|
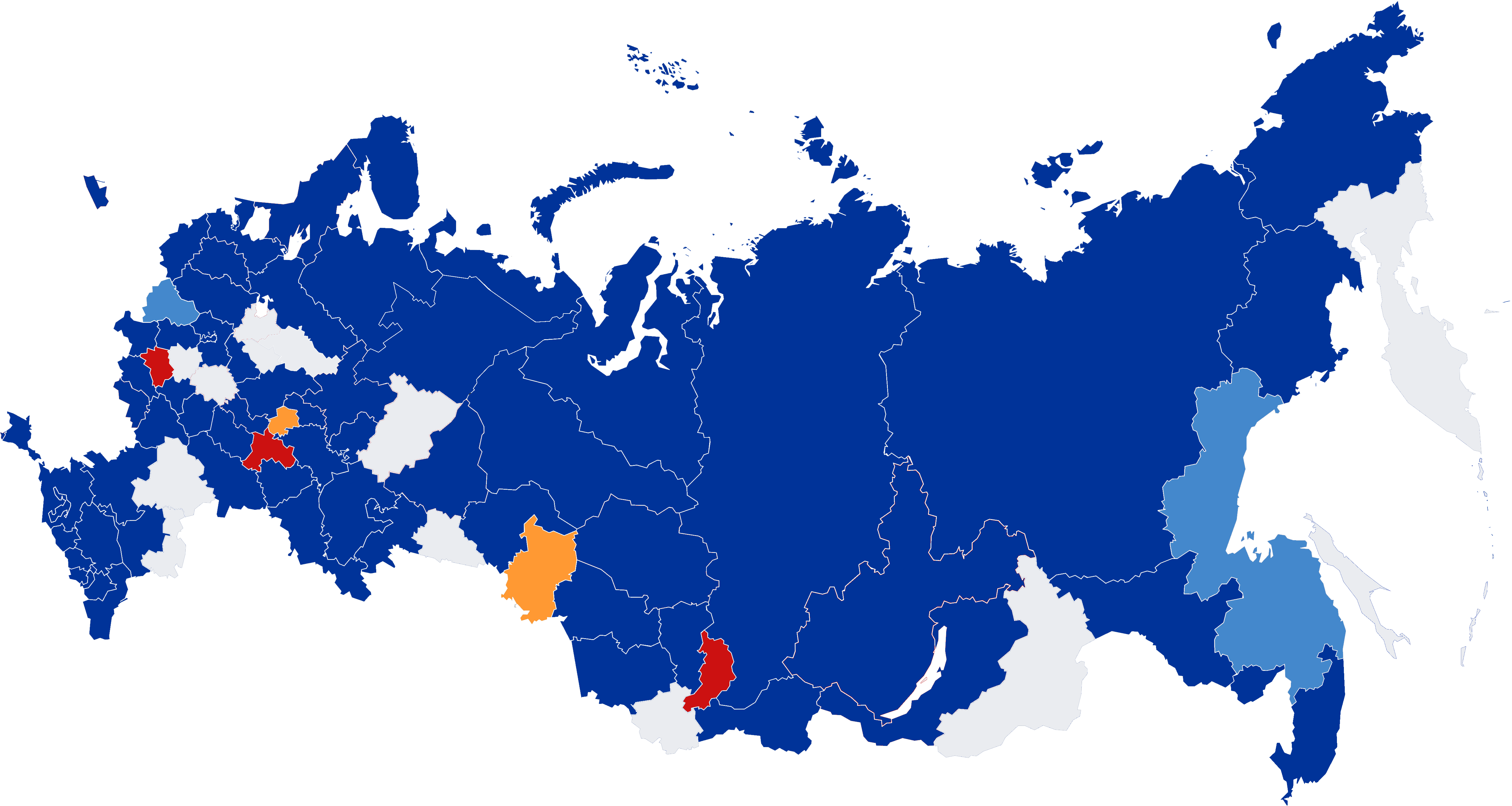
1998 Russian Gubernatorial Elections
Gubernatorial elections in 1998 took place in ten regions of the Russian Federation. Overview 1998 saw the re-election of the heads of administrations of the "first wave" elected in April 1993 in Lipetsk, Penza and Smolensk Oblasts and Krasnoyarsk Krai, as well as the presidents of Bashkortostan, Buryatia, Ingushetia and North Ossetia and the chairman of the government of Karelia. For the first time, direct elections were held in Mordovia. The transition to a presidential system was discussed in the last two parliamentary republics, Dagestan and Udmurtia. In Dagestan, on June 25, the Chairman of the State Council Magomedali Magomedov Magomedali Magomedovich Magomedov (russian: Магомедали Магомедович Магомедов; ; 15 June 1930 – 4 December 2022) was a Russian politician who served as the Head of the State Council of Dagestan from 1992 to 2006. ... was re-elected for a new term by the Constitutional Assembly, same as in 1994. In Udmurtia, membe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Current Heads Of Federal Subjects Of Russia
The following is a list of heads of the federal subjects of the Russian Federation. Republic of Crimea and the city of Sevastopol were annexed by Russia in 2014 and, according to its constitution, are Federal subjects. However, internationally these entities are recognized as part of Ukraine. Current Former This is a complete list of the former heads of the federal subjects of Russia. *Republic of Adygea: Aslan Tkhakushinov (2007–2017), Khazret Sovmen (2002–2007), Aslan Dzharimov (1992–2002) *Altai Republic: Alexander Berdnikov (2006–2019), Mikhail Lapshin (2002–2006), Semyon Zubakin (1998–2002), Vladilen Volkov (1997-1998), Valery Chaptynov (1994–1997) *Republic of Bashkortostan: Rustem Khamitov (2010–2018), Murtaza Rakhimov (1993–2010) *Republic of Buryatia: Vyacheslav Nagovitsyn (2007–2017), Leonid Potapov (1991–2007) *Chechen Republic: Alu Alkhanov (2004–2007), Sergey Abramov (2004, acting), Akhmad Kadyrov (2003–2004), Anatoly Popov (2003 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
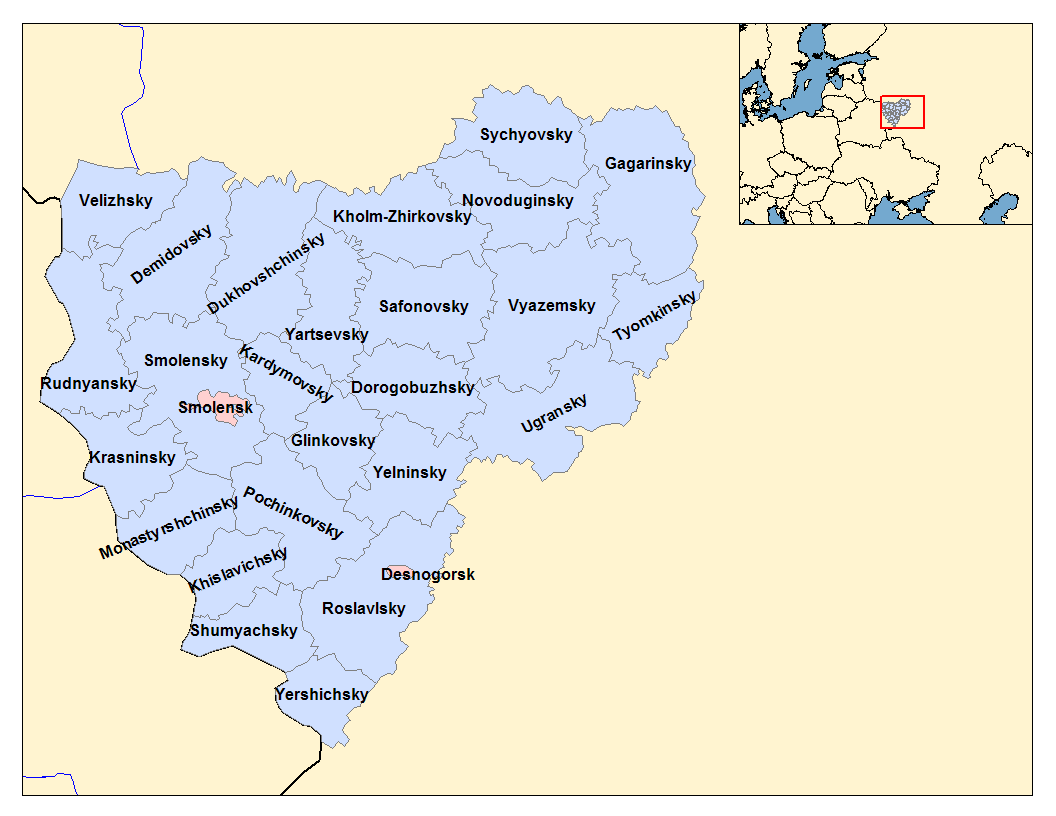
Smolensk Oblast
Smolensk Oblast (russian: Смоле́нская о́бласть, ''Smolenskaya oblast''; informal name — ''Smolenschina'' (russian: Смоле́нщина)) is a federal subject of Russia (an oblast). Its administrative centre is the city of Smolensk. As of the 2010 Census, its population was 985,537. Geography The oblast was founded on 27 September 1937.Исполнительный комитет Смоленского областного совета народных депутатов. Государственный архив Смоленской области. "Административно-территориальное устройство Смоленской области. Справочник", изд. "Московский рабочий", Москва 1981. Стр. 8 It borders Pskov Oblast in the north, Tver Oblast in the northeast, Moscow Oblast in the east, Kaluga Oblast in south, Bryansk Oblast in the southwest, and Mogilev and Vitebsk ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
People's Republican Party Of Russia
People's, branded as ''People's Viennaline'' until May 2018, and legally ''Altenrhein Luftfahrt GmbH'', is an Austrian airline headquartered in Vienna. It operates scheduled and charter passenger flights mainly from its base at St. Gallen-Altenrhein Airport in Switzerland. History Founded as People's Viennaline in 2010, the first revenue flight of the company took place on 27 March 2011. For several years, People's only operated a single scheduled route between its homebase and Vienna. However, the route network has since been expanded with some seasonal and charter services. In November 2016, People's inaugurated the world's shortest international jet route (and, after St. Maarten-Anguilla, second shortest international route overall). The flight from St. Gallen-Altenrhein Airport, Switzerland, to Friedrichshafen Airport, Germany, took only eight minutes of flight over Lake Constance and could have been booked individually. The airline faced severe criticism for this servic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Congress Of Russian Communities
The Congress of Russian Communities (CRC, russian: Конгресс русских общин, КРО, Kongress russkikh obschin, KRO) is a political organization in Russia. It was created in the early 1990s initially to promote the rights of ethnic Russians living in the newly independent countries of the former Soviet Union. The group contested a number of elections to the Duma in the 1990s. In the 1995 Duma election, the group took 4.3% of the vote, just missing the 5% threshold to gain seats. In 1999 it again failed to pass the 5% threshold, although KRO candidates did win a small number of single-mandate district seats. In 1996 Alexander Lebed used the KRO as the organisational vehicle for his campaign for the presidency. Lebed was surprisingly successful, taking 15% of the popular vote and later going on to become governor of Krasnoyarsk Krai. In 2006 the KRO was revived by Russian nationalist politician Dmitry Rogozin following the merger of his Rodina part ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alexander Lebed
Lieutenant General Alexander Ivanovich Lebed (russian: Алекса́ндр Ива́нович Ле́бедь, link=no; 20 April 1950 – 28 April 2002) was a Soviet and Russian military officer and politician who held senior positions in the Airborne Troops before running for president in the 1996 Russian presidential election. He did not win, but placed third behind incumbent Boris Yeltsin and the Communist Party leader Gennady Zyuganov, with roughly 14% of the vote nation-wide. Lebed later served as the Secretary of the Security Council in the Yeltsin administration, and eventually became the governor of Krasnoyarsk Krai, the second largest Russian region. He served four years in the latter position, until his death following a Mi-8 helicopter crash. He participated in most of Russia's military conflicts in the final decade of the Soviet Union, including the Soviet–Afghan War. From 1988 until 1991, General Lebed served as the commander of the 106th Guards Airborne Divisi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Krasnoyarsk Krai
Krasnoyarsk Krai ( rus, Красноя́рский край, r=Krasnoyarskiy kray, p=krəsnɐˈjarskʲɪj ˈkraj) is a federal subject of Russia (a krai), with its administrative center in the city of Krasnoyarsk, the third-largest city in Siberia (after Novosibirsk and Omsk). Comprising half of the Siberian Federal District, Krasnoyarsk Krai is the largest krai in the Russian Federation, the second largest federal subject (after neighboring Sakha) and the third largest subnational governing body by area in the world, after Sakha and the Australian state of Western Australia. The krai covers an area of , which is nearly one quarter the size of the entire country of Canada (the next-largest country in the world after Russia), constituting roughly 13% of the Russian Federation's total area and containing a population of 2,828,187 (more than a third of them in the city of Krasnoyarsk), or just under 2% of its population, per the 2010 Census. Geography The krai lies in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sergey Katanandov
Sergey Leonidovich Katanandov (russian: Сергей Леонидович Катанандов) is the former leader of the Republic of Karelia, an autonomous entity of Russia, in 1998–2010, first as Prime Minister, then as Head of the Republic. Katanandov was born in 1955, in the Karelian capital of Petrozavodsk. Educated in civil engineer A civil engineer is a person who practices civil engineering – the application of planning, designing, constructing, maintaining, and operating infrastructure while protecting the public and environmental health, as well as improving existing ...ing and law, Katanandov served as Mayor of Petrozavodsk from 1990 to 1998, and became Chairman of the Government of Karelia in 1998. From May 2002 till June 30, 2010, he was the Head of the Republic of Karelia. Biography Katanandov was born to Karelian parents in Petrozavodsk on April 21, 1955. He graduated from the Faculty of industrial and civil construction of Petrozavodsk State Universit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Viktor Stepanov (politician)
Viktor Nikolayevich Stepanov (russian: Виктор Николаевич Степанов, born 27 January 1947) is a Russian politician who was the prime minister of the Republic of Karelia in 1994–98. Biography Viktor Stepanov was born in 1947 in the village of Vidlitsa, Olonetsky District to a Karelian family. From 1964 to 1968 he was a carpenter at the Vidlinsky production site of the Ilyinsky sawmill. Party career Since 1968, the head of the organizational department, from 1970 to 1973 - the second, then the first secretary of the Olonetsky District Komsomol Committee. Since 1973 - an instructor, since 1974 - the head of the department, since 1976 - the second secretary of the Karelian regional committee of the Komsomol. Since 1980 - instructor of the Karelian regional committee of the CPSU. From 1980 to 1982 Stepanov was the second secretary of the Olonetsky district party committee, in 1982–84 he was the first secretary of the Pryazhinsky District committee. S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kommersant
''Kommersant'' (russian: Коммерсантъ, , ''The Businessman'' or Commerce Man, often shortened to Ъ) is a nationally distributed daily newspaper published in Russia mostly devoted to politics and business. The TNS Media and NRS Russia certified July 2013 circulation of the daily was 120,000–130,000. It is owned by Alisher Usmanov. History In 1989, with the onset of press freedom in Russia, ''Kommersant'' was founded under the ownership of businessman and publicist Vladimir Yakovlev. The first issue was released in January 1990. It was modeled after Western business journalism. The newspaper's title is spelled in Russian with a terminal hard sign (ъ) – a letter that is silent at the end of a word in modern Russian, and was thus largely abolished by the post-revolution Russian spelling reform, in reference to a pre-Soviet newspaper of the same name active between 1909 and 1917. This is played up in the Kommersant logo, which features a script hard sign at ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Karelia
Karelia ( Karelian and fi, Karjala, ; rus, Каре́лия, links=y, r=Karélija, p=kɐˈrʲelʲɪjə, historically ''Korjela''; sv, Karelen), the land of the Karelian people, is an area in Northern Europe of historical significance for Russia (including the Soviet era), Finland, and Sweden. It is currently divided between northwestern Russia (specifically the federal subjects of the Republic of Karelia and Leningrad Oblast) and Finland (the regions of South Karelia, North Karelia, and the eastern portion of modern-day Kymenlaakso). Use of name Various subdivisions may be called Karelia. Finnish Karelia was a historical province of Finland, and is now divided between Finland and Russia, often called just ''Karjala'' in Finnish. The eastern part of this chiefly Lutheran area was ceded to Russia after the Winter War of 1939–40. The Republic of Karelia is a Russian federal subject, including East Karelia with a chiefly Russian Orthodox population. Withi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CPRF
The Communist Party of the Russian Federation (CPRF; russian: Коммунистическая Партия Российской Федерации; КПРФ, Kommunisticheskaya Partiya Rossiyskoy Federatsii; KPRF) is a left-wing nationalist and communist political party in Russia that officially adheres to Marxist–Leninist philosophy. It is the second-largest political party in Russia after United Russia. The youth organisation of the party is the Leninist Young Communist League. The CPRF can trace its origins to the Russian Social Democratic Labour Party which was established in 1898 and the party split in 1903 into a Menshevik (minority) and Bolshevik (majority) faction; the latter, led by Vladimir Lenin, is the direct ancestor of the Communist Party of the Soviet Union (CPSU) and is the party that seized power in the October Revolution of 1917. After the CPSU was banned in 1991 by then–Russian President Boris Yeltsin in the aftermath of the failed coup attempt, the CP ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |