|
Ă— Celmearia
The multiplication sign (), also known as the times sign or the dimension sign, is a mathematical symbol used to denote the operation of multiplication, which results in a product. The symbol is also used in botany, in botanical hybrid names. The form is properly a four-fold rotationally symmetric saltire. The multiplication sign is similar to a lowercase X (). History The earliest known use of the symbol to indicate multiplication appears in an anonymous appendix to the 1618 edition of John Napier's . This appendix has been attributed to William Oughtred, who used the same symbol in his 1631 algebra text, , stating:Multiplication of species .e. unknownsconnects both proposed magnitudes with the symbol 'in' or : or ordinarily without the symbol if the magnitudes be denoted with one letter. Other works have been identified in which crossed diagonals appear in diagrams involving multiplied numbers, such as Robert Recorde's '' The Ground of Arts'' and Oswald Schreck ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glossary Of Mathematical Symbols
A mathematical symbol is a figure or a combination of figures that is used to represent a mathematical object, an action on mathematical objects, a relation between mathematical objects, or for structuring the other symbols that occur in a formula or a mathematical expression. More formally, a ''mathematical symbol'' is any grapheme used in mathematical formulas and expressions. As formulas and expressions are entirely constituted with symbols of various types, many symbols are needed for expressing all mathematics. The most basic symbols are the decimal digits (0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9), and the letters of the Latin alphabet. The decimal digits are used for representing numbers through the Hindu–Arabic numeral system. Historically, upper-case letters were used for representing points in geometry, and lower-case letters were used for variables and constants. Letters are used for representing many other types of mathematical object. As the number of these types has increased ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Numbers
A number is a mathematical object used to count, measure, and label. The most basic examples are the natural numbers 1, 2, 3, 4, and so forth. Numbers can be represented in language with number words. More universally, individual numbers can be represented by symbols, called ''numerals''; for example, "5" is a numeral that represents the number five. As only a relatively small number of symbols can be memorized, basic numerals are commonly organized in a numeral system, which is an organized way to represent any number. The most common numeral system is the Hindu–Arabic numeral system, which allows for the representation of any non-negative integer using a combination of ten fundamental numeric symbols, called digits. In addition to their use in counting and measuring, numerals are often used for labels (as with telephone numbers), for ordering (as with serial numbers), and for codes (as with ISBNs). In common usage, a ''numeral'' is not clearly distinguished from the ''nu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Historian
A historian is a person who studies and writes about the past and is regarded as an authority on it. Historians are concerned with the continuous, methodical narrative and research of past events as relating to the human species; as well as the study of all history in time. Some historians are recognized by publications or training and experience.Herman, A. M. (1998). Occupational outlook handbook: 1998–99 edition. Indianapolis: JIST Works. Page 525. "Historian" became a professional occupation in the late nineteenth century as research universities were emerging in Germany and elsewhere. Objectivity Among historians Ancient historians In the 19th century, scholars used to study ancient Greek and Roman historians to see how generally reliable they were. In recent decades, however, scholars have focused more on the constructions, genres, and meanings that ancient historians sought to convey to their audiences. History is always written with contemporary concerns and ancient hist ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crocosmia Ă— Crocosmiiflora
''Crocosmia'' Ă— ''crocosmiiflora'', or montbretia, is a garden hybrid of '' C. aurea'' and '' C. pottsii'', first bred in 1880 in France by Victor Lemoine. The basionym of the hybrid is ''Montbretia crocosmiiflora'' Lemoine. In 1932 it was reclassified as ''C.'' Ă— ''crocosmiiflora'' (Lemoine) N.E.Br., but the common name "montbretia" is still often found in horticultural literature, and is commonly used in the British Isles for orange-flowered cultivars that have naturalised, while "crocosmia" is reserved for less aggressive red-flowered cultivars. Description ''Crocosmia'' Ă— ''crocosmiiflora'' grows to 90 cm (36 in.) high, with long sword-shaped leaves, shorter than the flowering stem and arising from the plant base, ribbed and up to 20mm wide. The base is a corm, a swollen underground stem lasting one year. The flowers are up to 5 cm long and coloured deep orange. Cultivation In the United States, ''Crocosmia'' Ă— ''crocosmiiflora'' is considered suitab ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ceanothus Impressus
''Ceanothus impressus'' is a species of shrub in the family Rhamnaceae known by the common name Santa Barbara ceanothus.''Ceanothus impressus''. CalFlora.''Ceanothus impressus''. USDA PLANTS. It is to the Central Coast of California, where it is known from |
Ceanothus Papillosus
''Ceanothus papillosus'', the wartleaf ceanothus, is a species of plant in the genus '' Ceanothus''. It is endemic to California, where it grows in open habitat on the slopes of the coastal mountain ranges, such as woodland and chaparral. Description The evergreen leaves are alternately arranged, often in crowded clusters, each oblong to long-rectangular in shape and covered in glandular bumps. The edges are generally turned under and lined with glandular hairs. The inflorescence In botany, an inflorescence is a group or cluster of flowers arranged on a plant's Plant stem, stem that is composed of a main branch or a system of branches. An inflorescence is categorized on the basis of the arrangement of flowers on a mai ... is a cluster of bright blue flowers. The fruit is a bumpy capsule about 3 millimeters long. Image:Ceanothus papillosus 3.jpg, Flowers Image:Ceanothus papillosus 4.jpg, Leaves References External links Calflora Database: ''Ceanothus papillosus'' (wart ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biology
Biology is the scientific study of life and living organisms. It is a broad natural science that encompasses a wide range of fields and unifying principles that explain the structure, function, growth, History of life, origin, evolution, and distribution of life. Central to biology are five fundamental themes: the cell (biology), cell as the basic unit of life, genes and heredity as the basis of inheritance, evolution as the driver of biological diversity, energy transformation for sustaining life processes, and the maintenance of internal stability (homeostasis). Biology examines life across multiple biological organisation, levels of organization, from molecules and cells to organisms, populations, and ecosystems. Subdisciplines include molecular biology, physiology, ecology, evolutionary biology, developmental biology, and systematics, among others. Each of these fields applies a range of methods to investigate biological phenomena, including scientific method, observation, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magnification
Magnification is the process of enlarging the apparent size, not physical size, of something. This enlargement is quantified by a size ratio called optical magnification. When this number is less than one, it refers to a reduction in size, sometimes called ''de-magnification''. Typically, magnification is related to scaling up visuals or images to be able to see more detail, increasing resolution, using microscope, printing techniques, or digital processing. In all cases, the magnification of the image does not change the perspective of the image. Examples of magnification Some optical instruments provide visual aid by magnifying small or distant subjects. * A magnifying glass, which uses a positive (convex) lens to make things look bigger by allowing the user to hold them closer to their eye. * A telescope, which uses its large objective lens or primary mirror to create an image of a distant object and then allows the user to examine the image closely with a smaller ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Variable (mathematics)
In mathematics, a variable (from Latin language, Latin ) is a Mathematical symbol, symbol, typically a letter, that refers to an unspecified mathematical object. One says colloquially that the variable ''represents'' or ''denotes'' the object, and that any valid candidate for the object is the value (mathematics), value of the variable. The values a variable can take are usually of the same kind, often numbers. More specifically, the values involved may form a Set (mathematics), set, such as the set of real numbers. The object may not always exist, or it might be uncertain whether any valid candidate exists or not. For example, one could represent two integers by the variables and and require that the value of the square of is twice the square of , which in algebraic notation can be written . A definitive proof that this relationship is impossible to satisfy when and are restricted to integer numbers isn't obvious, but it has been known since ancient times and has had a big ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
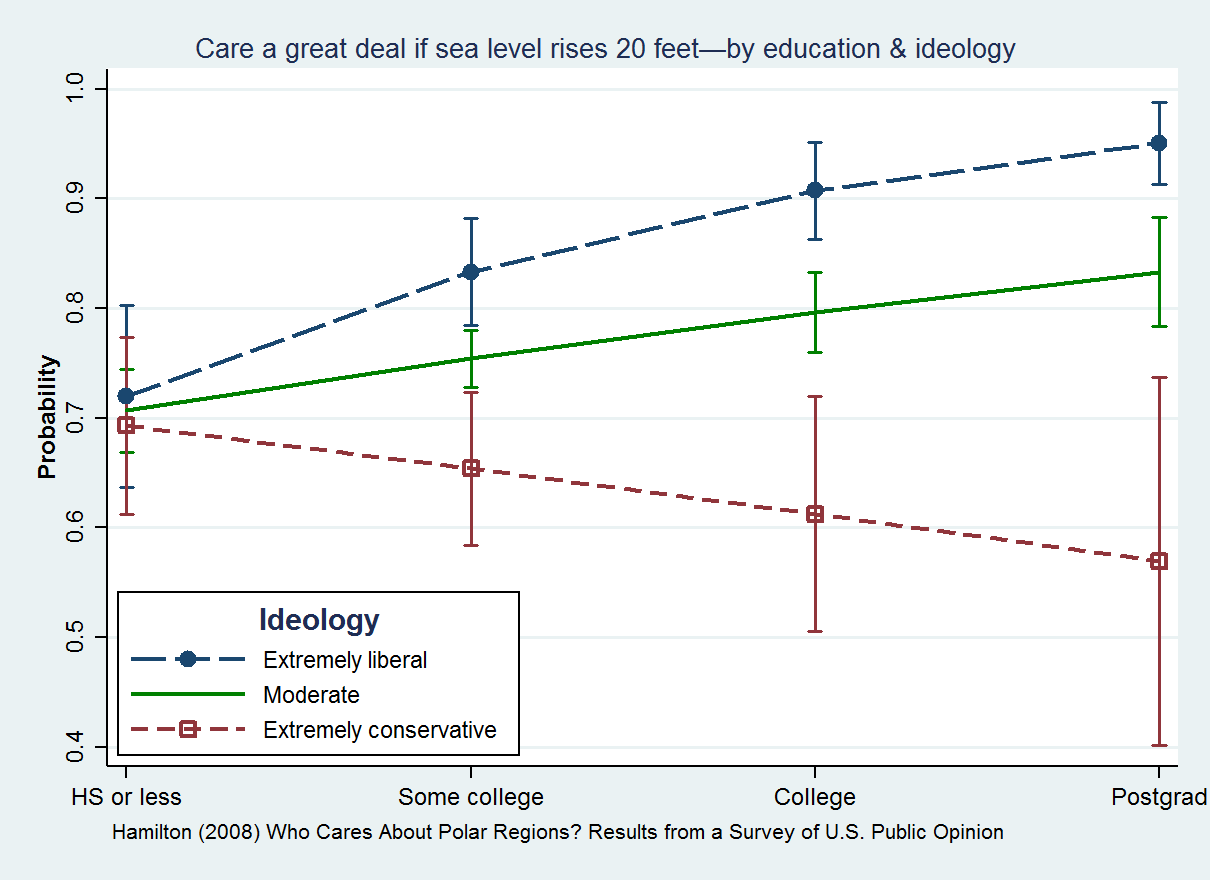
Interaction (statistics)
In statistics, an interaction may arise when considering the relationship among three or more Variable (statistics), variables, and describes a situation in which the effect of one causal variable on an outcome depends on the state of a second causal variable (that is, when effects of the two causes are not additive map, additive). Although commonly thought of in terms of Causality, causal relationships, the concept of an interaction can also describe non-causal associations (then also called Moderation (statistics), ''moderation'' or ''effect modification''). Interactions are often considered in the context of regression analysis, regression analyses or factorial experiments. The presence of interactions can have important implications for the interpretation of statistical models. If two variables of interest interact, the relationship between each of the interacting variables and a third "dependent variable" depends on the value of the other interacting variable. In practice, th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Matrix (mathematics)
In mathematics, a matrix (: matrices) is a rectangle, rectangular array or table of numbers, symbol (formal), symbols, or expression (mathematics), expressions, with elements or entries arranged in rows and columns, which is used to represent a mathematical object or property of such an object. For example, \begin1 & 9 & -13 \\20 & 5 & -6 \end is a matrix with two rows and three columns. This is often referred to as a "two-by-three matrix", a " matrix", or a matrix of dimension . Matrices are commonly used in linear algebra, where they represent linear maps. In geometry, matrices are widely used for specifying and representing geometric transformations (for example rotation (mathematics), rotations) and coordinate changes. In numerical analysis, many computational problems are solved by reducing them to a matrix computation, and this often involves computing with matrices of huge dimensions. Matrices are used in most areas of mathematics and scientific fields, either directly ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Display Resolution
The display resolution or display modes of a digital television, computer monitor, or other display device is the number of distinct pixels in each dimension that can be displayed. It can be an ambiguous term especially as the displayed resolution is controlled by different factors in cathode-ray tube (CRT) displays, flat-panel displays (including liquid-crystal displays) and projection displays using fixed picture-element (pixel) arrays. It is usually quoted as ', with the units in pixels: for example, ' means the width is 1024 pixels and the height is 768 pixels. This example would normally be spoken as "ten twenty-four by seven sixty-eight" or "ten twenty-four by seven six eight". One use of the term ''display resolution'' applies to fixed-pixel-array displays such as plasma display panels (PDP), liquid-crystal displays (LCD), Digital Light Processing (DLP) projectors, AMOLED, OLED displays, and similar technologies, and is simply the physical number of columns and rows of pi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |