|
5F-MET
5-Fluoro-MET (5F-MET, 5-fluoro-''N''-methyl-''N''-ethyltryptamine) is a psychedelic tryptamine derivative related to drugs such as 5-Fluoro-DMT and N-Methyl-N-ethyltryptamine (MET). It acts as an agonist at the 5-HT2A receptor with an EC50 of 20.6 nM and produces a head-twitch response in animal studies. Ring fluorination in this case increases efficacy at 5-HT2A, with 5F-MET having an efficacy of 87.6% vs 5-HT, vs 36.2% for the partial agonist MET. It is claimed to have antidepressant activity. See also * 5-Fluoro-AMT * 5-Fluoro-AET * 5-Fluoro-DET * 5-Fluoro-EPT * 5-MeO-MET 5-MeO-MET (5-Methoxy-N-methyl-N-ethyltryptamine) is a relatively rare designer drug from the substituted tryptamine family, related to compounds such as N-methyl-N-ethyltryptamine and 5-MeO-DMT. It was first synthesised in the 1960s and was studie ... References Psychedelic tryptamines Tryptamines Fluoroarenes {{pharm-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
5-Fluoro-DET
5-Fluoro-DET (5F-DET, 5-fluoro-''N,N''-diethyltryptamine) is a tryptamine derivative related to drugs such as DET and 5-MeO-DET. It acts as an inhibitor of the enzyme myeloperoxidase, and is also thought to be an agonist An agonist is a chemical that activates a receptor to produce a biological response. Receptors are cellular proteins whose activation causes the cell to modify what it is currently doing. In contrast, an antagonist blocks the action of the ago ... at the 5-HT2A receptor. See also * 5F-DMT * 5F-MET * 5F-EPT * 6F-DET References Psychedelic tryptamines Tryptamines Fluoroarenes {{nervous-system-drug-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Psychedelic
Psychedelics are a subclass of hallucinogenic drugs whose primary effect is to trigger non-ordinary states of consciousness (known as psychedelic experiences or "trips").Pollan, Michael (2018). ''How to Change Your Mind: What the New Science of Psychedelics Teaches Us About Consciousness, Dying, Addiction, Depression, and Transcendence'' Sometimes, they are called classic hallucinogens, serotonergic hallucinogens, or serotonergic psychedelics, and the term ''psychedelics'' is used more broadly to include all hallucinogens; this article uses the narrower definition of ''psychedelics''. Psychedelics cause specific psychological, visual, and auditory changes, and often a substantially altered state of consciousness.Leary, Timothy; Metzner, Ralph (1964). ''The Psychedelic Experience: A Manual Based on The Tibetan Book of the Dead'' Psychedelic states are often compared to meditative, psychodynamic or transcendental types of alterations of mind. The "classical" psychedelics, the p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antidepressant
Antidepressants are a class of medication used to treat major depressive disorder, anxiety disorders, chronic pain conditions, and to help manage addictions. Common side-effects of antidepressants include dry mouth, weight gain, dizziness, headaches, sexual dysfunction, and emotional blunting. There is a slight increased risk of suicidal thinking and behavior when taken by children, adolescents, and young adults. Discontinuation syndrome may occur after stopping any antidepressant which resembles recurrent depression. Some research regarding the effectiveness of antidepressants for depression in adults has found benefits, whilst other research has not. Evidence of benefit in children and adolescents is unclear. The twenty-one most commonly prescribed antidepressant medications are more effective than placebo for the short-term (acute) treatments of adults with major depressive disorder. There is debate in the medical community about how much of the observed effects of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Psychedelic Tryptamines
Psychedelics are a subclass of hallucinogenic drugs whose primary effect is to trigger non-ordinary states of consciousness (known as psychedelic experiences or "trips").Pollan, Michael (2018). ''How to Change Your Mind: What the New Science of Psychedelics Teaches Us About Consciousness, Dying, Addiction, Depression, and Transcendence'' Sometimes, they are called classic hallucinogens, serotonergic hallucinogens, or serotonergic psychedelics, and the term ''psychedelics'' is used more broadly to include all hallucinogens; this article uses the narrower definition of ''psychedelics''. Psychedelics cause specific psychological, visual, and auditory changes, and often a substantially altered state of consciousness.Leary, Timothy; Metzner, Ralph (1964). ''The Psychedelic Experience: A Manual Based on The Tibetan Book of the Dead'' Psychedelic states are often compared to meditative, psychodynamic or transcendental types of alterations of mind. The "classical" psychedelics, the psy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
5-MeO-MET
5-MeO-MET (5-Methoxy-N-methyl-N-ethyltryptamine) is a relatively rare designer drug from the substituted tryptamine family, related to compounds such as N-methyl-N-ethyltryptamine and 5-MeO-DMT. It was first synthesised in the 1960s and was studied to a limited extent, but was first identified on the illicit market in June 2012 in Sweden. It was made illegal in Norway in 2013, and is controlled under analogue provisions in numerous other jurisdictions. See also * 4-HO-MET * 5-HO-DiPT * 5-EtO-DMT * 5-Fluoro-MET * 5-MeO-EPT * 5-MeO-MALT * 5-MeO-MiPT 5-MeO-MiPT is a psychedelic and hallucinogenic drug, used by some as an entheogen. It has structural and pharmacodynamic properties similar to the drugs 5-MeO-DiPT, DiPT, and MiPT. It is commonly used as a "substitute" for 5-MeO-DiPT because ... References Tryptamines Methoxy compounds Substances discovered in the 1960s {{nervous-system-drug-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
5-Fluoro-EPT
5-Fluoro-EPT (5F-EPT, 5-fluoro-''N''-ethyl-''N''-propyltryptamine) is a psychedelic tryptamine derivative related to drugs such as EPT and 5-MeO-EPT. It acts as a potent full agonist at the 5-HT2A receptor with an EC50 of 5.54 nM and an efficacy of 104% (compared to serotonin). It produces a head-twitch response in animal studies, and is claimed to have antidepressant activity. See also * 5-Fluoro-AMT * 5-Fluoro-AET * 5-Fluoro-DMT * 5-Fluoro-DET 5-Fluoro-DET (5F-DET, 5-fluoro-''N,N''-diethyltryptamine) is a tryptamine derivative related to drugs such as DET and 5-MeO-DET. It acts as an inhibitor of the enzyme myeloperoxidase, and is also thought to be an agonist An agonist is a chem ... * 5-Fluoro-MET References Psychedelic tryptamines Tryptamines Fluoroarenes {{nervous-system-drug-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
5-Fluoro-AET
5-Fluoro-α-ethyltryptamine (5-F-AET) is a tryptamine derivative which acts as a serotonin–dopamine releasing agent and agonist of the 5-HT2A receptor. See also * 4-Methyl-AET * 5-Chloro-AMT * 5-Fluoro-AMT * 5-Fluoro-DMT * 5-Fluoro-MET * 5-MeO-AET * 6-Fluoro-AMT * 7-Chloro-AMT 7-Chloro-α-methyltryptamine (7-Cl-AMT) is a tryptamine derivative with stimulant effects, invented in the 1960s. It is a weak monoamine oxidase inhibitor but its pharmacology has not otherwise been studied by modern techniques, though several cl ... * 7-Methyl-DMT * 7-Methyl-AET References Designer drugs Psychedelic tryptamines Serotonin receptor agonists Fluoroarenes {{nervous-system-drug-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
5-Fluoro-AMT
5-Fluoro-α-methyltryptamine (5-Fluoro-αMT, 5F-AMT), also known as PAL-544, is a putative stimulant, entactogen, and psychedelic tryptamine derivative related to α-methyltryptamine (αMT). It has been found to act as a well-balanced serotonin-norepinephrine-dopamine releasing agent, a 5-HT2A receptor agonist, and a potent and specific MAO-A inhibitor. which suggests that 5-fluoro-αMT could be an active psychedelic in humans, although it is not known to have been tested in humans and could be dangerous due to its strong inhibition of MAO-A. See also * 5-Chloro-αMT * 5-Fluoro-AET * 5-Fluoro-DMT * 6-Fluoro-AMT * 7-Chloro-AMT * 7-Methyl-αET * Flucindole Flucindole is an antipsychotic with a tricyclic structure that was never marketed. It is the 6,8-difluoro derivative of cyclindole Ciclindole (INN; WIN-27,147-2), also known as cyclindole (USAN), is an antipsychotic with a tricyclic structur ... * 5-API (PAL-571) References Further reading * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Partial Agonist
In pharmacology, partial agonists are drugs that bind to and activate a given receptor, but have only partial efficacy at the receptor relative to a full agonist. They may also be considered ligands which display both agonistic and antagonistic effects—when both a full agonist and partial agonist are present, the partial agonist actually acts as a competitive antagonist , competing with the full agonist for receptor occupancy and producing a net decrease in the receptor activation observed with the full agonist alone. Clinically, partial agonists can be used to activate receptors to give a desired submaximal response when inadequate amounts of the endogenous ligand are present, or they can reduce the overstimulation of receptors when excess amounts of the endogenous ligand are present. Some currently common drugs that have been classed as partial agonists at particular receptors include buspirone, aripiprazole, buprenorphine, nalmefene and norclozapine. Examples of ligan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
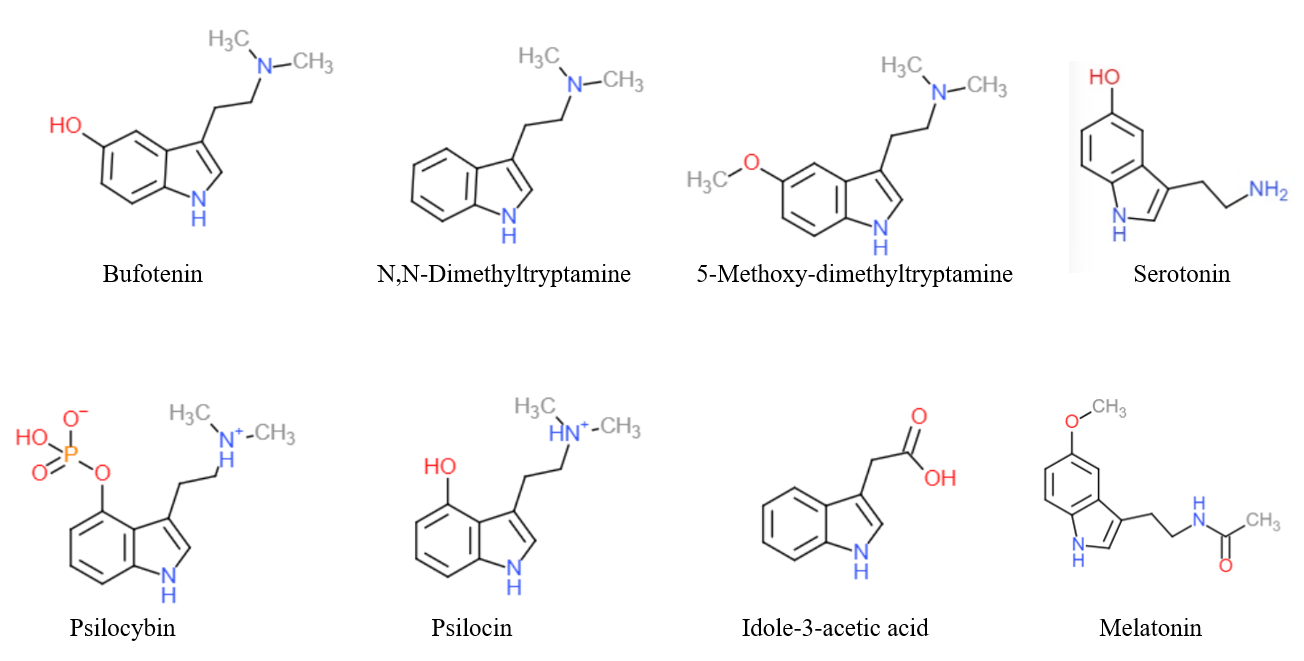
Tryptamine
Tryptamine is an indolamine metabolite of the essential amino acid, tryptophan. The chemical structure is defined by an indole ─ a fused benzene and pyrrole ring, and a 2-aminoethyl group at the second carbon (third aromatic atom, with the first one being the heterocyclic nitrogen). The structure of tryptamine is a shared feature of certain aminergic neuromodulators including melatonin, serotonin, bufotenin and psychedelic derivatives such as dimethyltryptamine (DMT), psilocybin, psilocin and others. Tryptamine has been shown to activate trace amine-associated receptors expressed in the mammalian brain, and regulates the activity of dopaminergic, serotonergic and glutamatergic systems. In the human gut, symbiotic bacteria convert dietary tryptophan to tryptamine, which activates 5-HT4 receptors and regulates gastrointestinal motility. Multiple tryptamine-derived drugs have been developed to treat migraines, while trace amine-associated receptors are being explored as a pot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Serotonin
Serotonin () or 5-hydroxytryptamine (5-HT) is a monoamine neurotransmitter. Its biological function is complex and multifaceted, modulating mood, cognition, reward, learning, memory, and numerous physiological processes such as vomiting and vasoconstriction. Approximately 90% of the serotonin that the body produces is in the intestinal tract. Biochemically, the indoleamine molecule derives from the amino acid tryptophan, via the (rate-limiting) Tryptophan hydroxylase, hydroxylation of the 5 position on the ring (forming the intermediate 5-Hydroxytryptophan, 5-hydroxytryptophan), and then Aromatic L-amino acid decarboxylase, decarboxylation to produce serotonin. Serotonin is primarily found in the enteric nervous system located in the human gastrointestinal tract, gastrointestinal tract (GI tract). However, it is also produced in the central nervous system (CNS), specifically in the raphe nuclei located in the brainstem, Merkel cells located in the skin, Neuroendocrine cell#Pulmo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Head-twitch Response
The head-twitch response (HTR) is a rapid side-to-side head movement that occurs in mice and rats after the serotonin 5-HT2A receptor is activated. The prefrontal cortex may be the neuroanatomical locus mediating the HTR. Many serotonergic hallucinogens, including lysergic acid diethylamide (LSD), induce the head-twitch response, and so the HTR is used as a behavioral model of hallucinogen effects. However while there is generally a good correlation between compounds that induce head twitch in mice and compounds that are hallucinogenic in humans, it is unclear whether the head twitch response is primarily caused by 5-HT2A receptors, 5-HT2C receptors or both, though recent evidence shows that the HTR is mediated by the 5-HT2A receptor and modulated by the 5-HT2C receptor. Also, the effect can be non-specific, with head twitch responses also produced by some drugs that do not act through 5-HT2 receptors, such as phencyclidine, yohimbine, atropine and cannabinoid receptor antagon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |