|
1713 In Canada
Events from the year 1713 in Canada. Incumbents *French Monarch: Louis XIV * British and Irish Monarch: Anne Governors * Governor General of New France: Philippe de Rigaud Vaudreuil * Colonial Governor of Louisiana: Jean-Baptiste Le Moyne de Bienville then Antoine de la Mothe Cadillac *Governor of Nova Scotia: Francis Nicholson * Governor of Plaisance: Philippe Pastour de Costebelle Events * The Treaty of Utrecht. The French cede Newfoundland and the Hudson Bay region. They retain Cape Breton Island and Île Saint-Jean ( Prince Edward Island). * Treaty of Utrecht cedes French Acadia, Newfoundland, Hudson Bay and the "country of the Iroquois" to England. * The Treaty of Utrecht ends Queen Anne's War, confirming British possession of Hudson Bay, Newfoundland and Acadia (except Île-Royale Cape Breton Island). France starts building Fortress Louisbourg near the eastern tip of Île-Royale. Births * Jean Baptiste de La Vérendrye born September 3, the eldest son of Pie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Canada
Canada is a country in North America. Its ten provinces and three territories extend from the Atlantic Ocean to the Pacific Ocean and northward into the Arctic Ocean, covering over , making it the world's second-largest country by total area. Its southern and western border with the United States, stretching , is the world's longest binational land border. Canada's capital is Ottawa, and its three largest metropolitan areas are Toronto, Montreal, and Vancouver. Indigenous peoples have continuously inhabited what is now Canada for thousands of years. Beginning in the 16th century, British and French expeditions explored and later settled along the Atlantic coast. As a consequence of various armed conflicts, France ceded nearly all of its colonies in North America in 1763. In 1867, with the union of three British North American colonies through Confederation, Canada was formed as a federal dominion of four provinces. This began an accretion of provinces and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
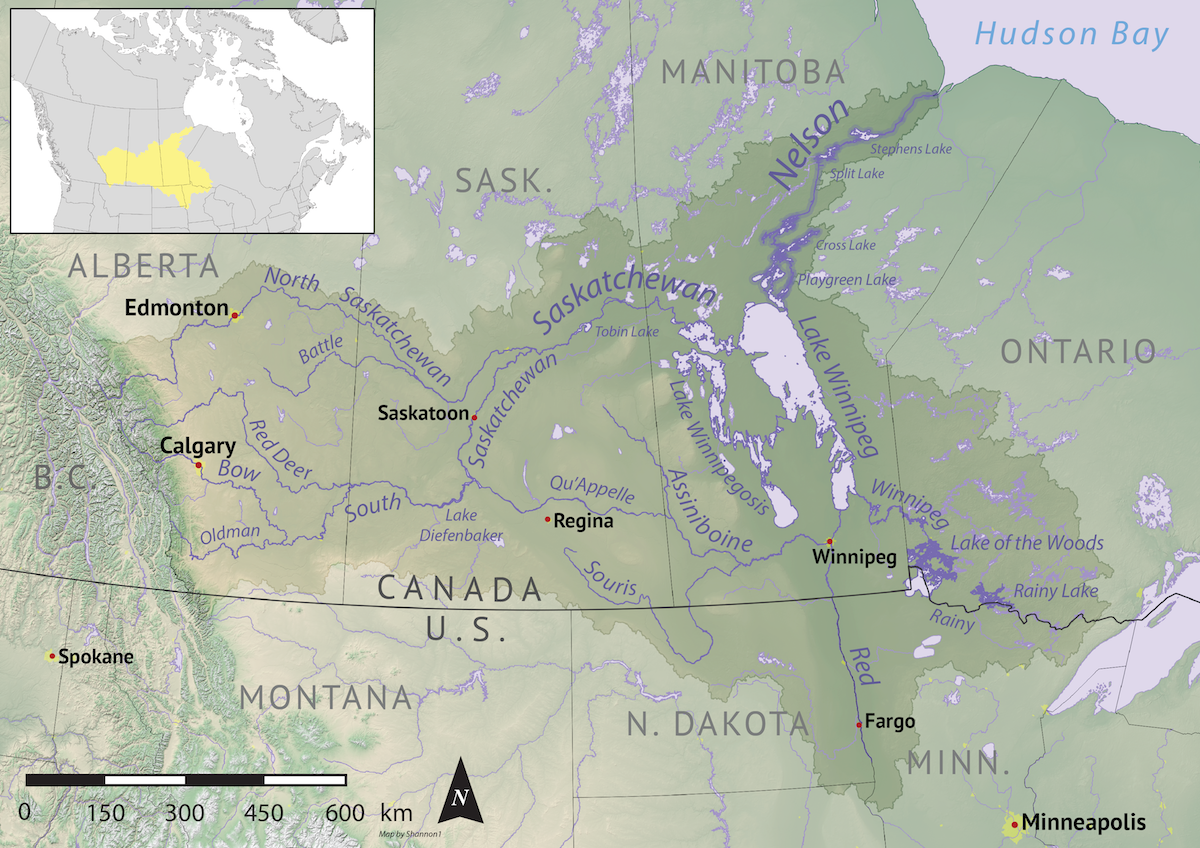
Hudson Bay
Hudson Bay ( crj, text=ᐐᓂᐯᒄ, translit=Wînipekw; crl, text=ᐐᓂᐹᒄ, translit=Wînipâkw; iu, text=ᑲᖏᖅᓱᐊᓗᒃ ᐃᓗᐊ, translit=Kangiqsualuk ilua or iu, text=ᑕᓯᐅᔭᕐᔪᐊᖅ, translit=Tasiujarjuaq; french: baie d'Hudson), sometimes called Hudson's Bay (usually historically), is a large body of saltwater in northeastern Canada with a surface area of . It is located north of Ontario, west of Quebec, northeast of Manitoba and southeast of Nunavut, but politically entirely part of Nunavut. Although not geographically apparent, it is for climatic reasons considered to be a marginal sea of the Arctic Ocean. It drains a very large area, about , that includes parts of southeastern Nunavut, Alberta, Saskatchewan, Ontario, Quebec, all of Manitoba, and parts of the U.S. states of North Dakota, South Dakota, Minnesota, and Montana. Hudson Bay's southern arm is called James Bay. The Eastern Cree name for Hudson and James Bay is (Southern dialect) or ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1713 In Canada
Events from the year 1713 in Canada. Incumbents *French Monarch: Louis XIV * British and Irish Monarch: Anne Governors * Governor General of New France: Philippe de Rigaud Vaudreuil * Colonial Governor of Louisiana: Jean-Baptiste Le Moyne de Bienville then Antoine de la Mothe Cadillac *Governor of Nova Scotia: Francis Nicholson * Governor of Plaisance: Philippe Pastour de Costebelle Events * The Treaty of Utrecht. The French cede Newfoundland and the Hudson Bay region. They retain Cape Breton Island and Île Saint-Jean ( Prince Edward Island). * Treaty of Utrecht cedes French Acadia, Newfoundland, Hudson Bay and the "country of the Iroquois" to England. * The Treaty of Utrecht ends Queen Anne's War, confirming British possession of Hudson Bay, Newfoundland and Acadia (except Île-Royale Cape Breton Island). France starts building Fortress Louisbourg near the eastern tip of Île-Royale. Births * Jean Baptiste de La Vérendrye born September 3, the eldest son of Pie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Michel Bénard
Michel Bénard ( – ?) was a councillor of the Conseil Supérieur of New France. From 1736 to 1748, Bénard was first secretary to the Intendant of New France The Intendant of New France was an administrative position in the French colony of New France. He controlled the colony's entire civil administration. He gave particular attention to settlement and economic development, and to the administration o ..., Gilles Hocquart. In 1757 he was made a regular councillor of the Sovereign Council, an office he held until the Conquest. References * 1710s births Year of death unknown People of New France {{Quebec-politician-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1736 In Canada
Events from the year 1736 in Canada. Incumbents * French Monarch: Louis XV * British and Irish Monarch: George II Governors *Governor General of New France: Charles de la Boische, Marquis de Beauharnois * Colonial Governor of Louisiana: Jean-Baptiste le Moyne de Bienville *Governor of Nova Scotia: Lawrence Armstrong * Commodore-Governor of Newfoundland: Jean-Baptiste Le Moyne de Bienville Events * Father Jean-Pierre Aulneau, Jean Baptiste de La Vérendrye and 19 French voyageurs were headed from Fort St. Charles to Montreal via Fort St. Pierre. On their first night out they were massacred by Sioux warriors on a nearby island in Lake of the Woods. The date was June 8. Deaths * March 25 - François-Marie Bissot, Sieur de Vincennes, explorer and soldier (born 1700). Full date unknown * Christopher Dufrost de La Jemeraye died May 10 of this year. In ill health he was travelling from Fort Maurepas (Canada) on the Red River to Fort St. Charles on Lake of the Woods. He wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pierre Gaultier De Varennes, Sieur De La Vérendrye
Pierre Gaultier de Varennes, sieur de La Vérendrye (17 November 1685 – 5 December 1749) was a French Canadian military officer, fur trader, and explorer. In the 1730s, he and his four sons explored the area west of Lake Superior and established trading posts there. They were part of a process that added Western Canada to the original New France territory that was centred along the Saint Lawrence basin. He was the first known European to reach present-day North Dakota and the upper Missouri River in the United States. In the 1740s, two of his sons crossed the prairie as far as present-day Wyoming, United States and were the first Europeans to see the Rocky Mountains north of New Mexico. Early life Born in Trois-Rivières, New France, Pierre was the eldest son of René Gaultier de Varennes, who came to Canada as a soldier in 1665, and Marie, the daughter of Pierre Boucher, the first Governor of Trois-Rivières. The Gaultier family were minor nobility or landowne ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jean Baptiste De La Vérendrye
Jean-Baptiste Gaultier de la Vérendrye (September 3, 1713 – June 6, 1736) was the eldest son of Pierre Gaultier de Varennes et de La Vérendrye and Marie-Anne Dandonneau Du Sablé. He was born on Île Dupas near Sorel, New France Jean Baptiste, with three brothers, Pierre Gaultier de La Vérendrye, François de La Vérendrye, and Louis-Joseph Gaultier de La Vérendrye, served in the expedition his father led west in 1731. When they arrived at Fort Kaministiquia some of the ''engagés'' (indentured employees), exhausted by the long journey by canoe from Montreal and discouraged by the difficult portages facing them, refused to go on. His father's second in command, Christopher Dufrost de La Jemeraye and Jean Baptiste led a smaller advance party west to Rainy Lake and established a fort they named Fort St. Pierre (after the parish church where Jean Baptiste was baptised). The following year Jean Baptiste was instrumental in founding Fort St. Charles on Lake of the Woods and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
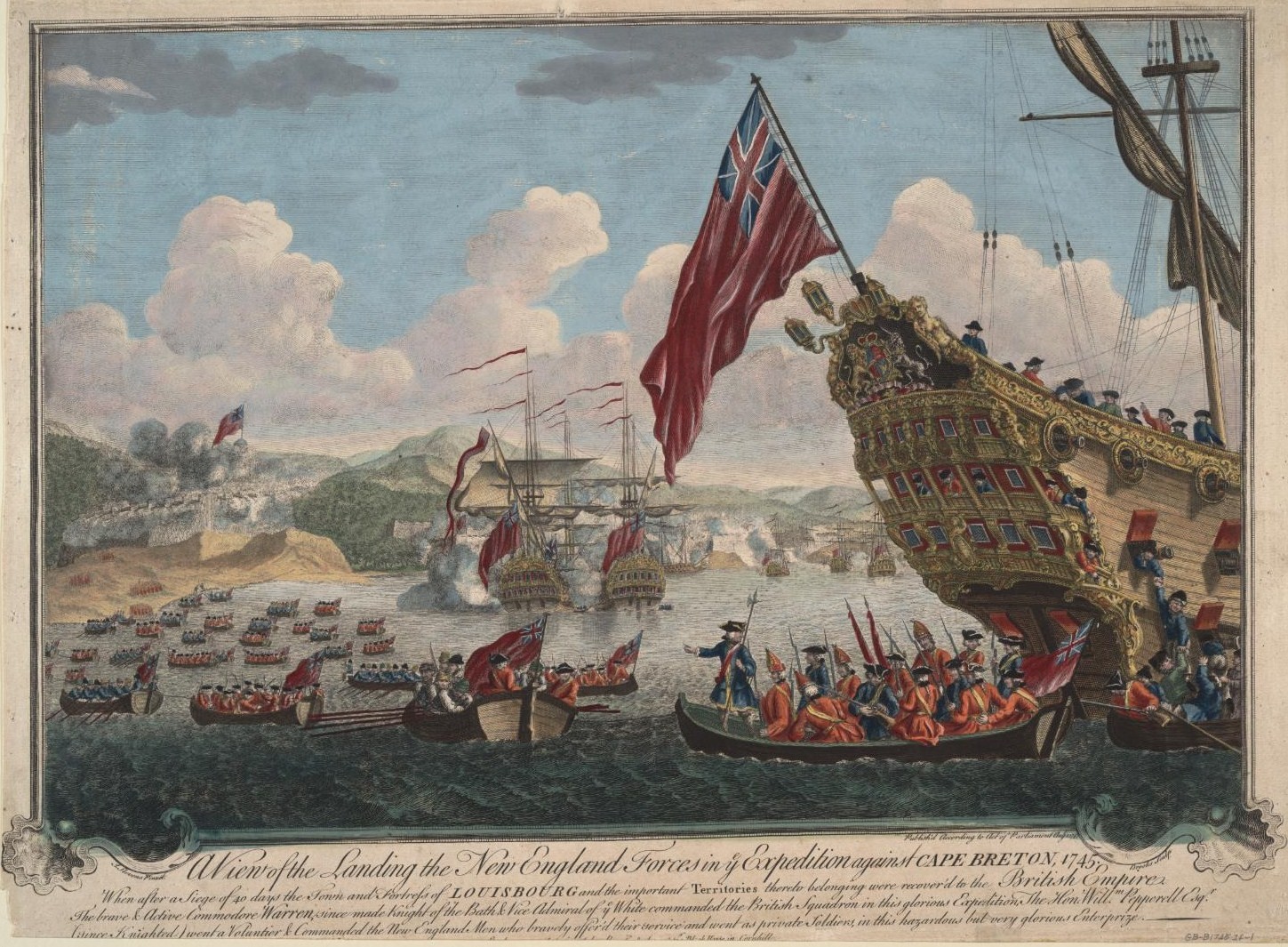
Fortress Louisbourg
The Fortress of Louisbourg (french: Forteresse de Louisbourg) is a National Historic Site and the location of a one-quarter partial reconstruction of an 18th-century French fortress at Louisbourg on Cape Breton Island, Nova Scotia. Its two sieges, especially that of 1758, were turning points in the Anglo-French struggle for what today is Canada. The original settlement was made in 1713, and initially called Havre à l'Anglois. Subsequently, the fishing port grew to become a major commercial port and a strongly defended fortress. The fortifications eventually surrounded the town. The walls were constructed mainly between 1720 and 1740. By the mid-1740s Louisbourg, named for Louis XIV of France, was one of the most extensive (and expensive) European fortifications constructed in North America. It was supported by two smaller garrisons on Île Royale located at present-day St. Peter's and Englishtown. The Fortress of Louisbourg suffered key weaknesses, since it was erected on l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Queen Anne's War
Queen Anne's War (1702–1713) was the second in a series of French and Indian Wars fought in North America involving the colonial empires of Great Britain, France, and Spain; it took place during the reign of Anne, Queen of Great Britain. In Europe, it is generally viewed as the American theater of the War of the Spanish Succession; in the Americas, it is more commonly viewed as a standalone conflict. It is also known as the Third Indian War. In France it was known as the Second Intercolonial War. Outline of the war The war broke out in 1701 and was primarily a conflict among French, Spanish and English colonists for control of the North American continent while the War of the Spanish Succession was being fought in Europe. Each side was allied with various Indigenous communities. It was fought on four fronts: # In the south, Spanish Florida and the English Province of Carolina attacked one another, and English colonists engaged French colonists based at Fort Louis de la Louis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acadia
Acadia (french: link=no, Acadie) was a colony of New France in northeastern North America which included parts of what are now the Maritime provinces, the Gaspé Peninsula and Maine to the Kennebec River. During much of the 17th and early 18th centuries, Norridgewock on the Kennebec River and Castine at the end of the Penobscot River were the southernmost settlements of Acadia. The French government specified land bordering the Atlantic coast, roughly between the 40th and 46th parallels. It was eventually divided into British colonies. The population of Acadia included the various indigenous First Nations that comprised the Wabanaki Confederacy, the Acadian people and other French settlers. The first capital of Acadia was established in 1605 as Port-Royal. An English force from Virginia attacked and burned down the town in 1613, but it was later rebuilt nearby, where it remained the longest-serving capital of French Acadia until the British siege of Port Royal in 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Canadian Encyclopedia
''The Canadian Encyclopedia'' (TCE; french: L'Encyclopédie canadienne) is the national encyclopedia of Canada, published online by the Toronto-based historical organization Historica Canada, with the support of Canadian Heritage. Available for free online in both English and French, ''The Canadian Encyclopedia'' includes more than 19,500 articles in both languages on numerous subjects including history, popular culture, events, people, places, politics, arts, First Nations, sports and science. The website also provides access to the ''Encyclopedia of Music in Canada'', the ''Canadian Encyclopedia Junior Edition'', ''Maclean's'' magazine articles, and ''Timelines of Canadian History''. , over 700,000 volumes of the print version of ''TCE'' have been sold and over 6 million people visit ''TCE'''s website yearly. History Background While attempts had been made to compile encyclopedic material on aspects of Canada, ''Canada: An Encyclopaedia of the Country'' (1898–1900 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prince Edward Island
Prince Edward Island (PEI; ) is one of the thirteen provinces and territories of Canada. It is the smallest province in terms of land area and population, but the most densely populated. The island has several nicknames: "Garden of the Gulf", "Birthplace of Confederation" and "Cradle of Confederation". Its capital and largest city is Charlottetown. It is one of the three Maritime provinces and one of the four Atlantic provinces. Part of the traditional lands of the Miꞌkmaq, it was colonized by the French in 1604 as part of the colony of Acadia. The island was ceded to the British at the conclusion of the French and Indian War in 1763 and became part of the colony of Nova Scotia, and in 1769 the island became its own British colony. Prince Edward Island hosted the Charlottetown Conference in 1864 to discuss a union of the Maritime provinces; however, the conference became the first in a series of meetings which led to Canadian Confederation in 1867. Prince Edward Island ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |