|
2013 Tyrolean State Election
The 2013 Tyrolean state election was held on 28 April 2013 to elect the members of the Landtag of Tyrol. The election was contested by a large number of parties and saw a significant shift in support between them. The governing Austrian People's Party (ÖVP) Social Democratic Party of Austria (SPÖ), while suffering relatively small losses, each suffered their worst results in history. The Greens finished in third place just 1.1 percentage points behind the SPÖ, while the Freedom Party of Austria (FPÖ) suffered a downswing. The most notable loss of the election was the Fritz Dinkhauser List, which collapsed from a second-placed 18% in 2008 to just 5.6% in this election, making it the smallest party in the Landtag. Three new parties were considered contenders to enter the Landtag, though only one succeeded, with Forward Tyrol winning 9.5% and four seats. The Citizens' Club Tyrol, a splinter from the Fritz party, narrowly failed to win seats, as did Team Stronach. Despite its r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tyrol (state)
Tyrol (; german: Tirol ; it, Tirolo) is a state (''Land'') in western Austria. It comprises the Austrian part of the historical Princely County of Tyrol. It is a constituent part of the present-day Euroregion Tyrol–South Tyrol–Trentino (together with South Tyrol and Trentino in Italy). The capital of Tyrol is Innsbruck. Geography The state of Tyrol is separated into two parts, divided by a strip. The larger territory is called North Tyrol (''Nordtirol'') and the smaller area is called East Tyrol (''Osttirol''). The neighbouring Austrian state of Salzburg stands to the east, while on the south Tyrol has a border with the Italian province of South Tyrol ( Trentino-Alto Adige/Südtirol) which was part of the Austro-Hungarian Empire before the First World War. With a land area of , Tyrol is the third-largest state in Austria. Tyrol shares its borders with the federal state of Salzburg in the east and Vorarlberg in the west. In the north, it adjoins to the German state ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Imst District
The Bezirk Imst is an administrative district ('' Bezirk'') in Tyrol, Austria. It borders the district Reutte in the north, as well as sharing a small border with Bavaria (Germany). It borders the district Innsbruck-Land in the east, South Tyrol (Italy) in the south, and the district Landeck in the west. Area of the district is , which makes it by area rank 4 of the districts of Tyrol, with a population of 57,734 (as of January 1, 2012) (Number 6 in Tyrol), and a population density of 33 persons per km². The administrative center of the district is Imst. Geography The district comprises a part of the upper Inn valley, with its tributary valleys Ötztal, Pitztal, and Gurgltal, and the Mieming Plateau. The area is dominated by high alpine mountains. Mountain ranges include the Stubai Alps, Ötztal Alps, and Mieminger Mountains. The District is around 35 km from west to east and 80 km from north to south. The Highest mountain is the Wildspitze (3.768 meters), the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Innsbruck
Innsbruck (; bar, Innschbruck, label=Austro-Bavarian ) is the capital of Tyrol and the fifth-largest city in Austria. On the River Inn, at its junction with the Wipp Valley, which provides access to the Brenner Pass to the south, it had a population of 132,493 in 2018. In the broad valley between high mountains, the so-called North Chain in the Karwendel Alps (Hafelekarspitze, ) to the north and Patscherkofel () and Serles () to the south, Innsbruck is an internationally renowned winter sports centre; it hosted the 1964 and 1976 Winter Olympics as well as the 1984 and 1988 Winter Paralympics. It also hosted the first Winter Youth Olympics in 2012. The name means "bridge over the Inn". History Antiquity The earliest traces suggest initial inhabitation in the early Stone Age. Surviving pre-Roman place names show that the area has been populated continuously. In the 4th century the Romans established the army station Veldidena (the name survives in today's urban district Wilt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2013 Tyrolean State Election - Composition Chart
Thirteen or 13 may refer to: * 13 (number), the natural number following 12 and preceding 14 * One of the years 13 BC, AD 13, 1913, 2013 Music * 13AD (band), an Indian classic and hard rock band Albums * ''13'' (Black Sabbath album), 2013 * ''13'' (Blur album), 1999 * ''13'' (Borgeous album), 2016 * ''13'' (Brian Setzer album), 2006 * ''13'' (Die Ärzte album), 1998 * ''13'' (The Doors album), 1970 * ''13'' (Havoc album), 2013 * ''13'' (HLAH album), 1993 * ''13'' (Indochine album), 2017 * ''13'' (Marta Savić album), 2011 * ''13'' (Norman Westberg album), 2015 * ''13'' (Ozark Mountain Daredevils album), 1997 * ''13'' (Six Feet Under album), 2005 * ''13'' (Suicidal Tendencies album), 2013 * ''13'' (Solace album), 2003 * ''13'' (Second Coming album), 2003 * ''13'' (Ces Cru EP), 2012 * ''13'' (Denzel Curry EP), 2017 * ''Thirteen'' (CJ & The Satellites album), 2007 * ''Thirteen'' (Emmylou Harris album), 1986 * ''Thirteen'' (Harem Scarem album), 2014 * ''Thirte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pirate Party Of Austria
The Pirate Party of Austria (german: Piratenpartei Österreichs, PIRAT) is a political party in Austria and part of the global Pirate Party movement which advocates what has come to be known as Pirate politics. It is mostly known for opposing the Anti-Counterfeiting Trade Agreement. The party was founded by Florian Hufsky and Jürgen 'Juxi' Leitner during the run-up to the 2006 election in Austria, but failed to gather the necessary signatures to contest the election. On 14 March 2010, the PPÖ ran for municipal elections for its first time in the city of Bregenz and received 1.62% of the vote, however failed to win any seats. Christopher Clay, Marlies Wawra, Rodrigo Jorquera, Lukas Daniel Klausner and André Igler have been elected on 28 October 2012 to board members in the General Assembly of the Pirate Party Austria. Albert Gugerell has been elected as treasurer. In January Alexander Ofer, former member of the Tyrolean State Pirate Party, was expelled together with all state ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Communist Party Of Austria
The Communist Party of Austria (german: Kommunistische Partei Österreichs, KPÖ) is a communist party in Austria. Established in 1918 as the Communist Party of German-Austria (KPDÖ), it is one of the world's oldest communist parties. The KPÖ was banned between 1933 and 1945 under both the Austrofascist regime and the Nazi German administration of Austria after the 1938 ''Anschluss''. It played an important role in the Austrian resistance against the Nazis. The party currently holds two seats in the Styrian ''Landtag'' (state parliament), but has not had representation in the National Council (''Nationalrat'', Austria's federal parliament) since 1959. In the legislative election held on 29 September 2019, it won only 0.7% of the votes (32,736 out of a total of 4,835,469), well below the 4% minimum to obtain seats in the National Council. At the local level, the KPÖ has held the mayorship of Graz, Austria's second largest city, since 2021, and holds over 130 seats on district ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
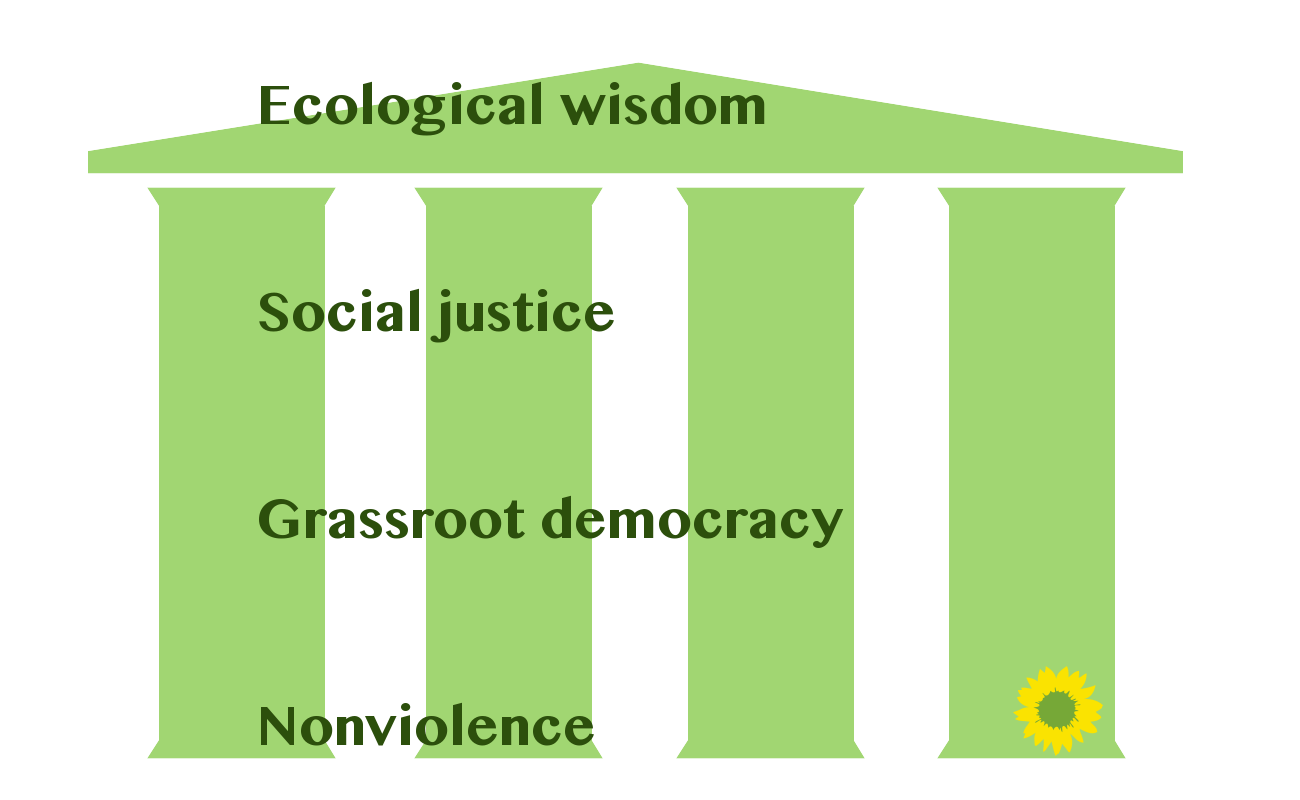
Green Politics
Green politics, or ecopolitics, is a political ideology that aims to foster an ecologically sustainable society often, but not always, rooted in environmentalism, nonviolence, social justice and grassroots democracy.#Wal10, Wall 2010. p. 12-13. It began taking shape in the western world in the 1970s; since then Green parties have developed and established themselves in many countries around the globe and have achieved some electoral success. The political term green was used initially in relation to ''Alliance '90/The Greens, die Grünen'' (German language, German for "the Greens"), a green party formed in the late 1970s. The term political ecology is sometimes used in academic circles, but it has come to represent an interdisciplinary field of study as the academic discipline offers wide-ranging studies integrating ecological social sciences with political economy in topics such as degradation and marginalization, environmental conflict, conservation and control and environmen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Euroscepticism
Euroscepticism, also spelled as Euroskepticism or EU-scepticism, is a political position involving criticism of the European Union (EU) and European integration. It ranges from those who oppose some EU institutions and policies, and seek reform (''Eurorealism'', ''Eurocritical'', or '' soft Euroscepticism''), to those who oppose EU membership and see the EU as unreformable (''anti-European Unionism'', ''anti-EUism'', or ''hard Euroscepticism''). The opposite of Euroscepticism is known as '' pro-Europeanism'', or ''European Unionism''. The main drivers of Euroscepticism have been beliefs that integration undermines national sovereignty and the nation state,''Euroscepticism or Europhobia: Voice vs Exit?'' [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Right-wing Populism
Right-wing populism, also called national populism and right-wing nationalism, is a political ideology that combines right-wing politics and populist rhetoric and themes. Its rhetoric employs anti-elitist sentiments, opposition to the Establishment, and speaking to or for the " common people". Recurring themes of right-wing populists include neo-nationalism, social conservatism, and economic nationalism. Frequently, they aim to defend a national culture, identity, and economy against perceived attacks by outsiders. Right-wing populism in the Western world is generally associated with ideologies such as anti-environmentalism, anti-globalization, nativism, and protectionism. In Europe, the term is often used to describe groups, politicians, and political parties generally known for their opposition to immigration, especially from the Muslim world, and for Euroscepticism. Right-wing populists may support expanding the welfare state, but only for those they deem fit to r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Social Democracy
Social democracy is a political, social, and economic philosophy within socialism that supports political and economic democracy. As a policy regime, it is described by academics as advocating economic and social interventions to promote social justice within the framework of a liberal-democratic polity and a capitalist-oriented mixed economy. The protocols and norms used to accomplish this involve a commitment to representative and participatory democracy, measures for income redistribution, regulation of the economy in the general interest, and social welfare provisions. Due to longstanding governance by social democratic parties during the post-war consensus and their influence on socioeconomic policy in Northern and Western Europe, social democracy became associated with Keynesianism, the Nordic model, the social-liberal paradigm, and welfare states within political circles in the late 20th century. It has been described as the most common form of Wester ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Populism
Populism refers to a range of political stances that emphasize the idea of "the people" and often juxtapose this group against " the elite". It is frequently associated with anti-establishment and anti-political sentiment. The term developed in the late 19th century and has been applied to various politicians, parties and movements since that time, often as a pejorative. Within political science and other social sciences, several different definitions of populism have been employed, with some scholars proposing that the term be rejected altogether. A common framework for interpreting populism is known as the ideational approach: this defines ''populism'' as an ideology which presents "the people" as a morally good force and contrasts them against "the elite", who are portrayed as corrupt and self-serving. Populists differ in how "the people" are defined, but it can be based along class, ethnic, or national lines. Populists typically present "the elite" as comprising the p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |