|
äuä
Bernese German (Standard German: ''Berndeutsch'', ) is the dialect of High Alemannic German spoken in the Swiss plateau (Mittelland) part of the canton of Bern and in some neighbouring regions. A form of Bernese German is spoken by the Swiss Amish affiliation of the Old Order Amish in Adams County, Indiana, United States, as well as and other settlements in the US, primarily in Indiana. Varieties There is a lot of regional variation within Bernese German dialects. However, with the increasing importance of the big agglomeration of Bern, the variety of Bern is spreading out, levelling the old village dialects. Until the second half of the 20th century, there was a considerable range of sociolects in the city of Bern where four different groups could be distinguished: *The patrician Bernese German of the high society. It has neither l-vocalisation nor nd-velarisation, it does not employ the alveolar trill but the French uvular trill, and it has more French loanwords than the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Canton Of Bern
The canton of Bern, or Berne (; ; ; ), is one of the Canton of Switzerland, 26 cantons forming the Switzerland, Swiss Confederation. Its capital city, Bern, is also the ''de facto'' capital of Switzerland. The bear is the heraldic symbol of the canton, displayed on a red-yellow background. Comprising Subdivisions of the canton of Bern, ten districts, Bern is the second-largest canton by both surface area and population. Located in west-central Switzerland, it is surrounded by eleven cantons. It borders the cantons of canton of Jura, Jura and canton of Solothurn, Solothurn to the north. To the west lie the cantons of canton of Neuchâtel, Neuchâtel, canton of Fribourg, Fribourg, and canton of Vaud, Vaud. To the south lies the cantons of canton of Valais, Valais. East of the canton of Bern lie the cantons of Canton of Uri, Uri, Canton of Nidwalden, Nidwalden, Canton of Obwalden, Obwalden, Canton of Lucerne, Lucerne and Canton of Aargau, Aargau. The geography of the canton includes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yiddish
Yiddish, historically Judeo-German, is a West Germanic language historically spoken by Ashkenazi Jews. It originated in 9th-century Central Europe, and provided the nascent Ashkenazi community with a vernacular based on High German fused with many elements taken from Hebrew language, Hebrew (notably Mishnaic Hebrew, Mishnaic) and to some extent Aramaic. Most varieties of Yiddish include elements of Slavic languages and the vocabulary contains traces of Romance languages.Aram Yardumian"A Tale of Two Hypotheses: Genetics and the Ethnogenesis of Ashkenazi Jewry".University of Pennsylvania. 2013. Yiddish has traditionally been written using the Hebrew alphabet. Prior to World War II, there were 11–13 million speakers. 85% of the approximately 6 million Jews who were murdered in the Holocaust were Yiddish speakers,Solomon Birnbaum, ''Grammatik der jiddischen Sprache'' (4., erg. Aufl., Hamburg: Buske, 1984), p. 3. leading to a massive decline in the use of the language. Jewish ass ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Question Tag
A tag question is a construction in which an interrogative element is added to a declarative or an imperative clause. The resulting speech act comprises an assertion paired with a request for confirmation. For instance, the English tag question "You're John, aren't you?" consists of the declarative clause "You're John" and the interrogative tag "aren't you?" Uses In most languages, tag questions are more common in spoken usage than in formal written usage. They can be an indicator of politeness, hedging, consensus seeking, emphasis and irony. They may suggest confidence or lack of confidence; they may be confrontational, defensive or tentative. Although they have the grammatical form of a question, they may be rhetorical (not expecting an answer). In other cases, when they do expect a response, they may differ from straightforward questions in that they cue the listener as to what response is desired. In legal settings, tag questions can often be found in a leading question. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shibboleth
A shibboleth ( ; ) is any custom or tradition—usually a choice of phrasing or single word—that distinguishes one group of people from another. Historically, shibboleths have been used as passwords, ways of self-identification, signals of loyalty and affinity, ways of maintaining traditional segregation, or protection from threats. It has also come to mean a moral formula held tenaciously and unreflectingly, or a taboo. Origin The term originates from the Hebrew word (), which means the part of a plant containing grain, such as the ear of a stalk of wheat or rye; or less commonly (but arguably more appropriately) 'flood, torrent'. Biblical account The modern use derives from an account in the Hebrew Bible, in which pronunciation of this word was used to distinguish Ephraimites, whose dialect used a different first consonant. The difference concerns the Hebrew letter '' shin'', which is now pronounced as (as in ''shoe''). In the Book of Judges chapter 12, after the inhab ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Numeral (linguistics)
In linguistics, a numeral in the broadest sense is a word or phrase that describes a numerical quantity. Some theories of grammar use the word "numeral" to refer to cardinal numbers that act as a determiner that specify the quantity of a noun, for example the "two" in "two hats". Some theories of grammar do not include determiners as a part of speech and consider "two" in this example to be an adjective. Some theories consider "numeral" to be a synonym for "number" and assign all numbers (including ordinal numbers like "first") to a part of speech called "numerals". Numerals in the broad sense can also be analyzed as a noun ("three is a small number"), as a pronoun ("the two went to town"), or for a small number of words as an adverb ("I rode the slide twice"). Numerals can express relationships like quantity (cardinal numbers), sequence (ordinal numbers), frequency (once, twice), and part (fraction). Identifying numerals Numerals may be attributive, as in ''two dogs'', or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grammatical Gender
In linguistics, a grammatical gender system is a specific form of a noun class system, where nouns are assigned to gender categories that are often not related to the real-world qualities of the entities denoted by those nouns. In languages with grammatical gender, most or all nouns inherently carry one value of the grammatical category called ''gender''. The values present in a given language, of which there are usually two or three, are called the ''genders'' of that language. Some authors use the term "grammatical gender" as a synonym of "noun class", whereas others use different definitions for each. Many authors prefer "noun classes" when none of the inflections in a language relate to Sex–gender distinction, sex or gender. According to one estimate, gender is used in approximately half of the world's languages. According to one definition: "Genders are classes of nouns reflected in the behavior of associated words." Overview Languages with grammatical gender usually h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Velarization
Velarization merican spelling/small> or velarisation ritish spelling/sup> is a secondary articulation of consonants by which the back of the tongue is raised toward the velum during the articulation of the consonant. In the International Phonetic Alphabet, velarization is transcribed by one of four diacritics: *A tilde or swung dash through the letter covers velarization, uvularization and pharyngealization, as in (the velarized equivalent of ) *A superscript Latin gamma after the letter standing for the velarized consonant, as in (a velarized ) *To distinguish velarization from a velar fricative release, may be used instead of *A superscript indicates either simultaneous velarization and labialization, as in or , or labialization of a velar consonant, as in . Although electropalatographic studies have shown that there is a continuum of possible degrees of velarization, the IPA does not specify any way to indicate degrees of velarization, as the difference has ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Triphthong
In phonetics, a triphthong ( , ) (from Greek , ) is a monosyllabic vowel combination involving a quick but smooth movement of the articulator from one vowel quality to another that passes over a third. While "pure" vowels, or monophthongs, are said to have one target articulator position, diphthongs have two and triphthongs three. Triphthongs are not to be confused with disyllabic sequences of a diphthong followed by a monophthong, as in German 'fire', where the final vowel is longer than those found in triphthongs. Examples Triphthongs that feature close elements typically analyzed as and in phonology are not listed. For instance, the Polish word 'tallow' is typically analyzed as - a sequence of a consonant followed by a vowel and another consonant. This is because the palatal approximant is resyllabified in some inflected forms, such as (instr. pl.), and also because occurs word-finally after a consonant just like does (compare 'industry' with 'Przemyśl'), wh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diphthong
A diphthong ( ), also known as a gliding vowel or a vowel glide, is a combination of two adjacent vowel sounds within the same syllable. Technically, a diphthong is a vowel with two different targets: that is, the tongue (and/or other parts of the speech apparatus) moves during the pronunciation of the vowel. In most varieties of English, the phrase "no highway cowboys" ( ) has five distinct diphthongs, one in every syllable. Diphthongs contrast with monophthongs, where the tongue or other speech organs do not move and the syllable contains only a single vowel sound. For instance, in English, the word ''ah'' is spoken as a monophthong (), while the word ''ow'' is spoken as a diphthong in most varieties (). Where two adjacent vowel sounds occur in different syllables (e.g. in the English word ''re-elect'') the result is described as hiatus, not as a diphthong. Diphthongs often form when separate vowels are run together in rapid speech during a conversation. However, there ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
L-vocalization
''L''-vocalization, in linguistics, is a process by which a lateral approximant sound such as , or, perhaps more often, velarized , is replaced by a vowel or a semivowel. Types There are two types of ''l''-vocalization: * A labiovelar approximant, velar approximant, or back vowel: > or > or * A front vowel or palatal approximant: > > West Germanic languages Examples of L-vocalization can be found in many West Germanic languages, including English, Scots, Dutch, and some German dialects. Early Modern English L-vocalization has occurred, since Early Modern English, in certain ''-al-'' and ''-ol-'' sequences before coronal consonant, coronal or velar consonant, velar consonants, or at the end of a word or morpheme. In those sequences, became and diphthonged to , while became and diphthonged to . At the end of a word or morpheme, it produced ''all'', ''ball'', ''call'', ''control'', ''droll'', ''extol'', ''fall'', ''gall'', ''hall'', ''knoll'', ''mall'', ''pall'', ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
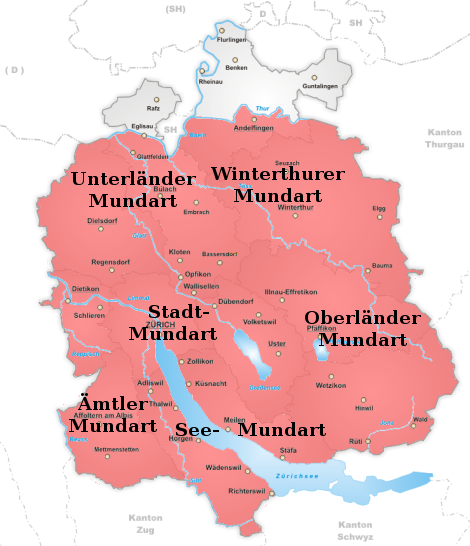
Zurich German
Zurich German (natively ; ) is the High Alemannic dialect spoken in the Canton of Zurich, Switzerland. Its area covers most of the canton, with the exception of the parts north of the Thur (Switzerland), Thur and the Rhine, which belong to the areal of the northeastern (Schaffhausen and Thurgau) Swiss dialects. Zurich German was traditionally divided into six sub-dialects, now increasingly homogenised owing to larger Zürich metropolitan area, commuting distances: *The dialect of the town of Zurich () *The dialect spoken around Lake Zurich () *The dialect of the Knonauer Amt west of the Albis () *The dialect of the area of Winterthur *The dialect of the Zürcher Oberland around Lake Pfäffikon and the upper Tösstal valley *The dialect of the Zürcher Unterland around Bülach and Dielsdorf Akin to all Swiss German dialects, it is essentially a spoken language, whereas the written language is Swiss Standard German, standard German. Likewise, there is no official orthography of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |