|
1 Kings 7
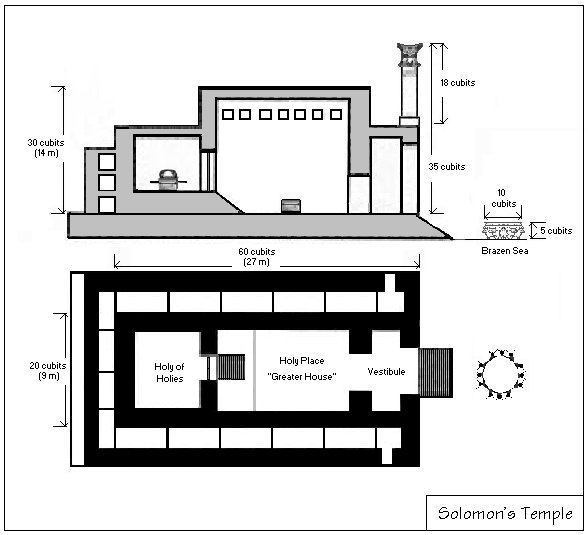
1 Kings 7 is the seventh Chapters and verses of the Bible, chapter of the Books of Kings in the Hebrew Bible or the First Book of Kings in the Old Testament of the Christianity, Christian Bible. The book is a compilation of various annals recording the acts of the kings of Israel and Judah by a Deuteronomic compiler in the seventh century BCE, with a supplement added in the sixth century BCE. This chapter belongs to the section focusing on the reign of Solomon over the unified kingdom of Judah and Israel (1 Kings 1 to 11). The focus of this chapter is the reign of Solomon, the king of Israel. Text This chapter was originally written in the Biblical Hebrew, Hebrew language and since the 16th century Chapters and verses of the Bible, is divided into 51 verses. Textual witnesses Some early manuscripts containing the text of this chapter in Biblical Hebrew, Hebrew are of the Masoretic Text tradition, which includes the Codex Cairensis (895), Aleppo Codex (10th century), and Leningrad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Books Of Kings
The Book of Kings (, ''Sefer (Hebrew), Sēfer Malik, Məlāḵīm'') is a book in the Hebrew Bible, found as two books (1–2 Kings) in the Old Testament of the Christian Bible. It concludes the Deuteronomistic history, a history of ancient Israel also including the books of Book of Joshua, Joshua, Book of Judges, Judges, and Books of Samuel, Samuel. Biblical commentators believe the Books of Kings mixes legends, folktales, miracle stories and "fictional constructions" in with the annals for the purpose of providing a Theology, theological explanation for the Siege of Jerusalem (587 BC), destruction of the Kingdom of Judah by Babylon in c. 586 BC and to provide a foundation for a return from Babylonian captivity, Babylonian exile.Sweeney, p1/ref> The two books of Kings present a history of ancient Israel and Judah, from the death of King David to the release of Jehoiachin from imprisonment in Babylon—a period of some 400 years (). Scholars tend to treat the books as cons ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Codex Vaticanus
The Codex Vaticanus ( The Vatican, Bibl. Vat., Vat. gr. 1209), is a manuscript of the Greek Bible, containing the majority of the Old Testament and the majority of the New Testament. It is designated by siglum B or 03 in the Gregory-Aland numbering of New Testament manuscripts, and as δ 1 in the von Soden numbering of New Testament manuscripts. It is one of the four great uncial codices. Along with Codex Alexandrinus and Codex Sinaiticus, it is one of the earliest and most complete manuscripts of the Bible. Using the study of comparative writing styles (palaeography), it has been dated to the 4th century. The manuscript became known to Western scholars as a result of correspondence between textual critic Desiderius Erasmus Roterodamus (known usually as Erasmus) and the prefects of the Vatican Library. Portions of the codex were collated by several scholars, but numerous errors were made during this process. The codex's relationship to the Latin Vulgate and the value Jerome ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Freemasonry
Freemasonry (sometimes spelled Free-Masonry) consists of fraternal groups that trace their origins to the medieval guilds of stonemasons. Freemasonry is the oldest secular fraternity in the world and among the oldest still-existing organizations in history. Modern Freemasonry broadly consists of three main traditions: *Anglo-American Freemasonry, Anglo-American style Freemasonry, which insists that a "volume of sacred law", such as the Bible, Quran, or other religious text be open in a working Masonic lodge, lodge, that every member professes belief in a God, supreme being, that only men be admitted, and discussion of religion or politics does not take place within the lodge. *Continental Freemasonry or Liberal Freemasonry which has continued to evolve beyond these restrictions, particularly regarding religious belief and political discussion. *Co-Freemasonry, Women Freemasonry or Co-Freemasonry, which includes organizations that either admit women exclusively (such as the Ord ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Allegory
As a List of narrative techniques, literary device or artistic form, an allegory is a wikt:narrative, narrative or visual representation in which a character, place, or event can be interpreted to represent a meaning with moral or political significance. Authors have used allegory throughout history in all forms of art to illustrate or convey complex ideas and concepts in ways that are comprehensible or striking to its viewers, readers, or listeners. Writers and speakers typically use allegories to convey (semi-) hidden or complex meanings through symbolism (arts), symbolic figures, actions, imagery, or events, which together create the moral, spiritual, or political meaning the author wishes to convey. Many allegories use personification of abstract concepts. Etymology First attested in English in 1382, the word ''allegory'' comes from Latin ''allegoria'', the latinisation (literature), latinisation of the Greek language, Greek ἀλληγορία (''allegoría''), "veiled ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hiram Abiff
Hiram Abiff (also Hiram Abif or the Widow's son) is the central character of an allegory presented to all candidates during the third Masonic degrees, degree in Freemasonry. Hiram is presented as the chief architect of Solomon's Temple, King Solomon's Temple. He is murdered inside this Temple by three ruffians, after they failed to obtain from him the Master Masons' secrets. The themes of the allegory are the importance of fidelity, and the certainty of death. The Masonic legend of Hiram Abiff The legend of Hiram Abiff as related in Anglo-American Masonic jurisdictions underpins the Third Degree and first appeared in the early 1720s. It generally starts with his arrival in Jerusalem, and his appointment by Solomon as chief architect and master of works at the construction of his temple. As the temple is nearing completion, three fellowcraft masons from the workforce ambush him as he leaves the building, demanding the secrets of a master mason. Hiram is challenged by each in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1 Kings 5
1 Kings 5 is the fifth chapter of the Books of Kings in the Hebrew Bible or the First Book of Kings in the Old Testament of the Christian Bible. The book is a compilation of various annals recording the acts of the kings of Israel and Judah by a Deuteronomic compiler in the seventh century BCE, with a supplement added in the sixth century BCE. This chapter belongs to the section focusing on the reign of Solomon over the unified kingdom of Judah and Israel (1 Kings 1 to 11). The focus of this chapter is the reign of Solomon, the king of Israel. Text This chapter was originally written in the Hebrew language and since the 16th century is divided into 18 verses. Textual witnesses Some early manuscripts containing the text of this chapter in Hebrew are of the Masoretic Text tradition, which includes the Codex Cairensis (895), Aleppo Codex (10th century), and Codex Leningradensis (1008). There is also a translation into Koine Greek known as the Septuagint, made in the last few cen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Modern English Version
The Modern English Version (MEV) is an English language, English Bible translations, translation of the Bible begun in 2005 and completed in 2014. The work was edited by James F. Linzey, and is an update of the King James Version (KJV), re-translated from the Masoretic Text and the ''Textus Receptus.'' History In June 2005, Southern Baptist Convention, Southern Baptist minister, chief editor, and executive director Rev. James F. Linzey assembled and directed the Committee on Bible Translation, which included Stanley M. Horton serving as the senior editorial advisor. The Committee produced an updated edition of the KJV called the MEV, which is the KJV in a more modern English vernacular. The translators began the work on June 2, 2005; they completed the New Testament on October 25, 2011, and the Old Testament on May 28, 2014."Preface," ''MEV Thinline Reference Bible, Modern English Version'', (p. xi) 2014. Passio Committee members include Eugene C. Ulrich, Stephen L. Herring, Eric ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pulpit Commentary
The ''Pulpit Commentary'' is a homiletic commentary on the Bible first published between 1880 and 1919 Vol. 4 at Barnes & Noble. Accessed 28 Feb 2024. and created under the direction of Rev. Joseph S. Exell and Henry Donald Maurice Spence-Jones. It consists of 23 volumes with 22,000 pages and 95,000 entries, and was written over a 30-year period with 100 contributors. Rev. Joseph S. Exell M.A. served as the editor of ''Clerical World'', ''The Homiletical Quarterly'' and the ''Monthly Interpreter''. Exell was also the editor for several other large commentary sets like ''The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antiquities Of The Jews
''Antiquities of the Jews'' (; , ''Ioudaikē archaiologia'') is a 20-volume historiographical work, written in Greek, by the Roman-Jewish historian Josephus in the 13th year of the reign of the Roman emperor Domitian, which was 94 CE. It contains an account of the history of the Jewish people for Josephus's gentile patrons. In the first ten volumes Josephus follows the events of the Hebrew Bible beginning with the creation of Adam and Eve. The second ten volumes continues the history of the Jewish people beyond the biblical text and up to the First Jewish–Roman War (66–73 CE). This work, along with Josephus's other major work, '' The Jewish War'' (''De Bello Iudaico''), provides valuable background material for historians wishing to understand 1st-century CE Judaism and the early Christian period. Stephen L. Harris, ''Understanding the Bible'', (Palo Alto: Mayfield, 1985). Content Josephus' ''Antiquities of the Jews'' is a vital source for the history of the intertes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Josephus
Flavius Josephus (; , ; ), born Yosef ben Mattityahu (), was a Roman–Jewish historian and military leader. Best known for writing '' The Jewish War'', he was born in Jerusalem—then part of the Roman province of Judea—to a father of priestly descent and a mother who claimed Hasmonean royal ancestry. He initially fought against the Roman Empire during the First Jewish–Roman War as general of the Jewish forces in Galilee, until surrendering in AD 67 to the Roman army led by military commander Vespasian after the six-week siege of Yodfat. Josephus claimed the Jewish messianic prophecies that initiated the First Jewish–Roman War made reference to Vespasian becoming Roman emperor. In response, Vespasian decided to keep him as a slave and presumably interpreter. After Vespasian became emperor in AD 69, he granted Josephus his freedom, at which time Josephus assumed the Emperor's family name of '' Flavius''. Flavius Josephus fully defected to the Roman s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |