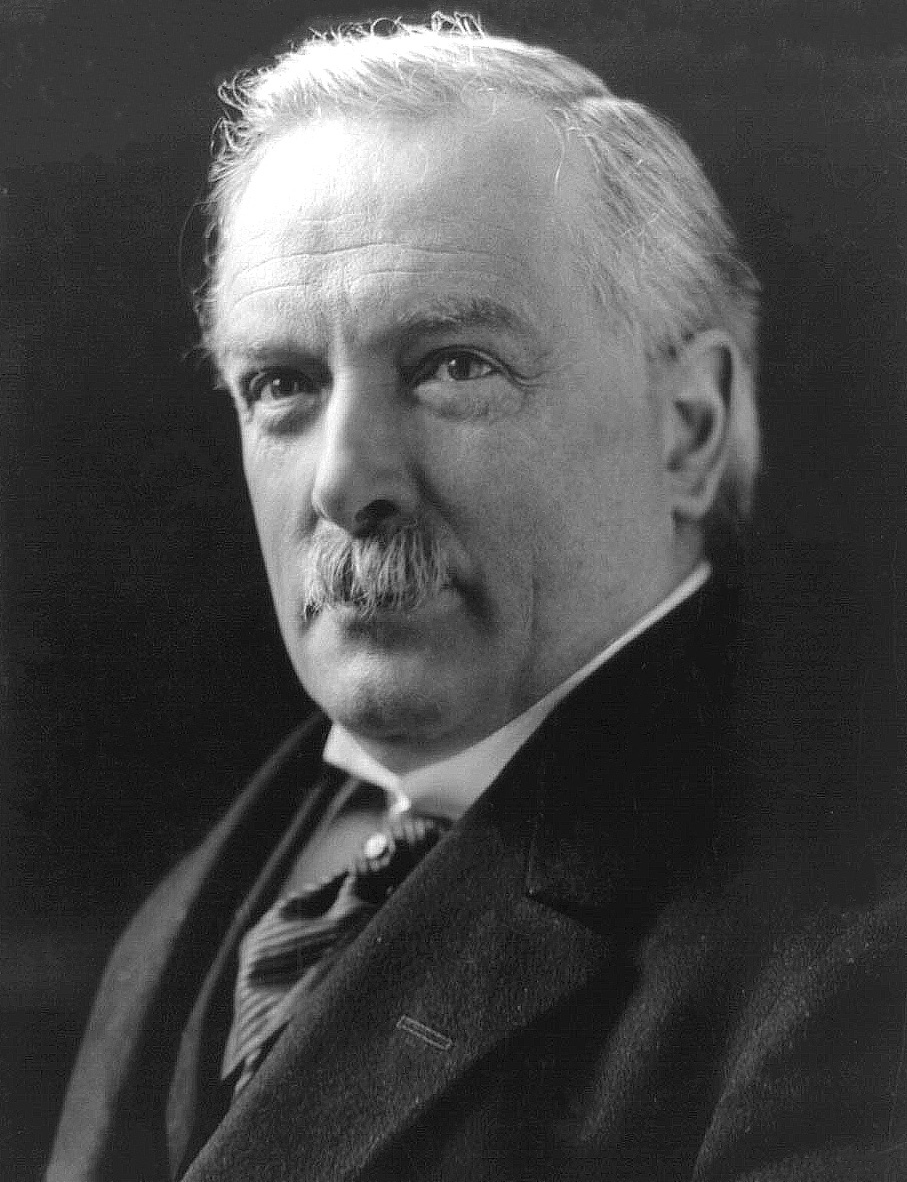|
1929 UK General Election
The 1929 United Kingdom general election was held on Thursday, 30 May 1929, with Parliament dissolved on 10 May. It resulted in a hung parliament: despite receiving fewer votes than the Conservative Party (UK), Conservative Party, led by Prime Minister of the United Kingdom, Prime Minister Stanley Baldwin, Ramsay MacDonald's Labour Party (UK), Labour Party won the most seats in the House of Commons of the United Kingdom, House of Commons, with the Liberal Party (UK), Liberal Party, led again by former Prime Minister David Lloyd George, regaining some of the ground lost in 1924 United Kingdom general election, 1924 and holding the balance of power. The election was often referred to as the "Flapper Election", because it was the first in which women aged 21–29 had the right to vote (owing to the Representation of the People Act 1928). Women over 30, with some property qualifications, had been able to vote since the 1918 United Kingdom general election, 1918 general election, but ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Constituency Election Results In The 1929 United Kingdom General Election
This is a complete alphabetical list of constituency election results to the 35th Parliament of the United Kingdom at the 1929 United Kingdom general election, 1929 general election, held on 30 May 1929. Notes *Change in % vote and swing is calculated between the winner and second place and their respective performances at the 1924 election. A plus denotes a swing to the winner and a minus against the winner. England Wales Scotland Northern Ireland Universities Notes References [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Liberal Party (UK)
The Liberal Party was one of the two Major party, major List of political parties in the United Kingdom, political parties in the United Kingdom, along with the Conservative Party (UK), Conservative Party, in the 19th and early 20th centuries. Beginning as an alliance of Whigs (British political party), Whigs, free trade–supporting Peelites, and reformist Radicals (UK), Radicals in the 1850s, by the end of the 19th century, it had formed four governments under William Ewart Gladstone. Despite being divided over the issue of Irish Home Rule, the party returned to government in 1905 and won a landslide victory in the 1906 United Kingdom general election, 1906 general election. Under Prime Minister of the United Kingdom, prime ministers Henry Campbell-Bannerman (1905–1908) and H. H. Asquith (1908–1916), the Liberal Party passed Liberal welfare reforms, reforms that created a basic welfare state. Although Asquith was the Leader of the Liberal Party (UK), party leader, its domin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1983 United Kingdom General Election
The 1983 United Kingdom general election was held on Thursday 9 June 1983. It gave the Conservative Party (UK), Conservative Party under the leadership of Margaret Thatcher the most decisive election victory since that of the Labour Party (UK), Labour Party in 1945 United Kingdom general election, 1945, with a majority of 144 seats and the first of two consecutive landslide victories. Thatcher's first term as Prime Minister of the United Kingdom, Prime Minister had not been an easy time. Unemployment increased during the first three years of her premiership and the economy went Early 1980s recession, through a recession. However, the British victory in the Falklands War led to a recovery of her personal popularity, and economic growth had begun to resume. By the time Thatcher called the election in May 1983, opinion polls pointed to a Conservative victory, with most national newspapers backing the re-election of the Conservative government. The resulting win earned the Conserv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plaid Cymru
Plaid Cymru ( ; , ; officially Plaid Cymru – the Party of Wales, and often referred to simply as Plaid) is a centre-left, Welsh nationalist list of political parties in Wales, political party in Wales, committed to Welsh independence from the United Kingdom. It campaigns on a platform of social democracy and civic nationalism. The party is a supporter of the European Union and is a member of the European Free Alliance (EFA). The party holds 4 of 32 Welsh seats in the UK Parliament, 12 of 60 seats in the Senedd, and 202 of 1,231 principal local authority councillors. Plaid was formed in 1925 under the name ''Plaid Genedlaethol Cymru'' (English: The National Party of Wales) and Gwynfor Evans won the first Westminster seat for the party at the 1966 Carmarthen by-election. In 1999 National Assembly for Wales election, 1999 (in the first devolved Senedd, Welsh Assembly election), Plaid Cymru gained considerable ground in traditionally Labour heartlands. These breakthroughs were pa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Liberal Party (UK, 1922)
The National Liberal Party was a liberal political party in the United Kingdom from 1922 to 1923. It was created as a formal party organisation for those Liberals, led by Prime Minister David Lloyd George, who supported the Coalition Government (1918–22) and subsequently a revival of the Coalition, after it ceased holding office. It was officially a breakaway from the Liberal Party. The National Liberals ceased to exist in 1923 when Lloyd George agreed to a merger with the Liberal Party. History Origin The " Coalition Coupon", often referred to as "the coupon", referred to the letter sent to parliamentary candidates at the 1918 general election, endorsing them as official representatives of the Coalition Government. The overdue 1918 general election took place in the heady atmosphere of victory following the First World War and the desire for revenge against Germany and its allies. Receiving the coupon was interpreted by the electorate as a sign of patriotism that helped candi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Independent Liberal Party (UK, 1918)
The Independent Liberal Party is a name used for the Parliamentary Liberal Party created in 1918 and led by H. H. Asquith, in opposition to the Coalition government led by the Liberal David Lloyd George. The Coalition candidates (whether Conservatives or Liberal) were marked at the 1918 election by the Coalition Coupon. In fact, the parliamentary party was not independent from the Liberal Party, of which it formed part. Rather, it was independent of Lloyd George. It was sometimes known by the epithet the Wee Free Party. The issuing of the Coalition Coupon to some Liberals, but not to others, led Asquith's followers to form a Parliamentary Liberal Party in opposition to them, so that in most constituencies the election of 1918 saw a three-way contest between the Coalition Government, the Independent Liberal Party, and the Labour Party. After the 1918 election, the party remained in existence in parliament until 1922, although greatly weakened. Only 28 were returned, and even A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Second Baldwin Ministry
Stanley Baldwin of the Conservative Party formed the second Baldwin ministry upon his reappointment as Prime Minister of the United Kingdom by King George V after the 1924 general election. His second ministry ended following the so-called " Flapper Election" of May 1929. Cabinet November 1924 – June 1929 * Stanley Baldwin – Prime Minister and Leader of the House of Commons * George Cave, 1st Viscount Cave – Lord High Chancellor of Great Britain * George Curzon, 1st Marquess Curzon of Kedleston – Leader of the House of Lords and Lord President of the Council * James Gascoyne-Cecil, 4th Marquess of Salisbury – Lord Keeper of the Privy Seal *Winston Churchill – Chancellor of the Exchequer *Sir William Joynson-Hicks – Secretary of State for the Home Department *Sir Austen Chamberlain – Secretary of State for Foreign Affairs and Deputy Leader of the House of Commons * Leo Amery – Secretary of State for the Colonies * Sir Laming Worthington-Evans, 1st B ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1926 United Kingdom General Strike
The 1926 general strike in the United Kingdom was a general strike that lasted nine days, from 4 to 12 May 1926. It was called by the General Council of the Trades Union Congress (TUC) in an unsuccessful attempt to force the British government to act to prevent wage reductions and worsening conditions for 1.2 million locked-out coal mining, coal miners. Some 1.7 million workers went out, especially in transport and heavy industry. It was a sympathy strike, with many of those who were not miners and not directly affected striking to support the locked-out miners. The government was well prepared, and enlisted middle class volunteers to maintain essential services. There was little violence and the TUC gave up in defeat. Causes From 1914 to 1918, the United Kingdom History of the United Kingdom during the First World War, participated in World War I. Heavy domestic use of coal during the war depleted once-rich Coal seam, seams. Britain exported less coal during the war ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Interwar Unemployment And Poverty In The United Kingdom
Unemployment was the dominant issue of British society during the interwar years. Unemployment levels rarely dipped below 1,000,000 and reached a peak of more than 3,000,000 in 1933, a figure which represented more than 20% of the working population. The unemployment rate was even higher in areas including South Wales and Liverpool. The Government extended unemployment insurance schemes in 1920 to alleviate the effects of unemployment. Causes There were several reasons for the decline in industry after the First World War. The end of the war brought a boom. In the shipping industry, businesses expanded rapidly in order to take advantage of the increase in demand. However, the boom was short-lived and this rapid expansion caused a slump from oversupply. Structural weaknesses in the British economy meant a disproportionate number of jobs were in the traditional industries. A combination of a lack of pre-war technological development and post-war competition damaged the economy and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Age Of Majority
The age of majority is the threshold of legal adulthood as recognized or declared in law. It is the moment when a person ceases to be considered a minor (law), minor, and assumes legal control over their person, actions, and decisions, thus terminating the control and legal responsibilities of their parents or guardian over them. Most countries set the age of majority at 18, but some jurisdictions have a higher age and others lower. The word ''majority'' here refers to having greater years and being of full age as opposed to ''minority'', the state of being a minor. The law in a given jurisdiction may not actually use the term "age of majority". The term refers to a collection of laws bestowing the status of adulthood. Explanation The term ''age of majority'' can be confused with the similar concept of the ''age of license''. As a legal term, ''license'' means ''permission'', referring to a legally enforceable right or privilege. Thus, the age of license for a specific activit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Universal Suffrage
Universal suffrage or universal franchise ensures the right to vote for as many people bound by a government's laws as possible, as supported by the " one person, one vote" principle. For many, the term universal suffrage assumes the exclusion of the young and non-citizens (among others). At the same time, some insist that more inclusion is needed before suffrage can be truly universal. Democratic theorists, especially those hoping to achieve more universal suffrage, support presumptive inclusion, where the legal system would protect the voting rights of all subjects unless the government can clearly prove that disenfranchisement is necessary. Universal full suffrage includes both the right to vote, also called active suffrage, and the right to be elected, also called passive suffrage. History In the first modern democracies, governments restricted the vote to those with property and wealth, which almost always meant a minority of the male population. In some jurisdiction ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1918 United Kingdom General Election
The 1918 United Kingdom general election was called immediately after the Armistice with Germany which ended the First World War, and was held on Saturday, 14 December 1918. The governing coalition, under Prime Minister David Lloyd George, sent letters of endorsement to candidates who supported the coalition government. These were nicknamed " Coalition Coupons", and led to the election being known as the "coupon election". The result was a massive landslide in favour of the coalition, comprising primarily the Conservatives and Coalition Liberals, with massive losses for Liberals who were not endorsed. Nearly all the Liberal MPs without coupons were defeated, including party leader H. H. Asquith. It was the first general election to be held after enactment of the Representation of the People Act 1918. It was thus the first election in which women over the age of 30 (with some property qualifications), and all men over the age of 21, could vote. Previously, all women and many ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |