|
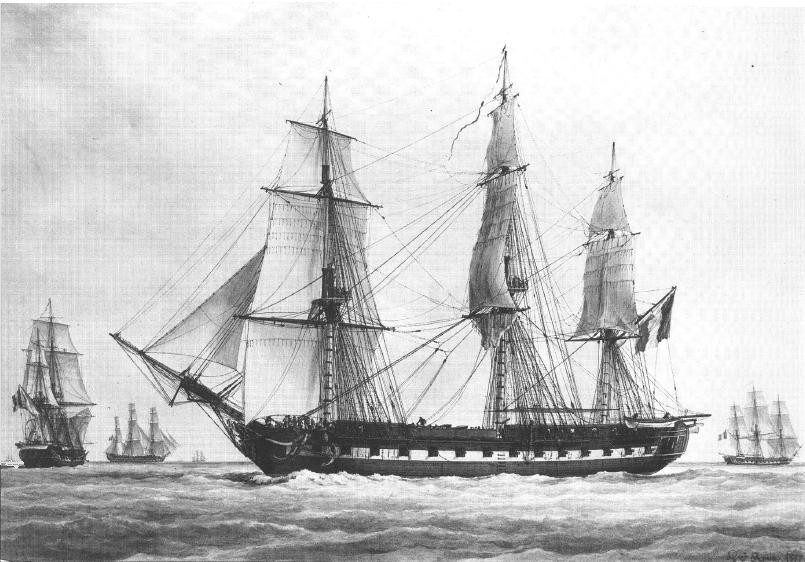
74-gun
The "seventy-four" was a type of two- decked sailing ship of the line, which nominally carried 74 guns. It was developed by the French navy in the 1740s, replacing earlier classes of 60- and 62-gun ships, as a larger complement to the recently developed 64-gun ships. Impressed with the performance of several captured French seventy-fours, the British Royal Navy quickly adopted similar designs, classing them as third rates. The type then spread to the Spanish, Dutch, Danish and Russian navies. The design was considered a good balance between firepower and sailing qualities. Hundreds of seventy-fours were constructed, becoming the dominant form of ship-of-the-line. They remained the mainstay of most major fleets into the early 19th century. From the 1820s, they began to be replaced by larger two-decked ships mounting more guns. However, some seventy-fours remained in service until the late 19th century, when they were finally supplanted by ironclads. Standardising on a common s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
64-gun Ship
The 64-gun ship of the line was a type of two-decker warship defined during the 18th century, named after the number of their guns. 64-guns had a lower battery of 24-pounders and an upper battery of 12-pounders. Heavier variants with 18-pounders on the upper deck also existed. History The French Navy used "64-gun" as a typology for its ships. In the British History of the Royal Navy, Royal Navy, such lighter two-deckers were considered to be Third-rates, like 74-guns and 80-guns. During the reign of Louis XIV of France, Louis XIV, numerous ships carried 60 or 62 guns, with a lower battery pierced for 12 guns on each side. During the reign of Louis XV of France, Louis XV, standardisation efforts were undertaken to rationalise the design and construction of these ships, with a common armament of 24-pounder long gun, 24-pounder, 12-pounder long gun, 12-pounder, and 8-pounder long guns. The first 64-gun in this sense was ''Borée'', launched in 1734 and pierced with 13 gun ports on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
18-pounder Long Gun
The 18-pounder long gun was an intermediary calibre piece of naval artillery mounted on warships of the Age of Sail. They were used as main guns on the most typical frigates of the early 19th century, on the second deck of third-rate ships of the line, and even on the third deck of late first-rate ships of the line. Usage As the 18-pounder calibre was consistent with both the French and the British calibre systems, it was used in many European navies between the 17th and the 19th century. It was a heavy calibre for early ships of the line, arming, for instance, the main batteries of in 1636. From the late 18th century, the French Navy used the 18-pounder in three capacities: as the main gun on frigates, as the battery on the upper gundeck of two-deckers, and lastly on the top deck of three-deckers. French frigates began carrying the 18-pounder under Louis XV, when the two frigates, originally designed to carry 24-pounders, were equipped with it; at the time, a typical frig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ship Of The Line
A ship of the line was a type of naval warship constructed during the Age of Sail from the 17th century to the mid-19th century. The ship of the line was designed for the naval tactics in the Age of Sail, naval tactic known as the line of battle, which involved the two columns of opposing warships manoeuvering to volley fire with the naval cannon, cannons along their Broadside (naval), broadsides. In conflicts where opposing ships were both able to fire from their broadsides, the faction with more cannons firingand therefore more firepowertypically had an advantage. From the end of the 1840s, the introduction of steam engine, steam power brought less dependence on the wind in battle and led to the construction of propeller, screw-driven wooden-hulled ships of the line; a number of purely sail-powered ships were converted to this propulsion mechanism. However, the rise of the ironclad warship, ironclad frigate, starting in 1859, made steam-assisted ships of the line obsolete. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
24-pounder Long Gun
The 24-pounder long gun was a heavy calibre piece of artillery mounted on warships of the Age of Sail. 24-pounders were in service in the navies of France, Spain, Great Britain, the Netherlands, Sweden, and the United States. They were comparable to the Canon de 24 Gribeauval used by the French Army as its largest piece of siege artillery. 24-pounders were used as main guns on the heaviest frigates of the early 19th century and on fourth-rate ships of the line, on the second deck of first-rate ships of the line, and on the second deck of a few large third-rates. Usage The 24-pounder calibre was consistent with both the French and the British calibre systems, and was a widespread gun amongst nations between the 17th and the 19th century. From the late 18th century, the French Navy used the 24-pounder in two capacities: as main gun on frigates and 64-guns, or as secondary artillery on three-deckers and even enlarged versions two-deckers. Under Louis XV, a typical heavy fri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Frigate
A frigate () is a type of warship. In different eras, the roles and capabilities of ships classified as frigates have varied. The name frigate in the 17th to early 18th centuries was given to any full-rigged ship built for speed and maneuverability, intended to be used in scouting, escort and patrol roles. The term was applied loosely to ships varying greatly in design. In the second quarter of the 18th century, what is now generally regarded as the 'true frigate' was developed in France. This type of vessel was characterised by possessing only one armed deck, with an unarmed deck below it used for berthing the crew. Late in the 19th century (British and French prototypes were constructed in 1858), a type of powerful ironclad warships was developed, and because they had a single gun deck, the term 'frigate' was used to describe them. Later developments in ironclad ships rendered the 'frigate' designation obsolete and the term fell out of favour. During the Second World War ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
36-pounder Long Gun
The 36-pounder long gun was the largest piece of naval artillery in the Age of Sail, artillery mounted on French warships of the Age of Sail. They were also used for Coastal defense and fortification. They largely exceeded the heaviest guns fielded by the Army, which were 24-pounder long guns. The nominal weight of shot was 36 French units of measurement, French ''livres'', . Usage Installed on the lower deck of the larger warships, the 36-pounder long gun was the largest caliber used in the Navy of the Age of the Sail. Attempts to use 48-pounders were made, for instance on French ship Royal Louis (1692), ''Royal Louis'', but these proved impractical to use on ships, partly because their weight allowed for only a few pieces, and because the heavy balls were unwieldy to load by hand. However, some coastal batteries fielded 48-pounders and even 64-pounders. In the Royal Navy, a similar role was fulfilled by 32-pounder long guns. History French warships began to carry 36-pounders ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Two-decker
A two-decker is a sail warship which carried her guns on two fully armed decks. Usually additional guns were carried on the upper works (forecastle and quarterdeck), but this was not a continuous battery and thus not counted as a full gun deck. Two-deckers ranged all the way from the small 40-gun Fifth rate up to 80- or even 90-gun ships of the line, with the third-rate of seventy-four guns, or " seventy-four", being the archetype. See also * Three-decker A three-decker was a sailing warship which carried her principal carriage-mounted guns on three fully armed decks. Usually additional (smaller) guns were carried on the upper works (forecastle and quarterdeck), but this was not a continuous ba ... References Naval sailing ship types {{navy-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Third Rate
In the rating system of the Royal Navy, a third rate was a ship of the line which from the 1720s mounted between 64 and 80 guns, typically built with two gun decks (thus the related term two-decker). Rating When the rating system was first established in the 1620s, the third rate was defined as those ships having at least 200 but not more than 300 men; previous to this, the type had been classified as "middling ships". By the 1660s, the means of classification had shifted from the number of men to the number of carriage-mounted guns, and third rates at that time mounted between 48 and 60 guns. By the turn of the century, the criterion boundaries had increased and third rate carried more than 60 guns, with second rates having between 90 and 98 guns, while first rates had 100 guns or more, and fourth rates between 48 and 60 guns. By the latter half of the 18th century, they carried between 500 and 720 men. This designation became especially common because it included the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
French Navy
The French Navy (, , ), informally (, ), is the Navy, maritime arm of the French Armed Forces and one of the four military service branches of History of France, France. It is among the largest and most powerful List of navies, naval forces in the world recognised as being a blue-water navy. The French Navy is capable of operating globally and conducting expeditionary missions, maintaining a significant Standing French Navy Deployments, overseas presence. The French Navy is one of eight naval forces currently operating Fixed-wing aircraft, fixed-wing aircraft carriers,Along with the United States Navy, U.S., Royal Navy, U.K., People's Liberation Army Navy, China, Russian Navy, Russia, Italian Navy, Italy, Indian Navy, India, and Spanish Navy, Spain with its flagship being the only Nuclear marine propulsion, nuclear-powered aircraft carrier outside the United States Navy, and one of two non-American vessels to use Aircraft catapult, catapults to launch aircraft. Founded in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ship Rig
A full-rigged ship or fully rigged ship is a sailing ship, sailing vessel with a sail plan of three or more mast (sailing), masts, all of them square rig, square-rigged. Such a vessel is said to have a ship rig or be ship-rigged, with each mast stepped in three segments: lower, top, and topgallant. Masts The Mast (sailing), masts of a full-rigged ship, from Bow (ship), bow to stern, are: * Foremast, which is the second tallest mast * Mainmast, the tallest * Mizzenmast, the third tallest * Jiggermast, which may not be present but will be fourth tallest if so If the masts are of wood, each mast is in three or more pieces. They are (in order, from bottom up): * Th''e mast or the lower.'' * Topmast * Topgallant mast * Royal mast, if fitted On steel-masted vessels, the masts are not constructed in the same way, but the corresponding sections of the mast are still named after the traditional wooden sections. Sails The lowest and normally largest sail on a mast is the course ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United States Navy
The United States Navy (USN) is the naval warfare, maritime military branch, service branch of the United States Department of Defense. It is the world's most powerful navy with the largest Displacement (ship), displacement, at 4.5 million tons in 2021. It has the world's largest aircraft carrier fleet, with List of aircraft carriers in service, eleven in service, one undergoing trials, two new carriers under construction, and six other carriers planned as of 2024. With 336,978 personnel on active duty and 101,583 in the Ready Reserve, the U.S. Navy is the third largest of the United States military service branches in terms of personnel. It has 299 deployable combat vessels and about 4,012 operational aircraft as of 18 July 2023. The U.S. Navy is one of six United States Armed Forces, armed forces of the United States and one of eight uniformed services of the United States. The United States Navy traces its origins to the Continental Navy, which was established during ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Draft (hull)
The draft or draught of a ship is a determined depth of the vessel below the waterline, measured vertically to its hull's lowest—its propellers, or keel, or other reference point. Draft varies according to the loaded condition of the ship. A deeper draft means the ship will have greater vertical depth below the waterline. Draft is used in under keel clearance calculations, where the draft is calculated with the available depth of water (from Electronic navigational charts) to ensure the ship can navigate safely, without grounding. Navigators can determine their draught by calculation or by visual observation (of the ship's painted load lines). Related terminology A ship's draft/draught is the "depth of the vessel below the waterline measured vertically to the lowest part of the hull, propellers, or other reference point". That is, the draft or draught is the maximum depth of any part of the vessel, including appendages such as rudders, propellers and drop keels if de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |