|
Ňěehsuvar Bey
Shah Suwar (; ; before 1432 ‚Äď 24 August 1472) was the ruler of Beylik of Dulkadir, Dulkadir from April 1466 to 4 June 1472. Upon the assassination of his brother, Malik Arslan (), he competed for the throne against his other brother Shah Budak (), who took over with the support of the Mamluk Sultanate. Shah Suwar was welcomed by the Ottoman Empire, Ottoman Sultan Mehmed II (), who appointed him to a number of positions in his realm. Six months into Shah Budak's reign, Shah Suwar defeated him and instead became the new ruler in April 1466. The Mamluks fiercely disputed Shah Suwar's reign. The Sultans Sayf al-Din Khushqadam, Khushqadam () and Qaitbay () launched multiple consecutive campaigns to subdue him. Shah Suwar initially triumphed over the Mamluks and expanded his territory, occupying the entirety of the Ramadanid Emirate, Ramadanid realm. Shah Suwar started loosening his ties with the Ottomans, who disapproved of the constant warfare between him and the Mamluks. In 1468, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coinage
Coinage may refer to: * Coins, standardized as currency * Coining (mint), the process of manufacturing coins * '' COINage'', a numismatics magazine * Tin coinage, a tax on refined tin * Coinage, a protologism or neologism In linguistics, a neologism (; also known as a coinage) is any newly formed word, term, or phrase that has achieved popular or institutional recognition and is becoming accepted into mainstream language. Most definitively, a word can be considered ... See also * Coin (other) * Coining (other) {{disambig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sayf Al-Din Khushqadam
Al-Malik al-ŠļíńĀhir Sayf al-Dńęn AbŇę Sa Ņńęd Khushqadam ibn ŅAbdallńĀh al-NńĀŠĻ£irńę l-Mu ĺayyadńę (; ‚Äď 9 October 1467) was a Mamluk sultan of Egypt and Syria from 28 June 1461 to 9 October 1467. He was born in Cairo, Egypt. Early life and career Originally from Sultanate of Rum, Khushqadam was a slave purchased by Al-Mu'ayyad Shaykh, and later served in the ''j√Ęmd√Ęr'' corps. He eventually became a member of the sultan's guards during the reign of his son, Al-Muzaffar Ahmad. He ascended to the rank of "emir of ten" in Damascus by 1446. In 1448, Khushqadam was in Kozan, where a mosque was dedicated in his honor. He later became the head of the court military in Cairo in 1450 and served as minister of war during Sayf al-Din Inal's reign in 1456, leading expeditions against the Karamanids. Reign Upon Inal's death in February 1461, his son Shihab al-Din Ahmad succeeded him and Khushqadam assumed the role of ''atabeg''. However, the sultan was abducted four months later du ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Uzun Hasan
Uzun Hasan or Uzun Hassan (; February or March 1425 ‚Äď January 6, 1478) was a ruler of the Turkoman (ethnonym), Turkoman Aq Qoyunlu state and is generally considered to be its strongest ruler. Hasan ruled between 1452 and 1478 and presided over the confederation's territorial apex, when it included parts or all of present-day Iraq, Turkey, Azerbaijan, Iran, Transcaucasia and Syria. Reign Timur, the founder and ruler of the Timurid Empire, had appointed Uzun Hasan's grandfather, Kara Osman, Kara Y√ľl√ľk Osman, as a governor of DiyarbakńĪr, with the cities of Erzincan, Mardin, Ruha (or Urfa), and Sivas. Later, Persia was divided between two Timurid dynasty, Timurid rulers, Jahan Shah of Qara Qoyunlu (the Black Sheep Turkoman) and Uzun Hasan. After twenty years of fighting, Uzun Hasan eventually defeated Jahan Shah in a Battle of Chapakchur, battle near the sanjak of Bing√∂l Province, √áapak√ßur in present-day eastern Turkey on October 30 (or November 11), 1467. Upon the def ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
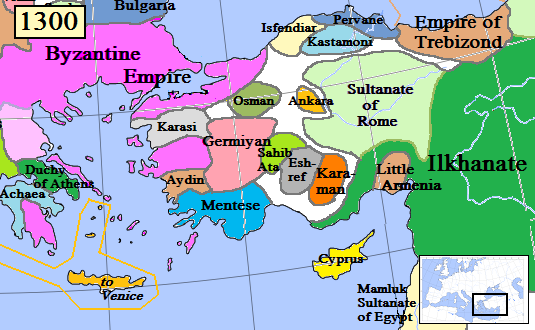
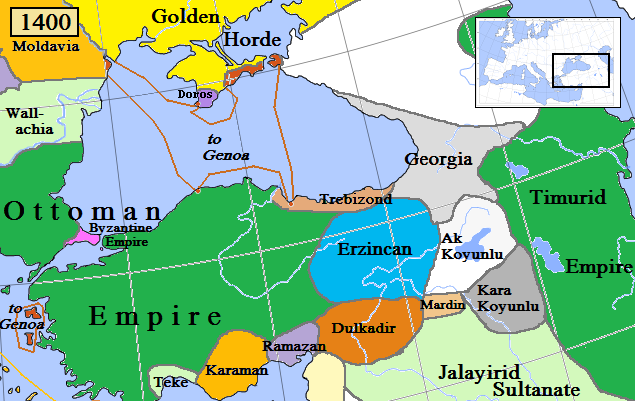
Karamanids
The Karamanids ( or ), also known as the Emirate of Karaman and Beylik of Karaman (), was a Turkish people, Turkish Anatolian beyliks, Anatolian beylik (principality) of Salur tribe origin, descended from Oghuz Turks, centered in South-Central Anatolia around the present-day Karaman Province. From the mid 14th century until its fall in 1487, the Karamanid dynasty was one of the most powerful beyliks in Anatolia. states and territories disestablished in the 1480s History The Karamanids traced their ancestry from Hodja Sad al-Din and his son Nure Sofi, Nure Sufi Bey, who emigrated from Arran (Caucasus), Arran (roughly encompassing modern-day Azerbaijan) to Sivas because of The Mongol Invasions, the Mongol invasion in 1230. The Karamanids were members of the Salur tribe of Oghuz Turks. According to others, they were members of the Afshar tribe,Cahen, Claude, ''Pre-Ottoman Turkey: A General Survey of the Material and Spiritual Culture and History c. 1071‚Äď1330'', trans. J. Jone ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mehmed Of Dulkadir
Nasir al-Din Mehmed Beg (; before 1362 ‚Äď October 1442) was the ruler of Dulkadir, a state in southern Anatolia, from 1399 until his death. After his father, Ghars al-Din Khalil (), died, Mehmed repudiated the reign of his uncle, Shaban Suli () and clashed with him on several occasions, relying on the support of the Mamluk Sultanate that ruled Egypt and Syria. Following Suli's murder, his son, Sadaqa, rose to the throne. Mehmed succeeded in claiming power shortly after with the intervention of the Ottoman Sultan Bayezid I (). During the Ottoman Interregnum (1402‚Äď13), Mehmed supported Bayezid's son Mehmed Chelebi, who became the new sultan. While Nasir al-Din Mehmed was involved in sporadic skirmishes with the Mamluks, he enjoyed peace with them towards the end of his reign, marrying his daughter to the Mamluk Sultan Jaqmaq () and commissioning the construction of madrasas and other buildings in Mamluk-controlled regions, such as Jerusalem. Background and early life Mehmed' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Barquq
Al-Malik Az-Zahir Sayf ad-Din Barquq (; born ) was the first Sultan of the Circassians, Circassian Mamluk Burji dynasty of Mamluk Sultanate (Cairo), Egypt ruling from 1382 to 1389 and 1390 to 1399. Born to a Christianity, Christian father in Circassia, Barquq was enslaved and later arrived in Egypt. He deposed sultan al-Salih Hajji to claim the throne for himself. Once in power, he placed many of his family members in positions of power. Rebelling governors in 1389 restored Hajji to the throne but Barquq was able to reclaim the throne shortly after and ruled until his death in 1399 and was succeeded by his An-Nasir Faraj, son. The name Barquq is of Circassian origin and is his birth name.Tekindańü, Ňěehabeddin. ''Berkuk Devrinde Meml√Ľk SultanlńĪńüńĪ (XIV. y√ľzyńĪl MńĪsńĪr tarihine dair araŇütńĪrmalar)'' Early life Barquq was of Circassians, Circassian origin,Tekindańü, Ňěehabeddin. ''Berkuk Devrinde Meml√Ľk SultanlńĪńüńĪ (XIV. y√ľzyńĪl MńĪsńĪr tarihine dair araŇütńĪrmalar)'' and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shaban Suli
Shaban Suli Beg (; died May 1398), also known as Sevli Beg, was the third ruler of Dulkadir from 1386 to 1398. Suli's father was Zayn al-Din Qaraja (), a Turkoman chieftain, who founded the state of Dulkadir in southern Anatolia and northern Syria as a client of the Mamluk Sultanate. Suli succeeded his older brother Ghars al-Din Khalil (), who was assassinated on the orders of the Mamluk Sultan Barquq (). Suli was involved in a series of clashes with the Mamluks, in which he was initially victorious, forcing Barquq to recognize him as the new ruler. Barquq continued supporting Suli's rivals, and in 1389, Suli joined a rebellion against the state. He was pardoned in January 1391 but this time allied himself with Timur (), perpetrating an invasion of Syria. Suli faced a major loss at the hands of the Mamluks in March 1395 and was assassinated in May 1398 on the order of Barquq. The throne was inherited by his son, Sadaqa (). Early life and background The region around Marash in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ghars Al-Din Khalil
Ghars al-Din Khalil Beg (; died April 1386) was the second ruler of the Turkoman (ethnonym), Turkoman Dulkadirid principality, reigning from 1353 to 1386. Having actively taken part in military pursuits during his father Zayn al-Din Qaraja's rule, he further expanded the influence of the Dulkadirids and clashed with the Mamluk Sultanate, Mamluk suzerainty, contributing to the growing tension between the Mamluks and Dulkadirids. Raids by Khalil in the northern frontier with the Mamluks prompted the Mamluk sultan to provoke dissension in the Dulkadir dynasty. The sultan incited Khalil's brother Sarim al-Din Ibrahim, who sought Mamluk recognition for his domains near Harpoot, to assassinate the ruler, Khalil. Ghars al-Din was killed in an ambush and was succeeded by his other brother Shaban Suli. Early life and background Khalil was the son of Zayn al-Din Qaraja, a Turkoman (ethnonym), Turkoman chieftain who, after a series of clashes with other local Turkoman lords and Mamluk gover ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Syria (region)
Syria, ( or ''Shaam'') also known as Greater Syria or Syria-Palestine, is a historical region located east of the Mediterranean Sea in West Asia, broadly synonymous with the Levant. The region boundaries have changed throughout history. However, in modern times, the term "Syria" alone is used to refer to the Syria, Syrian Arab Republic. The term is originally derived from Assyria, an Ancient Semitic-speaking peoples, ancient Semitic-speaking civilization centered in northern Mesopotamia, modern-day Iraq. During the Hellenistic period, the term Syria was applied to the entire Levant as Coele-Syria. Under Roman Empire, Roman rule, the term was used to refer to the Roman Syria, province of Syria, later divided into Phoenice (Roman province), Syria Phoenicia and Coele-Syria, Coele Syria, and to the province of Syria Palaestina. Under the Byzantine Empire, Byzantines, the provinces of Syria Prima and Syria Secunda emerged out of Coele Syria. After the Muslim conquest of the Levant ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anatolia
Anatolia (), also known as Asia Minor, is a peninsula in West Asia that makes up the majority of the land area of Turkey. It is the westernmost protrusion of Asia and is geographically bounded by the Mediterranean Sea to the south, the Aegean Sea to the west, the Turkish Straits to the northwest, and the Black Sea to the north. The eastern and southeastern limits have been expanded either to the entirety of Asiatic Turkey or to an imprecise line from the Black Sea to the Gulf of Alexandretta. Topographically, the Sea of Marmara connects the Black Sea with the Aegean Sea through the Bosporus and the Dardanelles, and separates Anatolia from Thrace in Southeast Europe. During the Neolithic, Anatolia was an early centre for the development of farming after it originated in the adjacent Fertile Crescent. Beginning around 9,000 years ago, there was a major migration of Anatolian Neolithic Farmers into Neolithic Europe, Europe, with their descendants coming to dominate the continent a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oghuz Turks
The Oghuz Turks ( Middle Turkic: , ) were a western Turkic people who spoke the Oghuz branch of the Turkic language family. In the 8th century, they formed a tribal confederation conventionally named the Oghuz Yabgu State in Central Asia. Today, much of the populations of Turkey, Azerbaijan and Turkmenistan are descendants of Oghuz Turks. The term Oghuz was gradually supplanted by the terms Turkmen and Turcoman ( or ''T√ľrkm√Ęn'') by the 13th century.Lewis, G. ''The Book of Dede Korkut''. Penguin Books, 1974, p. 10. The Oghuz confederation migrated westward from the Jeti-su area after a conflict with the Karluk allies of the Uyghurs. In the 9th century, the Oghuz from the Aral steppes drove Pechenegs westward from the Emba and Ural River region. In the 10th century, the Oghuz inhabited the steppe of the rivers Sari-su, Turgai and Emba north of Lake Balkhash in modern-day Kazakhstan. They embraced Islam and adapted their traditions and institutions to the Islam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zayn Al-Din Qaraja
Zayn al-Din Qaraja Beg (; 1279 ‚Äď 11 December 1353) was a Turkoman (ethnonym), Turkoman chieftain who founded the Dulkadirid principality in southern Anatolia and northern Syria (region), Syria, ruling from 1337 to 1353. Before his ascendance, Qaraja competed with Taraqlu, another local Turkoman warlord, over the administration of the northern frontier of the Mamluk Sultanate, Mamluks. After gaining recognition from the Mamluk Sultan Al-Nasir Muhammad, he became the head of a client state on their Anatolian extremity. During his rule, Qaraja grew more ambitious and clashed with various Mamluk governors who were against his expanding influence. Qaraja took advantage of the political turmoil within the Mamluks and declared independence in 1348. However, this led to his imprisonment and subsequent execution in 1353. Early life and background During the thirteenth century, the region around Marash in southern Anatolia was ruled by the Armenian Kingdom of Cilicia. The region came u ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |