|
4-Hydroxymandelic Acid
4-Hydroxymandelic acid is a chemical compound used to synthesize atenolol. The compound typically occurs as a monohydrate. Synthesis and occurrence It is produced from 4-hydroxypyruvic acid by the action of the enzyme (''S'')-''p''-hydroxymandelate synthase: :HOC6H4CH2C(O)CO2H + O2 → HOC6H4CH(OH)CO2H + CO2 4-Hydroxymandelic acid can be synthesized by the condensation reaction of phenol and glyoxylic acid Glyoxylic acid or oxoacetic acid is an organic compound. Together with acetic acid, glycolic acid, and oxalic acid, glyoxylic acid is one of the C2 carboxylic acids. It is a colourless solid that occurs naturally and is useful industrially. Str ...: :HOC6H5 + CHOCO2H → HOC6H4CH(OH)CO2H See also * Vanillyl mandelic acid * 4-Hydroxyphenylacetic acid References {{DEFAULTSORT:Hydroxymandelic acid, 4- 4-Hydroxyphenyl compounds Acetic acids Alpha hydroxy acids ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chemical Compound
A chemical compound is a chemical substance composed of many identical molecules (or molecular entities) containing atoms from more than one chemical element held together by chemical bonds. A molecule consisting of atoms of only one element is therefore not a compound. A compound can be transformed into a different substance by a chemical reaction, which may involve interactions with other substances. In this process, bonds between atoms may be broken or new bonds formed or both. There are four major types of compounds, distinguished by how the constituent atoms are bonded together. Molecular compounds are held together by covalent bonds; ionic compounds are held together by ionic bonds; intermetallic compounds are held together by metallic bonds; coordination complexes are held together by coordinate covalent bonds. Non-stoichiometric compounds form a disputed marginal case. A chemical formula specifies the number of atoms of each element in a compound molecule, usin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atenolol
Atenolol is a beta blocker medication primarily used to treat high blood pressure and angina, heart-associated chest pain. Although used to treat high blood pressure, it does not seem to improve mortality rate, mortality in those with the condition. Other uses include the prevention of migraines and treatment of certain arrhythmia, irregular heart beats. It is taken oral administration, orally (by mouth) or by intravenous injection (injection into a vein). It can also be used with other blood pressure medications. Common side effects include fatigue (medical), feeling tired, heart failure, dizziness, depression (mood), depression, and shortness of breath. Other serious side effects include bronchospasm, bronchial spasm. Use is not recommended during pregnancy and alternative drugs are preferred when breastfeeding. It works by blocking Beta-1 adrenergic receptor, β1-adrenergic receptors in the heart, thus decreasing heart rate, cardiac contractility, force of heart beats, and b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monohydrate
In chemistry, a hydrate is a substance that contains water or its constituent elements. The chemical state of the water varies widely between different classes of hydrates, some of which were so labeled before their chemical structure was understood. Chemical nature Inorganic chemistry Hydrates are not inorganic salts "containing water molecules combined in a definite ratio as an integral part of the crystal" that are either bound to a metal center or that have crystallized with the metal complex. Such hydrates are also said to contain ''water of crystallization'' or ''water of hydration''. If the water is heavy water in which the constituent hydrogen is the isotope deuterium, then the term ''deuterate'' may be used in place of ''hydrate''. A colorful example is cobalt(II) chloride, which turns from blue to red upon hydration, and can therefore be used as a water indicator. The notation "''hydrated compound''⋅''n''", where ''n'' is the number of water molecules per formu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
(S)-p-hydroxymandelate Synthase
In enzymology, a 4-hydroxymandelate synthase () is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction :4-hydroxyphenylpyruvate + O2 \rightleftharpoons 4-hydroxymandelate + CO2 Thus, the two substrates of this enzyme are 4-hydroxyphenylpyruvate and oxygen, whereas its two products are 4-hydroxymandelate and carbon dioxide. This enzyme belongs to the family of oxidoreductases, specifically those acting on single donors with O2 as oxidant and incorporation of two atoms of oxygen into the substrate (oxygenases). The oxygen incorporated need not be derived from O2. The systematic name A systematic name is a name given in a systematic way to one unique group, organism, object or chemical substance, out of a specific population or collection. Systematic names are usually part of a nomenclature. A semisystematic name or semitrivi ... of this enzyme class is 4-hydroxyphenylpyruvate:oxygen oxidoreductase (decarboxylating). This enzyme is also called 4-hydroxyphenylpyruvate dioxygenase II ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phenol
Phenol (also known as carbolic acid, phenolic acid, or benzenol) is an aromatic organic compound with the molecular formula . It is a white crystalline solid that is volatile and can catch fire. The molecule consists of a phenyl group () bonded to a hydroxy group (). Mildly acidic, it requires careful handling because it can cause chemical burns. It is acutely toxic and is considered a health hazard. Phenol was first extracted from coal tar, but today is produced on a large scale (about 7 million tonnes a year) from petroleum-derived feedstocks. It is an important industrial commodity as a precursor to many materials and useful compounds, and is a liquid when manufactured. It is primarily used to synthesize plastics and related materials. Phenol and its chemical derivatives are essential for production of polycarbonates, epoxies, explosives such as picric acid, Bakelite, nylon, detergents, herbicides such as phenoxy herbicides, and numerous pharmaceuti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
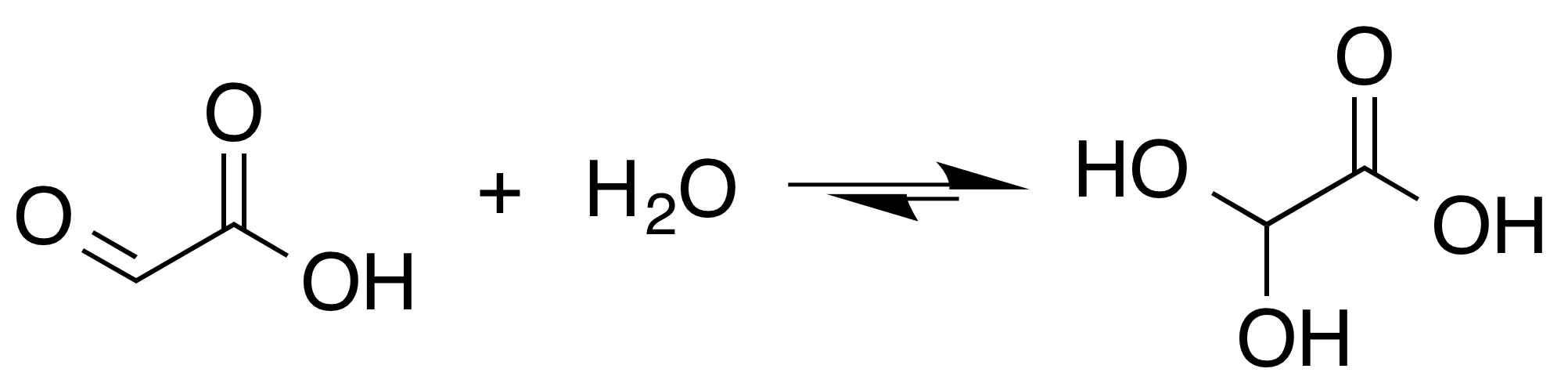
Glyoxylic Acid
Glyoxylic acid or oxoacetic acid is an organic compound. Together with acetic acid, glycolic acid, and oxalic acid, glyoxylic acid is one of the C2 carboxylic acids. It is a colourless solid that occurs naturally and is useful industrially. Structure and nomenclature The structure of glyoxylic acid is shown as having an aldehyde functional group. The aldehyde is only a minor component of the form most prevalent in some situations. Instead, glyoxylic acid often exists as a hydrate or a cyclic dimer (chemistry), dimer. For example, in the presence of water, the carbonyl rapidly converts to a geminal diol (described as the "monohydrate"). The equilibrium constant (''K'') is 300 for the formation of dihydroxyacetic acid at room temperature: Dihydroxyacetic acid has been characterized by X-ray crystallography. : In aqueous solution, this monohydrate exists in equilibrium with a hemiacylal dimer form:Georges Mattioda and Yani Christidis “Glyoxylic Acid” Ullmann's Encyclopedia of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vanillyl Mandelic Acid
Vanillylmandelic acid (VMA) is a chemical intermediate in the synthesis of artificial vanilla flavorings and is an end-stage metabolite of the catecholamines (epinephrine, and norepinephrine). It is produced via intermediary metabolites. Chemical synthesis VMA synthesis is the first step of a two-step process practiced by Rhodia since the 1970s to synthesize artificial vanilla. Specifically the reaction entails the condensation of guaiacol and glyoxylic acid in an ice cold, aqueous solution with sodium hydroxide. Biological elimination VMA is found in the urine, along with other catecholamine metabolites, including homovanillic acid (HVA), metanephrine, and normetanephrine. In timed urine tests the quantity excreted (usually per 24 hours) is assessed along with creatinine clearance, and the quantity of cortisols, catecholamines, and metanephrines excreted is also measured. Clinical significance Urinary VMA is elevated in patients with tumors that secrete catecholamines. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acetic Acids
Acetic acid , systematically named ethanoic acid , is an acidic, colourless liquid and organic compound with the chemical formula (also written as , , or ). Vinegar is at least 4% acetic acid by volume, making acetic acid the main component of vinegar apart from water. Historically, vinegar was produced from the third century BC and was likely the first acid to be produced in large quantities. Acetic acid is the second simplest carboxylic acid (after formic acid). It is an important chemical reagent and industrial chemical across various fields, used primarily in the production of cellulose acetate for photographic film, polyvinyl acetate for wood glue, and synthetic fibres and fabrics. In households, diluted acetic acid is often used in descaling agents. In the food industry, acetic acid is controlled by the food additive code E260 as an acidity regulator and as a condiment. In biochemistry, the acetyl group, derived from acetic acid, is fundamental to all forms of life ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |