Pharmacology on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Pharmacology is a branch of
 Pharmacology can be applied within clinical sciences.
Pharmacology can be applied within clinical sciences.
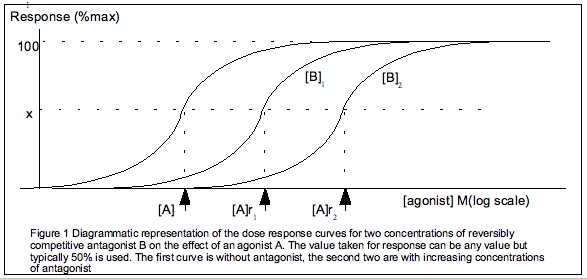 The study of chemicals requires intimate knowledge of the biological system affected. With the knowledge of cell biology and
The study of chemicals requires intimate knowledge of the biological system affected. With the knowledge of cell biology and
 Pharmacology is typically studied with respect to particular systems, for example endogenous neurotransmitter systems. The major systems studied in pharmacology can be categorised by their ligand (biochemistry), ligands and include acetylcholine, adrenaline, glutamate, GABA, dopamine, histamine, serotonin, cannabinoid and opioid.
Molecular targets in pharmacology include receptor (biochemistry), receptors,
Pharmacology is typically studied with respect to particular systems, for example endogenous neurotransmitter systems. The major systems studied in pharmacology can be categorised by their ligand (biochemistry), ligands and include acetylcholine, adrenaline, glutamate, GABA, dopamine, histamine, serotonin, cannabinoid and opioid.
Molecular targets in pharmacology include receptor (biochemistry), receptors,
American Society for Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics
British Pharmacological Society
International Conference on Harmonisation
US Pharmacopeia
International Union of Basic and Clinical Pharmacology
IUPHAR Committee on Receptor Nomenclature and Drug Classification
IUPHAR/BPS Guide to Pharmacology
medicine
Medicine is the science and practice of caring for a patient, managing the diagnosis, prognosis, prevention, treatment, palliation of their injury or disease, and promoting their health. Medicine encompasses a variety of health care pract ...
, biology
Biology is the scientific study of life. It is a natural science with a broad scope but has several unifying themes that tie it together as a single, coherent field. For instance, all organisms are made up of cells that process hereditary i ...
and pharmaceutical sciences
Pharmacy is the science and practice of discovering, producing, preparing, dispensing, reviewing and monitoring medications, aiming to ensure the safe, effective, and affordable use of medicines. It is a miscellaneous science as it links healt ...
concerned with drug
A drug is any chemical substance that causes a change in an organism's physiology or psychology when consumed. Drugs are typically distinguished from food and substances that provide nutritional support. Consumption of drugs can be via insuffla ...
or medication
A medication (also called medicament, medicine, pharmaceutical drug, medicinal drug or simply drug) is a drug used to diagnose, cure, treat, or prevent disease. Drug therapy (pharmacotherapy) is an important part of the medical field and re ...
action, where a drug may be defined as any artificial, natural, or endogenous (from within the body) molecule which exerts a biochemical or physiological effect on the cell, tissue, organ, or organism (sometimes the word ''pharmacon'' is used as a term to encompass these endogenous and exogenous
In a variety of contexts, exogeny or exogeneity () is the fact of an action or object originating externally. It contrasts with endogeneity or endogeny, the fact of being influenced within a system.
Economics
In an economic model, an exogeno ...
bioactive species). More specifically, it is the study of the interactions that occur between a living organism and chemicals that affect normal or abnormal biochemical function. If substances have medicinal properties, they are considered pharmaceuticals.
The field encompasses drug composition and properties,functions,sources,synthesis and drug design, molecular and cellular mechanisms, organ/systems mechanisms, signal transduction/cellular communication, molecular diagnostics
Molecular diagnostics is a collection of techniques used to analyze biological markers in the genome and proteome, and how their cells express their genes as proteins, applying molecular biology to medical testing. In medicine the technique is ...
, interaction
Interaction is action that occurs between two or more objects, with broad use in philosophy and the sciences. It may refer to:
Science
* Interaction hypothesis, a theory of second language acquisition
* Interaction (statistics)
* Interactions o ...
s, chemical biology, therapy, and medical applications and antipathogenic capabilities. The two main areas of pharmacology are pharmacodynamics
Pharmacodynamics (PD) is the study of the biochemical and physiologic effects of drugs (especially pharmaceutical drugs). The effects can include those manifested within animals (including humans), microorganisms, or combinations of organisms ...
and pharmacokinetics. Pharmacodynamics studies the effects of a drug on biological systems, and pharmacokinetics studies the effects of biological systems on a drug. In broad terms, pharmacodynamics discusses the chemicals with biological receptors
Receptor may refer to:
*Sensory receptor, in physiology, any structure which, on receiving environmental stimuli, produces an informative nerve impulse
*Receptor (biochemistry), in biochemistry, a protein molecule that receives and responds to a n ...
, and pharmacokinetics discusses the absorption, distribution, metabolism
Metabolism (, from el, μεταβολή ''metabolē'', "change") is the set of life-sustaining chemical reactions in organisms. The three main functions of metabolism are: the conversion of the energy in food to energy available to run cell ...
, and excretion
Excretion is a process in which metabolic waste
is eliminated from an organism. In vertebrates this is primarily carried out by the lungs, kidneys, and skin. This is in contrast with secretion, where the substance may have specific tasks after ...
(ADME) of chemicals from the biological systems.
Pharmacology is not synonymous with pharmacy and the two terms are frequently confused. Pharmacology, a biomedical science
Biomedical sciences are a set of sciences applying portions of natural science or formal science, or both, to develop knowledge, interventions, or technology that are of use in healthcare or public health. Such disciplines as medical microbi ...
, deals with the research, discovery, and characterization of chemicals which show biological effects and the elucidation of cellular and organismal function in relation to these chemicals. In contrast, pharmacy, a health services profession, is concerned with the application of the principles learned from pharmacology in its clinical settings; whether it be in a dispensing or clinical care role. In either field, the primary contrast between the two is their distinctions between direct-patient care, pharmacy practice, and the science-oriented research field, driven by pharmacology.
Etymology
The word ''pharmacology'' is derived fromGreek
Greek may refer to:
Greece
Anything of, from, or related to Greece, a country in Southern Europe:
*Greeks, an ethnic group.
*Greek language, a branch of the Indo-European language family.
**Proto-Greek language, the assumed last common ancestor ...
, ''pharmakon'', "drug, poison
Poison is a chemical substance that has a detrimental effect to life. The term is used in a wide range of scientific fields and industries, where it is often specifically defined. It may also be applied colloquially or figuratively, with a broa ...
" and , '' -logia'' "study of", "knowledge of" (cf. the etymology of ''pharmacy''). Pharmakon is related to pharmakos
A pharmakós ( el, φαρμακός, plural ''pharmakoi'') in Ancient Greek religion was the ritualistic sacrifice or exile of a human scapegoat or victim.
Ritual
A slave, a cripple, or a criminal was chosen and expelled from the community at tim ...
, the ritualistic sacrifice or exile of a human scapegoat or victim in Ancient Greek religion
Religious practices in ancient Greece encompassed a collection of beliefs, rituals, and mythology, in the form of both popular public religion and cult practices. The application of the modern concept of "religion" to ancient cultures has been ...
.
The modern term ''pharmacon'' is used more broadly than the term ''drug
A drug is any chemical substance that causes a change in an organism's physiology or psychology when consumed. Drugs are typically distinguished from food and substances that provide nutritional support. Consumption of drugs can be via insuffla ...
'' because it includes endogenous substances, and biologically active substances which are not used as drugs. Typically it includes pharmacological agonists
An agonist is a chemical that activates a receptor to produce a biological response. Receptors are cellular proteins whose activation causes the cell to modify what it is currently doing. In contrast, an antagonist blocks the action of the agon ...
and antagonists
An antagonist is a character in a story who is presented as the chief foe of the protagonist.
Etymology
The English word antagonist comes from the Greek ἀνταγωνιστής – ''antagonistēs'', "opponent, competitor, villain, enemy, riv ...
, but also enzyme
Enzymes () are proteins that act as biological catalysts by accelerating chemical reactions. The molecules upon which enzymes may act are called substrates, and the enzyme converts the substrates into different molecules known as products. A ...
inhibitors (such as monoamine oxidase inhibitors).
History
The origins ofclinical pharmacology
Clinical pharmacology has been defined as "that discipline that teaches, does research, frames policy, gives information and advice about the actions and proper uses of medicines in humans and implements that knowledge in clinical practice". Clinic ...
date back to the Middle Ages
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the late 5th to the late 15th centuries, similar to the post-classical period of global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire a ...
, with pharmacognosy and Avicenna's ''The Canon of Medicine
''The Canon of Medicine'' ( ar, القانون في الطب, italic=yes ''al-Qānūn fī al-Ṭibb''; fa, قانون در طب, italic=yes, ''Qanun-e dâr Tâb'') is an encyclopedia of medicine in five books compiled by Persian physician-phi ...
'', Peter of Spain
__NOTOC__
Peter of Hispania ( la, Petrus Hispanus; Portuguese and es, Pedro Hispano; century) was the author of the ', later known as the ', an important medieval university textbook on Aristotelian logic. As the Latin ''Hispania'' was consider ...
's ''Commentary on Isaac'', and John of St Amand John of St Amand, Canon of Tournay (c. 1230–1303), also known as Jean de Saint-Amand and Johannes de Sancto Amando, was a Medieval author on pharmacology, teaching at the University of Paris. He wrote treatises on a variety of topics including mag ...
's ''Commentary on the Antedotary of Nicholas''. Early pharmacology focused on herbalism
Herbal medicine (also herbalism) is the study of pharmacognosy and the use of medicinal plants, which are a basis of traditional medicine. With worldwide research into pharmacology, some herbal medicines have been translated into modern reme ...
and natural substances, mainly plant extracts. Medicines were compiled in books called pharmacopoeia
A pharmacopoeia, pharmacopeia, or pharmacopoea (from the obsolete typography ''pharmacopœia'', meaning "drug-making"), in its modern technical sense, is a book containing directions for the identification of compound medicines, and published by ...
s. Crude drug
Crude drugs are plant or animal drugs that contain natural substances that have undergone only the processes of collection and drying. The term natural substances refers to those substances found in nature that have not had man-made changes made i ...
s have been used since prehistory as a preparation of substances from natural sources. However, the active ingredient
An active ingredient is any ingredient that provides biologically active or other direct effect in the diagnosis, cure, mitigation, treatment, or prevention of disease or to affect the structure or any function of the body of humans or animals. The ...
of crude drugs are not purified and the substance is adulterated with other substances.
Traditional medicine
Traditional medicine (also known as indigenous medicine or folk medicine) comprises medical aspects of traditional knowledge that developed over generations within the folk beliefs of various societies, including indigenous peoples, before the ...
varies between cultures and may be specific to a particular culture, such as in traditional Chinese
Chinese can refer to:
* Something related to China
* Chinese people, people of Chinese nationality, citizenship, and/or ethnicity
**''Zhonghua minzu'', the supra-ethnic concept of the Chinese nation
** List of ethnic groups in China, people of ...
, Mongolian, Tibetan
Tibetan may mean:
* of, from, or related to Tibet
* Tibetan people, an ethnic group
* Tibetan language:
** Classical Tibetan, the classical language used also as a contemporary written standard
** Standard Tibetan, the most widely used spoken dial ...
and Korean medicine
Traditional Korean medicine (known in North Korea as Koryo medicine) refers to the forms of traditional medicine practiced in Korea.
History
Korean medicine traditions originated in ancient and prehistoric times and can be traced back as far a ...
. However much of this has since been regarded as pseudoscience
Pseudoscience consists of statements, beliefs, or practices that claim to be both scientific and factual but are incompatible with the scientific method. Pseudoscience is often characterized by contradictory, exaggerated or falsifiability, unfa ...
. Pharmacological substances known as entheogen
Entheogens are psychoactive substances that induce alterations in perception, mood, consciousness, cognition, or behavior for the purposes of engendering spiritual development or otherwiseRätsch, Christian, ''The Encyclopedia of Psychoac ...
s may have spiritual and religious use and historical context.
In the 17th century, the English physician Nicholas Culpeper
Nicholas Culpeper (18 October 1616 – 10 January 1654) was an English botanist, herbalist, physician and astrologer.Patrick Curry: "Culpeper, Nicholas (1616–1654)", ''Oxford Dictionary of National Biography'' (Oxford, UK: OUP, 2004) His boo ...
translated and used pharmacological texts. Culpeper detailed plants and the conditions they could treat. In the 18th century, much of clinical pharmacology was established by the work of William Withering
William Withering FRS (17 March 1741 – 6 October 1799) was an English botanist, geologist, chemist, physician and first systematic investigator of the bioactivity of digitalis.
Withering was born in Wellington, Shropshire, the son of a surg ...
. Pharmacology as a scientific discipline did not further advance until the mid-19th century amid the great biomedical resurgence of that period. Before the second half of the nineteenth century, the remarkable potency and specificity of the actions of drugs such as morphine
Morphine is a strong opiate that is found naturally in opium, a dark brown resin in poppies (''Papaver somniferum''). It is mainly used as a analgesic, pain medication, and is also commonly used recreational drug, recreationally, or to make ...
, quinine
Quinine is a medication used to treat malaria and babesiosis. This includes the treatment of malaria due to '' Plasmodium falciparum'' that is resistant to chloroquine when artesunate is not available. While sometimes used for nocturnal le ...
and digitalis
''Digitalis'' ( or ) is a genus of about 20 species of herbaceous perennial plants, shrubs, and biennials, commonly called foxgloves.
''Digitalis'' is native to Europe, western Asia, and northwestern Africa. The flowers are tubular in shap ...
were explained vaguely and with reference to extraordinary chemical powers and affinities to certain organs or tissues. The first pharmacology department was set up by Rudolf Buchheim in 1847, at University of Tartu, in recognition of the need to understand how therapeutic drugs and poisons produced their effects. Subsequently, the first pharmacology department in England
England is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. It shares land borders with Wales to its west and Scotland to its north. The Irish Sea lies northwest and the Celtic Sea to the southwest. It is separated from continental Europe b ...
was set up in 1905 at University College London
, mottoeng = Let all come who by merit deserve the most reward
, established =
, type = Public research university
, endowment = £143 million (2020)
, budget = ...
.
Pharmacology developed in the 19th century as a biomedical science that applied the principles of scientific experimentation to therapeutic contexts. The advancement of research techniques propelled pharmacological research and understanding. The development of the organ bath
An organ chamber, organ bath, or isolated tissue bath is a chamber in which isolated organs or tissues can be administered with drugs, or stimulated electrically, in order to measure their function. The tissue in the organ bath is typically oxyg ...
preparation, where tissue samples are connected to recording devices, such as a myograph
A myograph is any device used to measure the force produced by a muscle when under contraction. Such a device is commonly used in myography, the study of the velocity and intensity of muscular contraction.
A myograph can take several forms: for ...
, and physiological responses are recorded after drug application, allowed analysis of drugs' effects on tissues. The development of the ligand binding assay A ligand binding assay (LBA) is an assay, or an analytic procedure, which relies on the binding of ligand molecules to receptors, antibodies or other macromolecules. A detection method is used to determine the presence and extent of the ligand-re ...
in 1945 allowed quantification of the binding affinity
In biochemistry and pharmacology, a ligand is a substance that forms a complex with a biomolecule to serve a biological purpose. The etymology stems from ''ligare'', which means 'to bind'. In protein-ligand binding, the ligand is usually a m ...
of drugs at chemical targets. Modern pharmacologists use techniques from genetics
Genetics is the study of genes, genetic variation, and heredity in organisms.Hartl D, Jones E (2005) It is an important branch in biology because heredity is vital to organisms' evolution. Gregor Mendel, a Moravian Augustinian friar wor ...
, molecular biology
Molecular biology is the branch of biology that seeks to understand the molecular basis of biological activity in and between cells, including biomolecular synthesis, modification, mechanisms, and interactions. The study of chemical and physi ...
, biochemistry
Biochemistry or biological chemistry is the study of chemical processes within and relating to living organisms. A sub-discipline of both chemistry and biology, biochemistry may be divided into three fields: structural biology, enzymology and ...
, and other advanced tools to transform information about molecular mechanisms and targets into therapies directed against disease, defects or pathogens, and create methods for preventive care, diagnostics, and ultimately personalized medicine
Personalized medicine, also referred to as precision medicine, is a medical model that separates people into different groups—with medical decisions, practices, interventions and/or products being tailored to the individual patient based on the ...
.
Divisions
The discipline of pharmacology can be divided into many sub disciplines each with a specific focus.Systems of the body
Pharmacology can also focus on specific systems comprising the body. Divisions related to bodily systems study the effects of drugs in different systems of the body. These includeneuropharmacology
Neuropharmacology is the study of how drugs affect function in the nervous system, and the neural mechanisms through which they influence behavior. There are two main branches of neuropharmacology: behavioral and molecular. Behavioral neuropharmac ...
, in the central
Central is an adjective usually referring to being in the center of some place or (mathematical) object.
Central may also refer to:
Directions and generalised locations
* Central Africa, a region in the centre of Africa continent, also known as ...
and peripheral nervous system
The peripheral nervous system (PNS) is one of two components that make up the nervous system of bilateral animals, with the other part being the central nervous system (CNS). The PNS consists of nerves and ganglia, which lie outside the brain ...
s; immunopharmacology in the immune system. Other divisions include cardiovascular
The blood circulatory system is a system of organs that includes the heart, blood vessels, and blood which is circulated throughout the entire body of a human or other vertebrate. It includes the cardiovascular system, or vascular system, tha ...
, renal
The kidneys are two reddish-brown bean-shaped organs found in vertebrates. They are located on the left and right in the retroperitoneal space, and in adult humans are about in length. They receive blood from the paired renal arteries; bloo ...
and endocrine pharmacology. Psychopharmacology
Psychopharmacology (from Greek grc, ψῡχή, psȳkhē, breath, life, soul, label=none; grc, φάρμακον, pharmakon, drug, label=none; and grc, -λογία, -logia, label=none) is the scientific study of the effects drugs have on mo ...
is the study of the use of drugs that affect the psyche
Psyche (''Psyché'' in French) is the Greek term for "soul" (ψυχή).
Psyche may also refer to:
Psychology
* Psyche (psychology), the totality of the human mind, conscious and unconscious
* ''Psyche'', an 1846 book about the unconscious by Car ...
, mind and behavior (e.g. antidepressants) in treating mental disorders (e.g. depression). It incorporates approaches and techniques from neuropharmacology, animal behavior and behavioral neuroscience, and is interested in the behavioral and neurobiological mechanisms of action of psychoactive drugs. The related field of neuropsychopharmacology
Neuropsychopharmacology, an interdisciplinary science related to psychopharmacology (study of effects of drugs on the mind) and fundamental neuroscience, is the study of the neural mechanisms that drugs act upon to influence behavior. It entails ...
focuses on the effects of drugs at the overlap between the nervous system and the psyche.
Pharmacometabolomics
Pharmacometabolomics, also known as pharmacometabonomics, is a field which stems from metabolomics, the quantification and analysis of metabolites produced by the body. It refers to the direct measurement of metabolites in an individual's bodily fl ...
, also known as pharmacometabonomics, is a field which stems from metabolomics
Metabolomics is the scientific study of chemical processes involving metabolites, the small molecule substrates, intermediates, and products of cell metabolism. Specifically, metabolomics is the "systematic study of the unique chemical fingerprin ...
, the quantification and analysis of metabolites
In biochemistry, a metabolite is an intermediate or end product of metabolism.
The term is usually used for small molecules. Metabolites have various functions, including fuel, structure, signaling, stimulatory and inhibitory effects on enzymes, ...
produced by the body. It refers to the direct measurement of metabolites
In biochemistry, a metabolite is an intermediate or end product of metabolism.
The term is usually used for small molecules. Metabolites have various functions, including fuel, structure, signaling, stimulatory and inhibitory effects on enzymes, ...
in an individual's bodily fluids, in order to predict or evaluate the metabolism
Metabolism (, from el, μεταβολή ''metabolē'', "change") is the set of life-sustaining chemical reactions in organisms. The three main functions of metabolism are: the conversion of the energy in food to energy available to run cell ...
of pharmaceutical
A medication (also called medicament, medicine, pharmaceutical drug, medicinal drug or simply drug) is a drug used to diagnose, cure, treat, or prevent disease. Drug therapy (pharmacotherapy) is an important part of the medical field and re ...
compounds, and to better understand the pharmacokinetic profile of a drug. Pharmacometabolomics can be applied to measure metabolite
In biochemistry, a metabolite is an intermediate or end product of metabolism.
The term is usually used for small molecules. Metabolites have various functions, including fuel, structure, signaling, stimulatory and inhibitory effects on enzymes, c ...
levels following the administration of a drug, in order to monitor the effects of the drug on metabolic pathways. Pharmacomicrobiomics
Pharmacomicrobiomics, first proposed by Prof. Marco Candela for the ERC-2009-StG project call (proposal n. 242860, titled "PharmacoMICROBIOMICS, study of the microbiome determinants of the different drug responses between individuals") and later pu ...
studies the effect of microbiome variations on drug disposition, action, and toxicity. Pharmacomicrobiomics is concerned with the interaction between drugs and the gut microbiome
A microbiome () is the community of microorganisms that can usually be found living together in any given habitat. It was defined more precisely in 1988 by Whipps ''et al.'' as "a characteristic microbial community occupying a reasonably wel ...
. Pharmacogenomics
Pharmacogenomics is the study of the role of the genome in drug response. Its name ('' pharmaco-'' + ''genomics'') reflects its combining of pharmacology and genomics. Pharmacogenomics analyzes how the genetic makeup of an individual affects the ...
is the application of genomic technologies to drug discovery and further characterization of drugs related to an organism's entire genome. For pharmacology regarding individual genes, pharmacogenetics
Pharmacogenomics is the study of the role of the genome in drug response. Its name ('' pharmaco-'' + ''genomics'') reflects its combining of pharmacology and genomics. Pharmacogenomics analyzes how the genetic makeup of an individual affects the ...
studies how genetic variation gives rise to differing responses to drugs. Pharmacoepigenetics studies the underlying epigenetic marking patterns that lead to variation in an individual's response to medical treatment.
*
Clinical practice and drug discovery
 Pharmacology can be applied within clinical sciences.
Pharmacology can be applied within clinical sciences. Clinical pharmacology
Clinical pharmacology has been defined as "that discipline that teaches, does research, frames policy, gives information and advice about the actions and proper uses of medicines in humans and implements that knowledge in clinical practice". Clinic ...
is the application of pharmacological methods and principles in the study of drugs in humans. An example of this is posology, which is the study of how medicines are dosed.
Pharmacology is closely related to toxicology
Toxicology is a scientific discipline, overlapping with biology, chemistry, pharmacology, and medicine, that involves the study of the adverse effects of chemical substances on living organisms and the practice of diagnosing and treating e ...
. Both pharmacology and toxicology are scientific disciplines that focus on understanding the properties and actions of chemicals. However, pharmacology emphasizes the therapeutic effects of chemicals, usually drugs or compounds that could become drugs, whereas toxicology is the study of chemical's adverse effects and risk assessment.
Pharmacological knowledge is used to advise pharmacotherapy
Pharmacotherapy is therapy using pharmaceutical drugs, as distinguished from therapy using surgery (surgical therapy), radiation (radiation therapy), movement (physical therapy), or other modes. Among physicians, sometimes the term ''medical ther ...
in medicine
Medicine is the science and practice of caring for a patient, managing the diagnosis, prognosis, prevention, treatment, palliation of their injury or disease, and promoting their health. Medicine encompasses a variety of health care pract ...
and pharmacy.
Drug discovery
Drug discovery is the field of study concerned with creating new drugs. It encompasses the subfields ofdrug design
Drug design, often referred to as rational drug design or simply rational design, is the inventive process of finding new medications based on the knowledge of a biological target. The drug is most commonly an organic small molecule that acti ...
and development
Development or developing may refer to:
Arts
*Development hell, when a project is stuck in development
*Filmmaking, development phase, including finance and budgeting
*Development (music), the process thematic material is reshaped
* Photograph ...
. Drug discovery starts with drug design, which is the inventive process of finding new drugs. In the most basic sense, this involves the design of molecules that are complementary in shape
A shape or figure is a graphics, graphical representation of an object or its external boundary, outline, or external Surface (mathematics), surface, as opposed to other properties such as color, Surface texture, texture, or material type.
A pl ...
and charge
Charge or charged may refer to:
Arts, entertainment, and media Films
* '' Charge, Zero Emissions/Maximum Speed'', a 2011 documentary
Music
* ''Charge'' (David Ford album)
* ''Charge'' (Machel Montano album)
* ''Charge!!'', an album by The Aqu ...
to a given biomolecular target. After a lead compound
A lead compound (, i.e. a "leading" compound, not to be confused with various compounds of the metallic element lead) in drug discovery is a chemical compound that has pharmacology, pharmacological or biological activity likely to be therapeutical ...
has been identified through drug discovery, drug development involves bringing the drug to the market. Drug discovery is related to pharmacoeconomics
Pharmacoeconomics refers to the scientific discipline that compares the value of one pharmaceutical drug or drug therapy to another. It is a sub-discipline of health economics. A pharmacoeconomic study evaluates the cost (expressed in monetary te ...
, which is the sub-discipline of health economics
Health economics is a branch of economics concerned with issues related to efficiency, effectiveness, value and behavior in the production and consumption of health and healthcare. Health economics is important in determining how to improv ...
that considers the value of drugs Pharmacoeconomics evaluates the cost and benefits of drugs in order to guide optimal healthcare resource allocation. The techniques used for the discovery
Discovery may refer to:
* Discovery (observation), observing or finding something unknown
* Discovery (fiction), a character's learning something unknown
* Discovery (law), a process in courts of law relating to evidence
Discovery, The Discover ...
, formulation, manufacturing and quality control of drugs discovery is studied by pharmaceutical engineering
Pharmaceutical engineering is a branch of engineering focused on discovering, formulating, and manufacturing medication, analytical and quality control processes, and on designing, building, and improving manufacturing sites that produce drugs. I ...
, a branch of engineering
Engineering is the use of scientific method, scientific principles to design and build machines, structures, and other items, including bridges, tunnels, roads, vehicles, and buildings. The discipline of engineering encompasses a broad rang ...
. Safety pharmacology specialises in detecting and investigating potential undesirable effects of drugs.
Drug development, Development of medication is a vital concern to medicine
Medicine is the science and practice of caring for a patient, managing the diagnosis, prognosis, prevention, treatment, palliation of their injury or disease, and promoting their health. Medicine encompasses a variety of health care pract ...
, but also has strong economical and political implications. To protect the consumer and prevent abuse, many governments regulate the manufacture, sale, and administration of medication. In the United States, the main body that regulates pharmaceuticals is the Food and Drug Administration; they enforce Technical standard, standards set by the United States Pharmacopoeia. In the European Union, the main body that regulates pharmaceuticals is the European Medicines Agency, EMA, and they enforce standards set by the European Pharmacopoeia.
The metabolic stability and the reactivity of a library of candidate drug compounds have to be assessed for drug metabolism and toxicological studies. Many methods have been proposed for quantitative predictions in drug metabolism; one example of a recent computational method is SPORCalc. A slight alteration to the chemical structure of a medicinal compound could alter its medicinal properties, depending on how the alteration relates to the structure of the substrate or receptor site on which it acts: this is called the structural activity relationship (SAR). When a useful activity has been identified, chemists will make many similar compounds called analogues, to try to maximize the desired medicinal effect(s). This can take anywhere from a few years to a decade or more, and is very expensive. One must also determine how safe the medicine is to consume, its stability in the human body and the best form for delivery to the desired organ system, such as tablet or aerosol. After extensive testing, which can take up to six years, the new medicine is ready for marketing and selling.
Because of these long timescales, and because out of every 5000 potential new medicines typically only one will ever reach the open market, this is an expensive way of doing things, often costing over 1 billion dollars. To recoup this outlay pharmaceutical companies may do a number of things:
* Carefully research the demand for their potential new product before spending an outlay of company funds.
* Obtain a patent on the new medicine preventing other companies from producing that medicine for a certain allocation of time.
The inverse benefit law describes the relationship between a drugs therapeutic benefits and its marketing.
When designing drugs, the placebo effect must be considered to assess the drug's true therapeutic value.
Drug development uses techniques from medicinal chemistry to chemically design drugs. This overlaps with the biological approach of finding targets and physiological effects.
Wider contexts
Pharmacology can be studied in relation to wider contexts than the physiology of individuals. For example, pharmacoepidemiology concerns the variations of the effects of drugs in or between populations, it is the bridge betweenclinical pharmacology
Clinical pharmacology has been defined as "that discipline that teaches, does research, frames policy, gives information and advice about the actions and proper uses of medicines in humans and implements that knowledge in clinical practice". Clinic ...
and epidemiology. Pharmacoenvironmentology or environmental pharmacology is the study of the effects of used pharmaceuticals and personal care products (PPCPs) on the environment after their elimination from the body. Human health and ecology are intimately related so environmental pharmacology studies the environmental effect of drugs and pharmaceuticals and personal care products in the environment.
Drugs may also have ethnocultural importance, so ethnopharmacology studies the ethnic and cultural aspects of pharmacology.
Emerging fields
Photopharmacology is an emerging approach inmedicine
Medicine is the science and practice of caring for a patient, managing the diagnosis, prognosis, prevention, treatment, palliation of their injury or disease, and promoting their health. Medicine encompasses a variety of health care pract ...
in which drugs are activated and deactivated with light. The energy of light is used to change for shape and chemical properties of the drug, resulting in different biological activity. This is done to ultimately achieve control when and where drugs are active in a reversible manner, to prevent side effects and pollution of drugs into the environment.
Theory of pharmacology
 The study of chemicals requires intimate knowledge of the biological system affected. With the knowledge of cell biology and
The study of chemicals requires intimate knowledge of the biological system affected. With the knowledge of cell biology and biochemistry
Biochemistry or biological chemistry is the study of chemical processes within and relating to living organisms. A sub-discipline of both chemistry and biology, biochemistry may be divided into three fields: structural biology, enzymology and ...
increasing, the field of pharmacology has also changed substantially. It has become possible, through molecular analysis of receptor (biochemistry), receptors, to design chemicals that act on specific cellular signaling or metabolic pathways by affecting sites directly on cell-surface receptors (which modulate and mediate cellular signaling pathways controlling cellular function).
Chemicals can have pharmacologically relevant properties and effects. Pharmacokinetics describes the effect of the body on the chemical (e.g. half-life and volume of distribution), and pharmacodynamics
Pharmacodynamics (PD) is the study of the biochemical and physiologic effects of drugs (especially pharmaceutical drugs). The effects can include those manifested within animals (including humans), microorganisms, or combinations of organisms ...
describes the chemical's effect on the body (desired or toxic).
Systems, receptors and ligands
enzyme
Enzymes () are proteins that act as biological catalysts by accelerating chemical reactions. The molecules upon which enzymes may act are called substrates, and the enzyme converts the substrates into different molecules known as products. A ...
s and membrane transport proteins. Enzymes can be targeted with enzyme inhibitors. Receptors are typically categorised based on structure and function. Major receptor types studied in pharmacology include G protein coupled receptors, ligand gated ion channels and receptor tyrosine kinases.
Pharmacodynamics
Pharmacodynamics is defined as how the body reacts to the drugs. Pharmacology models include the Hill equation (biochemistry), Hill equation, Cheng-Prusoff equation and Schild regression. Pharmacodynamics theory often investigates the binding affinity of ligand (biochemistry), ligands to their receptors. Medication is said to have a narrow or wide ''therapeutic index,'' certain safety factor or ''therapeutic window''. This describes the ratio of desired effect to toxic effect. A compound with a narrow therapeutic index (close to one) exerts its desired effect at a dose close to its toxic dose. A compound with a wide therapeutic index (greater than five) exerts its desired effect at a dose substantially below its toxic dose. Those with a narrow margin are more difficult to dose and administer, and may require therapeutic drug monitoring (examples are warfarin, some antiepileptics, aminoglycoside antibiotics). Most anti-cancer drugs have a narrow therapeutic margin: toxic side-effects are almost always encountered at doses used to kill tumors. The effect of drugs can be described with Loewe additivity which is one of several common reference models.Pharmacokinetics
Pharmacokinetics is the study of the bodily absorption, distribution, metabolism, and excretion of drugs. When describing the pharmacokinetic properties of the chemical that is the active ingredient or Active ingredient, active pharmaceutical ingredient (API), pharmacologists are often interested in ''L-ADME'': * Liberation (pharmacology), Liberation – How is the API disintegrated (for solid oral forms (breaking down into smaller particles), dispersed, or dissolved from the medication? * Absorption (digestive), Absorption – How is the API absorbed (through the human skin, skin, the intestine, the oral mucosa)? * Distribution (pharmacology), Distribution – How does the API spread through the organism? * Drug metabolism, Metabolism – Is the API converted chemically inside the body, and into which substances. Are these active (as well)? Could they be toxic? * Excretion – How is the API excreted (through the bile, urine, breath, skin)? Drug metabolism is assessed in pharmacokinetics and is important in drug research and prescribing.Administration, drug policy and safety
Drug policy
In the United States, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) is responsible for creating guidelines for the approval and use of drugs. The FDA requires that all approved drugs fulfill two requirements: # The drug must be found to be effective against the disease for which it is seeking approval (where 'effective' means only that the drug performed better than placebo or competitors in at least two trials). # The drug must meet safety criteria by being subject to animal and controlled human testing. Gaining FDA approval usually takes several years. Testing done on animals must be extensive and must include several species to help in the evaluation of both the effectiveness and toxicity of the drug. The dosage of any drug approved for use is intended to fall within a range in which the drug produces a therapeutic effect or desired outcome. The safety and effectiveness of prescription drugs in the U.S. are regulated by the federal Prescription Drug Marketing Act (PDMA), Prescription Drug Marketing Act of 1987. The Medicines and Healthcare products Regulatory Agency (MHRA) has a similar role in the UK. Medicare Part D is a prescription drug plan in the U.S. The Prescription Drug Marketing Act (PDMA) is an act related to drug policy. Prescription drugs are drugs regulated by legislation.Societies and education
Societies and administration
The International Union of Basic and Clinical Pharmacology, Federation of European Pharmacological Societies and European Association for Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics are organisations representing standardisation and regulation of clinical and scientific pharmacology. Systems for medical classification of drugs with pharmaceutical codes have been developed. These include the National Drug Code (NDC), administered by Food and Drug Administration.; Drug Identification Number (DIN), administered by Health Canada under the Food and Drugs Act; Department of Health (Hong Kong)#Hong Kong Drug Registration, Hong Kong Drug Registration, administered by the Pharmaceutical Service of the Department of Health (Hong Kong) and National Pharmaceutical Product Index in South Africa. Hierarchical systems have also been developed, including the Anatomical Therapeutic Chemical Classification System (AT, or ATC/DDD), administered by World Health Organization; Generic Product Identifier (GPI), a hierarchical classification number published by MediSpan and SNOMED, C axis. Ingredients of drugs have been categorised by Unique Ingredient Identifier.Education
The study of pharmacology overlaps with biomedical sciences and is the study of the effects of drugs on living organisms. Pharmacological research can lead to new drug discoveries, and promote a better understanding of human physiology. Students of pharmacology must have a detailed working knowledge of aspects in physiology, pathology, and chemistry. They may also require knowledge of plants as sources of pharmacologically-active compounds. Modern pharmacology is interdisciplinary and involves biophysical and computational sciences, and analytical chemistry. A pharmacist needs to be well-equipped with knowledge on pharmacology for application in pharmaceutical research or pharmacy practice in hospitals or commercial organisations selling to customers. Pharmacologists, however, usually work in a laboratory undertaking research or development of new products. Pharmacological research is important in academic research (medical and non-medical), private industrial positions, science writing, scientific patents and law, consultation, biotech and pharmaceutical employment, the alcohol industry, food industry, forensics/law enforcement, public health, and environmental/ecological sciences. Pharmacology is often taught to pharmacy and medicine students as part of a Medical School curriculum.See also
References
External links
American Society for Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics
British Pharmacological Society
International Conference on Harmonisation
US Pharmacopeia
International Union of Basic and Clinical Pharmacology
IUPHAR Committee on Receptor Nomenclature and Drug Classification
IUPHAR/BPS Guide to Pharmacology
Further reading
* * * {{Authority control Pharmacology, Biochemistry Life sciences industry