroitic language, Meroitic: 𐦲𐦤𐦧, ; Biblical Hebrew: ''Parʿō'') was the title of the monarch of ancient Egypt from the First Dynasty of Egypt, First Dynasty () until the Roman Egypt, annexation of Egypt by the Roman Republic in 30 BCE. However, the equivalent Egyptian language, Egyptian word for "king" was the term used most frequently by the ancient Egyptians for their monarchs, regardless of gender, through the middle of the Eighteenth Dynasty during the New Kingdom of Egypt, New Kingdom. The earliest confirmed instances of "pharaoh" used contemporaneously for a ruler were a letter to Akhenaten (reigned –1336 BCE) or an inscription possibly referring to Thutmose III (–1425 BCE). In the early dynasties, ancient Egyptian kings had as many as ancient Egyptian royal titulary, three titles: the Horus name, Horus, the prenomen (Ancient Egypt), Sedge and Bee (wikt:nswt-bjtj, ''nswt-bjtj''), and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Horemheb
Horemheb, also spelled Horemhab, Haremheb or Haremhab (, meaning "Horus is in Jubilation"), was the last pharaoh of the Eighteenth Dynasty of Egypt, 18th Dynasty of Egypt (1550–1292 BC). He ruled for at least 14 years between 1319 BC and 1292 BC. He had no relation to the preceding royal family other than by marriage to Mutnedjmet, who is thought (though disputed) to have been the daughter of his predecessor, Ay (pharaoh), Ay; he is believed to have been of common birth. Before he became pharaoh Horemheb was the commander-in-chief of the Military of ancient Egypt, army under the reigns of Tutankhamun and Ay (pharaoh), Ay. After his accession to the throne, he reformed the Egyptian state and it was during his reign that official action against the preceding Amarna rulers began, which is why he is considered the ruler who restabilized his country after the troublesome and divisive Amarna Period. Horemheb demolished monuments of Akhenaten, reusing the rubble in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
KV57
Tomb KV57 is the royal tomb of Horemheb, the last pharaoh of the Eighteenth Dynasty of Egypt, Eighteenth Dynasty and is located in the Valley of the Kings, Egypt. The tomb was located by Edward R. Ayrton, Edward Ayrton in February 1908 for Theodore M. Davis, Theodore Davis. Due to its location in the valley floor, the tomb was filled with debris that had washed down during occasional flash-flooding. The tomb is markedly different from previous Eighteenth Dynasty royal tombs as it has a straightened axis, and has painted reliefs instead of murals; the Book of Gates also appears for the first time. The king's red granite sarcophagus was found with its lid broken, though otherwise intact. The tomb contained the remains of several burials, none of them conclusively belonging to Horemheb. Layout The tomb consists of a descending entrance stair, a sloping passageway leading to another descending stair, and another passageway that ends in a well shaft. Beyond the well chamber is the fir ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quartzite
Quartzite is a hard, non- foliated metamorphic rock that was originally pure quartz sandstone.Essentials of Geology, 3rd Edition, Stephen Marshak, p 182 Sandstone is converted into quartzite through heating and pressure usually related to tectonic compression within orogenic belts, and hence quartzite is a metasandstone. Pure quartzite is usually white to grey, though quartzites often occur in various shades of pink and red due to varying amounts of hematite. Other colors, such as yellow, green, blue and orange, are due to other minerals. The term ''quartzite'' is also sometimes used for very hard but unmetamorphosed sandstones that are composed of quartz grains thoroughly cemented with additional quartz. Such sedimentary rock has come to be described as orthoquartzite to distinguish it from metamorphic quartzite, which is sometimes called metaquartzite to emphasize its metamorphic origins. Quartzite is very resistant to chemical weathering and often forms ridges and resist ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Osiris
Osiris (, from Egyptian ''wikt:wsjr, wsjr'') was the ancient Egyptian deities, god of fertility, agriculture, the Ancient Egyptian religion#Afterlife, afterlife, the dead, resurrection, life, and vegetation in ancient Egyptian religion. He was classically depicted as a green-skinned deity with a Pharaoh, pharaoh's beard, partially mummy-wrapped at the legs, wearing a distinctive atef crown and holding a symbolic crook and flail. He was one of the first to be associated with the mummy wrap. When his brother Set (deity), Set cut him to pieces after killing him, with her sister Nephthys, Osiris' sister-wife, Isis, searched Egypt to find each part of Osiris. She collected all but one – Osiris’s genitalia. She then wrapped his body up, enabling him to return to life. Osiris was widely worshipped until the decline of ancient Egyptian religion during the Christianization of the Roman Empire, rise of Christianity in the Roman Empire. Osiris was at times considered the eldest son of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |