|
2012 Indian Ocean Earthquakes
The 2012 Indian Ocean earthquakes were Moment magnitude scale, magnitude 8.6 and 8.2 Submarine earthquake, undersea earthquakes that struck near the Indonesian province of Aceh on 11 April at 15:38 local time. Initially, authorities feared that the initial earthquake would cause a tsunami and warnings were issued across the Indian Ocean; however, these warnings were subsequently cancelled. These were unusually large intraplate earthquakes and the largest strike-slip earthquake ever recorded. Tectonic setting The 2012 earthquake's epicenter was located within the Indo-Australian plate, which is divided into two sub- or proto-plates: the Indian, and Australian. At their boundary, the Indian and Australian plates converge at per year in a NNW–SSE direction. This convergence is accommodated by a broad zone of wikt:diffuse, diffuse deformation. As part of that intraplate deformation, north–south trending fracture zones have been reactivated from the Ninety East Ridge as far e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fault (geology)
In geology, a fault is a Fracture (geology), planar fracture or discontinuity in a volume of Rock (geology), rock across which there has been significant displacement as a result of rock-mass movements. Large faults within Earth's crust (geology), crust result from the action of Plate tectonics, plate tectonic forces, with the largest forming the boundaries between the plates, such as the megathrust faults of subduction, subduction zones or transform faults. Energy release associated with rapid movement on active faults is the cause of most earthquakes. Faults may also displace slowly, by aseismic creep. A ''fault plane'' is the Plane (geometry), plane that represents the fracture surface of a fault. A ''fault trace'' or ''fault line'' is a place where the fault can be seen or mapped on the surface. A fault trace is also the line commonly plotted on geological maps to represent a fault. A ''fault zone'' is a cluster of parallel faults. However, the term is also used for the zone ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
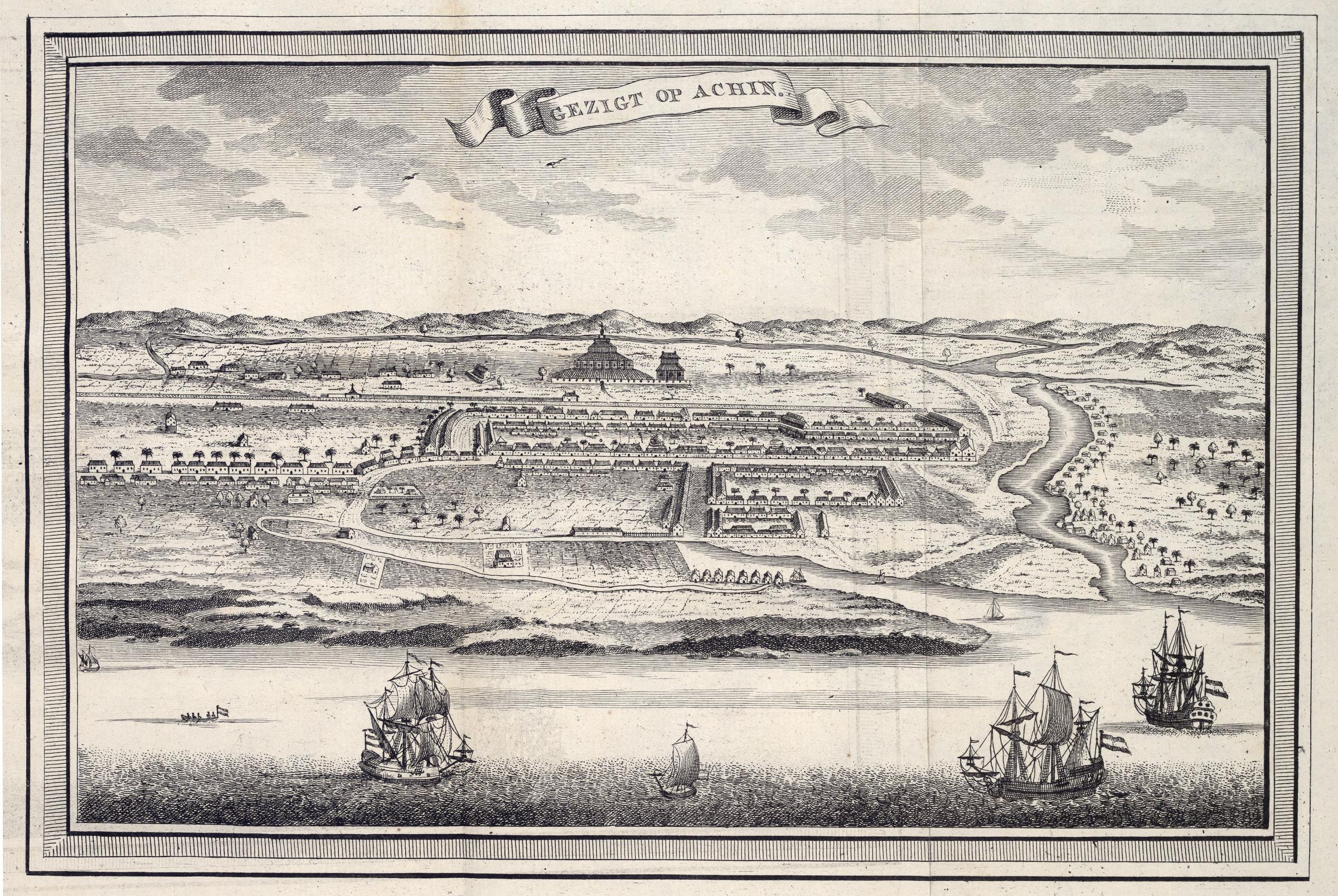
Banda Aceh
Banda Aceh (; , Jawi script, Jawi: ) is the capital and largest city in the province of Aceh, Indonesia. It is located on the island of Sumatra and has an elevation of 35 metres. The city covers an area of and had a population of 223,446 people at the 2010 Census,Biro Pusat Statistik, Jakarta, 2011. rising to 252,899 at the 2020 Census.Badan Pusat Statistik, Jakarta, 2021. The official estimate as at mid 2023 was 259,538.Badan Pusat Statistik, Jakarta, 26 September 2024, ''Kota Banda Aceh Dalam Angka 2024'' (sum of returns from District Katalogs as referenced below) Banda Aceh is located on the northwestern tip of Indonesia at the mouth of the Aceh River. Banda Aceh itself is a semi-enclave within Aceh Besar Regency, as Banda Aceh is surrounded by Aceh Besar to the south, east, and west, while it borders with the Strait of Malacca to the north. Many suburbs of the city have developed in adjacent districts of Acah Besar Regency beyond the city limits, notably to the south in Dar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lithosphere
A lithosphere () is the rigid, outermost rocky shell of a terrestrial planet or natural satellite. On Earth, it is composed of the crust and the lithospheric mantle, the topmost portion of the upper mantle that behaves elastically on time scales of up to thousands of years or more. The crust and upper mantle are distinguished on the basis of chemistry and mineralogy. Earth's lithosphere Earth's lithosphere, which constitutes the hard and rigid outer vertical layer of the Earth, includes the crust and the lithospheric mantle (or mantle lithosphere), the uppermost part of the mantle that is not convecting. The layer below the lithosphere is called the asthenosphere, which is the weaker, hotter, and deeper part of the upper mantle that is able to convect. The lithosphere–asthenosphere boundary is defined by a difference in response to stress. The lithosphere remains rigid for very long periods of geologic time in which it deforms elastically and through brittle f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Serpentinization
Serpentinization is a hydration and Metamorphic rock, metamorphic transformation of ferromagnesian minerals, such as olivine and pyroxene, in mafic and ultramafic rock to produce serpentinite. Minerals formed by serpentinization include the Serpentine subgroup, serpentine group minerals (antigorite, lizardite, chrysotile), brucite, talc, Ni-Fe alloys, and magnetite. The mineral alteration is particularly important at the sea floor at plate tectonics, tectonic plate boundaries. Formation and petrology Serpentinization is a form of low-temperature (0 to ~600 °C) metamorphism of ferromagnesian minerals in mafic and ultramafic rocks, such as dunite, harzburgite, or lherzolite. These are rocks low in silica and composed mostly of olivine (), pyroxene (), and chromite (approximately ). Serpentinization is driven largely by Mineral hydration, hydration and oxidation of olivine and pyroxene to serpentine subgroup, serpentine group minerals (antigorite, lizardite, and chrysotile), bru ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Upper Mantle (Earth)
The upper mantle of Earth is a very thick layer of rock inside the planet, which begins just beneath the crust (at about under the oceans and about under the continents) and ends at the top of the lower mantle the . Temperatures range from approximately at the upper boundary with the crust to approximately at the boundary with the lower mantle. Upper mantle material that has come up onto the surface comprises about 55% olivine, 35% pyroxene, and 5 to 10% of calcium oxide and aluminum oxide minerals such as plagioclase, spinel, or garnet, depending upon depth. Seismic structure The density profile through Earth is determined by the velocity of seismic waves. Density increases progressively in each layer, largely due to compression of the rock at increased depths. Abrupt changes in density occur where the material composition changes. The upper mantle begins just beneath the crust and ends at the top of the lower mantle. The upper mantle causes the tectonic plates to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Supershear Earthquake
In seismology, a supershear earthquake is when the propagation of the Earthquake rupture, rupture along the Fault (geology), fault surface occurs at speeds in excess of the seismic S wave, shear wave (S wave) velocity. This causes an effect analogous to a sonic boom. Rupture propagation velocity During seismic events along a fault surface the displacement initiates at the focus and then propagates outwards. Typically for large earthquakes the focus lies towards one end of the slip surface and much of the propagation is unidirectional (e.g. the 2008 Sichuan earthquake, 2008 Sichuan and 2004 Indian Ocean earthquakes). Theoretical studies have in the past suggested that the upper bound for propagation velocity is that of Rayleigh waves, approximately 0.92 of the shear wave velocity. However, evidence of propagation at velocities between S wave and P wave, compressional wave (P wave) values have been reported for several earthquakesArchuleta,R.J. 1984A faulting model for the 1979 Impe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geophysical Research Letters
''Geophysical Research Letters'' is a biweekly peer-reviewed scientific journal of geoscience published by the American Geophysical Union that was established in 1974. The editor-in-chief iKristopher Karnauskas Aims and scope The journal aims for rapid publication of concise research reports on one or more of the disciplines covered by the American Geophysical Union, such as atmospheric sciences, solid Earth, space science, oceanography, hydrology, land surface processes, and the cryosphere. The journal also publishes invited reviews that cover advances achieved during the past two or three years. The target readership is the earth science community, the broader scientific community, and the general public. Abstracting and indexing This journal is abstracted and indexed in: According to the 2020 ''Journal Citation Reports'', the journal has a 2019 impact factor of 4.58. ''Geophysical Research Letters'' was also the 5th most cited publication on climate change Pres ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Strike Slip Fault
In geology, a fault is a planar fracture or discontinuity in a volume of rock across which there has been significant displacement as a result of rock-mass movements. Large faults within Earth's crust result from the action of plate tectonic forces, with the largest forming the boundaries between the plates, such as the megathrust faults of subduction zones or transform faults. Energy release associated with rapid movement on active faults is the cause of most earthquakes. Faults may also displace slowly, by aseismic creep. A ''fault plane'' is the plane that represents the fracture surface of a fault. A '' fault trace'' or ''fault line'' is a place where the fault can be seen or mapped on the surface. A fault trace is also the line commonly plotted on geological maps to represent a fault. A ''fault zone'' is a cluster of parallel faults. However, the term is also used for the zone of crushed rock along a single fault. Prolonged motion along closely spaced faults can blur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Focal Mechanism
The focal mechanism of an earthquake describes the Fault (geology)#Slip.2C heave.2C throw, deformation in the Hypocenter, source region that generates the seismic waves. In the case of a Fault (geology), fault-related event, it refers to the orientation of the fault plane that slipped, and the slip Euclidean vector, vector and is also known as a fault-plane solution. Focal mechanisms are derived from a solution of the moment tensor for the earthquake, which itself is estimated by an analysis of observed seismic waveforms. The focal mechanism can be derived from observing the pattern of "first motions", whether the first arriving P waves break up or down. This method was used before waveforms were recorded and analysed digitally, and this method is still used for earthquakes too small for easy moment tensor solution. Focal mechanisms are now mainly derived using semi-automatic analysis of the recorded waveforms. Moment tensor solutions The moment tensor solution is displayed gra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
USGS Map Of The 2012 Indian Ocean Earthquake
The United States Geological Survey (USGS), founded as the Geological Survey, is an agency of the U.S. Department of the Interior whose work spans the disciplines of biology, geography, geology, and hydrology. The agency was founded on March 3, 1879, to study the landscape of the United States, its natural resources, and the natural hazards that threaten it. The agency also makes maps of planets and moons, based on data from U.S. space probes. The sole scientific agency of the U.S. Department of the Interior, USGS is a fact-finding research organization with no regulatory responsibility. It is headquartered in Reston, Virginia, with major offices near Lakewood, Colorado; at the Denver Federal Center; and in NASA Research Park in California. In 2009, it employed about 8,670 people. The current motto of the USGS, in use since August 1997, is "science for a changing world". The agency's previous slogan, adopted on its hundredth anniversary, was "Earth Science in the Public Ser ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
India
India, officially the Republic of India, is a country in South Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by area, seventh-largest country by area; the List of countries by population (United Nations), most populous country since 2023; and, since its independence in 1947, the world's most populous democracy. Bounded by the Indian Ocean on the south, the Arabian Sea on the southwest, and the Bay of Bengal on the southeast, it shares land borders with Pakistan to the west; China, Nepal, and Bhutan to the north; and Bangladesh and Myanmar to the east. In the Indian Ocean, India is near Sri Lanka and the Maldives; its Andaman and Nicobar Islands share a maritime border with Thailand, Myanmar, and Indonesia. Modern humans arrived on the Indian subcontinent from Africa no later than 55,000 years ago., "Y-Chromosome and Mt-DNA data support the colonization of South Asia by modern humans originating in Africa. ... Coalescence dates for most non-European populations averag ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maldives
The Maldives, officially the Republic of Maldives, and historically known as the Maldive Islands, is an Archipelagic state, archipelagic country in South Asia located in the Indian Ocean. The Maldives is southwest of Sri Lanka and India, about from the Asian continent's mainland. The Maldives' chain of Atolls of the Maldives, 26 atolls stretches across the equator from Atolls of the Maldives#Ihavandhippolhu, Ihavandhippolhu Atoll in the north to Addu Atoll in the south. The Maldives is the smallest List of sovereign states and dependent territories in Asia, country in Asia. Its land area is only , but this is spread over roughly of the sea, making it one of the world's most spatially dispersed sovereign states. With a population of 515,132 in the 2022 census, it is the second List of Asian countries by population, least populous country in Asia and the List of countries and dependencies by area, ninth-smallest country by area, but also one of the List of countries and depend ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |