|
1990 Saxony State Election
The 1990 Saxony state election was held on 14 October 1990 to elect the members of the first Landtag of Saxony. It was the first election held in Saxony since the reunification of Germany, which took place on 3 October. The Christian Democratic Union (CDU) led by Kurt Biedenkopf dominated the election with 53.8% of the vote, followed by the Social Democratic Party (SPD) with 19.1%. Biedenkopf subsequently became Saxony's first post-reunification Minister-President. Parties The table below lists parties which won seats in the election. Election result , - ! colspan="2" , Party ! Votes ! % ! Seats ! Seats % , - , bgcolor=, , align=left , Christian Democratic Union (CDU) , align= 1,417,332 , align= 53.8 , align= 92 , align= 57.5 , - , bgcolor=, , align=left , Social Democratic Party (SPD) , align= 502,755 , align= 19.1 , align= 32 , align= 20.0 , - , bgcolor=, , align=left , Party of Democratic Socialism (PDS) , align= 269,420 , align= 10.2 , align= ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Landtag Of Saxony
The Landtag of Saxony (), also known in English as the Saxon State Parliament, is the legislature of the Free State of Saxony, one of Germany's sixteen states. It is responsible for legislation, control of the government, and electing some state officials. The Landtag has existed in various forms since 1831, but the current body was established during German reunification in 1990. The Landtag is directly elected and has a term of five years. Powers As the legislative body of the Free State of Saxony, the Landtag is responsible for drafting and passing laws, including the state budget, as well as overseeing the activities of the state government and electing the Minister-President, the head of government. Draft laws may be introduced to the Landtag in various ways: by the proposal of at least six members, by any parliamentary group, by the state government, or by public petition. Draft laws are first sent by the President of the Landtag to a relevant committee, which considers ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Social Democracy
Social democracy is a Social philosophy, social, Economic ideology, economic, and political philosophy within socialism that supports Democracy, political and economic democracy and a gradualist, reformist, and democratic approach toward achieving social equality. In modern practice, social democracy has taken the form of predominantly capitalist economies, a robust welfare state, policies promoting social justice, market regulation, and a more Redistribution of income and wealth, equitable distribution of income. Social democracy maintains a commitment to Representative democracy, representative and participatory democracy. Common aims include curbing Social inequality, inequality, eliminating the oppression of Social privilege, underprivileged groups, eradicating poverty, and upholding universally accessible public services such as child care, Universal education, education, elderly care, Universal health care, health care, and workers' compensation. Economically, it support ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Elections In Saxony
An election is a formal group decision-making process whereby a population chooses an individual or multiple individuals to hold public office. Elections have been the usual mechanism by which modern representative democracy has operated since the 17th century. Elections may fill offices in the legislature, sometimes in the executive and judiciary, and for regional and local government. This process is also used in many other private and business organizations, from clubs to voluntary association and corporations. The global use of elections as a tool for selecting representatives in modern representative democracies is in contrast with the practice in the democratic archetype, ancient Athens, where the elections were considered an oligarchic institution and most political offices were filled using sortition, also known as allotment, by which officeholders were chosen by lot. Electoral reform describes the process of introducing fair electoral systems where they are not ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
German Social Union (East Germany)
The German Social Union (, DSU) is a small conservative political party mainly active in the new states of Germany. It was founded in 1990 as a right-wing opposition group during the '' Wende'' transition to democracy in East Germany, when it was part of the Alliance for Germany electoral coalition. After 1990, it fell into insignificance, only holding a few seats on the local level. Ideology According to its 2006 basic programme, the DSU refers to itself as a conservative, democratic and social party. Ideologically, the party's goals are to preserve and uphold Western-Christian civilization, and to dismantle the welfare state.. The party can thus be seen as right-wing (anti-socialistic) national-conservative. It strongly differentiates itself from the National Democratic Party (NPD) and German People's Union (DVU), who tend more towards national socialism. Its closest ideological ally among the right-wing parties is The Republicans. Historically, and as its name implies, it i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SN Landtagswahl 1990
SN, Sn, sn, .sn, or s.n. may refer to: Businesses and organizations *Brussels Airlines (IATA code: SN) ** Sabena **SN Brussels Airlines (IATA code: SN) *Servant of the People (''Sluha Narodu''), political party in Ukraine * Slovaks Forward (''Slovaci Napred''), a political party in Serbia *Standards Norway, the main standards organization of Norway * (National Party), a Polish political party *Supreme Court of Poland (''Sąd Najwyższy''), the court of last resort for non-administrative matters Places *Senegal (ISO country code SN) *Shaanxi, a province of China (Guobiao abbreviation SN) *South Sulawesi, a province of Indonesia (ISO 3166-2:ID code) *Saxony, a state of Germany *SN postcode area, the UK postcode district containing Swindon and much of North Wiltshire Religion * Samyutta Nikaya or SN, a Buddhist scripture *Sutta Nipata or Sn, a Buddhist scripture Science, technology, and mathematics Computing * .sn, the country-code top level domain of Senegal *sn, the ''surname' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Classical Liberalism
Classical liberalism is a political tradition and a branch of liberalism that advocates free market and laissez-faire economics and civil liberties under the rule of law, with special emphasis on individual autonomy, limited government, economic freedom, political freedom and freedom of speech. Classical liberalism, contrary to progressive branches like social liberalism, looks more negatively on social policies, taxation and the state involvement in the lives of individuals, and it advocates deregulation. Until the Great Depression and the rise of social liberalism, classical liberalism was called economic liberalism. Later, the term was applied as a retronym, to distinguish earlier 19th-century liberalism from social liberalism. By modern standards, in the United States, the bare term ''liberalism'' often means social or progressive liberalism, but in Europe and Australia, the bare term ''liberalism'' often means classical liberalism. Classical liberalism ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Free Democratic Party (Germany)
The Free Democratic Party (, FDP, ) is a liberalism, liberal political party in Germany. The FDP was founded in 1948 by members of former liberal political parties in Germany before World War II, namely the German Democratic Party and the German People's Party. For most of the second half of the 20th century, particularly from 1961 to 1982, the FDP held the Balance of power (parliament), balance of power in the Bundestag. It has been a junior coalition partner to both the CDU/CSU (1949–1956, 1961–1966, 1982–1998, and 2009–2013) and Social Democratic Party of Germany, Social Democratic Party (SPD; 1969–1982 and 2021–2024). In the 2013 German federal election, 2013 federal election, the FDP failed to win any directly elected seats in the Bundestag and came up short of the Electoral threshold#Germany, 5 percent threshold to qualify for list representation, being left without representation in the Bundestag for the first time in its history. In the 2017 German federal el ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
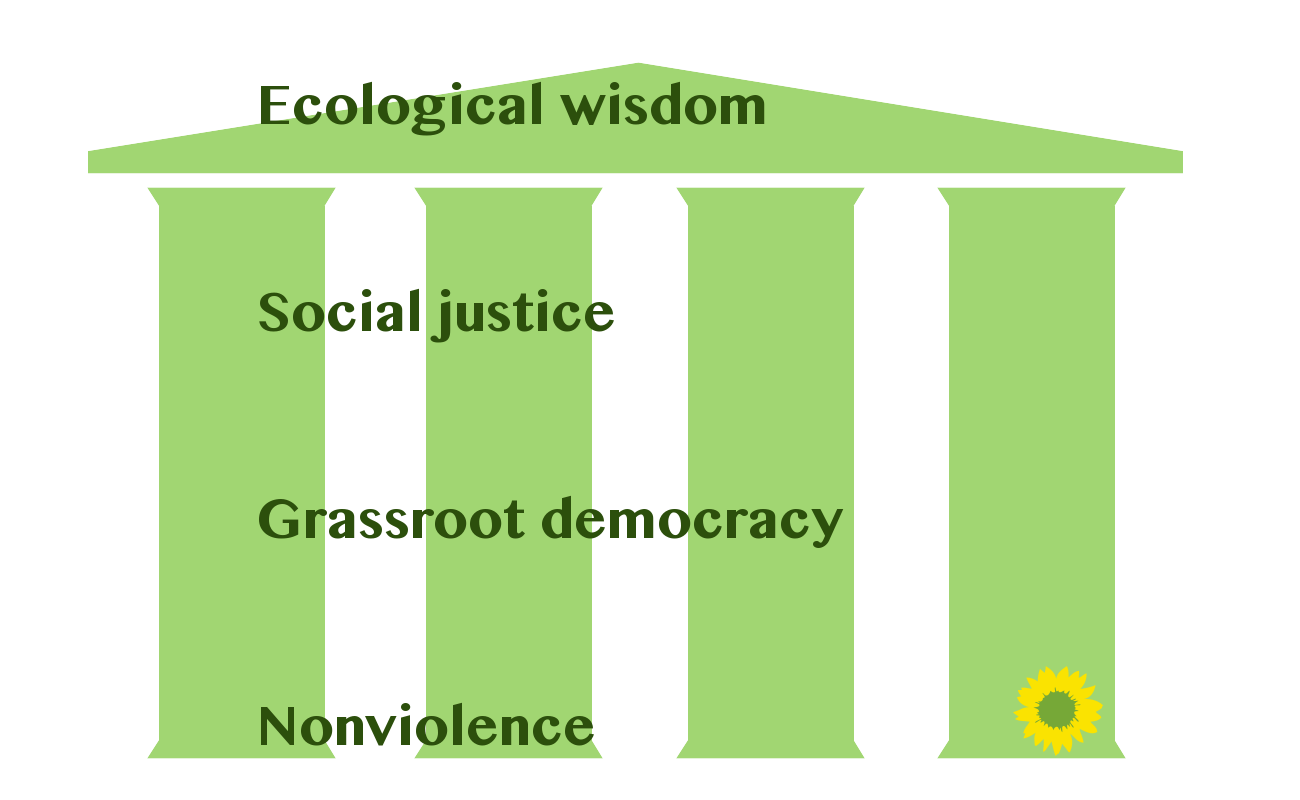
Green Politics
Green politics, or ecopolitics, is a political ideology that aims to foster an ecologically sustainable society often, but not always, rooted in environmentalism, nonviolence, social justice and grassroots democracy.#Wal10, Wall 2010. p. 12-13. It began taking shape in the Western world in the 1970s; since then, green parties have developed and established themselves in many countries around the globe and have achieved some electoral success. The political term ''green'' was used initially in relation to ''Alliance 90/The Greens, die Grünen'' (German for "the Greens"), a green party formed in the late 1970s. The term ''political ecology'' is sometimes used in academic circles, but it has come to represent an interdisciplinary field of study as the academic discipline offers wide-ranging studies integrating ecological social sciences with political economy in topics such as degradation and marginalization, environmental conflict, conservation and control and environmental identi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Democratic Socialism
Democratic socialism is a left-wing economic ideology, economic and political philosophy that supports political democracy and some form of a socially owned economy, with a particular emphasis on economic democracy, workplace democracy, and workers' self-management within a market socialist, decentralised planned, or democratic Centrally planned economies, centrally planned socialist economy. Democratic socialists argue that capitalism is inherently incompatible with the values of freedom, Egalitarianism, equality, and solidarity and that these Ideal (ethics), ideals can only be achieved through the realisation of a socialist society. Although most democratic socialists seek a gradual transition to socialism, democratic socialism can support revolutionary or reformist politics to establish socialism. ''Democratic socialism'' was popularised by socialists who opposed the backsliding towards a one-party state in the Soviet Union and other countries during the 20th century. The his ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Party Of Democratic Socialism (Germany)
A party is a gathering of people who have been invited by a host for the purposes of socializing, conversation, recreation, or as part of a festival or other commemoration or celebration of a special occasion. A party will often feature food and beverages, and often conversation, music, dancing, or other forms of entertainment. Some parties are held in honor of a specific person, day, or event, such as a birthday party, a Super Bowl party, or a St. Patrick's Day party. Parties of this kind are often called celebrations. A party is not necessarily a private occasion. Public parties are sometimes held in restaurants, pubs, beer gardens, nightclubs, or bars, and people attending such parties may be charged an admission fee by the host. Large parties in public streets may celebrate events such as Mardi Gras or the signing of a peace treaty ending a long war. Types Balls Banquets Birthday party A birthday party is a celebration of the anniversary of the birt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Christian Democracy
Christian democracy is an ideology inspired by Christian social teaching to respond to the challenges of contemporary society and politics. Christian democracy has drawn mainly from Catholic social teaching and neo-scholasticism, as well as the Neo-Calvinist tradition within Christianity; it later gained ground with Lutherans and Pentecostals, among other denominational traditions of Christianity in various parts of the world. During the nineteenth century, its principal concerns were to reconcile Catholicism with democracy, to answer the " social question" surrounding capitalism and the working class, and to resolve the tensions between church and state. In the twentieth century, Christian democrats led postwar Western and Southern Europe in building modern welfare states and constructing the European Union. Furthermore; in the late twentieth and early twenty-first century, Christian democracy has gained support in Eastern Europe among former communist states sufferi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |