|
ANKRD2
Ankyrin Repeat, PEST sequence and Proline-rich region (ARPP), also known as Ankyrin repeat domain-containing protein 2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''ANKRD2'' gene. ARPP is a member of the muscle ankyrin repeat proteins (MARP), which also includes CARP and DARP, and is highly expressed in cardiac and skeletal muscle and in other tissues. Expression of ARPP has been shown to be altered in patients with dilated cardiomyopathy and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. A role for Ankrd2 in tumor progression and metastases spreading has also been described. Structure Two isoforms of ARPP have been documented; a 39.8 kDa protein isoform composed of 360 amino acids and a 36.2 kDa protein isoform composed of 327 amino acids. ''ANKRD2'' has nine exons, four of which encode ankyrin repeats in the middle region of the protein, a PEST-like and Lysine-rich sequence in the N-terminal region, and a Proline-rich sequence containing consensus sequences for phosphorylation in the C-term ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ANKRD23
Ankyrin repeat domain-containing protein 23 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''ANKRD23'' gene. This gene is a member of the muscle ankyrin repeat protein (MARP) family and encodes a protein with four tandem ankyrin-like repeats. The protein is localized to the nucleus, functioning as a transcriptional regulator. Expression of this protein is induced during recovery following starvation. Interactions ANKRD23 has been shown to interact with Titin and MYPN Myopalladin is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''MYPN'' gene. Myopalladin is a muscle protein responsible for tethering proteins at the Z-disc and for communicating between the sarcomere and the nucleus in cardiac and skeletal muscle .... References External links * Further reading * * * * * * * {{refend ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ANKRD1
Ankyrin repeat domain-containing protein 1, or Cardiac ankyrin repeat protein is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''ANKRD1'' gene also known as ''CARP''. CARP is highly expressed in cardiac and skeletal muscle, and is a transcription factor involved in development and under conditions of stress. CARP has been implicated in several diseases, including dilated cardiomyopathy, hypertrophic cardiomyopathy, and several skeletal muscle myopathies. Structure Human cardiac ankyrin repeat protein is a 36.2kDa protein composed of 319 amino acids., though in cardiomyocytes, CARP can exist as multiple alternatively spliced forms. CARP contains five tandem ankyrin repeats. Studies have shown that CARP can homodimerize. Studies have also shown that CARP is N-terminally, post-translationally cleaved by calpain-3 in skeletal muscle, suggesting alternate bioactive forms of CARP exist. CARP has been localized to nuclei and Z-discs in animal and human muscle cells, and at intercalate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Titin
Titin (contraction for Titan protein) (also called connectin) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''TTN'' gene. Titin is a giant protein, greater than 1 µm in length, that functions as a molecular spring that is responsible for the passive elasticity of muscle. It comprises 244 individually folded protein domains connected by unstructured peptide sequences. These domains unfold when the protein is stretched and refold when the tension is removed. Titin is important in the contraction of striated muscle tissues. It connects the Z line to the M line in the sarcomere. The protein contributes to force transmission at the Z line and resting tension in the I band region. It limits the range of motion of the sarcomere in tension, thus contributing to the passive stiffness of muscle. Variations in the sequence of titin between different types of striated muscle (cardiac or skeletal) have been correlated with differences in the mechanical properties of these muscles. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
TP53
p53, also known as Tumor protein P53, cellular tumor antigen p53 (UniProt name), or transformation-related protein 53 (TRP53) is a regulatory protein that is often mutated in human cancers. The p53 proteins (originally thought to be, and often spoken of as, a single protein) are crucial in vertebrates, where they prevent cancer formation. As such, p53 has been described as "the guardian of the genome" because of its role in conserving stability by preventing genome mutation. Hence ''TP53'' ''italics'' are used to denote the ''TP53'' gene name and distinguish it from the protein it encodes is classified as a tumor suppressor gene. The name p53 was given in 1979 describing the apparent molecular mass; SDS-PAGE analysis indicates that it is a 53- kilodalton (kDa) protein. However, the actual mass of the full-length p53 protein (p53α) based on the sum of masses of the amino acid residues is only 43.7 kDa. This difference is due to the high number of proline residues in the protein, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Promyelocytic Leukemia Protein
Promyelocytic leukemia protein (PML) (also known as MYL, RNF71, PP8675 or TRIM19) is the protein product of the PML gene. PML protein is a tumor suppressor protein required for the assembly of a number of nuclear structures, called PML-nuclear bodies, which form amongst the chromatin of the cell nucleus. These nuclear bodies are present in mammalian nuclei, at about 1 to 30 per cell nucleus. PML-NBs are known to have a number of regulatory cellular functions, including involvement in programmed cell death, genome stability, antiviral effects and controlling cell division. PML mutation or loss, and the subsequent dysregulation of these processes, has been implicated in a variety of cancers. History PML was poorly understood until described in the findings of Grignani ''et al'' in their 1996 study of patients with acute promyelocytic leukemia (APL). It was found that the karyotype of 90% of APL patients included a reciprocal translocation, resulting in the fusion of the Retinoic A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brain
The brain is an organ that serves as the center of the nervous system in all vertebrate and most invertebrate animals. It consists of nervous tissue and is typically located in the head ( cephalization), usually near organs for special senses such as vision, hearing and olfaction. Being the most specialized organ, it is responsible for receiving information from the sensory nervous system, processing those information (thought, cognition, and intelligence) and the coordination of motor control (muscle activity and endocrine system). While invertebrate brains arise from paired segmental ganglia (each of which is only responsible for the respective body segment) of the ventral nerve cord, vertebrate brains develop axially from the midline dorsal nerve cord as a vesicular enlargement at the rostral end of the neural tube, with centralized control over all body segments. All vertebrate brains can be embryonically divided into three parts: the forebrain (prosencep ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Myoblast
Myogenesis is the formation of skeletal muscular tissue, particularly during embryonic development. Muscle fibers generally form through the fusion of precursor myoblasts into multinucleated fibers called ''myotubes''. In the early development of an embryo, myoblasts can either proliferate, or differentiate into a myotube. What controls this choice in vivo is generally unclear. If placed in cell culture, most myoblasts will proliferate if enough fibroblast growth factor (FGF) or another growth factor is present in the medium surrounding the cells. When the growth factor runs out, the myoblasts cease division and undergo terminal differentiation into myotubes. Myoblast differentiation proceeds in stages. The first stage, involves cell cycle exit and the commencement of expression of certain genes. The second stage of differentiation involves the alignment of the myoblasts with one another. Studies have shown that even rat and chick myoblasts can recognise and align with one a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
C2C12
C2C12 is an immortalized mouse myoblast cell line. The C2C12 cell line is a subclone of myoblasts that were originally obtained by Yaffe and Saxel at the Weizmann Institute of Science in Israel in 1977. Developed for '' in vitro'' studies of myoblasts isolated from the complex interactions of ''in vivo'' conditions, C2C12 cells are useful in biomedical research. These cells are capable of rapid proliferation under high serum conditions and differentiation into myotubes under low serum conditions. Mononucleated myoblasts can later fuse to form multinucleated myotubes under low serum conditions or starvation, leading to the precursors of contractile skeletal muscle cells in the process of myogenesis. C2C12 cells are used to study the differentiation of myoblasts, osteoblasts, and myogenesis, to express various target proteins, and to explore mechanistic biochemical pathways. Morphology Wild-type C2C12 cells have a radial branching morphology consisting of long fibers extendi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Desmin
Desmin is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''DES'' gene. Desmin is a muscle-specific, type III intermediate filament that integrates the sarcolemma, Z disk, and nuclear membrane in sarcomeres and regulates sarcomere architecture. Structure Desmin is a 53.5 kD protein composed of 470 amino acids, encoded by the human ''DES'' gene located on the long arm of chromosome 2. There are three major domains to the desmin protein: a conserved alpha helix rod, a variable non alpha helix head, and a carboxy-terminal tail. Desmin, as all intermediate filaments, shows no polarity when assembled. The rod domain consists of 308 amino acids with parallel alpha helical coiled coil dimers and three linkers to disrupt it. The rod domain connects to the head domain. The head domain 84 amino acids with many arginine, serine, and aromatic residues is important in filament assembly and dimer-dimer interactions. The tail domain is responsible for the integration of filaments and interacti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Actin
Actin is a protein family, family of Globular protein, globular multi-functional proteins that form microfilaments in the cytoskeleton, and the thin filaments in myofibril, muscle fibrils. It is found in essentially all Eukaryote, eukaryotic cells, where it may be present at a concentration of over 100 micromolar, μM; its mass is roughly 42 kDa, with a diameter of 4 to 7 nm. An actin protein is the monomeric Protein subunit, subunit of two types of filaments in cells: microfilaments, one of the three major components of the cytoskeleton, and thin filaments, part of the Muscle contraction, contractile apparatus in muscle cells. It can be present as either a free monomer called G-actin (globular) or as part of a linear polymer microfilament called F-actin (filamentous), both of which are essential for such important cellular functions as the Motility, mobility and contraction of cell (biology), cells during cell division. Actin participates in many important cellular pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rhabdomyosarcoma
Rhabdomyosarcoma (RMS) is a highly aggressive form of cancer that develops from mesenchymal cells that have failed to fully differentiate into myocytes of skeletal muscle. Cells of the tumor are identified as rhabdomyoblasts. There are four subtypes – embryonal rhabdomyosarcoma, alveolar rhabdomyosarcoma, pleomorphic rhabdomyosarcoma, and spindle cell/sclerosing rhabdomyosarcoma. Embryonal, and alveolar are the main groups, and these types are the most common soft tissue sarcomas of childhood and adolescence. The pleomorphic type is usually found in adults. It is generally considered to be a disease of childhood, as the vast majority of cases occur in those below the age of 18. It is commonly described as one of the small-blue-round-cell tumors of childhood due to its appearance on an H&E stain. Despite being relatively rare, it accounts for approximately 40% of all recorded soft tissue sarcomas. RMS can occur in any soft tissue site in the body, but is primarily found in th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
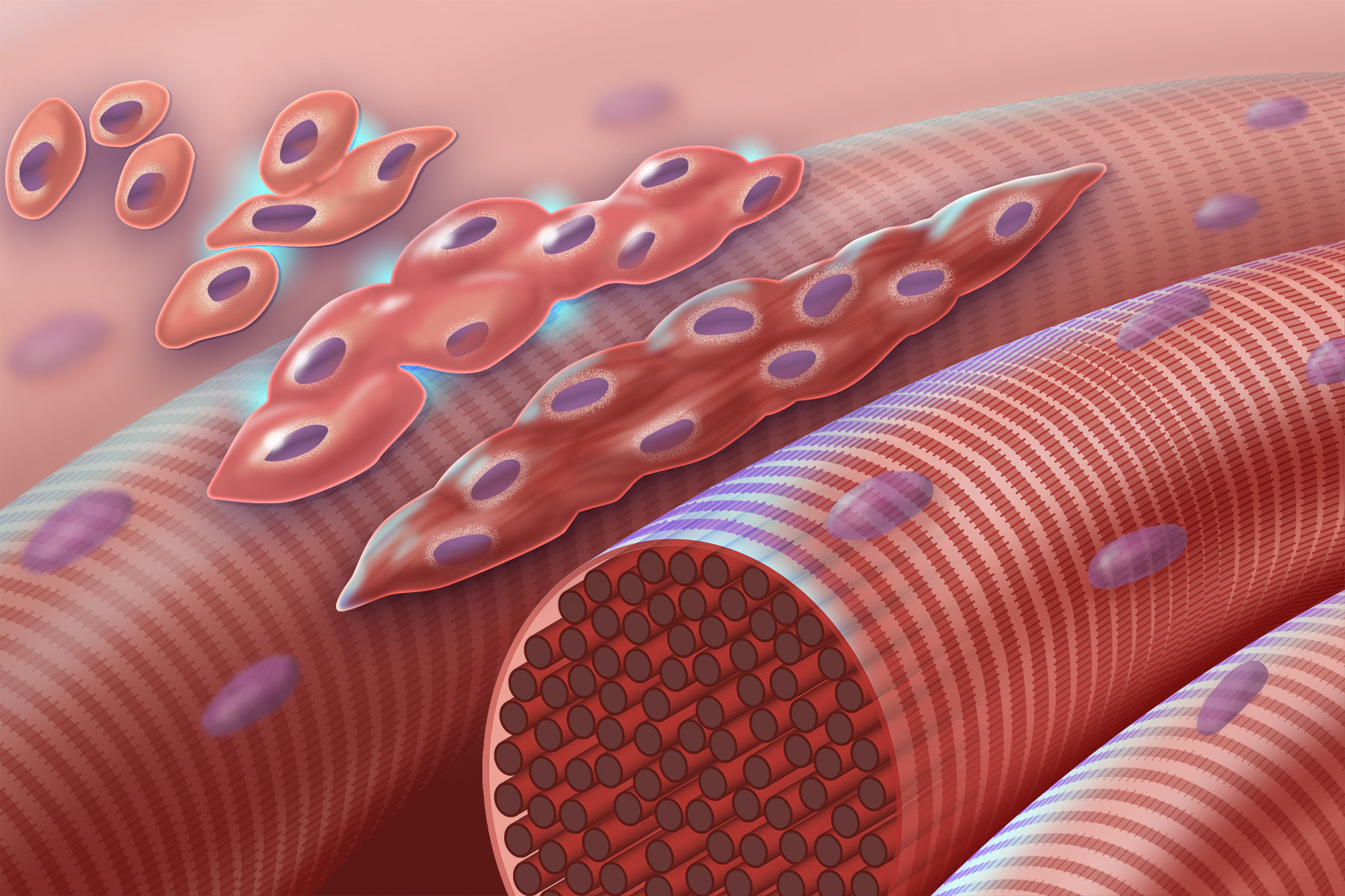
Myocyte
A muscle cell is also known as a myocyte when referring to either a cardiac muscle cell (cardiomyocyte), or a smooth muscle cell as these are both small cells. A skeletal muscle cell is long and threadlike with many nuclei and is called a muscle fiber. Muscle cells (including myocytes and muscle fibers) develop from embryonic precursor cells called myoblasts. Myoblasts fuse to form multinucleated skeletal muscle cells known as syncytia in a process known as myogenesis. Skeletal muscle cells and cardiac muscle cells both contain myofibrils and sarcomeres and form a striated muscle tissue. Cardiac muscle cells form the cardiac muscle in the walls of the heart chambers, and have a single central nucleus. Cardiac muscle cells are joined to neighboring cells by intercalated discs, and when joined in a visible unit they are described as a ''cardiac muscle fiber''. Smooth muscle cells control involuntary movements such as the peristalsis contractions in the esophagus and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |