|
–ê–Ω–∞–ª–∏—Ç–∏–∫
Analitik () is a programming language, developed in 1968 at the Institute of Cybernetics of the Academy of Sciences of the Ukrainian SSR in the USSR. It is a development on the ALMIR-65 language, keeping compatibility with it. Distinctive features of the language are abstract data types, calculations in arbitrary algebras, and analytic transformations. It was implemented on MIR-2 machines. Later, a version of Analitik-74 was developed, implemented on MIR-3 machines. At the moment, the language exists as a computer algebra system, Analitik-2010, which is being developed jointly by the Institute of Mathematical Machines and Systems of the National Academy of Sciences of Ukraine and the Poltava National Technical University. References {{DEFAULTSORT:Programming Language Programming languages created in 1968 Programming languages A programming language is a system of notation for writing computer programs. Programming languages are described in terms of their syntax ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MIR-3
MIR-3 () is a third-generation computer that was released in the 1970s in the Soviet Union. It collected all the achievements of microelectronics in the 1970s. The main task of the MIR-3 computer was to solve computational problems for engineers. MIR-3 consisted of keyboard, TV (display), a means of reading magnetic tapes and disks, a processor. The size of MIR-3 has decreased. Now it was the size of a regular desk. True, the size was without the means of reading magnetic tapes and disks. The speed of the MIR-3 computer was 105 (100,000) - 107 (10,000,000) actions per second. The memory capacity was up to 106 knocks. Essentially, the MIR-3 computer consisted of several computers. The microprocessor consists of several processors, each of which was responsible for the operation of a separate MIR-3 unit. For example, one for reading information from magnetic tapes and transferring information, the other for processing and calculations, the third for printing on the keyboard, and so on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
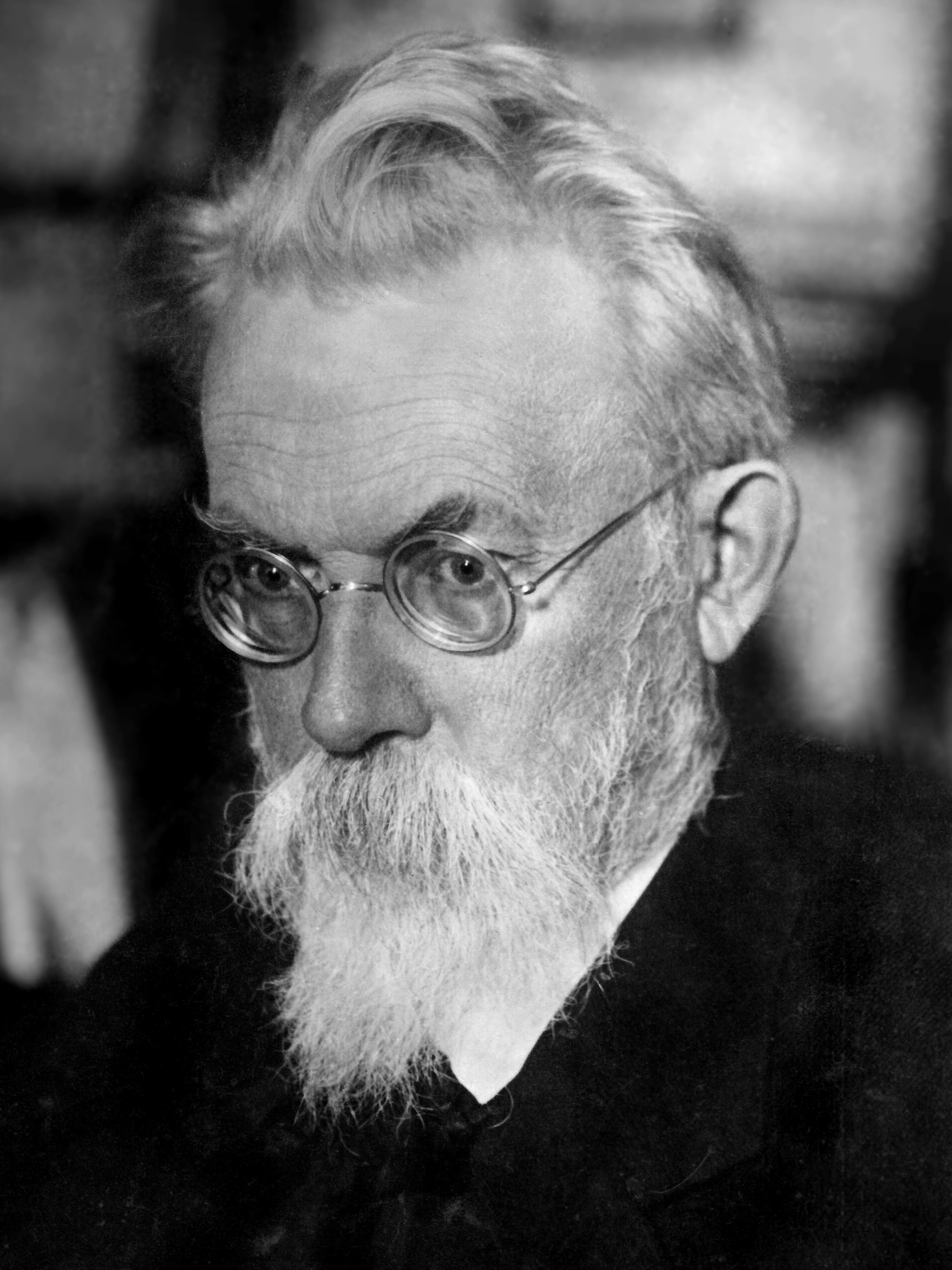
Victor Glushkov
Victor Mikhailovich Glushkov (; August 24, 1923 – January 30, 1982) was a Soviet computer scientist. He is considered to be the founding father of information technology in the Soviet Union and one of the founding fathers Soviet cybernetics. Biography He was born in Rostov-on-Don, Russian SFSR, in the family of a mining engineer. Glushkov graduated from Rostov State University in 1948, and in 1952 proposed solutions to Hilbert's fifth problem and defended his thesis at Moscow State University. In 1956, he began working with computers and worked in Kiev as a Director of the Computational Center of the Academy of Science of Ukraine. In 1958, he became a member of the Communist Party. In 1962, Glushkov established the famous Institute of Cybernetics of the National Academy of Science of Ukraine and became its first director. He made contributions to the theory of automata. He and his followers (Kapitonova, Letichevskiy and others) successfully applied that theory to enhance ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Poltava National Technical University
The National University "Poltava Polytechnic" (named after Yuri Kondratyuk, ) is a Ukrainian public university in Poltava (previously known as Poltava National Technical Yuri Kondratyuk University, PoltNTU). History Source: Early history The Central Building of the university is a monument of architecture of the first hald of 19th century, built in the classical style. The building was architectured by Louis Charlemagne a part of the Empire-style ensemble of Poltava city center, and constructed in 1828–1832. The Institute of Noble Maidens, founded on December 12, 1818, by Varvara Riepina in Poltava, became the first educational institution of closed type for noble girls in the Russian empire's principal town of a province. Over the hundred-year activity period, various famous Ukrainian, Russian and Czech culture activists had worked at the institute. 20th century In January, 1918, the Institute of Noble Maidens was evacuated to Vladikavkaz due to the October Revolution ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
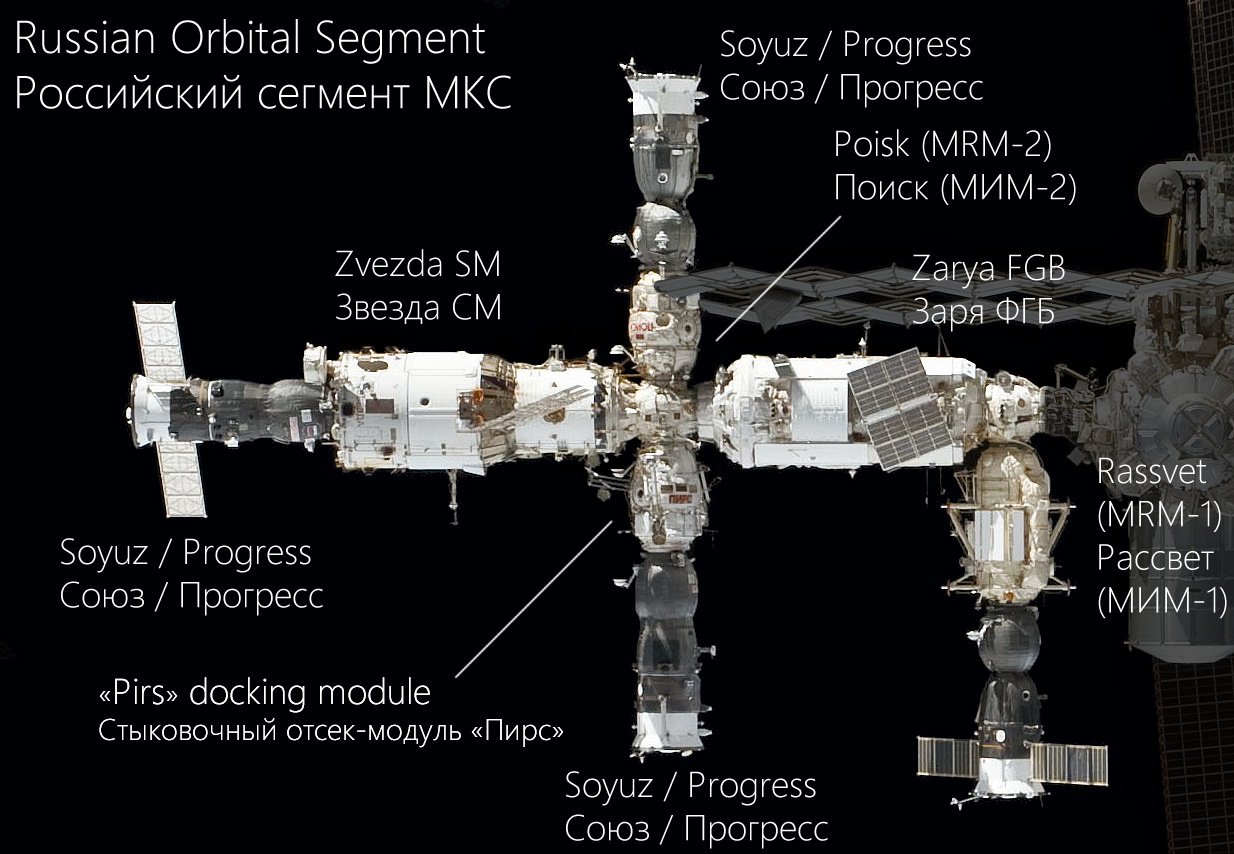
MIR-2
''Mir''-2 was a Soviet space station project which began in February 1976. Some of the modules built for ''Mir''-2 have been incorporated into the International Space Station (ISS). The project underwent many changes, but was always based on the DOS-8 base block space station core module, built as a back-up to the DOS-7 base block used in the ''Mir'' station. The DOS-8 base block was eventually used as the '' Zvezda'' module of the ISS. Its design lineage extends back to the original Salyut stations. Project history The evolution of the ''Mir''-2 project 1981 to 1987: KB Salyut Mir-2 The prototype of the central module was as Polyus. ''Mir''-2 would be capable of docking at least four modules in ordinary operation. December 14, 1987: NPO Energia Mir-2 Designated as OSETS (Orbital Assembly and Operations Centre). The station would be built in a 65 degree orbit and consist of 90 ton modules. *Launch 1 – DOS 8, providing housing for the assembly crew. *Launch 2 – 90 ton ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Programming Language
A programming language is a system of notation for writing computer programs. Programming languages are described in terms of their Syntax (programming languages), syntax (form) and semantics (computer science), semantics (meaning), usually defined by a formal language. Languages usually provide features such as a type system, Variable (computer science), variables, and mechanisms for Exception handling (programming), error handling. An Programming language implementation, implementation of a programming language is required in order to Execution (computing), execute programs, namely an Interpreter (computing), interpreter or a compiler. An interpreter directly executes the source code, while a compiler produces an executable program. Computer architecture has strongly influenced the design of programming languages, with the most common type (imperative languages—which implement operations in a specified order) developed to perform well on the popular von Neumann architecture. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Academy Of Sciences Of Ukraine
The National Academy of Sciences of Ukraine (NASU; , ; ''NAN Ukrainy'') is a self-governing state-funded organization in Ukraine that is the main center of development of Science and technology in Ukraine, science and technology by coordinating a system of research institutes in the country. It is the main research oriented organization along with the five other academies in Ukraine specialized in various scientific disciplines. NAS Ukraine consists of numerous departments, sections, research institutes, scientific centers and various other supporting scientific organizations. The Academy reports on the annual basis to the Cabinet of Ministers of Ukraine. The presidium of the academy is located at vulytsia Volodymyrska, 54, across the street from the Ukrainian Club Building, Building of Pedagogical Museum, which was used to host the Central Rada, Central Council during the independence period of 1917-18. In 1919–1991 it was a republican branch of the Academy of Sciences ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ukrainian Soviet Socialist Republic
The Ukrainian Soviet Socialist Republic, abbreviated as the Ukrainian SSR, UkrSSR, and also known as Soviet Ukraine or just Ukraine, was one of the Republics of the Soviet Union, constituent republics of the Soviet Union from 1922 until 1991. Under the Soviet One-party state, one-party model, the Ukrainian SSR was governed by the Communist Party of the Soviet Union through its Soviet democracy, republican branch, the Communist Party of Ukraine (Soviet Union), Communist Party of Ukraine. The first iterations of the Ukrainian SSR were established during the Russian Revolution, particularly after the October Revolution, Bolshevik Revolution. The outbreak of the Ukrainian–Soviet War in the former Russian Empire saw the Bolsheviks defeat the independent Ukrainian People's Republic, during the conflict against which they founded the Ukrainian People's Republic of Soviets, which was governed by the Russian Soviet Federative Socialist Republic (RSFSR), in December 1917; it was later ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
USSR
The Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR), commonly known as the Soviet Union, was a List of former transcontinental countries#Since 1700, transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 until Dissolution of the Soviet Union, it dissolved in 1991. During its existence, it was the list of countries and dependencies by area, largest country by area, extending across Time in Russia, eleven time zones and sharing Geography of the Soviet Union#Borders and neighbors, borders with twelve countries, and the List of countries and dependencies by population, third-most populous country. An overall successor to the Russian Empire, it was nominally organized as a federal union of Republics of the Soviet Union, national republics, the largest and most populous of which was the Russian SFSR. In practice, Government of the Soviet Union, its government and Economy of the Soviet Union, economy were Soviet-type economic planning, highly centralized. As a one-party state go ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |