|
6-chloronicotinic Acid
Neonicotinoids (sometimes shortened to neonics ) are a class of neuro-active insecticides chemically similar to nicotine, developed by scientists at Shell and Bayer in the 1980s. Neonicotinoids are among the widest-used insecticides in crop protection. They are also widely employed for veterinary purposes including tick and flea control. The first generation of neonicotinoids includes acetamiprid, clothianidin, dinotefuran, imidacloprid, nitenpyram, nithiazine, thiacloprid and thiamethoxam. The more recently marketed generation of neonicotinoids includes cycloxaprid, imidaclothiz, paichongding, sulfoxaflor, guadipyr, and flupyradifurone. Imidacloprid has been the most widely used insecticide in the world from 1999 through . Because they affect the central nervous system of insects, neonicotinoids kill or deleteriously affect a wide variety of both target and non-target insects. They are often applied to seeds before planting as a prophylactic treatment against herbivorous inse ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Insecticide
Insecticides are pesticides used to kill insects. They include ovicides and larvicides used against insect eggs and larvae, respectively. The major use of insecticides is in agriculture, but they are also used in home and garden settings, industrial buildings, for vector control, and control of insect parasites of animals and humans. Acaricides, which kill mites and ticks, are not strictly insecticides, but are usually classified together with insecticides. Some insecticides (including common bug sprays) are effective against other non-insect arthropods as well, such as scorpions, spiders, etc. Insecticides are distinct from insect repellents, which repel but do not kill. Sales In 2016 insecticides were estimated to account for 18% of worldwide pesticide sales. Worldwide sales of insecticides in 2018 were estimated as $ 18.4 billion, of which 25% were neonicotinoids, 17% were pyrethroids, 13% were diamides, and the rest were many other classes which sold for less th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flupyradifurone
} Flupyradifurone is a systemic butenolide insecticide developed by Bayer CropScience under the name Sivanto. Flupyradifurone protects crops from sap-feeding pests such as aphids and is safer for non-target organisms compared to other insecticides. Sivanto was launched in 2014 since it obtained its first commercial registration in central America (Guatemala and Honduras). Insecticide Resistance Action Committee (IRAC) classified Flupyradifurone as 4D subset (butenolide) and it is the first pesticide in the butenolide category. It was approved by European Union in 2015. Characteristics Sap-feeding insects have developed resistance to nearly all other kinds of insecticides but flupyradifurone is effective at controlling aphids and whitefly, thereby maintaining yields of crops such as vegetables, fruits, cotton, and coffee. It also demonstrated positive toxicological and ecotoxicological safety. According to a study by Bayer, who developed the compound, flupyradifurone has a high r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
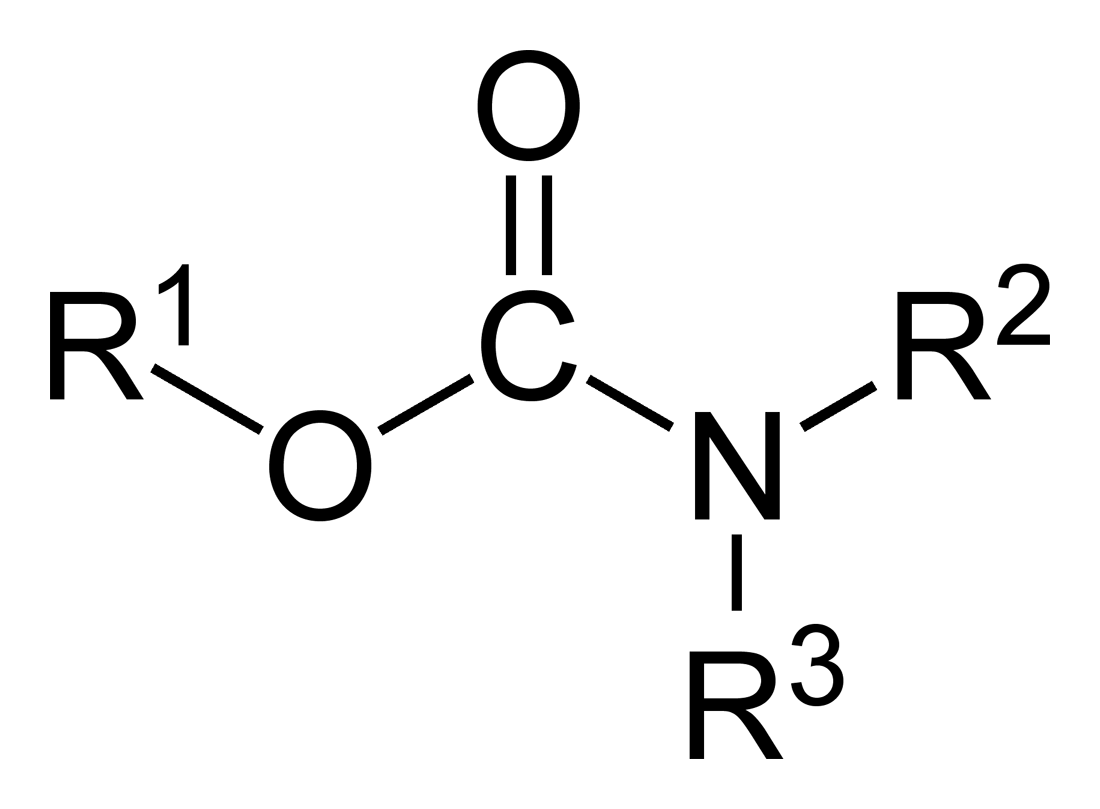
Carbamates
In organic chemistry, a carbamate is a category of organic compounds with the general formula and structure , which are formally derived from carbamic acid (). The term includes organic compounds (e.g., the ester ethyl carbamate), formally obtained by replacing one or more of the hydrogen atoms by other organic functional groups; as well as salts with the carbamate anion (e.g. ammonium carbamate). Polymers whose repeat units are joined by carbamate like groups are an important family of plastics, the polyurethanes. See for clarification. Properties While carbamic acids are unstable, many carbamate esters and salts are stable and well known. Equilibrium with carbonate and bicarbonate In water solutions, the carbamate anion slowly equilibrates with the ammonium cation and the carbonate or bicarbonate anions: : : Calcium carbamate is soluble in water, whereas calcium carbonate is not. Adding a calcium salt to an ammonium carbamate/carbonate solution will precipitate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Organophosphate
In organic chemistry, organophosphates (also known as phosphate esters, or OPEs) are a class of organophosphorus compounds with the general structure , a central phosphate molecule with alkyl or aromatic substituents. They can be considered as esters of phosphoric acid. Organophosphates are best known for their use as pesticides. Like most functional groups, organophosphates occur in a diverse range of forms, with important examples including key biomolecules such as DNA, RNA and ATP, as well as many insecticides, herbicides, nerve agents and flame retardants. OPEs have been widely used in various products as flame retardants, plasticizers, and performance additives to engine oil. The low cost of production and compatibility to diverse polymers made OPEs to be widely used in industry including textile, furniture, electronics as plasticizers and flame retardants. These compounds are added to the final product physically rather than by chemical bond. Due to this, OPEs leak in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acetylcholinesterase Inhibitor
Acetylcholinesterase inhibitors (AChEIs) also often called cholinesterase inhibitors, inhibit the enzyme acetylcholinesterase from breaking down the neurotransmitter acetylcholine into choline and acetate, thereby increasing both the level and duration of action of acetylcholine in the central nervous system, autonomic ganglia and neuromuscular junctions, which are rich in acetylcholine receptors. Acetylcholinesterase inhibitors are one of two types of cholinesterase inhibitors; the other being butyryl-cholinesterase inhibitors. Acetylcholinesterase is the primary member of the cholinesterase enzyme family. Acetylcholinesterase inhibitors are classified as reversible, irreversible, or quasi-irreversible (also called pseudo-irreversible). Mechanism of action Organophosphates Organophosphates like tetraethyl pyrophosphate (TEPP) and sarin inhibit cholinesterases, enzymes that hydrolyze the neurotransmitter acetylcholine. The active centre of cholinesterases feature ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parasympathomimetic Drug
A parasympathomimetic drug, sometimes called a cholinomimetic drug or cholinergic receptor stimulating agent, is a substance that stimulates the parasympathetic nervous system (PSNS). These chemicals are also called cholinergic drugs because acetylcholine (ACh) is the neurotransmitter used by the PSNS. Chemicals in this family can act either directly by stimulating the nicotinic or muscarinic receptors (thus mimicking acetylcholine), or indirectly by inhibiting cholinesterase, promoting acetylcholine release, or other mechanisms. Common uses of parasympathomimetics include glaucoma, Sjögren syndrome and underactive bladder. Some chemical weapons such as sarin or VX, non-lethal riot control agents such as tear gas, and insecticides such as diazinon fall into this category. Structure activity relationships for parasympathomimetic drugs For a cholinergic agent, the following criteria describe the structure activity relationship: # Ing's Rule of 5: there should be no ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shell Oil Company
Shell USA, Inc. (formerly Shell Oil Company, Inc.) is the United States–based wholly owned subsidiary of Shell plc, a UK-based transnational corporation " oil major" which is among the largest oil companies in the world. Approximately 18,000 Shell employees are based in the U.S. Its U.S. headquarters are in Houston, Texas. Shell USA, including its consolidated companies and its share in equity companies, is one of America's largest oil and natural gas producers, natural gas marketers, fuel marketers and petrochemical manufacturers. History In 1979, Shell purchased Belridge Oil Company for $3.65 billion, which at the time was called the "biggest cash takeover in American history" by US government sources. In 1997, Shell and Texaco entered into two refining/marketing joint ventures. One combined their Midwestern and Western operations and was known as Equilon. The other, known as Motiva Enterprises, combined the Eastern and Gulf Coast operations of Shell Oil and Star Enterpr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Precursor (chemistry)
In chemistry, a precursor is a compound that participates in a chemical reaction that produces another compound. In biochemistry Biochemistry, or biological chemistry, is the study of chemical processes within and relating to living organisms. A sub-discipline of both chemistry and biology, biochemistry may be divided into three fields: structural biology, enzymology, a ..., the term "precursor" often refers more specifically to a chemical compound preceding another in a metabolic pathway, such as a protein precursor. Illicit drug precursors In 1988, the United Nations Convention Against Illicit Traffic in Narcotic Drugs and Psychotropic Substances introduced detailed provisions and requirements relating the control of precursors used to produce drugs of abuse. In Europe the Regulation (EC) No. 273/2004 of the European Parliament and of the Council on drug precursors was adopted on 11 February 2004. ( European law on drug precursors) Illicit explosives precursors On Ja ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Guardian
''The Guardian'' is a British daily newspaper. It was founded in Manchester in 1821 as ''The Manchester Guardian'' and changed its name in 1959, followed by a move to London. Along with its sister paper, ''The Guardian Weekly'', ''The Guardian'' is part of the Guardian Media Group, owned by the Scott Trust Limited. The trust was created in 1936 to "secure the financial and editorial independence of ''The Guardian'' in perpetuity and to safeguard the journalistic freedom and liberal values of ''The Guardian'' free from commercial or political interference". The trust was converted into a limited company in 2008, with a constitution written so as to maintain for ''The Guardian'' the same protections as were built into the structure of the Scott Trust by its creators. Profits are reinvested in its journalism rather than distributed to owners or shareholders. It is considered a newspaper of record in the UK. The editor-in-chief Katharine Viner succeeded Alan Rusbridger in 2015. S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
European Union
The European Union (EU) is a supranational union, supranational political union, political and economic union of Member state of the European Union, member states that are Geography of the European Union, located primarily in Europe. The union has a total area of and an estimated population of over 449million as of 2024. The EU is often described as a ''sui generis'' political entity combining characteristics of both a federation and a confederation. Containing 5.5% of the world population in 2023, EU member states generated a nominal gross domestic product (GDP) of around €17.935 trillion in 2024, accounting for approximately one sixth of global economic output. Its cornerstone, the European Union Customs Union, Customs Union, paved the way to establishing European Single Market, an internal single market based on standardised European Union law, legal framework and legislation that applies in all member states in those matters, and only those matters, where the states ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United States Environmental Protection Agency
The Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) is an independent agency of the United States government tasked with environmental protection matters. President Richard Nixon proposed the establishment of EPA on July 9, 1970; it began operation on December 2, 1970, after Nixon signed an executive order. The order establishing the EPA was ratified by committee hearings in the House and Senate. The agency is led by its administrator, who is appointed by the president and approved by the Senate. The current administrator is Lee Zeldin. The EPA is not a Cabinet department, but the administrator is normally given cabinet rank. The EPA has its headquarters in Washington, D.C. There are regional offices for each of the agency's ten regions, as well as 27 laboratories around the country. The agency conducts environmental assessment, research, and education. It has the responsibility of maintaining and enforcing national standards under a variety of environmental laws, in consultat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
European Food Safety Authority
The European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) is the agency of the European Union (EU) that provides independent scientific advice and communicates on existing and emerging risks associated with the food chain. EFSA was established in February 2002 in Parma, Italy. It had a yearly budget of €118.6 million, and a total staff of 542 as of 2021. The work of EFSA covers all matters with a direct or indirect impact on food and feed safety, including animal health and welfare, plant protection and plant health and nutrition. EFSA supports the European Commission, the European Parliament and EU member states in taking effective and timely risk management decisions that ensure the protection of the health of European consumers and the safety of the food and feed chain. EFSA also communicates to the public in an open and transparent way on all matters within its remit. Structure Based on a regulation of 2002, the EFSA is composed of four bodies: * Management Board * Executive Direc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |