|
1638 In Literature
This article contains information about the literary events and publications of 1638. Events *January 3 – Joost van den Vondel's historical play '' Gijsbrecht van Aemstel'' is first performed, to mark the opening of the Schouwburg of Van Campen, Amsterdam's first public theatre (postponed from 26 December 1637). It is then performed annually in the city on New Year's Day until 1968. *February 6 – '' Luminalia'', a masque written by Sir William Davenant and designed by Inigo Jones, is staged at the English Court. *March 27 – The King's Men perform Chapman's tragedy '' Bussy D'Ambois'' at the English Court. *May – English poet John Milton sets out for a tour of the European continent. He spends the summer in Florence where he later claims to have met the incarcerated Galileo. * October 27 – The King's Men act Ben Jonson's satirical city comedy '' Volpone'' (1606) at the Blackfriars Theatre in London. *''unknown dates'' **An Armenian language edition of the Psal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Florence
Florence ( ; ) is the capital city of the Italy, Italian region of Tuscany. It is also the most populated city in Tuscany, with 362,353 inhabitants, and 989,460 in Metropolitan City of Florence, its metropolitan province as of 2025. Florence was a centre of Middle Ages, medieval European trade and finance and one of the wealthiest cities of that era. It is considered by many academics to have been the birthplace of the Renaissance, becoming a major artistic, cultural, commercial, political, economic and financial center. During this time, Florence rose to a position of enormous influence in Italy, Europe, and beyond. Its turbulent political history includes periods of rule by the powerful House of Medici, Medici family and numerous religious and republican revolutions. From 1865 to 1871 the city served as the capital of the Kingdom of Italy. The Florentine dialect forms the base of Italian language, standard Italian and it became the language of culture throughout Italy due to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peking Gazette
The ''Peking Gazette'' was an official bulletin published with changing frequency in Beijing until 1912, when the Qing dynasty fell and Republican China was born. The translated name, as it is known to Western sources, comes from Ming dynasty-era Jesuits, who followed the bulletin for its political contents. The ''Peking Gazette'' became a venue for political grievances and infighting during the reign of the Wanli Emperor in the late Ming dynasty, when '' literati'' factions would submit politicized memorials that the Emperor often abstained from reviewing. From around 1730, the publication was in Chinese called ''Jing Bao'' (京报, sometimes transliterated ''Ching Pao''), literally "the Capital Report". It contained information on court appointments, edicts, and the official memorials submitted to the emperor, and the decisions made or deferred.Wolfgang Mohr, ''Die moderne chinesische Tagespresse'', vol. 1 (Wiesbaden, 1976), pp. 13–14. Author J.C. Sun in his book ''Modern Chi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Persia
Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran (IRI) and also known as Persia, is a country in West Asia. It borders Iraq to the west, Turkey, Azerbaijan, and Armenia to the northwest, the Caspian Sea to the north, Turkmenistan to the northeast, Afghanistan to the east, Pakistan to the southeast, and the Gulf of Oman and the Persian Gulf to the south. With a Ethnicities in Iran, multi-ethnic population of over 92 million in an area of , Iran ranks 17th globally in both List of countries and dependencies by area, geographic size and List of countries and dependencies by population, population. It is the List of Asian countries by area, sixth-largest country entirely in Asia and one of the world's List of mountains in Iran, most mountainous countries. Officially an Islamic republic, Iran is divided into Regions of Iran, five regions with Provinces of Iran, 31 provinces. Tehran is the nation's Capital city, capital, List of cities in Iran by province, largest city and financial ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Isfahan
Isfahan or Esfahan ( ) is a city in the Central District (Isfahan County), Central District of Isfahan County, Isfahan province, Iran. It is the capital of the province, the county, and the district. It is located south of Tehran. The city has a population of approximately 2,220,000, making it the third-most populous city in Iran, after Tehran and Mashhad, and the second-largest metropolitan area. Isfahan is located at the intersection of the two principal routes that traverse Iran, north–south and east–west. Isfahan flourished between the 9th and 18th centuries. Under the Safavid Iran, Safavid Empire, Isfahan became the capital of Iran, for the second time in its history, under Abbas the Great. It is known for its Persian architecture, Persian–Islamic architecture, Muslim architecture, grand boulevards, covered bridges, palaces, tiled mosques, and minarets. Isfahan also has many historical buildings, monuments, paintings, and artifacts. The fame of Isfahan led to the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New Julfa
New Julfa (, ''Now Jolfā'', or , ''Jolfâ-ye Now''; , ''Nor Jugha'') is the Armenians, Armenian quarter of Isfahan, Iran, located along the south bank of the Zayanderud. Established and named after the Gülüstan, Nakhchivan, older city of Julfa in the early 17th century (now divided as Jolfa, Iran and Julfa, Azerbaijan (city), Julfa, Azerbaijan), it is still one of the oldest and largest List of Armenian ethnic enclaves, Armenian quarters in the world (:hy:Նոր Ջուղայի գաղութ, hy). History New Julfa was established in 1606 as an Armenian quarter by the mandate of Abbas the Great, sultan of Safavid Iran. Over 150,000 Armenians of Julfa, Armenians were Great Surgun, forcibly moved there from Gülüstan, Nakhchivan, Julfa (also known as ''Jugha'' or ''Juła'', and now as Old Julfa) (:hy:Հայերի բռնագաղթն Իրան (1603-1604), hy). Iranian sources state that the Armenians came to Iran fleeing the Ottoman Empire's persecution. Nevertheless, historical ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Psalms
The Book of Psalms ( , ; ; ; ; , in Islam also called Zabur, ), also known as the Psalter, is the first book of the third section of the Tanakh (Hebrew Bible) called ('Writings'), and a book of the Old Testament. The book is an anthology of Biblical Hebrew, Hebrew religious hymns. In the Judaism, Jewish and Western Christianity, Western Christian traditions, there are 150 psalms, and several more in the Eastern Christianity, Eastern Christian churches. The book is divided into five sections, each ending with a doxology, a hymn of praise. There are several types of psalms, including hymns or songs of praise, communal and individual laments, royal psalms, Imprecatory Psalms, imprecation, and individual thanksgivings. The book also includes psalms of communal thanksgiving, wisdom, pilgrimage and other categories. Many of the psalms contain attributions to the name of David, King David and other Biblical figures including Asaph (biblical figure), Asaph, the Korahites, sons of Kora ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Armenian Language
Armenian (endonym: , , ) is an Indo-European languages, Indo-European language and the sole member of the independent branch of the Armenian language family. It is the native language of the Armenians, Armenian people and the official language of Armenia. Historically spoken in the Armenian highlands, today Armenian is also widely spoken throughout the Armenian diaspora. Armenian is written in its own writing system, the Armenian alphabet, introduced in 405 AD by Saint Mesrop Mashtots. The estimated number of Armenian speakers worldwide is between five and seven million. History Classification and origins Armenian is an independent branch of the Indo-European languages. It is of interest to linguists for its distinctive phonological changes within that family. Armenian exhibits Centum and satem languages, more satemization than centumization, although it is not classified as belonging to either of these subgroups. Some linguists tentatively conclude that Armenian, Greek ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
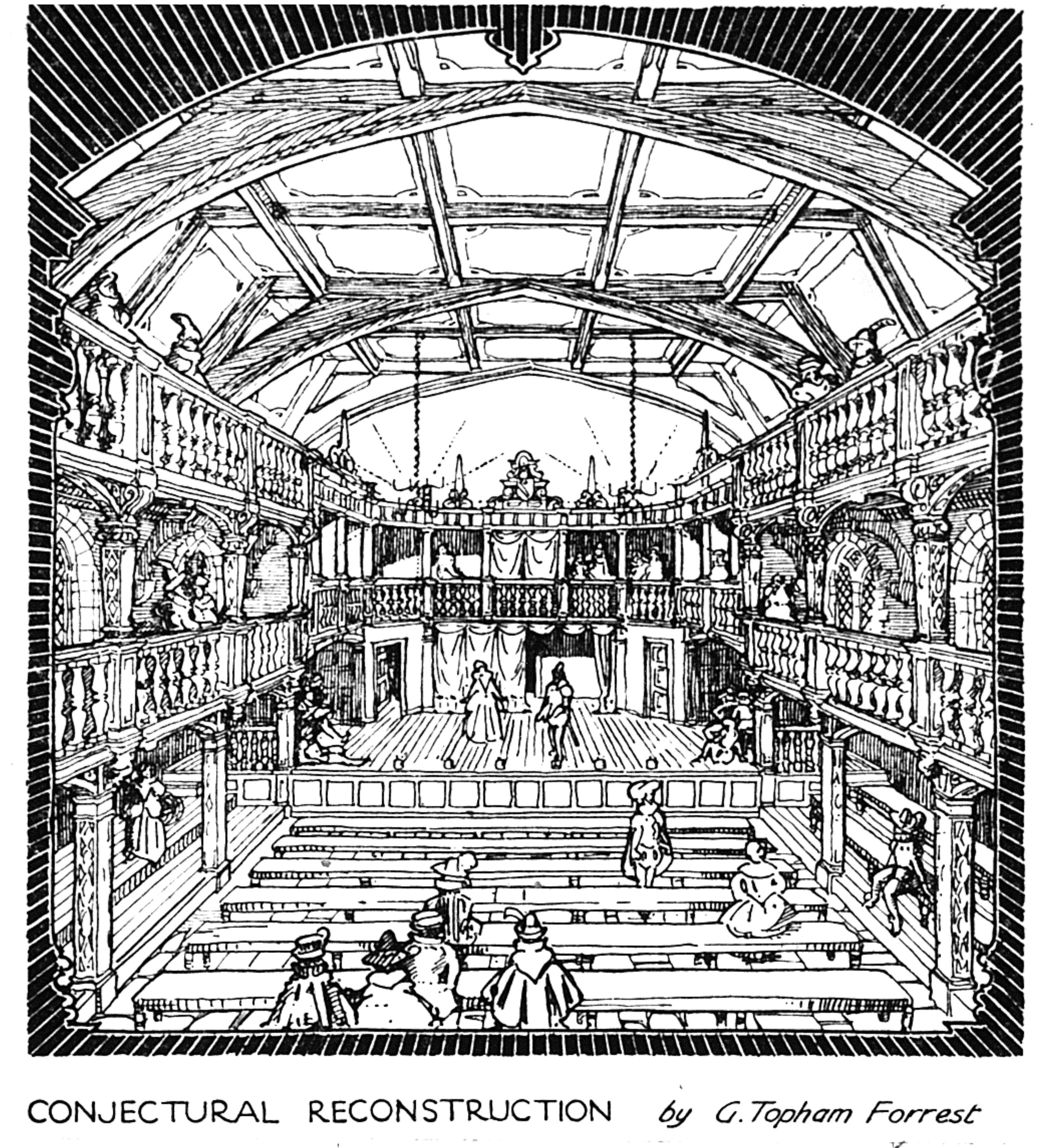
Blackfriars Theatre
Blackfriars Theatre was the name given to two separate theatres located in the former Blackfriars Dominican priory in the City of London during the Renaissance. The first theatre began as a venue for the Children of the Chapel Royal, child actors associated with the Queen's chapel choirs, and who from 1576 to 1584 staged plays in the vast hall of the former monastery. The second theatre dates from the purchase of the upper part of the priory and another building by James Burbage in 1596, which included the Parliament Chamber on the upper floor that was converted into the playhouse. The Children of the Chapel played in the theatre beginning in the autumn of 1600 until the King's Men took over in 1608. They successfully used it as their winter playhouse until all the theatres were closed in 1642 when the English Civil War began. In 1666, the entire area was destroyed in the Great Fire of London. First theatre Blackfriars Theatre was built on the grounds of the former Do ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Volpone
''Volpone'' (, Italian for "sly fox") is a comedy play by English playwright Ben Jonson first produced in 1605–1606, drawing on elements of city comedy and beast fable. A merciless satire of greed and lust, it remains Jonson's most-performed play, and it is ranked among the finest Jacobean era comedies. Characters * Volpone (the Sly Fox) – a greedy and rich childless Venetian ''magnifico'' * Mosca (the Fly) – his servant * Voltore (the Vulture) – a lawyer * Corbaccio (the Raven) – an avaricious old miser * Bonario – Corbaccio's son * Corvino (the Carrion Crow) – a merchant * Celia – Corvino's wife * Sir Politic Would-Be – ridiculous Englishman and husband of Lady Would-Be * Lady Would-Be (the parrot) – English lady and wife of Sir Politic Would-Be * Peregrine ("Pilgrim") – another, more sophisticated, English traveller * Nano – a dwarf, companion of Volpone * Androgyno – a hermaphrodite, companion of Volpone * Castrone – a eunuch, companion of V ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
City Comedy
City comedy, also known as citizen comedy, is a genre of comedy in the English early modern theatre. Definition Emerging from Ben Jonson's late-Elizabethan comedies of humours (1598–1599), the conventions of city comedy developed rapidly in the first decade of the Jacobean era, as one playwright's innovations were soon adopted by others, such that by about 1605 the new genre was fully established. Its principal playwrights were Jonson himself, Thomas Middleton, and John Marston, though many others also contributed to its development, including Thomas Heywood, Thomas Dekker, John Day, and John Webster. Once the companies of boy players—the Children of Paul's and the Children of the Chapel—had resumed public performances from 1600 onwards, most of their plays were city comedies. The closest that William Shakespeare's plays come to the genre is the slightly earlier ''The Merry Wives of Windsor'' (c. 1597), which is his only play set entirely in England; it avoids the ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ben Jonson
Benjamin Jonson ( 11 June 1572 – ) was an English playwright, poet and actor. Jonson's artistry exerted a lasting influence on English poetry and stage comedy. He popularised the comedy of humours; he is best known for the satire, satirical plays ''Every Man in His Humour'' (1598), ''Volpone, Volpone, or The Fox'' (), ''The Alchemist (play), The Alchemist'' (1610) and ''Bartholomew Fair (play), Bartholomew Fair'' (1614) and for his Lyric poetry, lyric and epigrammatic poetry. He is regarded as "the second most important English dramatist, after William Shakespeare, during the reign of James VI and I, James I."The Editors of Encyclopaedia Britannica (12 June 2024)"Ben Jonson" ''Encyclopedia Britannica''. Archived frothe originalon 12 July 2024. Jonson was a Classics, classically educated, well-read and cultured man of the English Renaissance with an appetite for controversy (personal and political, artistic and intellectual). His cultural influence was of unparalleled breadth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |