|
93rd Infantry Division (Wehrmacht)
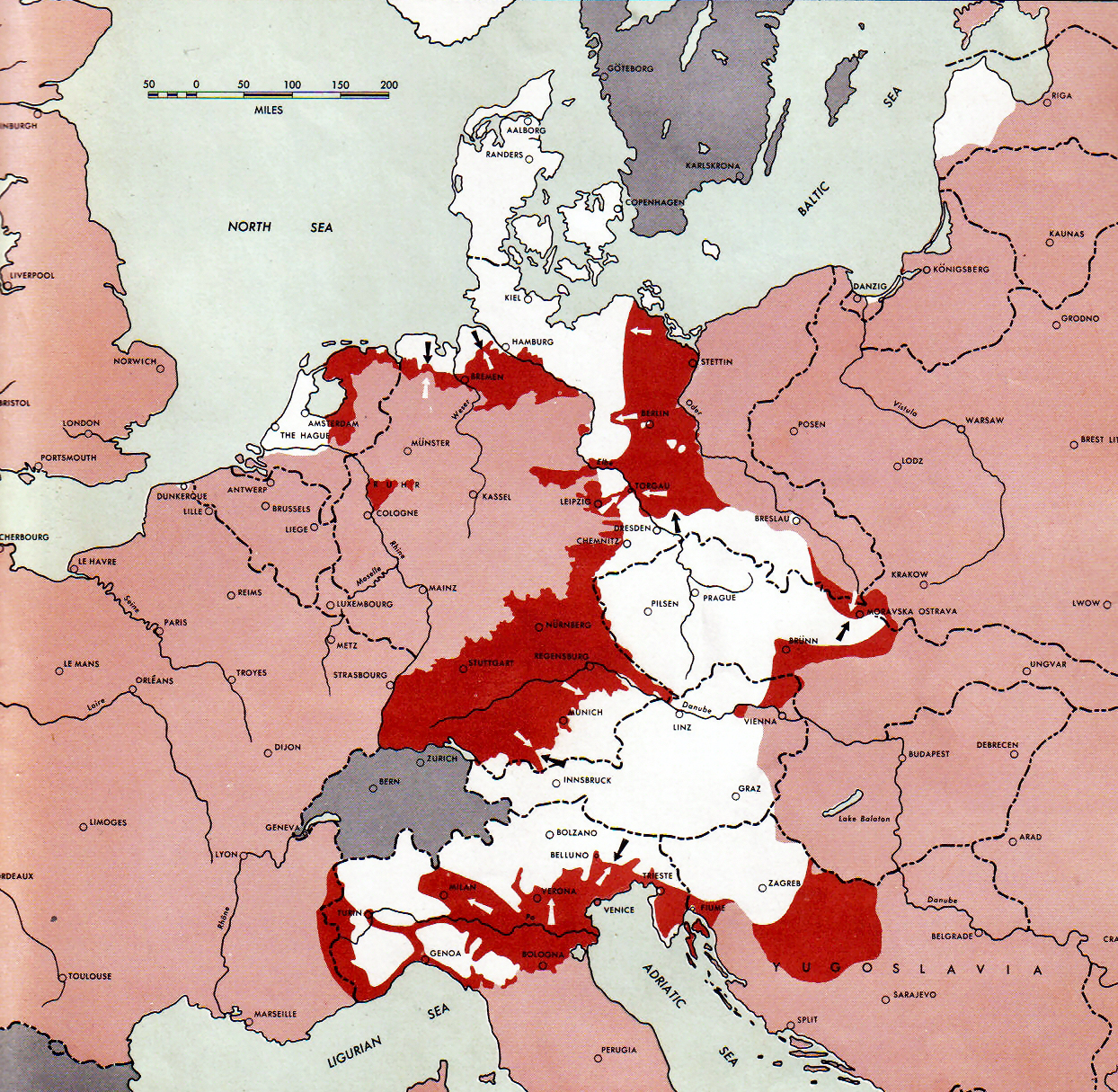
The 93rd Infantry Division (German ''93. Infanterie-Division'') was a German infantry division (military), division that was formed in the fall of 1939. The division fought in the World War II, Second World War in both the Battle of France and on the Eastern Front (World War II), Eastern Front. It was ultimately destroyed by the Red Army in March 1945 while defending East Prussia, East Prussia. France In the spring and early summer of 1940, the division was located near the Maginot Line at Saarbrücken. On 15 June 1940 the division launched its attack south of the city, breaking through the French line and continuing its advance across the Seille (Moselle), Seille and Meurthe (river), Meurthe rivers, south to the region of the River Moselle, Moselle river. It consolidated between Nancy, France, Nancy and Epinal and was ordered to stop on 25 June. Eastern Front After the campaign in France, the division was stationed along the French coast until June 1941, when it was reattache ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
German Army (Wehrmacht)
The German Army (, 'army') is the land component of the armed forces of Federal Republic of Germany, Germany. The present-day German Army was founded in 1955 as part of the newly formed West German together with the German Navy, ''Marine'' (German Navy) and the German Air Force, ''Luftwaffe'' (German Air Force). , the German Army had a strength of 63,047 soldiers. History Overview A German army equipped, organized, and trained following a single doctrine and permanently unified under one command was created in 1871 during the unification of Germany under the leadership of Prussia. From 1871 to 1919, the title ''German Army (German Empire), Deutsches Heer'' (German Army) was the official name of the German land forces. Following the German defeat in World War I and the end of the German Empire, the main army was dissolved. From 1921 to 1935 the name of the German land forces was the ''Reichswehr, Reichsheer'' (Army of the Realm) and from 1935 to 1945 the name ''German Army (We ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saarbrücken
Saarbrücken (; Rhenish Franconian: ''Sabrigge'' ; ; ; ; ) is the capital and largest List of cities and towns in Germany, city of the state of Saarland, Germany. Saarbrücken has 181,959 inhabitants and is Saarland's administrative, commercial and cultural centre. It is located on the Saar River (a tributary of the Moselle), directly borders the French department of Moselle (department), Moselle, and is Germany's second-westernmost state capital after Düsseldorf. The modern city of Saarbrücken was created in 1909 by the merger of the three cities of Saarbrücken (now called ''Alt-Saarbrücken''), Sankt Johann (Saarbrücken), St. Johann a. d. Saar, and Malstatt-Burbach. It was the industrial and transport centre of the Saar coal basin. Products included iron and steel, sugar, beer, pottery, optical instruments, machinery, and construction materials. Historic landmarks in the city include the stone bridge across the Saar (river), Saar (1546), the Gothic church of St. Ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Infantry Divisions Of Germany During World War II
Infantry, or infantryman are a type of soldier who specialize in ground combat, typically fighting dismounted. Historically the term was used to describe foot soldiers, i.e. those who march and fight on foot. In modern usage, the term broadly encompasses a wide variety of subspecialties, including light infantry, irregular infantry, heavy infantry, mountain infantry, motorized infantry, mechanized infantry, airborne infantry, air assault infantry, and naval infantry. Other subtypes of infantry, such as line infantry and mounted infantry, were once commonplace but fell out of favor in the 1800s with the invention of more accurate and powerful weapons. Etymology and terminology In English, use of the term ''infantry'' began about the 1570s, describing soldiers who march and fight on foot. The word derives from Middle French , from older Italian (also Spanish) ''infanteria'' (foot soldiers too inexperienced for cavalry), from Latin '' īnfāns'' (without speech, newbo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sambia Peninsula
Sambia () or Samland () or Kaliningrad Peninsula (official name, , ''Kaliningradsky poluostrov'') is a peninsula in the Kaliningrad Oblast of Russia, on the southeastern shore of the Baltic Sea. The peninsula is bounded by the Curonian Lagoon to the north-east, the Vistula Lagoon in the southwest, the Pregolya, Pregolya River in the south, and the Deyma River in the east. As Sambia is surrounded on all sides by water, it is technically an island. Historically it formed an important part of the historic region of Prussia (region), Prussia. Etymology Sambia is named after the Sambians, an extinct tribe of Old Prussians. ''Samland'' is the name for the peninsula in the Germanic languages. Polish language, Polish and Latin speakers call the area ''Sambia'', while the Lithuanian language, Lithuanian name is ''Semba''. Geography and geology Baedeker describes Sambia as "a fertile and wooded district, with several lakes, lying to the north of Königsberg" (since 1946 Kaliningrad). T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Army Group Courland
Army Group Courland () was a Nazi Germany, German Army Group on the Eastern Front (World War II), Eastern Front. It was created from remnants of the Army Group North, blockade, isolated in the Courland Peninsula by the advancing Soviet Army forces during the 1944 Baltic Offensive of the Second World War. The army group remained isolated in the Courland Pocket until the end of World War II in Europe. All units of the Army Group were ordered to surrender by the capitulated Wehrmacht command on 8 May 1945. At the time agreed for all German armed forces to end hostilities (see the German Instrument of Surrender, 1945), the 16th Army (Wehrmacht), Sixteenth and 18th Army (Wehrmacht), Eighteenth armies of Army Group Courland, commanded by General (of Infantry) Carl Hilpert, ended hostilities at 23:00, on 8 May 1945, surrendering to Leonid Govorov, commander of the Leningrad Front. By the evening of 9 May 1945 189,000 German troops, including 42 officers in the rank of general, in the C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Courland Pocket
The Courland Pocket was a Pocket (military), pocket located on the Courland Peninsula in Latvia on the Eastern Front (World War II), Eastern Front of World War II from 9 October 1944 to 10 May 1945. Army Group North of the ''Wehrmacht'' were surrounded in western Latvia by the Red Army after the Baltic Offensive, when forces of the 1st Baltic Front reached the Baltic Sea near Klaipėda, Memel (Klaipėda) after the collapse of Army Group Centre during Operation Bagration. Army Group North retreated to the Courland Pocket and was renamed Army Group Courland on 25 January, holding off six Red Army Offensive (military), offensives until the German Instrument of Surrender was signed on 8 May 1945. Army Group Courland were in a communication "Blackout (broadcasting), blackout" and did not get the official order until 10 May, becoming one of the last German groups to European theatre of World War II, surrender in Europe. Background In June 1941, Nazi Germany launched Operation Bar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
60th Infantry Division (Wehrmacht)
The 60th Infantry Division was formed in late 1939, from Gruppe Eberhardt, a collection of SA units that had been engaged in the capture of Danzig during the Invasion of Poland. This division was unusual in that its manpower was largely drawn from the SA and the police. History This division participated in the invasion of France (1940) as part of the 1st Army, and was in July 1940 transferred back to Poland where it was upgraded to 60th Infantry Division (motorized). During this upgrading it was reduced to two regiments (the Inf.Rgt 92 and Inf.Rgt 244) and the other regiment (Inf.Rgt 243) was reassigned. In January 1941 the division was moved to Romania and in April took part in the invasion of Yugoslavia and Greece. This division participated in Operation Barbarossa, advancing through Uman and across the Dnieper River as part of the 1st Panzergruppe (commanded by General Von Kleist). It took part in the attack and occupation of Rostov until it was pulled back along wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sturmabteilung
The (; SA; or 'Storm Troopers') was the original paramilitary organisation under Adolf Hitler and the Nazi Party of Germany. It played a significant role in Adolf Hitler's rise to power, Hitler's rise to power in the 1920s and early 1930s. Its primary purposes were providing protection for Nazi rallies and assemblies, disrupting the meetings of opposing parties, fighting against the paramilitary units of the opposing parties, especially the ''Roter Frontkämpferbund'' of the Communist Party of Germany (KPD) and the ''Reichsbanner Schwarz-Rot-Gold'' of the Social Democratic Party of Germany (SPD), and intimidating Romani people, Romani, trade unionists, and especially Jews. The SA were colloquially called Brownshirts () because of the colour of their Uniforms and insignia of the Sturmabteilung, uniform's shirts, similar to Benito Mussolini's Blackshirts. The official uniform of the SA was a brown shirt with a brown tie. The color came about because a large shipment of Paul von ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Operation Barbarossa
Operation Barbarossa was the invasion of the Soviet Union by Nazi Germany and several of its European Axis allies starting on Sunday, 22 June 1941, during World War II. More than 3.8 million Axis troops invaded the western Soviet Union along a front, with the main goal of capturing territory up to a line between Arkhangelsk and Astrakhan, known as the A-A line. The attack became the largest and costliest military offensive in history, with around 10 million combatants taking part in the opening phase and over 8 million casualties by the end of the operation on 5 December 1941. It marked a major escalation of World War II, opened the Eastern Front—the largest and deadliest land war in history—and brought the Soviet Union into the Allied powers. The operation, code-named after the Holy Roman Emperor Frederick Barbarossa ("red beard"), put into action Nazi Germany's ideological goals of eradicating communism and conquering the western Soviet Union to repopulate it w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Army Group North
Army Group North () was the name of three separate army groups of the Wehrmacht during World War II. Its rear area operations were organized by the Army Group North Rear Area. The first Army Group North was deployed during the invasion of Poland and subsequently renamed Army Group B. The second Army Group North was created on 22 June 1941 from the former Army Group C and used in the northern sector of the Eastern Front from 1941 to January 1945. By then, this second Army Group North had gotten trapped in the Courland Pocket and was accordingly redesignated Army Group Courland. On the same day, the former Army Group Center, which was now defending the northernmost sector of the contiguous Eastern Front, was renamed Army Group North, assuming the status of the third and final iteration of the army group. First deployment of Army Group North: September – October 1939 The staff of Army Group North was formally assembled on 2 September 1939 from the headquarters of 2nd ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nancy, France
Nancy is the Prefectures in France, prefecture of the northeastern Departments of France, French department of Meurthe-et-Moselle. It was the capital of the Duchy of Lorraine, which was Lorraine and Barrois, annexed by France under King Louis XV in 1766 and replaced by a Provinces of France, province, with Nancy maintained as capital. Following its rise to prominence in the Age of Enlightenment, it was nicknamed the "capital of Eastern France" in the late 19th century. The metropolitan area of Nancy had a population of 508,793 inhabitants as of 2021, making it the 16th-largest functional area (France), functional urban area in France and Lorraine's largest. The population of the city of Nancy proper is 104,387 (2022). The motto of the city is —a reference to the thistle, which is a symbol of Lorraine. Place Stanislas, a large square built between 1752 and 1756 by architect Emmanuel Héré under the direction of Stanislaus I of Poland to link the medieval old town of Nancy and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |