MIR-2 on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
''Mir''-2 was a
 Russian elements of the
Russian elements of the
Mir-2 on Astronautix
{{Russian human spaceflight programs Cancelled space stations Cancelled Soviet spacecraft
Soviet
The Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR), commonly known as the Soviet Union, was a List of former transcontinental countries#Since 1700, transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 until Dissolution of the Soviet ...
space station
A space station (or orbital station) is a spacecraft which remains orbital spaceflight, in orbit and human spaceflight, hosts humans for extended periods of time. It therefore is an artificial satellite featuring space habitat (facility), habitat ...
project which began in February 1976. Some of the modules built for ''Mir''-2 have been incorporated into the International Space Station
The International Space Station (ISS) is a large space station that was Assembly of the International Space Station, assembled and is maintained in low Earth orbit by a collaboration of five space agencies and their contractors: NASA (United ...
(ISS). The project underwent many changes, but was always based on the DOS-8 base block space station core module, built as a back-up to the DOS-7 base block used in the ''Mir
''Mir'' (, ; ) was a space station operated in low Earth orbit from 1986 to 2001, first by the Soviet Union and later by the Russia, Russian Federation. ''Mir'' was the first modular space station and was assembled in orbit from 1986 to ...
'' station. The DOS-8 base block was eventually used as the '' Zvezda'' module of the ISS. Its design lineage extends back to the original Salyut
The ''Salyut'' programme (, , meaning "salute" or "fireworks") was the first space station programme, undertaken by the Soviet Union. It involved a series of four crewed scientific research space stations and two crewed military reconnaissa ...
stations.
Project history
The evolution of the ''Mir''-2 project
1981 to 1987: KB Salyut Mir-2
The prototype of the central module was as Polyus. ''Mir''-2 would be capable of docking at least four modules in ordinary operation.December 14, 1987: NPO Energia Mir-2
Designated as OSETS (Orbital Assembly and Operations Centre). The station would be built in a 65 degree orbit and consist of 90 ton modules. *Launch 1 – DOS 8, providing housing for the assembly crew. *Launch 2 – 90 ton module. *Launch 3 – Truss and solar arrays. *Launches 4 to 6 – additional 90 ton modules.1991: "Mir-1.5"
This would involve launch of the DOS-8, after which the Buran shuttle would grapple the module, rendezvous with ''Mir'', and attach it to the old DOS-7 base block. This plan was later altered so that DOS-8 would maneuver and dock itself to ''Mir''. It would remain attached for two years.1992: "Mir-2"
The station would consist of the DOS-8 core module and a cross beam called the NEP ( Science Power Platform). This was equipped with MSB retractable solar panels, Sfora thruster packages and small scientific packages. Four 3 to 4 ton modules were planned: *Docking Module - with the APDS universal androgynous docking system, and a side hatch for space walks *Resource Module - Equipped with gyrodynes for orienting the station and a passive docking port for docking of Soyuz or Progress ferry spacecraft *Technology Module - with materials experiments *Biotechnology ModuleNovember 1993: International Space Station built around Mir-2
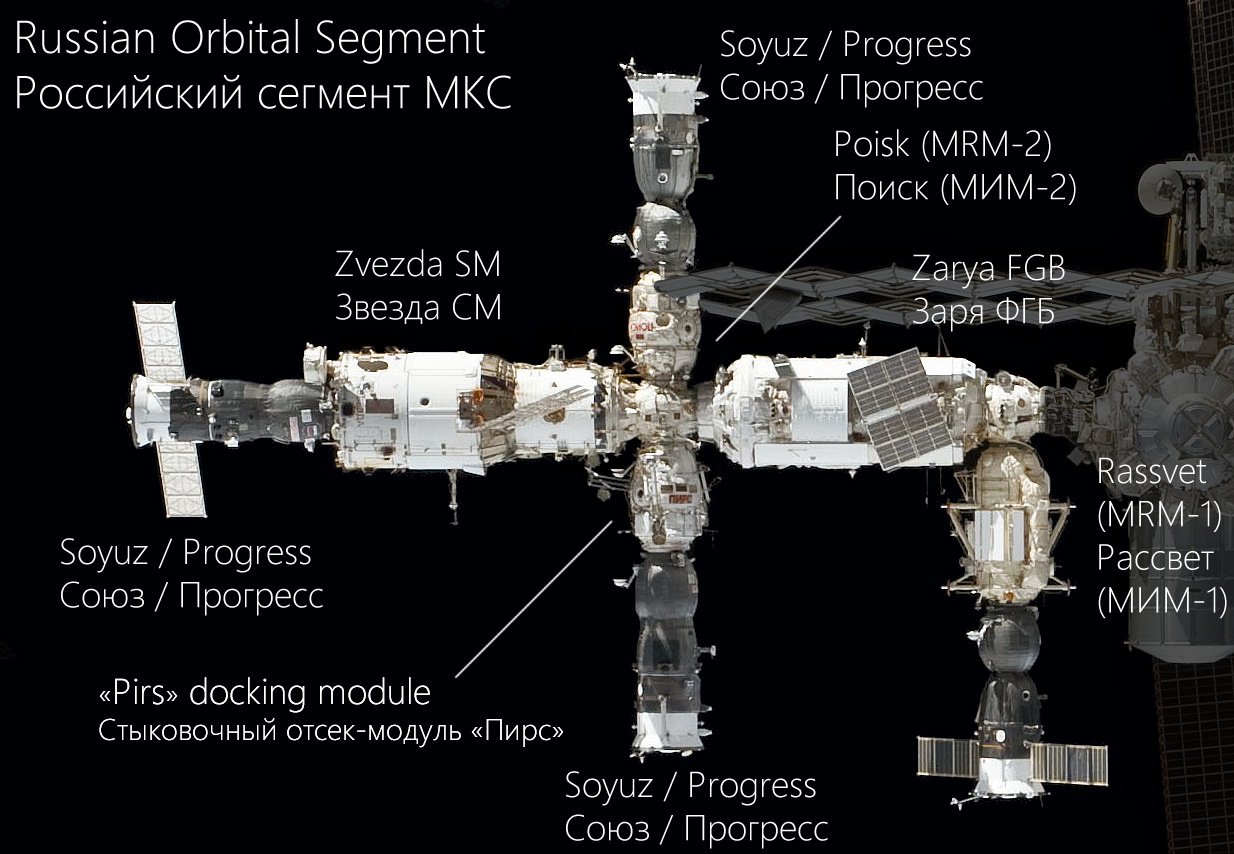
 Russian elements of the
Russian elements of the International Space Station
The International Space Station (ISS) is a large space station that was Assembly of the International Space Station, assembled and is maintained in low Earth orbit by a collaboration of five space agencies and their contractors: NASA (United ...
include:
* Zarya FGB, the first element launched. This was a US-funded TKS
The TK (TK-3) and TKS were Poland, Polish tankettes developed during the 1930s and used in the Second World War.
Design and development
The TK (also known as the TK-3) tankette was a Polish design produced from 1931 based on the chassis of the ...
-derived propulsion module built by KB Salyut.
* Zvezda Service Module - this is the DOS-8 block, which was launched as the third major ISS module in July 2000.
*SO-1 Pirs - one of the docking modules originally designed for Buran/''Mir''-2 was added to the station in September 2001, and later deorbited in July 2021 to make room for Nauka.
*SO-2 Poisk - a module similar to Pirs. Poisk also provides extra space for scientific experiments, and power-supply outlets and data-transmission interfaces for external scientific payloads.
* Rassvet - the only module delivered by NASA shuttle, in a barter exchange for the launch 'owed' for Zarya. Rassvet was built from a test article for the pressurized shell portion of NEP. It is used for cargo storage, science, and as a docking port for visiting spacecraft.
* Nauka FGB-2 - this is Russia's largest module and only module dedicated wholly to science, and was launched in July 2021, with the European Robotic Arm attached.
* Prichal UM - the 'nodal module', meant to host four additional laboratory and power modules and a docking port as part of the since-cancelled OPSEK
The Orbital Piloted Assembly and Experiment Complex (, ''Orbital'nyj Pilotirujemyj Sborochno-Eksperimental'nyj Kompleks''; ОПСЭК, OPSEK) was a 2009–2017 proposed third-generation Russian space program, Russian modular space station fo ...
plan. It launched in November 2021.
See also
*List of space stations
Past stations
These stations have re-entered the atmosphere and disintegrated.
The Soviet Union ran two programs simultaneously in the 1970s, both of which were called Salyut program, Salyut publicly. The Long Duration Orbital Station (DOS ...
* Lunar Orbital Station
The Lunar Orbital Station (; LOS) is a proposed Russian space station which would orbit around the Moon. The design was presented in 2007 at a conference at the Gagarin Cosmonaut Training Center in Star City, Russia, Star City. It is one of the tw ...
* Soviet space stations
References
External links
Mir-2 on Astronautix
{{Russian human spaceflight programs Cancelled space stations Cancelled Soviet spacecraft