|
6-EAPB
6-EAPB (1-(benzofuran-6-yl)-N-ethylpropan-2-amine) is a potentially psychedelic and potentially entactogenic drug of the benzofuran class; it is structurally related to 6-APB and MDMA 3,4-Methylenedioxymethamphetamine (MDMA), commonly seen in tablet form (ecstasy) and crystal form (molly or mandy), is a potent empathogen–entactogen with stimulant properties primarily used for recreational purposes. The desired .... Legality As an N-ethyl derivative of 6-APB, 6-EAPB fell outside the scope of the Temporary Class Drug ban issued by the Home Office on June 10, 2013. The ACMD has advised that 6-EAPB (and other benzofurans) are moved to Class B, this came into action on 10 June 2014. References Substituted amphetamines 6-Benzofuranethanamines Designer drugs Serotonin-norepinephrine-dopamine releasing agents Serotonin receptor agonists Entactogens and empathogens {{hallucinogen-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MDMA
3,4-Methylenedioxymethamphetamine (MDMA), commonly seen in tablet form (ecstasy) and crystal form (molly or mandy), is a potent empathogen–entactogen with stimulant properties primarily used for recreational purposes. The desired effects include altered sensations, increased energy, empathy, and pleasure. When taken by mouth, effects begin in 30 to 45 minutes and last 3 to 6 hours. MDMA was first developed in 1912 by Merck. It was used to enhance psychotherapy beginning in the 1970s and became popular as a street drug in the 1980s. MDMA is commonly associated with dance parties, raves, and electronic dance music. It may be mixed with other substances such as ephedrine, amphetamine, and methamphetamine. In 2016, about 21 million people between the ages of 15 and 64 used ecstasy (0.3% of the world population). This was broadly similar to the percentage of people who use cocaine or amphetamines, but lower than for cannabis or opioids. In the United States, as of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Benzofuran
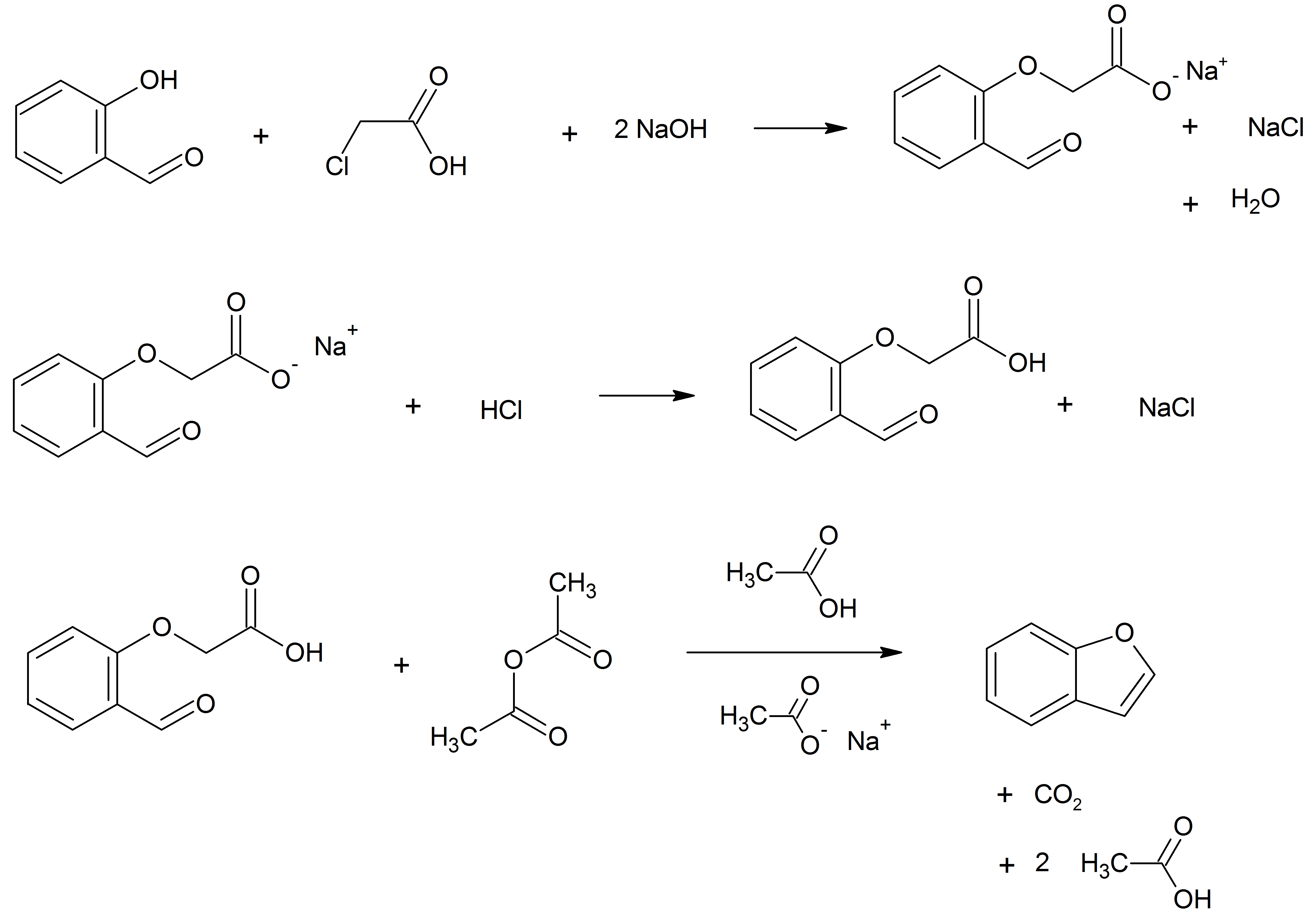
Benzofuran is the heterocyclic compound consisting of fused benzene and furan rings. This colourless liquid is a component of coal tar. Benzofuran is the "parent" of many related compounds with more complex structures. For example, psoralen is a benzofuran derivative that occurs in several plants. Production Benzofuran is extracted from coal tar. It is also obtained by dehydrogenation of 2-ethylphenol. Laboratory methods Benzofurans can be prepared by various methods in the laboratory. Notable examples include: *''O''-alkylation of salicylaldehyde with chloroacetic acid followed by dehydration (cyclication) of the resulting ether and decarboxylation. *Perkin rearrangement, where a coumarin is reacted with a hydroxide: : *Diels–Alder reaction of nitro vinyl furans with various dienophiles: : Diels–Alder reaction yielding a substituted benzofuran, 450px *Cycloisomerization of alkyne ortho-substituted phenols: : Benzofurans via Cycloisomerization, 400px Related compo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
6-APB
6-APB (6-(2-aminopropyl)benzofuran) is an empathogenic psychoactive compound of the substituted benzofuran and substituted phenethylamine classes. 6-APB and other compounds are sometimes informally called "Benzofury" in newspaper reports. It is similar in structure to MDA, but differs in that the 3,4- methylenedioxyphenyl ring system has been replaced with a benzofuran ring. 6-APB is also the unsaturated benzofuran derivative of 6-APDB. It may appear as a tan grainy powder. While the drug never became particularly popular, it briefly entered the rave and underground clubbing scene in the UK before its sale and import were banned. It falls under the category of research chemicals, sometimes called "legal highs." Because 6-APB and other substituted benzofurans have not been explicitly outlawed in some countries, they are often technically legal, contributing to their popularity. Pharmacology Pharmacodynamics 6-APB is a serotonin–norepinephrine–dopamine reuptake i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Substituted Amphetamines
Substituted amphetamines are a class of compounds based upon the amphetamine structure; it includes all derivative compounds which are formed by replacing, or substituting, one or more hydrogen atoms in the amphetamine core structure with substituents. The compounds in this class span a variety of pharmacological subclasses, including stimulants, empathogens, and hallucinogens, among others. Examples of substituted amphetamines are amphetamine (itself), methamphetamine, ephedrine, cathinone, phentermine, mephentermine, bupropion, methoxyphenamine, selegiline, amfepramone (diethylpropion), pyrovalerone, MDMA (ecstasy), and DOM (STP). Some of amphetamine's substituted derivatives occur in nature, for example in the leaves of '' Ephedra'' and khat plants. Amphetamine was first produced at the end of the 19th century. By the 1930s, amphetamine and some of its derivative compounds found use as decongestants in the symptomatic treatment of colds and also occasionally ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Designer Drugs
A designer drug is a structural or functional analog of a controlled substance that has been designed to mimic the pharmacological effects of the original drug, while avoiding classification as illegal and/or detection in standard drug tests. Designer drugs include psychoactive substances that have been designated by the European Union as new psychoactive substances (NPS) as well as analogs of performance-enhancing drugs such as designer steroids. Some of these were originally synthesized by academic or industrial researchers in an effort to discover more potent derivatives with fewer side effects, and shorter duration (and possibly also because it is easier to apply for patents for new molecules) and were later co-opted for recreational use. Other designer drugs were prepared for the first time in clandestine laboratories. Because the efficacy and safety of these substances have not been thoroughly evaluated in animal and human trials, the use of some of these drugs may result i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Serotonin Receptor Agonists
Serotonin () or 5-hydroxytryptamine (5-HT) is a monoamine neurotransmitter. Its biological function is complex and multifaceted, modulating mood, cognition, reward, learning, memory, and numerous physiological processes such as vomiting and vasoconstriction. Approximately 90% of the serotonin that the body produces is in the intestinal tract. Biochemically, the indoleamine molecule derives from the amino acid tryptophan, via the (rate-limiting) hydroxylation of the 5 position on the ring (forming the intermediate 5-hydroxytryptophan), and then decarboxylation to produce serotonin. Serotonin is primarily found in the enteric nervous system located in the gastrointestinal tract (GI tract). However, it is also produced in the central nervous system (CNS), specifically in the raphe nuclei located in the brainstem, Merkel cells located in the skin, pulmonary neuroendocrine cells and taste receptor cells in the tongue. Additionally, serotonin is stored in blood platelets and is rel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |