|
165 (number)
165 (one hundred ndsixty-five) is the natural number following 164 and preceding 166. In mathematics 165 is: *an odd number, a composite number, and a deficient number. *a sphenic number. *a tetrahedral number. *the number of prime knots with 10 crossings. *the sum of the sums of the divisors of the first 14 positive integers. *a self number in base 10. *a palindromic number A palindromic number (also known as a numeral palindrome or a numeric palindrome) is a number (such as 16361) that remains the same when its digits are reversed. In other words, it has reflectional symmetry across a vertical axis. The term ''palin ... in binary (101001012) and bases 14 (BB14), 32 (5532) and 54 (3354). *a unique period in base 2. References External links Number Facts and Trivia: 165The Number 165The Positive Integer 165 Integers {{Num-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Natural Number
In mathematics, the natural numbers are the numbers 0, 1, 2, 3, and so on, possibly excluding 0. Some start counting with 0, defining the natural numbers as the non-negative integers , while others start with 1, defining them as the positive integers Some authors acknowledge both definitions whenever convenient. Sometimes, the whole numbers are the natural numbers as well as zero. In other cases, the ''whole numbers'' refer to all of the integers, including negative integers. The counting numbers are another term for the natural numbers, particularly in primary education, and are ambiguous as well although typically start at 1. The natural numbers are used for counting things, like "there are ''six'' coins on the table", in which case they are called ''cardinal numbers''. They are also used to put things in order, like "this is the ''third'' largest city in the country", which are called ''ordinal numbers''. Natural numbers are also used as labels, like Number (sports), jersey ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
164 (number)
164 (one hundred ndsixty-four) is the natural number following 163 and preceding 165. In mathematics 164 is a zero of the Mertens function. In base 10 The decimal numeral system (also called the base-ten positional numeral system and denary or decanary) is the standard system for denoting integer and non-integer numbers. It is the extension to non-integer numbers (''decimal fractions'') of t ..., 164 is the smallest number that can be expressed as a concatenation of two squares in two different ways: as 1 concatenate 64 or 16 concatenate 4. External links Number Facts and Trivia: 164The Number 164The Positive Integer 164 {{DEFAULTSORT:164 (Number) Integers ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
166 (number)
166 (one hundred ndsixty-six) is the natural number following 165 and preceding 167. In mathematics 166 is an even number and a composite number. It is a centered triangular number. Given 166, the Mertens function returns 0. 166 is a Smith number in base 10. 166 in Roman numerals Roman numerals are a numeral system that originated in ancient Rome and remained the usual way of writing numbers throughout Europe well into the Late Middle Ages. Numbers are written with combinations of letters from the Latin alphabet, eac ... consists of the first 5 symbols, CLXVI. External links Number Facts and Trivia: 166The Number 166 166th Street (3rd Avenue El) References {{DEFAULTSORT:166 (Number) Integers ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Odd Number
In mathematics, parity is the property of an integer of whether it is even or odd. An integer is even if it is divisible by 2, and odd if it is not.. For example, −4, 0, and 82 are even numbers, while −3, 5, 23, and 69 are odd numbers. The above definition of parity applies only to integer numbers, hence it cannot be applied to numbers with decimals or fractions like 1/2 or 4.6978. See the section "Higher mathematics" below for some extensions of the notion of parity to a larger class of "numbers" or in other more general settings. Even and odd numbers have opposite parities, e.g., 22 (even number) and 13 (odd number) have opposite parities. In particular, the parity of zero is even. Any two consecutive integers have opposite parity. A number (i.e., integer) expressed in the decimal numeral system is even or odd according to whether its last digit is even or odd. That is, if the last digit is 1, 3, 5, 7, or 9, then it is odd; otherwise it is even—as the last digit of any ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Composite Number
A composite number is a positive integer that can be formed by multiplying two smaller positive integers. Accordingly it is a positive integer that has at least one divisor other than 1 and itself. Every positive integer is composite, prime number, prime, or the Unit (ring theory), unit 1, so the composite numbers are exactly the numbers that are not prime and not a unit. E.g., the integer 14 is a composite number because it is the product of the two smaller integers 2 × 7 but the integers 2 and 3 are not because each can only be divided by one and itself. The composite numbers up to 150 are: :4, 6, 8, 9, 10, 12, 14, 15, 16, 18, 20, 21, 22, 24, 25, 26, 27, 28, 30, 32, 33, 34, 35, 36, 38, 39, 40, 42, 44, 45, 46, 48, 49, 50, 51, 52, 54, 55, 56, 57, 58, 60, 62, 63, 64, 65, 66, 68, 69, 70, 72, 74, 75, 76, 77, 78, 80, 81, 82, 84, 85, 86, 87, 88, 90, 91, 92, 93, 94, 95, 96, 98, 99, 100, 102, 104, 105, 106, 108, 110, 111, 112, 114, 115, 116, 117, 118, 119, 120, 121, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deficient Number
In number theory, a deficient number or defective number is a positive integer for which the sum of divisors of is less than . Equivalently, it is a number for which the sum of proper divisors (or aliquot sum) is less than . For example, the proper divisors of 8 are , and their sum is less than 8, so 8 is deficient. Denoting by the sum of divisors, the value is called the number's deficiency. In terms of the aliquot sum , the deficiency is . Examples The first few deficient numbers are :1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 13, 14, 15, 16, 17, 19, 21, 22, 23, 25, 26, 27, 29, 31, 32, 33, 34, 35, 37, 38, 39, 41, 43, 44, 45, 46, 47, 49, 50, ... As an example, consider the number 21. Its divisors are 1, 3, 7 and 21, and their sum is 32. Because 32 is less than 42, the number 21 is deficient. Its deficiency is 2 × 21 − 32 = 10. Properties Since the aliquot sums of prime numbers equal 1, all prime numbers are deficient. More generally, all odd numbers with one or two distinct ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sphenic Number
In number theory, a sphenic number (from , 'wedge') is a positive integer that is the product of three distinct prime numbers. Because there are infinitely many prime numbers, there are also infinitely many sphenic numbers. Definition A sphenic number is a product ''pqr'' where ''p'', ''q'', and ''r'' are three distinct prime numbers. In other words, the sphenic numbers are the square-free 3- almost primes. Examples The smallest sphenic number is 30 = 2 × 3 × 5, the product of the smallest three primes. The first few sphenic numbers are : 30, 42, 66, 70, 78, 102, 105, 110, 114, 130, 138, 154, 165, ... The largest known sphenic number at any time can be obtained by multiplying together the three largest known primes. Divisors All sphenic numbers have exactly eight divisors. If we express the sphenic number as n = p \cdot q \cdot r, where ''p'', ''q'', and ''r'' are distinct primes, then the set of divisors of ''n'' will be: :\left\. The converse does not hold. F ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tetrahedral Number
A tetrahedral number, or triangular pyramidal number, is a figurate number that represents a pyramid (geometry), pyramid with a triangular base and three sides, called a tetrahedron. The th tetrahedral number, , is the sum of the first triangular numbers, that is, : Te_n = \sum_^n T_k = \sum_^n \frac = \sum_^n \left(\sum_^k i\right) The tetrahedral numbers are: :1, 4, 10, 20 (number), 20, 35 (number), 35, 56 (number), 56, 84 (number), 84, 120 (number), 120, 165 (number), 165, 220 (number), 220, ... Formula The formula for the th tetrahedral number is represented by the 3rd rising factorial of divided by the factorial of 3: :Te_n= \sum_^n T_k = \sum_^n \frac = \sum_^n \left(\sum_^k i\right)=\frac = \frac The tetrahedral numbers can also be represented as binomial coefficients: :Te_n=\binom. Tetrahedral numbers can therefore be found in the fourth position either from left or right in Pascal's triangle. Proofs of formula This proof uses the fact that the th triangular num ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Positive Integers
In mathematics, the natural numbers are the numbers 0, 1, 2, 3, and so on, possibly excluding 0. Some start counting with 0, defining the natural numbers as the non-negative integers , while others start with 1, defining them as the positive integers Some authors acknowledge both definitions whenever convenient. Sometimes, the whole numbers are the natural numbers as well as zero. In other cases, the ''whole numbers'' refer to all of the integers, including negative integers. The counting numbers are another term for the natural numbers, particularly in primary education, and are ambiguous as well although typically start at 1. The natural numbers are used for counting things, like "there are ''six'' coins on the table", in which case they are called ''cardinal numbers''. They are also used to put things in order, like "this is the ''third'' largest city in the country", which are called ''ordinal numbers''. Natural numbers are also used as labels, like jersey numbers on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Self Number
In number theory, a self number or Devlali number in a given number base b is a natural number that cannot be written as the sum of any other natural number n and the individual digits of n. 20 is a self number (in base 10), because no such combination can be found (all n 1 F_b : \mathbb \rightarrow \mathbb to be the following: :F_(n) = n + \sum_^ d_i. where k = \lfloor \log_ \rfloor + 1 is the number of digits in the number in base b, and :d_i = \frac is the value of each digit of the number. A natural number n is a b-self number if the preimage of n for F_b is the empty set. In general, for even bases, all odd numbers below the base number are self numbers, since any number below such an odd number would have to also be a 1-digit number which when added to its digit would result in an even number. For odd bases, all odd numbers are self numbers.Sándor & Crstici (2004) p.384 The set of self numbers in a given base b is infinite and has a positive asymptotic density: when b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
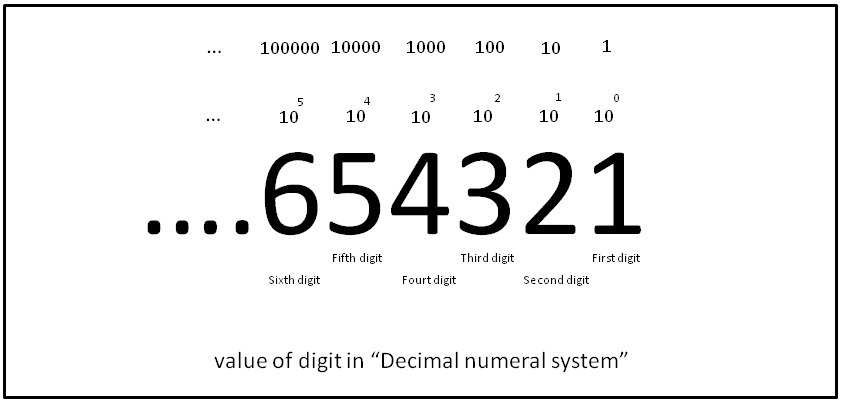
Base 10
The decimal numeral system (also called the base-ten positional numeral system and denary or decanary) is the standard system for denoting integer and non-integer numbers. It is the extension to non-integer numbers (''decimal fractions'') of the Hindu–Arabic numeral system. The way of denoting numbers in the decimal system is often referred to as ''decimal notation''. A decimal numeral (also often just ''decimal'' or, less correctly, ''decimal number''), refers generally to the notation of a number in the decimal numeral system. Decimals may sometimes be identified by a decimal separator (usually "." or "," as in or ). ''Decimal'' may also refer specifically to the digits after the decimal separator, such as in " is the approximation of to ''two decimals''". Zero-digits after a decimal separator serve the purpose of signifying the precision of a value. The numbers that may be represented in the decimal system are the decimal fractions. That is, fractions of the form , ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Palindromic Number
A palindromic number (also known as a numeral palindrome or a numeric palindrome) is a number (such as 16361) that remains the same when its digits are reversed. In other words, it has reflectional symmetry across a vertical axis. The term ''palindromic'' is derived from palindrome, which refers to a word (such as ''rotor'' or ''racecar'') whose spelling is unchanged when its letters are reversed. The first 30 palindromic numbers (in decimal) are: : 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 11, 22, 33, 44, 55, 66, 77, 88, 99, 101, 111, 121, 131, 141, 151, 161, 171, 181, 191, 202, ... . Palindromic numbers receive most attention in the realm of recreational mathematics. A typical problem asks for numbers that possess a certain property ''and'' are palindromic. For instance: * The palindromic primes are 2, 3, 5, 7, 11, 101, 131, 151, ... . * The palindromic square numbers are 0, 1, 4, 9, 121, 484, 676, 10201, 12321, ... . In any base there are infinitely many palindromic numbers, since ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |