Hobart on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Hobart ( ; Nuennonne/
 The first European settlement began in 1803 as a military camp at
The first European settlement began in 1803 as a military camp at
 Hobart is located on the estuary of the River Derwent in the state's south-east. Geologically Hobart is built predominantly on Jurassic
Hobart is located on the estuary of the River Derwent in the state's south-east. Geologically Hobart is built predominantly on Jurassic 
 Shipping is significant to the city's economy. Hobart is the home port for the Antarctic activities of Australia and France. The port loads around 2,000 tonnes of Antarctic cargo a year for the Australian research vessel '' Nuyina (previously the
Shipping is significant to the city's economy. Hobart is the home port for the Antarctic activities of Australia and France. The port loads around 2,000 tonnes of Antarctic cargo a year for the Australian research vessel '' Nuyina (previously the
 Hobart is an Antarctic gateway city, with geographical proximity to East Antarctica and the Southern Ocean. Infrastructure is provided by the port of Hobart for scientific research and cruise ships, and
Hobart is an Antarctic gateway city, with geographical proximity to East Antarctica and the Southern Ocean. Infrastructure is provided by the port of Hobart for scientific research and cruise ships, and
 Hobart serves as a focal point and mecca for tourism in the state of Tasmania. Hobart has been a significant tourist destination for many years, however tourism has evolved to a core industry in the last decade. This process has been termed the "MONA Effect" - referring to the significant influence of the Museum of New and Old Art (MONA), the Southern Hemisphere's largest private museum, on the local tourist economy - compared to the effect of the Guggenheim on
Hobart serves as a focal point and mecca for tourism in the state of Tasmania. Hobart has been a significant tourist destination for many years, however tourism has evolved to a core industry in the last decade. This process has been termed the "MONA Effect" - referring to the significant influence of the Museum of New and Old Art (MONA), the Southern Hemisphere's largest private museum, on the local tourist economy - compared to the effect of the Guggenheim on
 Hobart is known for its well-preserved
Hobart is known for its well-preserved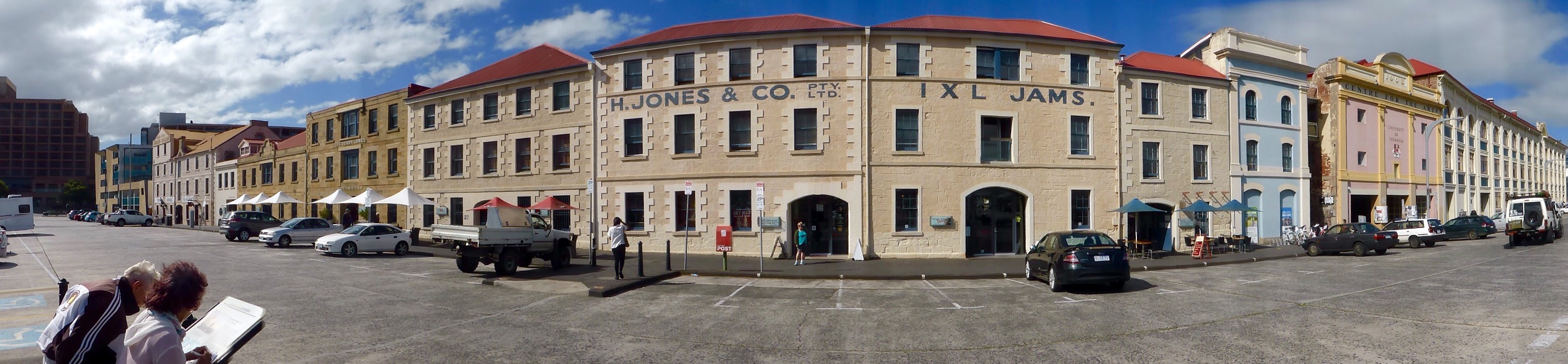 

 Hobart is home to Australia's oldest continuously operating theatre, the Theatre Royal, built in 1837. Other theatres in the city include the Playhouse theatre, the Backspace Theatre, and many smaller stage theatres.
The
Hobart is home to Australia's oldest continuously operating theatre, the Theatre Royal, built in 1837. Other theatres in the city include the Playhouse theatre, the Backspace Theatre, and many smaller stage theatres.
The 
 Hobart is internationally famous among the yachting community as the finish of the Sydney to Hobart Yacht Race which starts in Sydney on Boxing Day (the day after Christmas Day). The arrival of the yachts is celebrated as part of the
Hobart is internationally famous among the yachting community as the finish of the Sydney to Hobart Yacht Race which starts in Sydney on Boxing Day (the day after Christmas Day). The arrival of the yachts is celebrated as part of the
 Most professional Hobart-based sports teams represent Tasmania as a whole rather than exclusively the city.
Most professional Hobart-based sports teams represent Tasmania as a whole rather than exclusively the city.
 Five free-to-air television stations service Hobart:
*
Five free-to-air television stations service Hobart:
*
 Hobart is divided into five local government areas - three of which are designated as cities, City of Hobart,
Hobart is divided into five local government areas - three of which are designated as cities, City of Hobart,
 Hobart is home to the main campus of the
Hobart is home to the main campus of the
 The only
The only  Ferry services from Hobart's Eastern Shore into the city were once a common form of public transportation, but with lack of government funding, as well as a lack of interest from the private sector, there has been the demise of a regular commuter ferry service – leaving Hobart's commuters relying solely on travel by automobiles and buses. There is however a water taxi service operating from the Eastern Shore into Hobart which provides an alternative to the
Ferry services from Hobart's Eastern Shore into the city were once a common form of public transportation, but with lack of government funding, as well as a lack of interest from the private sector, there has been the demise of a regular commuter ferry service – leaving Hobart's commuters relying solely on travel by automobiles and buses. There is however a water taxi service operating from the Eastern Shore into Hobart which provides an alternative to the
 *
*
Palawa kani
Palawa kani is a constructed language created by the Tasmanian Aboriginal Centre as a composite Tasmanian languages, Tasmanian language, based on reconstructed vocabulary from the limited accounts of the various languages once spoken by the eas ...
: ''nipaluna'') is the capital and most populous city of the Australian island state of Tasmania
)
, nickname =
, image_map = Tasmania in Australia.svg
, map_caption = Location of Tasmania in AustraliaCoordinates:
, subdivision_type = Country
, subdi ...
. Home to almost half of all Tasmanians, it is the least-populated Australian state capital city, and second-smallest if territories are taken into account, before Darwin, Northern Territory. Hobart is located in Tasmania's south-east on the estuary of the River Derwent, making it the most southern of Australia's capital cities. Its skyline is dominated by the kunanyi/Mount Wellington, and its harbour forms the second-deepest natural port
A port is a maritime facility comprising one or more wharves or loading areas, where ships load and discharge cargo and passengers. Although usually situated on a sea coast or estuary, ports can also be found far inland, such as H ...
in the world, with much of the city's waterfront consisting of reclaimed land. The metropolitan area is often referred to as Greater Hobart, to differentiate it from the City of Hobart, one of the five local government areas that cover the city. It has a mild maritime climate
An oceanic climate, also known as a marine climate, is the humid temperate climate sub-type in Köppen classification ''Cfb'', typical of west coasts in higher middle latitudes of continents, generally featuring cool summers and mild winters ...
.
The city lies on country which was known by the local Mouheneener
The Aboriginal Tasmanians (Palawa kani: ''Palawa'' or ''Pakana'') are the Aboriginal people of the Australian island of Tasmania, located south of the mainland. For much of the 20th century, the Tasmanian Aboriginal people were widely, and ...
people as nipaluna, a name which includes surrounding features such as kunanyi/Mt. Wellington and timtumili minanya (River Derwent). Prior to British settlement, the land had been occupied for possibly as long as 35,000 years by the semi-nomadic Mouheneener people, a sub-group of the Nuennone, or "South-East tribe".
Founded in 1804 as a British penal colony
A penal colony or exile colony is a settlement used to exile prisoners and separate them from the general population by placing them in a remote location, often an island or distant colonial territory. Although the term can be used to refer to ...
, Hobart is Australia's second-oldest capital city after Sydney, New South Wales
)
, nickname =
, image_map = New South Wales in Australia.svg
, map_caption = Location of New South Wales in AustraliaCoordinates:
, subdivision_type = Country
, subdivision_name = Australia
, established_title = Before federation
, es ...
. Whaling
Whaling is the process of hunting of whales for their usable products such as meat and blubber, which can be turned into a type of oil that became increasingly important in the Industrial Revolution.
It was practiced as an organized industr ...
quickly emerged as a major industry in the area, and for a time Hobart served as the Southern Ocean
The Southern Ocean, also known as the Antarctic Ocean, comprises the southernmost waters of the World Ocean, generally taken to be south of 60° S latitude and encircling Antarctica. With a size of , it is regarded as the second-small ...
's main whaling port. Penal transportation ended in the 1850s, after which the city experienced periods of growth and decline. The early 20th century saw an economic boom on the back of mining, agriculture and other primary industries, and the loss of men who served in the world war
A world war is an international conflict which involves all or most of the world's major powers. Conventionally, the term is reserved for two major international conflicts that occurred during the first half of the 20th century, World WarI (1914 ...
s was counteracted by an influx of immigration. Despite the rise in migration from Asia and other non-English speaking regions, Hobart's population remains predominantly ethnically Anglo-Celtic
Anglo-Celtic people are descended primarily from British and Irish people. The concept is mainly relevant outside of Great Britain and Ireland, particularly in Australia, but is also used in Canada, the United States, New Zealand and South Africa, ...
, and has the highest percentage of Australian-born residents among Australia's capital cities.
Today, Hobart is the financial and administrative hub of Tasmania, serving as the home port for both Australian and French Antarctic operations and acting as a tourist destination, with over 1.192 million visitors in 2011–12. Well-known drawcards include its convict-era architecture, Salamanca Market
Salamanca Market is a street market in Salamanca Place, Hobart, Tasmania, Australia.
The Salamanca Market is one of Tasmania's most visited tourist attractions and has won many awards for excellence.
Located in historic Salamanca Place, ne ...
and the Museum of Old and New Art
The Museum of Old and New Art (MONA) is an art museum located within the Moorilla winery on the Berriedale peninsula in Hobart, Tasmania, Australia. It is the largest privately funded museum in the Southern Hemisphere. MONA houses ancient, mode ...
(MONA), the Southern Hemisphere's largest private museum.
History
 The first European settlement began in 1803 as a military camp at
The first European settlement began in 1803 as a military camp at Risdon Cove
Risdon Cove is a cove located on the east bank of the Derwent River, approximately north of Hobart, Tasmania. It was the site of the first British settlement in Van Diemen's Land, now Tasmania, the island state of Australia. The cove was name ...
on the eastern shores of the River Derwent, amid British concerns over the presence of French explorers
Exploration refers to the historical practice of discovering remote lands. It is studied by geographers and historians.
Two major eras of exploration occurred in human history: one of convergence, and one of divergence. The first, covering most ...
. In 1804, along with the military, settlers and convicts from the abandoned Port Phillip
Port Phillip ( Kulin: ''Narm-Narm'') or Port Phillip Bay is a horsehead-shaped enclosed bay on the central coast of southern Victoria, Australia. The bay opens into the Bass Strait via a short, narrow channel known as The Rip, and is com ...
settlement, the camp at Risdon Cove was moved by Captain David Collins to a better location at the present site of Hobart at Sullivans Cove. The city, initially known as ''Hobart Town'' or ''Hobarton'', was named after Lord Hobart
Robert Hobart, 4th Earl of Buckinghamshire, (6 May 17604 February 1816), styled Lord Hobart from 1793 to 1804, was a British Tory politician.
Life
Buckinghamshire was born at Hampden House, the son of George Hobart, 3rd Earl of Buckinghamshire ...
, the British Secretary of State for war and the colonies.
The area's indigenous inhabitants were members of the semi-nomadic ''Mouheneener'' tribe. Violent conflict with the European settlers, and the effects of diseases brought by them, dramatically reduced the aboriginal population, which was rapidly replaced by free settlers and the convict
A convict is "a person found guilty of a crime and sentenced by a court" or "a person serving a sentence in prison". Convicts are often also known as " prisoners" or "inmates" or by the slang term "con", while a common label for former conv ...
population. Charles Darwin
Charles Robert Darwin ( ; 12 February 1809 – 19 April 1882) was an English naturalist, geologist, and biologist, widely known for his contributions to evolutionary biology. His proposition that all species of life have descended ...
visited Hobart Town in February 1836 as part of the ''Beagle'' expedition. He writes of Hobart and the Derwent estuary in ''The Voyage of the Beagle
''The Voyage of the Beagle'' is the title most commonly given to the book written by Charles Darwin and published in 1839 as his ''Journal and Remarks'', bringing him considerable fame and respect. This was the third volume of ''The Narrative ...
'':
"...The lower parts of the hills which skirt the bay are cleared; and the bright yellow fields of corn, and dark green ones of potatoes, appear very luxuriant... I was chiefly struck with the comparative fewness of the large houses, either built or building. Hobart Town, from the census of 1835, contained 13,826 inhabitants, and the whole of Tasmania 36,505."The River Derwent was one of Australia's finest deepwater ports and was the centre of South Seas
whaling
Whaling is the process of hunting of whales for their usable products such as meat and blubber, which can be turned into a type of oil that became increasingly important in the Industrial Revolution.
It was practiced as an organized industr ...
and sealing trades. The settlement rapidly grew into a major port, with allied industries such as shipbuilding.
Hobart Town became a city on 21 August 1842, and was renamed Hobart from the beginning of 1881.
During the mid 20th century, the state and local governments invested in building Hobart's reputation as a tourist attraction - in 1956 the Lanherne Airport (now Hobart International Airport
Hobart Airport is an international airport located in Cambridge, north-east of Hobart. It is the major and fastest growing passenger airport in Tasmania.
The Federal government owned airport is operated by the Tasmanian Gateway Consort ...
) was opened. Australia's first legal casino, Wrest Point Hotel Casino
The Wrest Point Hotel Casino is a casino in Tasmania. It was Australia's first legal casino, opening in the suburb of Sandy Bay in Hobart, on 10 February 1973.
History
Historically, Dunkley's Point was a camping ground held by the semi-nomadic ...
opened in 1973. Despite these successes, Hobart faced significant challenges during the 20th century, including the 1967 Tasmanian fires
The 1967 Tasmanian fires were an Australian natural disaster which occurred on 7 February 1967, an event which came to be known as the Black Tuesday bushfires. They were the most deadly bushfires that Tasmania has ever experienced, leaving 62 p ...
, which claimed 62 lives in Hobart itself and destroyed over 1200 homes, and the 1975 Tasman Bridge disaster
The Tasman Bridge disaster occurred on the evening of 5 January 1975, in Hobart, the capital city of Australia's island state of Tasmania, when the bulk carrier ''Lake Illawarra'', travelling up the Derwent River, collided with several pylon ...
, when a bulk ore carrier collided with and destroyed the concrete span bridge that connected the city to its eastern suburbs.
Hobart within the 21st century was benefited as Tasmania's economy recovered from the 1990s recession, and the city's long-stagnant population growth began to reverse. A period of significant growth has followed, including the redevelopment of the former Macquarie Point railyards, Parliament Square, and new hotel developments throughout the city.
Geography
Topography
 Hobart is located on the estuary of the River Derwent in the state's south-east. Geologically Hobart is built predominantly on Jurassic
Hobart is located on the estuary of the River Derwent in the state's south-east. Geologically Hobart is built predominantly on Jurassic dolerite
Diabase (), also called dolerite () or microgabbro,
is a mafic, holocrystalline, subvolcanic rock equivalent to volcanic basalt or plutonic gabbro. Diabase dikes and sills are typically shallow intrusive bodies and often exhibit fine-grain ...
around the foothills interspersed with smaller areas of Triassic siltstone and Permian mudstone. Hobart extends along both sides of the River Derwent; on the western shore from the Derwent valley in the north through the flatter areas of Glenorchy which rests on older Triassic sediment and into the hilly areas of New Town, Lenah Valley. Both of these areas rest on the younger Jurassic dolerite deposits, before stretching into the lower areas such as the beaches of Sandy Bay in the south, in the Derwent estuary. South of the Derwent estuary lies Storm Bay and the Tasman Peninsula
The Tasman Peninsula, officially Turrakana / Tasman Peninsula, is a peninsula located in south-east Tasmania, Australia, approximately by the Arthur Highway, south-east of Hobart.
The Tasman Peninsula lies south and west of Forestier Peninsula ...
.
The Eastern Shore also extends from the Derwent valley area in a southerly direction hugging the Meehan Range in the east before sprawling into flatter land in suburbs such as Bellerive. These flatter areas of the eastern shore rest on far younger deposits from the Quaternary. From there the city extends in an easterly direction through the Meehan Range into the hilly areas of Rokeby and Oakdowns, before reaching into the tidal flatland area of Lauderdale
Lauderdale is the valley of the Leader Water (a tributary of the Tweed) in the Scottish Borders. It contains the town of Lauder, as well as Earlston. The valley is traversed from end to end by the A68 trunk road, which runs from Darlington to ...
.
Hobart has access to a number of beach areas including those in the Derwent estuary itself; Long Beach
Long Beach is a city in Los Angeles County, California. It is the 42nd-most populous city in the United States, with a population of 466,742 as of 2020. A charter city, Long Beach is the seventh-most populous city in California.
Incorporate ...
, Nutgrove Beach, Bellerive Beach
Bellerive Beach is a popular beach destination along the River Derwent in Bellerive, Hobart, Tasmania. The south facing beach neighbours the historic Kangaroo Battery coastal defences and has views of the Derwent estuary, Howrah, Tranmere a ...
, Cornelian Bay, Kingston, and Howrah Beaches as well as many more in Frederick Henry Bay such as; Seven Mile, Roaches, Cremorne, Clifton, and Goats Beaches.

Climate
Hobart has a mild temperate oceanic climate (Köppen Köppen is a German surname. Notable people with the surname include:
* Bernd Köppen (born 1951), German pianist and composer
* Carl Köppen (1833-1907), German military advisor in Meiji era Japan
* Edlef Köppen (1893–1939), German author and ...
: ''Cfb''). The highest temperature recorded was on 4 January 2013 and the lowest was on 25 June 1972 and 11 July 1981. Annually, Hobart receives only 40.8 clear days without rain. Compared to other major Australian cities, Hobart has the fewest daily average hours of sunshine, with only 5.9 hours per day. However, during the summer it has the same hours of daylight of any Australian city, with 15.3 hours on the summer solstice. By global standards, Hobart has cool summers and mild winters for its relative latitude, being heavily influenced by its seaside location.
Although Hobart itself rarely receives snow during the winter due to the foehn effect created by the Central Highlands (the city's geographic position causes a rainshadow
A rain shadow is an area of significantly reduced rainfall behind a mountainous region, on the side facing away from prevailing winds, known as its leeward side.
Evaporated moisture from water bodies (such as oceans and large lakes) is carrie ...
), the adjacent Kunanyi/ Mount Wellington is frequently seen with a snowcap throughout the year including in summer. During the 20th century, the city itself has received snowfalls at sea level on average only once every 5 years; however, outer suburbs lying higher on the slopes of Mount Wellington receive snow more often, owing to the more exposed position coupled with them resting at higher altitude. These snow-bearing winds often carry on through Tasmania and Victoria
Victoria most commonly refers to:
* Victoria (Australia), a state of the Commonwealth of Australia
* Victoria, British Columbia, provincial capital of British Columbia, Canada
* Victoria (mythology), Roman goddess of Victory
* Victoria, Seychelle ...
to the Snowy Mountains in Victoria and southern New South Wales.
The average temperature of the sea ranges from in September to in February.
Demographics
At the 2021 census, there were 247,068 people in the Greater Hobart. The City of Hobart local government area had a population of 55,077. As of 2021, the median weekly household income was $1,542, compared with $1,746 nationally. 18.1% of households total weekly income is less than $650 week, while 18.9% of households weekly income exceeds $3,000. This compares to national rates of 16.5% and 24.3% respectively. 35.4% of renting households, and 10.3% of owned households with a mortgage experiencehousing stress Housing stress describes a situation where the cost of housing (either as rental, or as a mortgage) is high relative to household income. It may also be used to describe inadequate housing for a proportion of the population.
As a rule of thumb, ...
, where rent or mortgage repayments exceed 30% of income.
At the 2016 census, The most common occupation categories were professionals (22.6%), clerical and administrative workers (14.7%), technicians and trades workers (13.3%), community and personal service workers (12.8%), and managers (11.3%).
Ancestry and immigration
4.5% of the population (11,216 people) areIndigenous Australians
Indigenous Australians or Australian First Nations are people with familial heritage from, and membership in, the ethnic groups that lived in Australia before British colonisation. They consist of two distinct groups: the Aboriginal peoples ...
(Aboriginal Australians
Aboriginal Australians are the various Indigenous peoples of the Australian mainland and many of its islands, such as Tasmania, Fraser Island, Hinchinbrook Island, the Tiwi Islands, and Groote Eylandt, but excluding the Torres Strait Isl ...
and Torres Strait Islanders
Torres Strait Islanders () are the Indigenous Melanesian people of the Torres Strait Islands, which are part of the state of Queensland, Australia. Ethnically distinct from the Aboriginal people of the rest of Australia, they are often groupe ...
).
At the 2021 census, the most commonly nominated ancestry groups include:
23.4% of the population was born overseas at the 2021 census. The five largest groups of overseas-born were from England
England is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. It shares land borders with Wales to its west and Scotland to its north. The Irish Sea lies northwest and the Celtic Sea to the southwest. It is separated from continental Europe b ...
(3.3%), Mainland China
"Mainland China" is a geopolitical term defined as the territory governed by the People's Republic of China (including islands like Hainan or Chongming), excluding dependent territories of the PRC, and other territories within Greater China. ...
(2.2%), Nepal
Nepal (; ne, :ne:नेपाल, नेपाल ), formerly the Federal Democratic Republic of Nepal ( ne,
सङ्घीय लोकतान्त्रिक गणतन्त्र नेपाल ), is a landlocked country in S ...
(1.7%), India
India, officially the Republic of India (Hindi: ), is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by area, the second-most populous country, and the most populous democracy in the world. Bounded by the Indian Ocean on the so ...
(1.6%) and New Zealand
New Zealand ( mi, Aotearoa ) is an island country in the southwestern Pacific Ocean. It consists of two main landmasses—the North Island () and the South Island ()—and over 700 smaller islands. It is the sixth-largest island count ...
(0.9%).
Language
At the 2021 census, 82.6% of the population spoke onlyEnglish
English usually refers to:
* English language
* English people
English may also refer to:
Peoples, culture, and language
* ''English'', an adjective for something of, from, or related to England
** English national ide ...
at home. The other languages most commonly spoken at home were Mandarin
Mandarin or The Mandarin may refer to:
Language
* Mandarin Chinese, branch of Chinese originally spoken in northern parts of the country
** Standard Chinese or Modern Standard Mandarin, the official language of China
** Taiwanese Mandarin, Stand ...
(2.6%), Nepali (1.8%), Punjabi (0.7%), Cantonese
Cantonese ( zh, t=廣東話, s=广东话, first=t, cy=Gwóngdūng wá) is a language within the Chinese (Sinitic) branch of the Sino-Tibetan languages originating from the city of Guangzhou (historically known as Canton) and its surrounding ar ...
(0.5%) and Vietnamese
Vietnamese may refer to:
* Something of, from, or related to Vietnam, a country in Southeast Asia
** A citizen of Vietnam. See Demographics of Vietnam.
* Vietnamese people, or Kinh people, a Southeast Asian ethnic group native to Vietnam
** Overse ...
(0.4%).
Religion
In the 2021 census, 49.9% of Greater Hobart residents specified no religion. Christianity comprised the largest religious affiliation (37.1%), with the largest denominations being Anglicanism (14.1%) and Catholicism (14.1%). Hinduism (2.6%), Buddhism (1.3%), Islam (1.3%) and Sikhism (0.6%) constitute the remaining largest religious affiliations. Hobart has a small community of 456 members ofThe Church of Jesus Christ of Latter Day Saints
The Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints, informally known as the LDS Church or Mormon Church, is a nontrinitarian Christian church that considers itself to be the restoration of the original church founded by Jesus Christ. The ch ...
, with meetinghouses in Glenorchy, Rosny, and Glen Huon
Glen Huon is a rural residential locality in the local government area of Huon Valley in the South-east region of Tasmania. It is located about west of the town of Huonville. The 2016 census has a population of 661 for the state suburb of Gle ...
. There is also a synagogue, with a Jewish community of 203 people. Hobart has a Baháʼí community, with a Baháʼí Centre of Learning, located within the city. In 2013, Hillsong Church established a Hillsong Connect campus in Hobart.
Economy
 Shipping is significant to the city's economy. Hobart is the home port for the Antarctic activities of Australia and France. The port loads around 2,000 tonnes of Antarctic cargo a year for the Australian research vessel '' Nuyina (previously the
Shipping is significant to the city's economy. Hobart is the home port for the Antarctic activities of Australia and France. The port loads around 2,000 tonnes of Antarctic cargo a year for the Australian research vessel '' Nuyina (previously the Aurora Australis
An aurora (plural: auroras or aurorae), also commonly known as the polar lights, is a natural light display in Earth's sky, predominantly seen in high-latitude regions (around the Arctic and Antarctic). Auroras display dynamic patterns of br ...
).'' The city is also a popular cruise ship
Cruise ships are large passenger ships used mainly for vacationing. Unlike ocean liners, which are used for transport, cruise ships typically embark on round-trip voyages to various ports-of-call, where passengers may go on tours known as ...
destination during the summer months, with 47 such ships docking during the course of the 2016–17 summer season.
The city also supports many other industries. Major local employers include catamaran builder Incat
Incat Tasmania is an Australian manufacturer of high-speed craft (HSC) catamaran ferries. Its greatest success has been with large, sea going passenger and vehicle ferries, but it has also built military transports and since 2015 it has built s ...
, zinc
Zinc is a chemical element with the symbol Zn and atomic number 30. Zinc is a slightly brittle metal at room temperature and has a shiny-greyish appearance when oxidation is removed. It is the first element in group 12 (IIB) of the periodi ...
refinery Nyrstar
Nyrstar is a global multi-metals business, with a market leading position in zinc and lead and growing positions in other base and precious metals, such as copper, gold and silver. Nyrstar has mining and smelting operations located in Europe, North ...
, Cascade Brewery
Cascade Brewery is a brewery established in 1824 in South Hobart, Tasmania and is the oldest continually operating brewery in Australia.
As well as beer, the site also produces a range of non-alcoholic products. It is home to a function cen ...
and Cadbury's Chocolate Factory, Norske Skog
Norske Skog ASA, formerly Norske Skogindustrier ASA, which translates as ''Norwegian Forest Industries'', is a Norwegian pulp and paper company established in 1962. The company has long been one of the world's leading manufacturers of newsprint ...
and Wrest Point Casino
The Wrest Point Hotel Casino is a casino in Tasmania. It was Australia's first legal casino, opening in the suburb of Sandy Bay in Hobart, on 10 February 1973.
History
Historically, Dunkley's Point was a camping ground held by the semi-nomadic ...
. The city also supports a host of light industry manufacturers, as well as a range of redevelopment projects, including the $689 million Royal Hobart Hospital Redevelopment – standing as the states largest ever Health Infrastructure project.
Tourism is a significant part of the economy, with visitors coming to the city to explore its historic inner suburbs and nationally acclaimed restaurants and cafes, as well as its vibrant music and nightlife culture. The two major draw-cards are the weekly market in Salamanca Place
Salamanca Place is a precinct of Hobart, the capital city of the Australian state of Tasmania.
Salamanca Place itself consists of rows of sandstone buildings, formerly warehouses for the port of Hobart Town that have since been converted into ...
, and the Museum of Old and New Art
The Museum of Old and New Art (MONA) is an art museum located within the Moorilla winery on the Berriedale peninsula in Hobart, Tasmania, Australia. It is the largest privately funded museum in the Southern Hemisphere. MONA houses ancient, mode ...
. The city is also used as a base from which to explore the rest of Tasmania.
The last 15–20 years have seen Hobart's wine industry thrive as many vineyards have developed in countryside areas outside of the city in the Coal River Wine Region and D'Entrecasteaux Channel
The D'Entrecasteaux Channel is a body of water located between Bruny Island and the south-east of the mainland of Tasmania, Australia. The channel is the mouth for the estuaries of the Derwent and the Huon Rivers and empties into the Tasman S ...
, including Moorilla Estate
Moorilla Estate is a winery located in the suburb of Berriedale, 12 km north of the city centre of Hobart, in Tasmania.
Establishment
It was established in 1958 by Italian-Australian former textile merchant Claudio Alcorso.
Moorilla Est ...
at Berriedale one of the most awarded vineyards in Australia.
Antarctic gateway
 Hobart is an Antarctic gateway city, with geographical proximity to East Antarctica and the Southern Ocean. Infrastructure is provided by the port of Hobart for scientific research and cruise ships, and
Hobart is an Antarctic gateway city, with geographical proximity to East Antarctica and the Southern Ocean. Infrastructure is provided by the port of Hobart for scientific research and cruise ships, and Hobart International Airport
Hobart Airport is an international airport located in Cambridge, north-east of Hobart. It is the major and fastest growing passenger airport in Tasmania.
The Federal government owned airport is operated by the Tasmanian Gateway Consort ...
supports an Antarctic Airlink to Wilkins Runway at Casey Station
Casey Station, commonly called Casey, is one of three permanent stations and research outposts in Antarctica managed by the Australian Antarctic Division (AAD). Casey lies on the northern side of the Bailey Peninsula overlooking Vincennes Bay ...
. Hobart is a logistics point for the French icebreaker ''L'Astrolabe''.
Hobart is the home port for the Australian and French Antarctic programs, and provides port services for other visiting Antarctic nations and Antarctic cruise ships. Antarctic and Southern Ocean expeditions are supported by a specialist cluster offering cold climate products, services and scientific expertise. The majority of these businesses and organisations are members of the Tasmanian polar network
{{unreferenced, date=November 2012
The Tasmanian Polar Network (TPN) is an industry body based in Hobart, an Antarctic gateway city in the state of Tasmania, Australia. It comprises scientific institutions, businesses and organisations which h ...
, supported in part by the Tasmanian State Government.
Tasmania has a high concentration of Antarctic and Southern Ocean scientists. Hobart is home to the following Antarctic and Southern Ocean scientific institutions:
* Australian Antarctic Division
The Australian Antarctic Division (AAD) is a division of the Department of Climate Change, Energy, the Environment and Water. The Division undertakes science programs and research projects to contribute to an understanding of Antarctica and the ...
* Commission for the Conservation of Antarctic Marine Living Resources
The Convention on the Conservation of Antarctic Marine Living Resources, also known as the Commission for the Conservation of Antarctic Marine Living Resources, and CCAMLR, is part of the Antarctic Treaty System.
The convention was opened for s ...
(CCAMLR)
* Agreement on the Conservation of Albatrosses and Petrels
The Agreement on the Conservation of Albatrosses and Petrels (ACAP) is a legally binding international agreement signed in 2001 and entered into force on 1 February 2004 when South Africa ratified as the fifth Party to the Agreement.
It was crea ...
(ACAP)
* The University of Tasmania
The University of Tasmania (UTAS) is a public research university, primarily located in Tasmania, Australia. Founded in 1890, it is Australia's fourth oldest university. Christ College, one of the university's residential colleges, first prop ...
(UTAS) – expertise in Antarctic and Southern Ocean science and research
* Institute for Marine and Antarctic Studies
The Institute for Marine and Antarctic Studies (IMAS) is a teaching and research institute of the University of Tasmania in Hobart, Tasmania. IMAS was established in 2010, building upon the university's partnership with CSIRO Oceans and Atmos ...
(IMAS) (established by UTAS)
*Integrated Marine Observing System (IMOS)
*Antarctic Climate and Ecosystems Cooperative Research Centre (ACE-CRC)
*International Antarctic Institute (IAI) (hosted by UTAS)
*Southern Ocean Observing System (hosted by UTAS/ IMAS)
* CSIRO Marine and Atmospheric Research
CSIRO Oceans and Atmosphere (O&A) is one of the current 8 Business Units (formerly: Flagships) of the Commonwealth Scientific and Industrial Research Organisation (CSIRO), Australia's largest government-supported science research agency.
Histor ...
Tourism
 Hobart serves as a focal point and mecca for tourism in the state of Tasmania. Hobart has been a significant tourist destination for many years, however tourism has evolved to a core industry in the last decade. This process has been termed the "MONA Effect" - referring to the significant influence of the Museum of New and Old Art (MONA), the Southern Hemisphere's largest private museum, on the local tourist economy - compared to the effect of the Guggenheim on
Hobart serves as a focal point and mecca for tourism in the state of Tasmania. Hobart has been a significant tourist destination for many years, however tourism has evolved to a core industry in the last decade. This process has been termed the "MONA Effect" - referring to the significant influence of the Museum of New and Old Art (MONA), the Southern Hemisphere's largest private museum, on the local tourist economy - compared to the effect of the Guggenheim on Bilbao
)
, motto =
, image_map =
, mapsize = 275 px
, map_caption = Interactive map outlining Bilbao
, pushpin_map = Spain Basque Country#Spain#Europe
, pushpin_map_caption ...
. Since opening in 2011, MONA had received 2.5 million visitors by 2022 and has helped establish a number of art and food venues and events, including MONA FOMA, and the winter festivals of Mid-Winter Fest and Dark Mofo
Dark Mofo is the winter version of the MONA FOMA festival, also held in Tasmania. With many of its events taking place at night, it celebrates the darkness of the southern winter solstice and features many musical acts, large scale light insta ...
. 27% of visitors to Tasmania visit the museum.
In 2016, Hobart received 1.8 million visitors, surpassing both Perth and Canberra, tying equally with Brisbane. Visitor numbers reached a low of 744,200 in 2021, primarily as a result of the Covid-19 Pandemic
The COVID-19 pandemic, also known as the coronavirus pandemic, is an ongoing global pandemic of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2). The novel virus was first identi ...
, with expectations that numbers would return to normal by 2023.
Many local tourist attractions focuses on the convict history of Hobart, the city's historic architecture, art experiences, and food and alcohol experiences. Hobart is home to a significant number of nationally known restaurants, boutique alcohol producers, including Sullivans Cove Wiskey, which won world's best single malt in 2014, boutique hotels, and art experiences. Other significant tourist attractions include Australia's second oldest botanic gardens, the Royal Tasmanian Botanical Gardens
The Royal Tasmanian Botanical Gardens (''RTBG''), which cover an area of approximately 14 hectares (34.6 acres), in Hobart located within the Queens Domain.
History
The gardens were established in 1818 and is the second oldest Botanical Garden ...
, which holds extensive significant plant collections, a range of public and private museums including the Tasmanian Museum and Art Gallery
The Tasmanian Museum and Art Gallery (TMAG) is a museum located in Hobart, Tasmania. The museum was established in 1846, by the Royal Society of Tasmania, the oldest Royal Society outside England.
The TMAG receives 400,000 visitors annually.
...
, and kunanyi/Mount Wellington, one of the dominant features of Hobart's skyline. At , the mountain has its own ecosystems, is rich in biodiversity and plays a large part in determining the local weather.
Architecture
 Hobart is known for its well-preserved
Hobart is known for its well-preserved Georgian
Georgian may refer to:
Common meanings
* Anything related to, or originating from Georgia (country)
** Georgians, an indigenous Caucasian ethnic group
** Georgian language, a Kartvelian language spoken by Georgians
**Georgian scripts, three scrip ...
and Victorian architecture
Victorian architecture is a series of architectural revival styles in the mid-to-late 19th century. ''Victorian'' refers to the reign of Queen Victoria (1837–1901), called the Victorian era, during which period the styles known as Victorian we ...
, giving the city a distinctly " Old World" feel. For locals, this became a source of discomfiture about the city's convict past, but is now a draw card for tourists. Regions within the city centre, such as Salamanca Place
Salamanca Place is a precinct of Hobart, the capital city of the Australian state of Tasmania.
Salamanca Place itself consists of rows of sandstone buildings, formerly warehouses for the port of Hobart Town that have since been converted into ...
and Battery Point
Battery Point is a suburb of the city of Hobart, Tasmania, Australia. It is immediately south of the central business district. It is in the local government area of City of Hobart.
Battery Point is named after the battery of guns which were est ...
, contain many of the city's heritage-listed buildings. Historic homes and mansions also exist in the suburbs, much of the inner-city neighbourhoods are dotted with weatherboard
Clapboard (), also called bevel siding, lap siding, and weatherboard, with regional variation in the definition of these terms, is wooden siding of a building in the form of horizontal boards, often overlapping.
''Clapboard'' in modern Americ ...
cottages and two-storey Victorian houses. Hobart has a signfiicant body of notable buildings, including the Cascades Female Factory
The Cascades Female Factory, a former Australian workhouse for female convicts in the penal colony of Van Diemen's Land, is located in Hobart, Tasmania. Operational between 1828 and 1856, the factory is now one of the 11 sites that collective ...
, one of the UNESCO Australian Convict Sites
Australian Convict Sites is a World Heritage property consisting of 11 remnant penal sites originally built within the British Empire during the 18th and 19th centuries on fertile Australian coastal strips at Sydney, Tasmania, Norfolk Island, ...
, the Hobart Synagogue
The Hobart Synagogue is a heritage-listed synagogue located in 59 Argyle Street, Hobart, Tasmania, Australia. The synagogue is the oldest synagogue building in Australia and is a rare example of the Egyptian Revival style of synagogue archite ...
, which is the oldest synagogue in Australia and a rare surviving example of an Egyptian Revival
Egyptian Revival is an architectural style that uses the motifs and imagery of ancient Egypt. It is attributed generally to the public awareness of ancient Egyptian monuments generated by Napoleon's conquest of Egypt and Admiral Nelson's defeat ...
synagogue, Hadley's Orient Hotel, on Hobart's Murray Street, which is the oldest continuously operating hotel in Australia, and the Theatre Royal, the oldest continually operating theatre in Australia.
Kelly's Steps
Kelly's Steps is an architectural landmark in Hobart, Tasmania. The steps, named after early Australian explorer and whaler James Kelly, connect the suburb of Battery Point to Salamanca Place
Salamanca Place is a precinct of Hobart, the ca ...
were built in 1839 by shipwright and adventurer James Kelly to provide a short-cut from Kelly Street and Arthur Circus in Battery Point to the warehouse and dockyards district of Salamanca Place. In 1835, John Lee Archer
John Lee Archer (26 April 1791 near Chatham, Kent, England – 4 December 1852 in Stanley, Tasmania, Australia) was the Civil Engineer and Colonial Architect in Van Diemen's Land, serving from 1827 to 1838. During his tenure, Archer was resp ...
designed and oversaw the construction of the sandstone Customs House
A custom house or customs house was traditionally a building housing the offices for a jurisdictional government whose officials oversaw the functions associated with importing and exporting goods into and out of a country, such as collecting ...
, facing Sullivans Cove. Completed in 1840, it was used as Tasmania's parliament house, and is now commemorated by a pub bearing the same name (built in 1844) which is frequented by yachtsmen after they have completed the Sydney to Hobart yacht race.
Hobart is also home to many historic churches. The Scots Church (formerly known as St Andrew's) was built in Bathurst Street from 1834 to 1836, and a small sandstone building within the churchyard was used as the city's first Presbyterian Church. The Salamanca Place warehouses and the Theatre Royal were also constructed in this period. The Greek revival St George's Anglican Church in Battery Point was completed in 1838, and a classical tower, designed by James Blackburn, was added in 1847. St Joseph's was built in 1840. St David's Cathedral, Hobart's first cathedral, was consecrated in 1874.
Hobart has very few high-rise buildings in comparison to other Australian capital cities. This is partly a result of height limits imposed due to Hobart's proximity to the River Derwent and Mount Wellington.

Culture
Arts and entertainment

 Hobart is home to Australia's oldest continuously operating theatre, the Theatre Royal, built in 1837. Other theatres in the city include the Playhouse theatre, the Backspace Theatre, and many smaller stage theatres.
The
Hobart is home to Australia's oldest continuously operating theatre, the Theatre Royal, built in 1837. Other theatres in the city include the Playhouse theatre, the Backspace Theatre, and many smaller stage theatres.
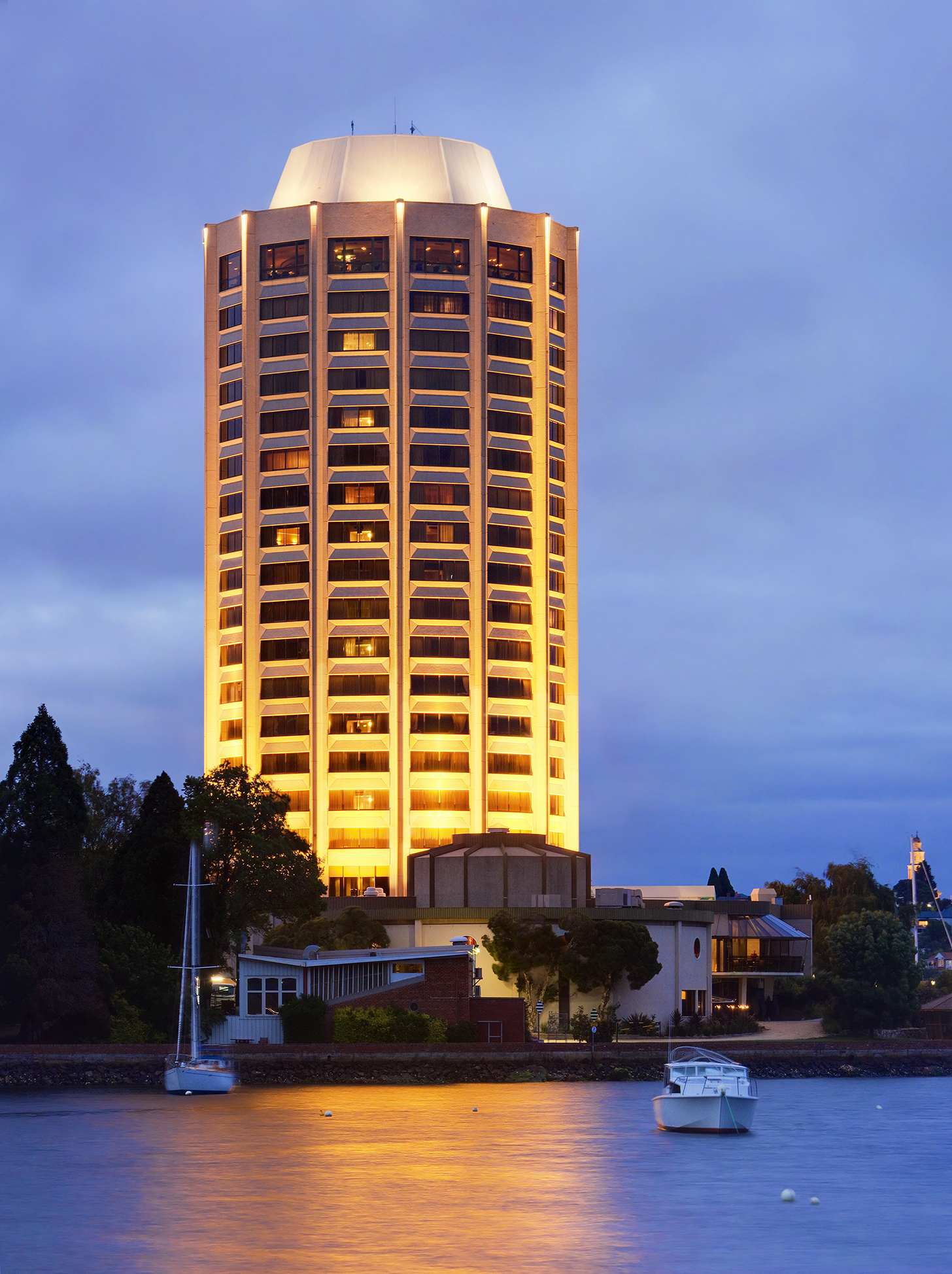
The Tasmanian Symphony Orchestra
The Tasmanian Symphony Orchestra (TSO) is a symphony orchestra based in Hobart, Tasmania, Australia. It is the smallest of the six orchestras established by the Australian Broadcasting Corporation (ABC).
History
The Tasmanian Symphony Orchestr ...
is based at the Federation Concert Hall
The Hotel Grand Chancellor Hobart is a twelve-storey hotel located on the waterfront of Hobart, Tasmania, Australia.
History
Originally part of a waterfront district called 'Wapping', the site where the Hotel Grand Chancellor is situated was ...
on the city's waterfront. The Federation Concert Hall also hosts the University of Tasmania's Australian International Symphony Orchestra Institute (AISOI) which fosters advanced young musicians from across Australia and internationally.
Australia's first novel, ''Quintus Servinton
Henry Savery (4 August 1791 – 6 February 1842) was a convict transported to Port Arthur, Tasmania, and Australia's first novelist. It is generally agreed that his writing is more important for its historical value than its literary merit.''Qu ...
'', was published in 1831 by convict Henry Savery
Henry Savery (4 August 1791 – 6 February 1842) was a convict transported to Port Arthur, Tasmania, and Australia's first novelist. It is generally agreed that his writing is more important for its historical value than its literary merit.''Qui ...
and published in Hobart, where he wrote the work during his imprisonment. A generally autobiographical work, it's the story of what happens to a well educated man from a relatively well to do family, who makes poor choices in life. Mary Leman Grimstone, whose book ''Woman's Love'' was written in Hobart between 1826 and 1829, holds the distinction of being the first non-biographical Australian novel. It was printed in London in 1832.
The city has also long been home to a thriving classical, jazz, folk, punk, hip-hop, electro, metal and rock music scene. Internationally recognised musicians such as metal acts Striborg
Striborg is a black metal / ambient project of Australian musician Russell Menzies. The project first began in 1994 under the name Kathaaria and during this time the stage name "Vvelkaarn" was used. The name Kathaaria was adapted from a Darkt ...
and Psycroptic
Psycroptic are an Australian technical death metal band formed in Hobart, Australia in 1999. Mainstay members are Dave Haley on drums and his brother Joe Haley on guitar. Their lead vocalist, Jason Peppiatt, joined in 2004. In 2008 they signe ...
, indie-electro bands The Paradise Motel
The Paradise Motel are an independent Australian rock band that formed in Hobart, Tasmania in 1994. They relocated to Melbourne and issued two albums on Mushroom Records, ''Still Life'' (1996) and '' Flight Paths'' (1998) before moving to the Un ...
and The Scientists of Modern Music
The Scientists of Modern Music were an electronic group from Hobart, Australia, consisting of Cal Young and Simon McIntosh.
History
In 2004, Cal Young & Simon McIntosh started wagging audio design classes together, in order to jam on a very ...
, singer-songwriters Sacha Lucashenko (of The Morning After Girls
The Morning After Girls are an Australian neo-psychedelia band. The group was originally formed in Melbourne, Victoria around 2003 by founding members Sacha Lucashenko (vocals and guitar) and Martin B. Sleeman (vocals and guitar), who relocate ...
), Michael Noga (of The Drones), and Monique Brumby
Monique Brumby (born 16 September 1974, in Devonport) is an Australian Indie pop/rock singer-songwriter, guitarist and producer. Her debut single, " Fool for You", peaked into the top 40 in the Australian Recording Industry Association (ARIA) ...
, two-thirds of indie rock band Love of Diagrams, post punk band Sea Scouts
Sea Scouts are a part of the Scout movement, with a particular emphasis on boating and other water-based activities on the sea, rivers or lakes (canoeing, rafting, scuba, sailboarding). Sea Scouts can provide a chance to sail, cruise on boats, ...
, theremin
The theremin (; originally known as the ætherphone/etherphone, thereminophone or termenvox/thereminvox) is an electronic musical instrument controlled without physical contact by the performer (who is known as a thereminist). It is named afte ...
player Miles Brown, blues guitarist Phil Manning (of blues-rock band Chain), power-pop group The Innocents, and TikTok
TikTok, known in China as Douyin (), is a short-form video hosting service owned by the Chinese company ByteDance. It hosts user-submitted videos, which can range in duration from 15 seconds to 10 minutes.
TikTok is an international version o ...
artist Kim Dracula
Samuel Wellings, known professionally as Kim Dracula, is an Australian trap metal/hardcore music artist from Hobart, Tasmania whose songs have achieved popularity on TikTok. They are known both for original work and for metal covers of songs n ...
all originated in Hobart. In addition, founding member of Violent Femmes
Violent Femmes are an American folk punk band from Milwaukee, Wisconsin. The band consists of founding members Gordon Gano (guitar, lead vocals) and Brian Ritchie (bass, backing vocals), joined by multi-instrumentalist Blaise Garza (joined 200 ...
, Brian Ritchie
Brian Ritchie (born November 21, 1960) is the bass guitarist for the alternative rock band Violent Femmes. Ritchie was born and raised in the United States and is currently a dual citizen of the U.S. and Australia, with his full-time residence i ...
, now calls Hobart home, and has formed a local band, The Green Mist. Ritchie also curates the annual international arts festival MONA FOMA, held at Salamanca Place
Salamanca Place is a precinct of Hobart, the capital city of the Australian state of Tasmania.
Salamanca Place itself consists of rows of sandstone buildings, formerly warehouses for the port of Hobart Town that have since been converted into ...
's waterfront venue, Princes Wharf, Shed No. 1. Hobart hosts many significant festivals including summer's Taste of Tasmania
The Taste of Tasmania is Tasmania's largest food and wine festival. Established in 1988, the Festival operates from 28 December–3 January and will celebrate its 32nd year in 2022. The festival is held in Hobart's Salamanca Place and waterfr ...
celebrating local produce, wine and music, ''Dark Mofo'' marking the winter solstice, Australia's premier festival celebration of voice the ''Festival of Voices'', and Tasmania's biennial international arts festival Ten Days On The Island 10 Days on the Island is a biennial cultural festival held in Tasmania, Australia. The first was held in 2001. It is Tasmania's premier cultural event, and presents exhibitions, performances and community events in 50 locations around the island.
...
. Other festivals, including the ''Hobart Fringe Festival'', Hobart Summer Festival
The Taste of Tasmania is Tasmania's largest food and wine festival. Established in 1988, the Festival operates from 28 December–3 January and will celebrate its 32nd year in 2022. The festival is held in Hobart's Salamanca Place and waterfr ...
, Southern Roots Festival
Southern Roots was an annual music festival in Australia, held in Hobart, Tasmania. Similar to the Big Day Out, it is common that the well-known headlining acts will play on the outdoor "Main Stage" which overlooks the venue, and the lesser kn ...
, the Falls Festival
Falls Music & Arts Festival (commonly known as Falls) is a multi-day music festival held annually in Lorne ( Victoria), Marion Bay (Tasmania), Byron Bay (New South Wales) and Fremantle (Western Australia), Australia over the New Year's Eve an ...
in Marion Bay and the Soundscape Festival also capitalise on Hobart's artistic communities.
Hobart is home to the Tasmanian Museum and Art Gallery
The Tasmanian Museum and Art Gallery (TMAG) is a museum located in Hobart, Tasmania. The museum was established in 1846, by the Royal Society of Tasmania, the oldest Royal Society outside England.
The TMAG receives 400,000 visitors annually.
...
. The Meadowbank Estate winery and restaurant features a floor mural by Tom Samek
Tom Samek (11 March 1950 – October 2021) was a Czech artist who lived and worked in Australia.
Bett Gallery, Hobart ...
, part funded by the Federal Government. The Bett Gallery, Hobart ...
Museum of Old and New Art
The Museum of Old and New Art (MONA) is an art museum located within the Moorilla winery on the Berriedale peninsula in Hobart, Tasmania, Australia. It is the largest privately funded museum in the Southern Hemisphere. MONA houses ancient, mode ...
(MONA) opened in 2011 to coincide with the third annual MONA FOMA festival. The multi-storey MONA gallery was built directly underneath the historic Sir Roy Grounds courtyard house, overlooking the River Derwent. This building serves as the entrance to the MONA Gallery. The Lady Franklin Gallery became Australia's first privately funded museum when established by Lady Jane Franklin in 1843. The Art Society of Tasmania has operated from the premises since 1949.
Hobart has a growing street art scene thanks to a program called ''Hobart Walls'', which was launched in association with the ''Vibrance Festival'', an annual mural-painting event. The City of Hobart and Vibrance Festival launched Hobart's first legal street art wall in Bidencopes Lane in 2018, allowing any artist to paint there, on any day of the week, provided they sign up for a permit and paint between 9am and 10pm.
Designed by the prolific architect Sir Roy Grounds
Sir Roy Burman Grounds (18 December 19052 March 1981) was an Australian architect. His early work included buildings influenced by the Moderne movement of the 1930s, and his later buildings of the 50s and 60s, such as the National Gallery of V ...
, the 17-storey Wrest Point Hotel Casino
The Wrest Point Hotel Casino is a casino in Tasmania. It was Australia's first legal casino, opening in the suburb of Sandy Bay in Hobart, on 10 February 1973.
History
Historically, Dunkley's Point was a camping ground held by the semi-nomadic ...
in Sandy Bay, opened as Australia's first legal casino
A casino is a facility for certain types of gambling. Casinos are often built near or combined with hotels, resorts, restaurants, retail shopping, cruise ships, and other tourist attractions. Some casinos are also known for hosting live entertai ...
in 1973.
The city's nightlife primarily revolves around Salamanca Place
Salamanca Place is a precinct of Hobart, the capital city of the Australian state of Tasmania.
Salamanca Place itself consists of rows of sandstone buildings, formerly warehouses for the port of Hobart Town that have since been converted into ...
, the waterfront area, Elizabeth St in North Hobart and Sandy Bay, but popular pub
A pub (short for public house) is a kind of drinking establishment which is licensed to serve alcoholic drinks for consumption on the premises. The term ''public house'' first appeared in the United Kingdom in late 17th century, and was ...
s, bars and nightclub
A nightclub (music club, discothèque, disco club, or simply club) is an entertainment venue during nighttime comprising a dance floor, lightshow, and a stage for live music or a disc jockey (DJ) who plays recorded music.
Nightclubs gener ...
s exist around the city as well. Major national and international music events are usually held at the Derwent Entertainment Centre
Derwent Entertainment Centre, also known as the DEC and known commercially as MyState Bank Arena, is the largest indoor arena in Tasmania and the multi-purpose arena is the primary venue in Hobart for large indoor functions/events. It was cons ...
, or the Casino
A casino is a facility for certain types of gambling. Casinos are often built near or combined with hotels, resorts, restaurants, retail shopping, cruise ships, and other tourist attractions. Some casinos are also known for hosting live entertai ...
. Popular restaurant strips include Elizabeth Street in North Hobart, and Salamanca Place
Salamanca Place is a precinct of Hobart, the capital city of the Australian state of Tasmania.
Salamanca Place itself consists of rows of sandstone buildings, formerly warehouses for the port of Hobart Town that have since been converted into ...
near the waterfront. These include numerous ethnic restaurants including Chinese
Chinese can refer to:
* Something related to China
* Chinese people, people of Chinese nationality, citizenship, and/or ethnicity
**''Zhonghua minzu'', the supra-ethnic concept of the Chinese nation
** List of ethnic groups in China, people of ...
, Thai
Thai or THAI may refer to:
* Of or from Thailand, a country in Southeast Asia
** Thai people, the dominant ethnic group of Thailand
** Thai language, a Tai-Kadai language spoken mainly in and around Thailand
*** Thai script
*** Thai (Unicode block ...
, Greek
Greek may refer to:
Greece
Anything of, from, or related to Greece, a country in Southern Europe:
*Greeks, an ethnic group.
*Greek language, a branch of the Indo-European language family.
**Proto-Greek language, the assumed last common ancestor ...
, Pakistani, Italian
Italian(s) may refer to:
* Anything of, from, or related to the people of Italy over the centuries
** Italians, an ethnic group or simply a citizen of the Italian Republic or Italian Kingdom
** Italian language, a Romance language
*** Regional Ita ...
, Indian
Indian or Indians may refer to:
Peoples South Asia
* Indian people, people of Indian nationality, or people who have an Indian ancestor
** Non-resident Indian, a citizen of India who has temporarily emigrated to another country
* South Asia ...
and Mexican. The major shopping street in the CBD is Elizabeth Street, with the pedestrianised Elizabeth Mall and the General Post Office.
Close Shave
Close Shave is one of Australia's longest serving male a cappella quartets. Based in Hobart, the quartet delights audiences at conferences, dinners, weddings, and other public functions with its diverse repertoire. In addition to the traditional B ...
, one of Australia's longest serving male a cappella quartets, is based in Hobart.

Events
 Hobart is internationally famous among the yachting community as the finish of the Sydney to Hobart Yacht Race which starts in Sydney on Boxing Day (the day after Christmas Day). The arrival of the yachts is celebrated as part of the
Hobart is internationally famous among the yachting community as the finish of the Sydney to Hobart Yacht Race which starts in Sydney on Boxing Day (the day after Christmas Day). The arrival of the yachts is celebrated as part of the Hobart Summer Festival
The Taste of Tasmania is Tasmania's largest food and wine festival. Established in 1988, the Festival operates from 28 December–3 January and will celebrate its 32nd year in 2022. The festival is held in Hobart's Salamanca Place and waterfr ...
, a food and wine festival beginning just after Christmas and ending in mid-January. The Taste of Tasmania
The Taste of Tasmania is Tasmania's largest food and wine festival. Established in 1988, the Festival operates from 28 December–3 January and will celebrate its 32nd year in 2022. The festival is held in Hobart's Salamanca Place and waterfr ...
is a major part of the festival, where locals and visitors can taste fine local and international food and wine.
The city is the finishing point of the Targa Tasmania
Targa Tasmania is a tarmac-based rally event held on the island state of Tasmania, Australia, annually since 1992. The event takes its name from the Targa Florio, a former motoring event held on the island of Sicily. The competition concept i ...
rally car event, which has been held annually in April since 1991.
The annual Tulip
Tulips (''Tulipa'') are a genus of spring-blooming perennial herbaceous bulbiferous geophytes (having bulbs as storage organs). The flowers are usually large, showy and brightly coloured, generally red, pink, yellow, or white (usually in warm ...
Festival at the Royal Tasmanian Botanical Gardens
The Royal Tasmanian Botanical Gardens (''RTBG''), which cover an area of approximately 14 hectares (34.6 acres), in Hobart located within the Queens Domain.
History
The gardens were established in 1818 and is the second oldest Botanical Garden ...
is a popular Spring celebration in the city.
The Australian Wooden Boat Festival
The Australian Wooden Boat Festival (AWBF) is a biennial event held in Hobart, Tasmania, celebrating wooden boats. AWBF is held concurrently with the Royal Hobart Regatta. The festival welcomes wooden boats of all sizes including wooden cano ...
is a biennial event held in Hobart celebrating wooden boats. It is held concurrently with the Royal Hobart Regatta
The Royal Hobart Regatta is a series of aquatic competitions and displays held annually in Hobart, Tasmania, Australia and is Tasmania's oldest sporting event. The regatta began in 1838.
The event runs for three days and incorporates a publi ...
, which began in 1830 and is therefore Tasmania's oldest surviving sporting event.
Sport
 Most professional Hobart-based sports teams represent Tasmania as a whole rather than exclusively the city.
Most professional Hobart-based sports teams represent Tasmania as a whole rather than exclusively the city.
Cricket
Cricket is a bat-and-ball game played between two teams of eleven players on a field at the centre of which is a pitch with a wicket at each end, each comprising two bails balanced on three stumps. The batting side scores runs by str ...
is a popular game of the city. The Tasmanian Tigers
The Tasmanian cricket team, nicknamed the Tigers, represents the Australian state of Tasmania in cricket. They compete annually in the Australian domestic senior men's cricket season, which consists of the first-class Sheffield Shield and the ...
cricket team plays its home games at the Bellerive Oval
Bellerive Oval, known commercially as Blundstone Arena for sponsorship reasons, is a cricket and Australian rules football ground located in Bellerive, a suburb on the eastern shore of Hobart, Australia, holding 20,000 people it is the largest ...
on the Eastern Shore. A new team, Hobart Hurricanes
The Hobart Hurricanes are an Australian professional men's T20 franchise cricket team based in Tasmania, Australia. They compete in Australia's domestic T20 cricket competition known as the Big Bash League, which is a league where many in ...
represent the city in the Big Bash League. Bellerive Oval
Bellerive Oval, known commercially as Blundstone Arena for sponsorship reasons, is a cricket and Australian rules football ground located in Bellerive, a suburb on the eastern shore of Hobart, Australia, holding 20,000 people it is the largest ...
has been the breeding ground of some world class cricket players including the former Australia captain Ricky Ponting.
Despite Australian rules football's huge popularity in the state of Tasmania, the state does not have a team in the Australian Football League. However, a bid for an Tasmanian AFL team is a popular topic among football fans. The State government is one of the potential sponsors of such a team. Local domestic club football is still played. Tasmanian State League
The Tasmanian State League (TSL), colloquially known as the "Tasmanian Football League (TFL)" (formerly known as the "Tasmanian Australian National Football League (TANFL)" and several other short-term names) is the highest ranked Australian r ...
football features five clubs from Hobart, and other leagues such as Southern Football League and the Old Scholars Football Association are also played each Winter.
The city has two local rugby league
Rugby league football, commonly known as just rugby league and sometimes football, footy, rugby or league, is a full-contact sport played by two teams of thirteen players on a rectangular field measuring 68 metres (75 yards) wide and 11 ...
football teams (Hobart Tigers and South Hobart Storm) that compete in the Tasmanian Rugby League
NRL Tasmania (abbreviated as NRLTas, and formerly the Tasmanian Rugby League) is the organisation responsible for administering the game of rugby league in the Australian state of Tasmania. Tasmania is an affiliated State of the overall Australi ...
.
Tasmania is not represented by teams in the NRL, Super Rugby, ANZ Championship
The ANZ Championship, also known as the Trans-Tasman Netball League, is a former netball league featuring teams from both Australia and New Zealand. Between 2008 and 2016, it was the top-level league in both countries. The competition was owned ...
or A-League. However, the Tasmania JackJumpers
The Tasmania JackJumpers are an Australian professional basketball team based in Hobart, Tasmania, who entered the National Basketball League (NBL) in the 2021–22 season, and play their home games at MyState Bank Arena and the Silverdome. T ...
entered the NBL in the 2021/22 season. The Hobart Chargers
Hobart Chargers is a NBL1 South club based in Hobart, Tasmania. The club fields a team in both the Men's and Women's NBL1 South. The Chargers play their home games at the Derwent Entertainment Centre and Kingborough Sports Centre.
Club history Ear ...
also represent Hobart in the second-tier South East Australian Basketball League
The South East Australian Basketball League (SEABL) was an Australian semi-professional basketball league. The league comprised both a men's and women's competition and was run by the country's governing body, Basketball Australia. The league wa ...
. Besides the bid for an AFL
AFL may refer to:
Sports
* American Football League (AFL), a name shared by several separate and unrelated professional American football leagues:
** American Football League (1926) (a.k.a. "AFL I"), first rival of the National Football Leagu ...
club which was passed over in favour of a second Queensland team, despite several major local businesses and the Premier pioneering for a club, there is also a Hobart bid for entry into the A-League.
The Tassie Tigers
Tassie Tigers is an Australia, Australian field hockey club based in Hobart, Tasmania. The club joined the Australian Hockey League in 1992 as a men's team. In 2019, the Tassie Tigers expanded to encompass both Tasmanian men's and women's teams, ...
field men's and women's representative sides in the national hockey league, Hockey One
The Sultana Bran Hockey One is a field hockey competition organised by Hockey Australia, which replaced the Australian Hockey League.
The competition serves as Australia's premier domestic hockey league, helping unearth future talent for select ...
(which replaced the Australian Hockey League in 2019). They play their home matches at the Tasmanian Hockey Centre
The Tasmanian Hockey Centre, is a government owned outdoor field hockey stadium located in New Town, a northern suburb of Hobart. It offers three international standard water-based hockey pitches which are used for both international and domest ...
in New Town near Cornelian Bay, which features three synthetic hockey pitches that have also hosted international competition such as the Men's FIH Pro League
The Men's FIH Pro League is an international men's field hockey competition organised by the International Hockey Federation (FIH), which replaces the Men's FIH Hockey World League. The competition also serves as a qualifier for the Hockey World ...
as recently as 2019. The Kookaburras
Kookaburras are terrestrial tree kingfishers of the genus ''Dacelo'' native to Australia and New Guinea, which grow to between in length and weigh around . The name is a loanword from Wiradjuri ''guuguubarra'', onomatopoeic of its call. The ...
current co-Captain and games record holder, Eddie Ockenden
Edward "Eddie" Clyve Ockenden (born 3 April 1987) is an Australian field hockey player. He plays in the midfielder and striker positions. He turned professional in 2008 and has played for teams in the Netherlands. He plays club hockey, having c ...
, is a product of the Hobart-based club North West Graduates.
The city co-hosted the basketball FIBA Oceania Championship 1975
The FIBA Oceania Championship for Men 1975 was the qualifying tournament of FIBA Oceania for the 1976 Summer Olympics. The tournament, a best-of-three series between and , was held in Melbourne, Hobart and Launceston. Australia won the series 3-0 ...
, where the Australian national basketball team
The Australian men's national basketball team, known as the Boomers after the slang term for a male kangaroo, represents Australia in international basketball competition.
Since the late 1980s, Australia has been placed among the world elite t ...
won the gold medal.
Media
 Five free-to-air television stations service Hobart:
*
Five free-to-air television stations service Hobart:
* ABC Tasmania
ABT is a television station operated by the publicly-owned Australian Broadcasting Corporation, with a transmission area covering southern Tasmania. ABT began broadcasting on VHF channel 2 on 4 June 1960, with studios in inner-city Hobart and ...
( ABT)
* SBS Tasmania ( SBS)
* Southern Cross Seven
Seven Regional is an Australian television network owned by Southern Cross Austereo that is available in Tasmania, Darwin, Spencer Gulf, Broken Hill and Remote Australia (Eastern and Central). The network is the primary affiliate of the Seven ...
Tasmania (TNT
Trinitrotoluene (), more commonly known as TNT, more specifically 2,4,6-trinitrotoluene, and by its preferred IUPAC name 2-methyl-1,3,5-trinitrobenzene, is a chemical compound with the formula C6H2(NO2)3CH3. TNT is occasionally used as a reagen ...
) – ''Seven Network
The Seven Network (commonly known as Channel Seven or simply Seven) is a major Australian commercial free-to-air television network. It is owned by Seven West Media Limited, and is one of five main free-to-air television networks in Australia ...
affiliate''
* Nine
9 is a number, numeral, and glyph.
9 or nine may also refer to:
Dates
* AD 9, the ninth year of the AD era
* 9 BC, the ninth year before the AD era
* 9, numerical symbol for the month of September
Places
* Nine, Portugal, a parish in the ...
Tasmania ( TVT) – '' Nine Network affiliate''
* Tasmanian Digital Television
TDT is a digital television station in Tasmania, Australia. It is jointly owned by WIN Corporation and Southern Cross Austereo, operating as ''Tasmanian Digital Television''.
History
In Australia, the major capital cities, and a majority of th ...
(TDT
Terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase (TdT), also known as DNA nucleotidylexotransferase (DNTT) or terminal transferase, is a specialized DNA polymerase expressed in immature, pre-B, pre-T lymphoid cells, and acute lymphoblastic leukemia/lymphom ...
) – ''Network 10
Network 10 (commonly known as Ten Network, Channel 10 or simply 10) is an Australian commercial television network owned by Ten Network Holdings, a division of the Paramount Networks UK & Australia subsidiary of Paramount Global. One of five ...
affiliate''
Each station broadcasts a primary channel and several multichannels.
Hobart is served by twenty-nine digital free-to-air
Free-to-air (FTA) services are television (TV) and radio services broadcast in unencrypted form, allowing any person with the appropriate receiving equipment to receive the signal and view or listen to the content without requiring a subscripti ...
television channels:
# ABC
ABC are the first three letters of the Latin script known as the alphabet.
ABC or abc may also refer to:
Arts, entertainment, and media Broadcasting
* American Broadcasting Company, a commercial U.S. TV broadcaster
** Disney–ABC Television ...
# ABC HD (ABC broadcast in HD)
# ABC TV Plus/KIDS
# ABC ME
ABC Me (stylised as ABC ME) is an Australian English language children's free-to-air television channel owned by the Australian Broadcasting Corporation. It was officially launched by Prime Minister Kevin Rudd on 4 December 2009 as ABC3.
Hist ...
# ABC News
ABC News is the news division of the American broadcast network ABC. Its flagship program is the daily evening newscast ''ABC World News Tonight, ABC World News Tonight with David Muir''; other programs include Breakfast television, morning ...
# SBS
# SBS HD
SBS is a national public television network in Australia. Launched on 24 October 1980, it is the responsibility of SBS's television division, and is available nationally. In 2018, SBS had a 7.7% audience share.
As of 2022, SBS is the lowest ...
(SBS broadcast in HD)
# SBS Viceland
SBS Viceland (stylised as SBS VICELAND) is an Australian free-to-air television channel owned by the Special Broadcasting Service (SBS). It began as SBS TWO on 1 June 2009, and was branded as SBS 2 between 2013 and 2016. On 8 April 2017, SBS ...
# SBS Viceland HD
SBS Viceland (stylised as SBS VICELAND) is an Australian free-to-air television channel owned by the Special Broadcasting Service (SBS). It began as SBS TWO on 1 June 2009, and was branded as SBS 2 between 2013 and 2016. On 8 April 2017, SBS ...
(SBS Viceland broadcast in HD)
# Food Network
Food Network is an American basic cable channel owned by Television Food Network, G.P., a joint venture and general partnership between Warner Bros. Discovery Networks (which holds a 69% ownership stake of the network) and Nexstar Media Group ( ...
# NITV
National Indigenous Television (NITV) is an Australian free-to-air television channel that broadcasts programming produced and presented largely by Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander people. It includes the half-hourly nightly ''NITV News'' ...
# 7 Tasmania (on relay from Melbourne)
# 7HD
7HD is an Australian television channel, owned by Seven West Media, originally launched on 15 October 2007 featuring unique breakaway programming from 10 December 2007 to 4 October 2009 and a HD simulcast of Seven until 25 September 2010. The ...
(Seven broadcast in HD)
# 7two
# 7mate
7mate is an Australian free-to-air digital television multichannel, which was launched by the Seven Network on 25 September 2010. The channel contains sport and regular programs aimed primarily to a male audience, with programming drawn from a c ...
# Racing.com
# Nine
9 is a number, numeral, and glyph.
9 or nine may also refer to:
Dates
* AD 9, the ninth year of the AD era
* 9 BC, the ninth year before the AD era
* 9, numerical symbol for the month of September
Places
* Nine, Portugal, a parish in the ...
(on relay from Melbourne)
# 9HD
9HD is an Australian television channel owned by Nine Entertainment, originally launched on 17 March 2008 featuring unique "breakaway" programming until 2009 and a high-definition simulcast of the Nine Network from 2009 to 2010 and again s ...
(Nine broadcast in HD)
# 9Gem
9Gem is an Australian free-to-air digital television multichannel, launched by the Nine Network in September 2010. The channel provides general entertainment and movie programming, from which the original name "GEM" is derived.
History
Nine N ...
# 9Go!
9Go! is an Australian free-to-air digital television multichannel, which was launched by the Nine Network on 9 August 2009, replacing Nine Guide. It is a youthful channel that offers a mix of comedy, reality, general entertainment, movies, ani ...
# 9Life
9Life is an Australian free-to-air digital television multichannel owned by Nine Entertainment. The channel airs mostly foreign lifestyle and reality programs, with the channel having a licensing agreement with Discovery Inc. (previously Scripp ...
# TVSN
TVSN (an acronym for "Television Shopping Network") is an Australian and New Zealand broadcast, cable television and satellite television network specializing in home shopping. It is owned by parent company Direct Group Pty Ltd, a home marketi ...
# Gold
Gold is a chemical element with the symbol Au (from la, aurum) and atomic number 79. This makes it one of the higher atomic number elements that occur naturally. It is a bright, slightly orange-yellow, dense, soft, malleable, and ductile me ...
# Sky News on WIN
Sky News Australia is an Australian news channel owned by News Corp Australia. Originally launched on 19 February 1996, it broadcasts rolling news coverage throughout the day, while its prime time lineup is dedicated to opinion-based programs f ...
# 10 (on relay from Melbourne)
# 10 HD
10 HD is an Australian free-to-air television channel that was originally launched on 16 December 2007 on channel 1. The channel was available to high definition digital television viewers through Network 10 owned-and-operated stations. The ...
(TDT broadcast in HD)
# 10 Bold
10 Bold is an Australian free-to-air digital television multichannel owned by Network 10. It originally launched on 26 March 2009 as One HD with a focus on broadcasting sports-based programming and events, but rebranded to One in April 2011 to ...
# 10 Peach
# 10 Shake
10 Shake is an Australian free-to-air digital television multichannel owned by Network 10. It launched on 27 September 2020 at 6am.
The channel includes a mix of shows for people aged forty and under. It broadcasts programming for children fr ...
The majority of pay television
Pay television, also known as subscription television, premium television or, when referring to an individual service, a premium channel, refers to subscription-based television services, usually provided by multichannel television providers, b ...
services are provided by Foxtel via satellite, although other smaller pay television providers do service Hobart.
Commercial radio stations licensed to cover the Hobart market include Triple M Hobart
Triple M Hobart (call sign: 7XXX) is part of the Southern Cross Austereo network of Triple M Network radio stations, Based in Hobart, Tasmania, Australia.
History
Triple M Hobart, formerly ''Heart 107.3'' and before that, ''Magic 107'', bega ...
, hit100.9 Hobart and 7HO FM
7HOFM (call sign: 7HHO) is one of three commercial radio stations in Hobart, Tasmania, Australia. It commenced broadcasting on 13 August 1930, as the first commercial radio station in its city.
The station's initial frequency was 890 kHz A ...
. Local community radio stations include Christian radio station Ultra106five
Ultra106five is a Christian radio station in Hobart, Tasmania. Ultra106five is Hobart's only Christian radio station, and was one of the first of its kind in Australia. The station provides a mixed format of Christian, Easy Listening and Hot ...
, Edge Radio
Edge Radio (call sign: 7EDG) is a community radio station situated in the Australian city of Hobart. It is a youth oriented station, with most of its presenters under the age of thirty.
Edge Radio focuses on local music, running a Tasmanian mu ...
and Hobart FM
Hobart FM (call sign: 7THE) is a radio station in Hobart, Australia broadcasting on 96.1 MHz and 92.1 MHz. They do not provide a track list.
History
Hobart FM Incorporated applied for and was granted a Public Radio Licence in 1977 un ...
which targets the wider community with specialist programmes. The five ABC radio networks available on analogue radio broadcast to Hobart via 936 ABC Hobart
ABC Radio Hobart (call sign: 7ZR) is the ABC Local Radio station for Hobart, Tasmania, owned by the Australian Broadcasting Corporation.
History
Officially opened on 22 June 1938, plans surrounding the initial broadcast of 7ZR were forced to be ...
, Radio National
Radio National, known on-air as RN, is an Australia-wide public service broadcasting radio network run by the Australian Broadcasting Corporation (ABC). From 1947 until 1985, the network was known as ABC Radio 2.
History
1937: Predecessors a ...
, Triple J
Triple J (stylised in all lowercase) is a government-funded, national Australian radio station intended to appeal to listeners of alternative music, which began broadcasting in January 1975. The station also places a greater emphasis on broad ...
, NewsRadio
''NewsRadio'' is an American sitcom television series that aired on NBC from March 21, 1995 to May 4, 1999, focusing on the work lives of the staff of a New York City AM news radio station. It had an ensemble cast featuring Dave Foley, Steph ...
and ABC Classic FM. Hobart is also home to the video creation company Biteable.
Hobart's major newspaper is '' The Mercury'', which was founded by John Davies in 1854 and has been continually published ever since. The paper is owned and operated by Rupert Murdoch
Keith Rupert Murdoch ( ; born 11 March 1931) is an Australian-born American business magnate. Through his company News Corp, he is the owner of hundreds of local, national, and international publishing outlets around the world, including ...
's News Limited
News Corp Australia is an Australian media conglomerate and wholly owned subsidiary of the American News Corp. One of Australia's largest media conglomerates, News Corp Australia employs more than 8,000 staff nationwide and approximately 3,0 ...
.
Government
City of Glenorchy
Glenorchy City Council (or City of Glenorchy) is a local government body in Tasmania, and one of the five municipalities that constitutes the Greater Hobart Area. The Glenorchy local government area has a population of 47,636, covering the sub ...
and City of Clarence
Clarence City Council (or City of Clarence) is a Local government in Australia, local government body in Tasmania, and one of the five municipalities that constitutes the Hobart, Greater Hobart Area. The Clarence local government area has a po ...
,. The remaining metropolitan area is within the Municipality of Kingborough
Kingborough Council is a local government body in Tasmania, and one of the five municipalities that constitutes the Greater Hobart Area. Kingborough is classified as an urban local government area and has a population of 37,734, it covers the ...
and the Municipality of Brighton. Each local government area has an elected council which manages functions delegated by the Tasmanian state government such as roads, planning, animal control and parks. Mains water and sewerage processing are serviced by TasWater
TasWater is Tasmania's water and sewage utility. It is responsible for providing drinking water across the state as well as collecting and treating sewage. It is owned by Tasmania's 29 local governments.
TasWater commenced operations on 1 July ...
, which is a state-wide authority part owned by the state government and local government areas.
Hobart is the seat of the Parliament of Tasmania
The Parliament of Tasmania is the bicameral legislature of the Australian state of Tasmania. It follows a Westminster-derived parliamentary system and consists of the Governor of Tasmania, the Tasmanian House of Assembly (the lower house), and ...
, located at Parliament House, Salamanca Place, and the location of the official residence of the Governor of Tasmania
The governor of Tasmania is the representative in the Australian state of Tasmania of the Monarch of Australia, currently King Charles III. The incumbent governor is Barbara Baker, who was appointed in June 2021. The official residence of the ...
, Government House
Government House is the name of many of the official residences of governors-general, governors and lieutenant-governors in the Commonwealth and the remaining colonies of the British Empire. The name is also used in some other countries.
Gover ...
. The senior sitting of the Supreme Court of Tasmania, and only sitting of the Court's appeal division, sit in Hobart.
Hobart was made the seat of government for the southern district of Tasmania (then called Van Diemen's Land
Van Diemen's Land was the colonial name of the island of Tasmania used by the British during the European exploration of Australia in the 19th century. A British settlement was established in Van Diemen's Land in 1803 before it became a sep ...
), Buckingham County in 1804, with the northern half of the state separately governed from Port Dalrymple
George Town (Palawa_kani: ''kinimathatakinta'') is a large town in north-east Tasmania, on the eastern bank of the mouth of the Tamar River. The Australian Bureau of Statistics records the George Town Municipal Area had a population of 6,764 as ...
, now George Town. At the time, Van Diemen's Land remained part of the Colony of New South Wales. In 1812, the northern lieutenant governorship ceased and Hobart become de facto seat of government for the entire island. Hobart officially became capital of an independent colony of Van Diemen's Land in 1825, and the seat of responsible self government in 1850 with the Australian Constitutions Act 1850
The Australian Constitutions Act 1850, or the Australian Colonies Government Act, was an Act of the Parliament of the United Kingdom which was enacted to formally established the Colony of Victoria by separating the District of Port Phillip fro ...
.
Infrastructure
Education
 Hobart is home to the main campus of the
Hobart is home to the main campus of the University of Tasmania
The University of Tasmania (UTAS) is a public research university, primarily located in Tasmania, Australia. Founded in 1890, it is Australia's fourth oldest university. Christ College, one of the university's residential colleges, first prop ...
, located in Sandy Bay. On-site accommodation colleges include Christ College, Jane Franklin Hall
Jane Franklin Hall in Hobart, Australia is an independent non-denominational residential college of the University of Tasmania. Familiarly referred to as "Jane", it was founded by the Tasmanian Council of Churches in 1950 as a residential col ...
and St John Fisher College
St. John Fisher University is a private liberal arts college in Pittsford, New York. It is named after John Fisher, an English Catholic cardinal and saint. It was named St. John Fisher College until July 1, 2022.
History
St. John Fisher Univer ...
. Other campuses are in Launceston and Burnie.
The Greater Hobart area contains 122 primary, secondary and pretertiary (College) schools distributed throughout Clarence, Glenorchy and Hobart City Councils and Kingborough and Brighton Municipalities. These schools are made up of a mix of public, catholic, private and independent run, with the heaviest distribution lying in the more densely populated West around the Hobart city core. TasTAFE TasTAFE is a Tasmanian tertiary education body of the Australian state-based Technical and Further Education system run by the Tasmanian State Government. The main campuses are located at Hobart, Warrane, Claremont, Glenorchy, Launceston, Alan ...
operates a total of seven polytechnic campuses within the Greater Hobart area that provide vocational education and training.
Health
Royal Hobart Hospital
The Royal Hobart Hospital is a public hospital in the Hobart CBD, Tasmania, Australia. The hospital also functions as a teaching hospital in co-operation with the University of Tasmania. The hospital's research facilities are known as the Roya ...
is a major public hospital
A public hospital, or government hospital, is a hospital which is government owned and is fully funded by the government and operates solely off the money that is collected from taxpayers to fund healthcare initiatives. In some countries, this typ ...
in central Hobart with 501 beds, which also serves as a teaching hospital
A teaching hospital is a hospital or medical centre that provides medical education and training to future and current health professionals. Teaching hospitals are almost always affiliated with one or more universities and are often co-located ...
for the University of Tasmania.
A private hospital, Hobart Private Hospital
The Hobart Private Hospital is a 146-bed private hospital located in the central business district of Hobart adjacent to the Royal Hobart Hospital. It is owned by Healthscope, one of Australia's leading providers of hospitals, medical and patho ...
is located adjacent to it and operated by Australian healthcare provider Healthscope
Healthscope is a for-profit Australian company which operates private hospitals, medical centres and rehabilitation hospitals. The company is headquartered on St Kilda Road, Melbourne. It operates medical/surgical hospitals and a number of psyc ...
. The company also owns another hospital in the city, the St. Helen's Private Hospital
ST, St, or St. may refer to:
Arts and entertainment
* Stanza, in poetry
* Suicidal Tendencies, an American heavy metal/hardcore punk band
* Star Trek, a science-fiction media franchise
* Summa Theologica, a compendium of Catholic philosophy ...
, which features a mother-baby unit.
Transport
 The only
The only public transportation
Public transport (also known as public transportation, public transit, mass transit, or simply transit) is a system of transport for passengers by group travel systems available for use by the general public unlike private transport, typical ...
within the city of Hobart is via a network of Metro Tasmania
Metro Tasmania, commonly called Metro, a Tasmanian Government business enterprise, is the largest bus operator in the state of Tasmania, Australia, with operations in three of the four largest urban centres of Hobart, , and . Urban services in ...
buses funded by
the Tasmanian Government and a small number of private bus services. Like many large Australian cities, Hobart once operated passenger tram services, a trolleybus
A trolleybus (also known as trolley bus, trolley coach, trackless trolley, trackless tramin the 1910s and 1920sJoyce, J.; King, J. S.; and Newman, A. G. (1986). ''British Trolleybus Systems'', pp. 9, 12. London: Ian Allan Publishing. .or trol ...
network consisting of six routes which operated until 1968. However, the tramway closed in the early 1960s. The tracks are still visible in the older streets of Hobart.
Suburban passenger trains, run by the Tasmanian Government Railways, were closed in 1974 and the intrastate passenger service, the Tasman Limited, ceased running in 1978. Recently though there has been a push from the city, and increasingly from government, to establish a light rail network, intended to be fast, efficient, and eco-friendly, along existing tracks in a North South corridor; to help relieve the frequent jamming of traffic in Hobart CBD.
The main arterial routes within the urban area are the Brooker Highway
The Brooker Highway is a highway in the State of Tasmania, Australia. As one of Hobart's 3 major radials, the highway connects traffic from the Hobart city centre with the northern suburbs and is the major road connection to the cities and tow ...
to Glenorchy and the northern suburbs, the Tasman Bridge
The Tasman Bridge is a bridge that carries the Tasman Highway over the Derwent River in Hobart, Tasmania, Australia. Including approaches, the bridge has a total length of and it provides the main traffic route from the Hobart city centre ( ...
and Bowen Bridge
The Bowen Bridge is a four-lane road bridge crossing the Derwent River in Tasmania, Australia.
Description
The bridge lies on the river about halfway between the Tasman Bridge and the Bridgewater Bridge. The bridge links the East Derwent Hi ...
across the river to Rosny and the Eastern Shore. The East Derwent Highway to Lindisfarne, Geilston Bay, and Northwards to Brighton, the South Arm Highway leading to Howrah, Rokeby, Lauderdale and Opossum Bay and the Southern Outlet south to Kingston and the D'Entrecasteaux Channel
The D'Entrecasteaux Channel is a body of water located between Bruny Island and the south-east of the mainland of Tasmania, Australia. The channel is the mouth for the estuaries of the Derwent and the Huon Rivers and empties into the Tasman S ...
. Leaving the city, motorists can travel the Lyell Highway
The Lyell Highway (Route A10) is a highway in Tasmania, running from Hobart to Queenstown.
It is the one of two transport routes that passes through the West Coast Range, the other being the Anthony Road.
Name
The name is derived from ...
to the west coast, Midland Highway to Launceston and the north, Tasman Highway
The Tasman Highway (or A3) is a highway in Tasmania, Australia. Like the Midland Highway, it connects the major cities of Hobart and Launceston – however it takes a different route, via the north-eastern and eastern coasts of the state. The ...
to the east coast, or the Huon Highway
The Huon Highway is an highway in southern Tasmania, Australia. The highway forms part of the A6 and connects Hobart with the southern parts of Tasmania. The original Huon Highway (now known as Huon Road) was a twisty two-lane road skirting ...
to the far south.
 Ferry services from Hobart's Eastern Shore into the city were once a common form of public transportation, but with lack of government funding, as well as a lack of interest from the private sector, there has been the demise of a regular commuter ferry service – leaving Hobart's commuters relying solely on travel by automobiles and buses. There is however a water taxi service operating from the Eastern Shore into Hobart which provides an alternative to the
Ferry services from Hobart's Eastern Shore into the city were once a common form of public transportation, but with lack of government funding, as well as a lack of interest from the private sector, there has been the demise of a regular commuter ferry service – leaving Hobart's commuters relying solely on travel by automobiles and buses. There is however a water taxi service operating from the Eastern Shore into Hobart which provides an alternative to the Tasman Bridge
The Tasman Bridge is a bridge that carries the Tasman Highway over the Derwent River in Hobart, Tasmania, Australia. Including approaches, the bridge has a total length of and it provides the main traffic route from the Hobart city centre ( ...
.
In 2021, State Government trialed a ferry service that operates on the Derwent between Brooke Street Pier and Bellerive. Due to the success of the trial, the ferry service was made permanent, with more than 2100 passengers in the first three weeks.
Hobart is served by Hobart International Airport
Hobart Airport is an international airport located in Cambridge, north-east of Hobart. It is the major and fastest growing passenger airport in Tasmania.
The Federal government owned airport is operated by the Tasmanian Gateway Consort ...
with flights to/from Adelaide, Auckland, Brisbane, Canberra, Gold Coast, Melbourne, Perth, Sydney, and regional destinations including the Bass Strait islands. The smaller Cambridge Aerodrome
Cambridge Aerodrome , also known as Cambridge Airport, is a minor airport located in Cambridge, a suburb of Hobart, Tasmania, Australia. It is located only a few kilometres from the primary airport, Hobart International Airport.
Cambridge ...
mainly serves small charter airlines offering local tourist flights. In the past decade, Hobart International Airport received a huge upgrade, with the airport now being a first class airport facility.
In 2009, it was announced that Hobart Airport would receive more upgrades, including a first floor, aerobridges (currently, passengers must walk on the tarmac) and shopping facilities. Possible new international flights to Asia and New Zealand, and possible new domestic flights to Darwin and Cairns have been proposed. A second runway, possibly to be constructed in the next 15 years, would assist with growing passenger numbers to Hobart. Hobart Control Tower may be renovated and fitted with new radar equipment, and the airport's carpark may be extended further. Also, new facilities will be built just outside the airport. A new service station, hotel and day care centre have already been built and the road leading to the airport has been maintained and re-sealed. In 2016, work began on a 500-metre extension of the existing runway in addition to a $100 million upgrade of the airport. The runway extension is expected to allow international flights to land and increase air-traffic with Antarctica
Antarctica () is Earth's southernmost and least-populated continent. Situated almost entirely south of the Antarctic Circle and surrounded by the Southern Ocean, it contains the geographic South Pole. Antarctica is the fifth-largest cont ...
. This upgrade was, in part, funded under a promise made during the 2013 federal election by the Abbott government.
On 9 August 2021, the Derwent River Ferry (owned by Roche Brothers' Navigator Group) was initiated as a year-long trial servicing between Brooke Street Pier
The Brooke Street Pier is a floating pontoon building at Sullivans Cove in the waterfront area of the city of Hobart, Tasmania, Australia. It was constructed in 2014–15 at a cost of . It weighs and was Australia's largest floating buildin ...
in Hobart centre to Bellerive Pier on the eastern shore. A one-way trip takes approximately 15 minutes, and the ferry operates on all weekdays, but not weekends. It starts the day at Bellerive and departs 8 times there from 6:20am as the first time and 5:30pm as the last (40-minute intervals), before returning from Brooke St Pier at 5:50pm to Bellerive for the next day. The ferry provides a convenient alternative to crossing the Tasman Bridge
The Tasman Bridge is a bridge that carries the Tasman Highway over the Derwent River in Hobart, Tasmania, Australia. Including approaches, the bridge has a total length of and it provides the main traffic route from the Hobart city centre ( ...
, with its purpose being to reduce traffic congestion at a cost of $175.5 million. It can hold 107 passengers as well as 15 bicycle spots on-board. It is seen as a first step in diversifying Hobart's transportation infrastructure to solve traffic problems that involves taking cars off the road rather than increasing capacity.
Notable residents
Arts
 *
* Asta
The General Students' Committee (German: Allgemeiner Studierendenausschuss) or AStA, is the acting executive board and the external representing agency of the (constituted) student body at universities in most German states. It is therefore consid ...
, singer-songwriter
* Phillip Borsos
Phillip Borsos (May 5, 1953 – February 2, 1995) was an Australian-born Canadian film director, producer, and screenwriter.The Mean Season
''The Mean Season'' is a 1985 American thriller film directed by Phillip Borsos and starring Kurt Russell, Mariel Hemingway, Richard Jordan, Richard Masur, Joe Pantoliano, Luis Tamayo and Andy García. The screenplay, written by Christopher Crow ...
'' (1985) and ''One Magic Christmas
''One Magic Christmas'' is a 1985 Christmas fantasy film directed by Phillip Borsos. It was released by Walt Disney Pictures and stars Mary Steenburgen and Harry Dean Stanton. It was shot in Meaford, Ontario with some scenes in Owen Sound, Ontari ...
'' (1985)
* Saroo Brierley, author of '' A Long Way Home'', adapted into the 2016 film '' Lion''.
* Jeanine Claes, artist, dancer, choreographer and dance teacher
* Essie Davis
Esther Davis (born 19 January 1970) is an Australian actress and singer, best known for her roles as Phryne Fisher in ''Miss Fisher's Murder Mysteries'' and its film adaptation, '' Miss Fisher & the Crypt of Tears'', and as Amelia Vanek in '' T ...
, actress
* Richard Flanagan, author
* Errol Flynn
Errol Leslie Thomson Flynn (20 June 1909 – 14 October 1959) was an Australian-American actor who achieved worldwide fame during the Golden Age of Hollywood. He was known for his romantic swashbuckler roles, frequent partnerships with Olivia ...
, Hollywood actor
* Frederick Frith, painter and photographer
* Lisa Gormley
Lisa Gormley (born 29 September 1984) is an English-born Australian actress and best known for playing Bianca Scott on the Channel 7 serial drama '' Home and Away''. She is a NIDA graduate.
Early life
Gormley was born in Bradford, West Y ...
, English-born Australian actress best known for playing Bianca Scott
Bianca Scott is a fictional character from the Australian Channel Seven soap opera '' Home and Away'', played by Lisa Gormley. Gormley had recently graduated from NIDA when she secured the role of Bianca, who was introduced as the sister of fel ...
on the Channel 7 serial drama '' Home and Away''
* Lucky Grills
Leo Dennis Grills OAM (26 May 1928 – 27 July 2007) professionally billed as Lucky Grills, was an Australian actor and comedian. His best known acting role was in the crime drama TV series '' Bluey'' playing the title role. Grills took his p ...
, best known for portraying the unconventional detective "Bluey" Hills in the television series '' Bluey'' in 1976.
* Robert Grubb
Robert Grubb (born 31 January 1950) is an Australian actor. He studied acting at National Institute of Dramatic Art (NIDA), where he graduated in 1978. There he was a fellow student of actor Mel Gibson.
Grubb played the role of Dr. Geoffrey St ...
, actor
* John Harwood, writer and poet
* Ernest
Ernest is a given name derived from Germanic word ''ernst'', meaning "serious". Notable people and fictional characters with the name include:
People
* Archduke Ernest of Austria (1553–1595), son of Maximilian II, Holy Roman Emperor
* Ernest, ...
, Tasman and Arthur Higgins, brothers and pioneering cinematographers during the silent era
* Don Kay, Australian classical composer
* William Kermode, artist
* Constantine Koukias
Constantine Koukias (born 14 October 1965) is a Tasmanian composer and opera director of Greek ancestry based in Amsterdam, where he is known by his Greek name of Konstantin Koukias. He is the co-founder and artistic director of IHOS Music Theatre ...
, Greek-Australian composer and flautist
The flute is a family of classical music instrument in the woodwind group. Like all woodwinds, flutes are aerophones, meaning they make sound by vibrating a column of air. However, unlike woodwind instruments with reeds, a flute is a reedless ...
* Louise Lovely
Louise Lovely (born Nellie Louise Carbasse; 28 February 1895 – 18 March 1980) was an Australian film actress of Swiss-Italian descent. She is credited by film historians for being the first Australian actress to have a successful career i ...
, the first Australian motion picture actress to find success in Hollywood
* Dennis Miller
Dennis Michael Miller (born November 3, 1953) is an American talk show host, political commentator, sports commentator, actor, and comedian.
He was a cast member of ''Saturday Night Live'' from 1985 to 1991, and he subsequently hosted a stri ...
, actor best known for his recurring role on ''Blue Heelers
''Blue Heelers'' is an Australian Police procedural, police drama series that was produced by Endemol Australia, Southern Star Group and ran for 12 years on the Seven Network, from 1994 to 2006. Although based around the policing of the town, ...
'' as Ex-Sergeant Pat Doyle (1994–2000).
* Richard Morgan, most noted for playing the long-running role of Terry Sullivan in the Australian television series ''The Sullivans
''The Sullivans'' is an Australian period drama television series produced by Crawford Productions which ran on the Nine Network from 15 November 1976 until 10 March 1983. The series tells the story of a fictional average middle-cla ...
''.
* Tara Morice
Tara Morice (born 23 June 1964) is an Australian actress.
Background
Born in Hobart, Tasmania, Morice also lived in Sydney, Alice Springs and Adelaide as a child. She is a fifth-generation Australian and is of English, Irish, Scottish, Latvia ...
, actress
* Gerda Nicolson
Gerda Maureen Nicolson (11 November 1937 – 12 June 1992) was an Australian theatre and television actress best known for several long-running television roles. She was best known for playing Governor Ann Reynolds of the Wentworth Detention Cen ...
, actress
* Len Reynolds
Leonard "Len" Reynolds is a fictional character from the British ITV soap opera ''Emmerdale'', played by Peter Martin.
Development
In May 2007, Martin's character Len is killed off, as Martin had accepted a role in a stage production of ...
, illustrator, caricaturist, painter, cartoonist
* Glenn Richards
Glenn Anthony Richards (born 29 December 1973) is an Australian musician, best known as the mainstay guitarist singer-songwriter for the Australian rock band Augie March.
Early life
Richards was born in Shepparton, Victoria on 29 December 1973. ...
, musician, singer, songwriter and guitarist with Augie March
Augie (sometimes spelled Auggie) is a nickname for variations of the name August, which derives from the Latin name Augustus. It may refer to:
People
* Augie Auer (1940–2007), meteorologist
* Augie Galan (1912–1993), Major League Baseball p ...
* Brian Ritchie
Brian Ritchie (born November 21, 1960) is the bass guitarist for the alternative rock band Violent Femmes. Ritchie was born and raised in the United States and is currently a dual citizen of the U.S. and Australia, with his full-time residence i ...
, musician, bassist of Violent Femmes
Violent Femmes are an American folk punk band from Milwaukee, Wisconsin. The band consists of founding members Gordon Gano (guitar, lead vocals) and Brian Ritchie (bass, backing vocals), joined by multi-instrumentalist Blaise Garza (joined 200 ...
* Clive Sansom, poet and playwright
* Don Sharp
Donald Herman Sharp (19 April 192114 December 2011) was an Australian film director.
His best known films were made for Hammer in the 1960s, and included ''The Kiss of the Vampire'' (1963) and ''Rasputin, the Mad Monk'' (1966). In 1965 he dire ...
, actor
* Michael Siberry
Michael Siberry (born 1956) is an Australian stage and screen actor.
Life and career
Siberry was born in Hobart, Tasmania, Australia. He graduated from the National Institute of Dramatic Art in Sydney, Australia and began his career in Adel ...
, actor
* Jaason Simmons
Jaason Simmons (born 12 July 1970) is an Australian actor best known for the role of Logan Fowler on the TV series ''Baywatch''.
Biography
Early life and career
Born as Jaason Matthew Simmons in Hobart, Tasmania, he attended ''Warrane Primar ...
, actor best known for his role as life guard Logan Fowler
This is a list of the characters in the TV series ''Baywatch'' and ''Baywatch: Hawaii''.
Cast timeline
;Cast notes
''Baywatch'' (1989–1990; 1991–1999)
;Mitch Buchannon, Mitchell "Mitch" Buchannon (David Hasselhoff, ''Baywatch: Panic at M ...
in the TV series ''Baywatch
''Baywatch'' is an American action drama television series about lifeguards who patrol the beaches of Los Angeles County, California, and Hawaii, starring David Hasselhoff. It was created by Michael Berk, Douglas Schwartz, and Gregory J. Bo ...
''
* Freya Stafford
Freya Stafford (born 21 January 1977) is an Australian actress who has appeared in the television programs '' Head Start'' and ''White Collar Blue'' as central characters.
Early life
Stafford was born in Sydney, New South Wales. In 1982 her fam ...
, actress who has appeared on TV programs such as '' Head Start'' and ''White Collar Blue
''White Collar Blue'' is an Australian television series made by Knapman Wyld Television for Network Ten from 2002 to 2003.
Starring Peter O'Brien as Joe Hill and Freya Stafford as Harriet Walker, the series dealt with a division of the po ...
'' and the 2010 horror film '' The Clinic''
* Amali Ward
The second season of ''Australian Idol'' debuted on 13 July 2004. Over 50,000 people throughout Australia auditioned.
Overview
As well as the five larger cities, the judges also visited Canberra, Hobart, Darwin, Northern Territory, Darwin and T ...
, '' Australian Idol'' Season 2 finalist
* Charles Woolley, photographer and artist
Sports
*Darrel Baldock
Darrel John Baldock AM (29 September 1938 – 2 February 2011) was an Australian sportsman and state politician. He played Australian rules football for the St Kilda Football Club in the Victorian Football League (VFL), East Devonport Footba ...
- Australian Rules footballer. Captain of St Kilda 1966 Grand Final victory over Collingwood. Legend status in the AFL Hall of Fame.
* Scott Bowden
Scott Bowden (born 4 April 1995) is an Australian mountain biking and road cyclist, who currently rides for French amateur team Bourg-en-Bresse Ain Cyclisme. He rode in the road race and the cross-country at the 2016 Summer Olympics, represe ...
– Australian cyclist
* Al Bourke
Al Bourke (born Alan Stamford; March 17, 1928) is an Australian professional boxer of the 1940s and 1950s who won the Victorian middleweight title, List of Australian middleweight boxing champions, Australian middleweight title, and List of Comm ...
– Australian boxer of the 1940s, and 1950s
* Josh Burdon
Josh Burdon (born 5 September 1992) is an Australian professional racing driver and 2016 Asian Formula Renault Series champion.He is currently driving for Hong Kong-based KC Motorgroup in the Intercontinental GT Challenge, Nürburgring Langstr ...
– Australian racing driver
* Roy Cazaly – Australian rules footballer who died in 1963 in Hobart, member of the Australian Football Hall of Fame
* Adam Coleman
Adam Coleman (born 7 October 1991) is an Australian rugby union player living in England who plays lock for London Irish in the Gallagher Premiership.
Career
Coleman attended New Town High School in Hobart Tasmania. He represented Tasmania in u ...
, rugby union
Rugby union, commonly known simply as rugby, is a close-contact team sport that originated at Rugby School in the first half of the 19th century. One of the two codes of rugby football, it is based on running with the ball in hand. In it ...
player
* Rodney Eade
Rodney Eade (born 4 April 1958) is a former Australian rules footballer and coach in the Australian Football League. He is a former coach of the Sydney Swans, the Western Bulldogs and the Gold Coast Football Club. He has, to date, coached 37 ...
– Australian rules footballer who played 259 games for Hawthorn
Hawthorn or Hawthorns may refer to:
Plants
* '' Crataegus'' (hawthorn), a large genus of shrubs and trees in the family Rosaceae
* ''Rhaphiolepis'' (hawthorn), a genus of about 15 species of evergreen shrubs and small trees in the family Rosace ...
and the Bears
Bears are carnivoran mammals of the family Ursidae. They are classified as caniforms, or doglike carnivorans. Although only eight species of bears are extant, they are widespread, appearing in a wide variety of habitats throughout the Nor ...
, former head coach of the Western Bulldogs
The Western Bulldogs are a professional Australian rules football team that competes in the Australian Football League (AFL), the sport's premier competition.
Founded in 1877 as the Footscray Football Club, and based in West Footscray in the o ...
until Round 21, 2011 and former head coach of the Gold Coast Suns.
* David Foster
David Walter Foster (born November 1, 1949) is a Canadian musician, composer, arranger, record producer and music executive who chaired Verve Records from 2012 to 2016. He has won 16 Grammy Awards from 47 nominations. His music career spans mor ...
– World Champion woodchopper
Woodchopping (also spelled wood-chopping or wood chopping), called woodchop for short, is a sport that has been around for hundreds of years in several cultures. In woodchopping competitions, skilled contestants attempt to be the first to cut or s ...
* Ryan Foster
Ryan Foster (born 26 August 1988) is an Australian middle distance runner and coach who specialises in the 800 metres. He graduated from Pennsylvania State University in 2011. He won four Big Ten 800 metres titles, was an All-American over 800 ...
– Middle-distance runner and first Tasmanian to break the 4-minute mile.
* Brendon Gale
Brendon Gale (born 18 July 1968) is a former Australian rules footballer who played for the Richmond Football Club in the Australian Football League (AFL).
After his AFL playing career, Gale practiced law with commercial law firm King Wood Ma ...
– former Australian rules footballer, and is CEO of the Richmond Football Club
* Royce Hart – Australian rules footballer, member of the Australian Football Hall of Fame with legend status and member of the Team of the Century
* Peter Hudson
Peter John Hudson AM (born 19 February 1946) is a former Australian rules footballer who played for the Hawthorn Football Club in the Victorian Football League (VFL) and for the New Norfolk Football Club and Glenorchy Football Club in the ...
AM – Australian rules footballer, considered one of the greatest full-forwards in the game's history, when playing for Glenorchy he kicked 616 goals in 81 games with some records stating he instead kicked 769 goals; he is also a member of the Australian Football Hall of Fame
* Peter 'Percy' Jones – Australian rules footballer, played 249 games for the Carlton Blues in the VFL
* Eddie Ockenden
Edward "Eddie" Clyve Ockenden (born 3 April 1987) is an Australian field hockey player. He plays in the midfielder and striker positions. He turned professional in 2008 and has played for teams in the Netherlands. He plays club hockey, having c ...
– midfielder and striker for Australia's national hockey team, the Kookaburras
* Tim Paine
Timothy David Paine (born 8 December 1984) is an Australian cricketer and a former captain of the Australia national cricket team in Test cricket. A right-handed batsman and a wicket-keeper, he plays for the Tasmanian Tigers in Australian dome ...
– Australian cricketer and wicketkeeper
* Alex Peroni
Alexander Peroni (born 27 November 1999) is an Australian racing driver, currently competing in the 2022 European Le Mans Series for Algarve Pro Racing. He has competed in the 2021 Indy Lights Series for Carlin Motorsport, and in the 2020 FIA ...
– Australian racing driver
* Steve Randell
Stephen Grant Randell (born 19 February 1956) is a former Australian Test cricket match umpire, the first to come from Tasmania. He was convicted in 1999 of 15 counts of sexual assault against nine schoolgirls of ages 10–12 while teaching a ...
– Australian Test cricket match umpire; convicted of 15 counts of sexual assault against nine schoolgirls
* Jack Riewoldt – Premiership winning Australian rules footballer for Richmond
Richmond most often refers to:
* Richmond, Virginia, the capital of Virginia, United States
* Richmond, London, a part of London
* Richmond, North Yorkshire, a town in England
* Richmond, British Columbia, a city in Canada
* Richmond, California, ...
, winner of the 2010 and 2012 Coleman and Jack Dyer Medal
The Jack Dyer Medal is an Australian rules football award given each season to the player or players adjudged best and fairest for the Richmond Football Club.
The award is now named in honour of Jack Dyer, a champion ruckman who won the award ...
, cousin of Nick
Nick may refer to:
* Nick (given name)
* A cricket term for a slight deviation of the ball off the edge of the bat
* British slang for being arrested
* British slang for a police station
* British slang for stealing
* Short for nickname
Place ...
.
* Nick Riewoldt
Nicholas Fredrick Riewoldt ( ; born 17 October 1982) is a former Australian rules footballer who played for the St Kilda Football Club in the Australian Football League (AFL). He was the first draft selection in the 2000 AFL draft. He was the ...
– Australian rules footballer, former captain of the St Kilda Football Club
* Ian Stewart – Australian rules footballer who played 127 games for St Kilda, including the club's first (and thus far only) Premiership in 1966; he is also a member of the Australian Football Hall of Fame with legend status and a triple Brownlow Medal
The Charles Brownlow Trophy, better known as the Brownlow Medal (and informally as "Charlie"), is awarded to the "best and fairest" player in the Australian Football League (AFL) during the home-and-away season, as determined by votes cast by t ...
winner
* Max Walker
Maxwell Henry Norman Walker (12 September 1948 – 28 September 2016) was an Australian sportsman who played both cricket and Australian rules football at high levels. After six years of balancing first-class cricket in summer, professional ...
– Australian rules footballer and Australian cricket
Cricket is a bat-and-ball game played between two teams of eleven players on a field at the centre of which is a pitch with a wicket at each end, each comprising two bails balanced on three stumps. The batting side scores runs by str ...
er, media commentator and motivational speaker
* Paul Williams – Australian Rules footballer who played 306 games for Collingwood and Sydney, also previously caretaker coach of the Western Bulldogs
The Western Bulldogs are a professional Australian rules football team that competes in the Australian Football League (AFL), the sport's premier competition.
Founded in 1877 as the Footscray Football Club, and based in West Footscray in the o ...
* Cameron Wurf – Australian road cyclist and member of the Cannondale Pro Cycling Team
The Cannondale Bicycle Corporation is an American division of Dutch conglomerate Pon Holdings that supplies bicycles. Its headquarters are in Wilton, Connecticut with engineering offices in Freiburg, Germany. Frames are manufactured in Taiwan ...
Others
*Elizabeth Blackburn
Elizabeth Helen Blackburn, (born 26 November 1948) is an Australian-American Nobel laureate who is the former president of the Salk Institute for Biological Studies. Previously she was a biological researcher at the University of California, ...
, Nobel Prize
The Nobel Prizes ( ; sv, Nobelpriset ; no, Nobelprisen ) are five separate prizes that, according to Alfred Nobel's will of 1895, are awarded to "those who, during the preceding year, have conferred the greatest benefit to humankind." Alfr ...
-winning biological researcher
* Bob Brown
Robert James Brown (born 27 December 1944) is a former Australian politician, medical doctor and environmentalist. He was a senator and the parliamentary leader of the Australian Greens. Brown was elected to the Australian Senate on the Tasma ...
, retired politician, former leader of the Australian Greens
* William Buckley, escaped convict who lived with the native Wathaurung
The Wathaurong nation, also called the Wathaurung, Wadawurrung and Wadda Wurrung, are an Aboriginal Australian people living in the area near Melbourne, Geelong and the Bellarine Peninsula in the state of Victoria. They are part of the Kulin al ...
people on the Bellarine Peninsula
The Bellarine Peninsula ( Wathawurrung: ''Balla-wein'' or ''Biteyong'') is a peninsula located south-west of Melbourne in Victoria, Australia, surrounded by Port Phillip, Corio Bay and Bass Strait. The peninsula, together with the Mornington ...
for over 30 years
* Alec Campbell
Alexander William Campbell (26 February 1899 – 16 May 2002) was the final surviving Australian participant of the Gallipoli campaign during the First World War.Shaw, John"Alec Campbell, Last Anzac at Gallipoli, Dies at 103" ''The New York Ti ...
, longest surviving war veteran from the Gallipoli Campaign
* Peter Conrad, academic and author, teaching at Christ Church, Oxford
* Mary Donaldson
Mary, Crown Princess of Denmark, Countess of Monpezat, (born Mary Elizabeth Donaldson; 5 February 1972) is the wife of Frederik, Crown Prince of Denmark. Frederik is the heir apparent to the throne, which means that should he succeed, Mary ...
, Crown Princess of Denmark
* Helene Chung Martin
Helene Dorothy Chung (born 20 January 1945), journalist and author (also known as Helene Chung Martin), is a former Beijing correspondent, the first female posted abroad by the Australian Broadcasting Corporation (ABC). She was formerly an adjun ...
, journalist and author, notable for being the first reporter of Asian descent to report on the ABC
ABC are the first three letters of the Latin script known as the alphabet.
ABC or abc may also refer to:
Arts, entertainment, and media Broadcasting
* American Broadcasting Company, a commercial U.S. TV broadcaster
** Disney–ABC Television ...
* Bernard Montgomery, general who grew up in Hobart; served in both world wars and is famous for his victory at the battle of El Alamein
* Alexander Pearce, convict and cannibal
* Joseph Potaski, convict and first Pole
Pole may refer to:
Astronomy
*Celestial pole, the projection of the planet Earth's axis of rotation onto the celestial sphere; also applies to the axis of rotation of other planets
*Pole star, a visible star that is approximately aligned with the ...
to come to Australia
* Harry Smith, Officer Commanding D Company, 6 RAR
6th Battalion, Royal Australian Regiment (6 RAR) is a mechanised infantry battalion of the Australian Army. It was originally raised in Brisbane, Queensland, on 6 June 1965 and has since then served in a number of overseas deployments and conf ...
during the Battle of Long Tan
The Battle of Long Tan (18 August 1966) took place in a rubber plantation near Long Tân, in Phước Tuy Province, South Vietnam, during the Vietnam War. The action was fought between Viet Cong (VC) and People's Army of Vietnam (PAVN) units ...
in the Vietnam War
The Vietnam War (also known by other names) was a conflict in Vietnam, Laos, and Cambodia from 1 November 1955 to the fall of Saigon on 30 April 1975. It was the second of the Indochina Wars and was officially fought between North Vietnam a ...
* Ernest Ewart Unwin, educationist
* David Walsh, art collector and founder of the Museum of Old and New Art
The Museum of Old and New Art (MONA) is an art museum located within the Moorilla winery on the Berriedale peninsula in Hobart, Tasmania, Australia. It is the largest privately funded museum in the Southern Hemisphere. MONA houses ancient, mode ...
* Charles Wooley
Charles Wooley (born 1948) is a Scottish-Australian journalist, reporter, writer, TV personality and radio presenter who reported for Channel Nine's ''60 Minutes''.
Early life and career
Wooley was born on the Isle of Arran in Scotland, and mo ...
, journalist, most famous for his role on Channel Nine's '' 60 Minutes''
Sister cities
*Yaizu
is a city located in central Shizuoka Prefecture, Japan. , the city had an estimated population of 139,578 in 57,593 households, and a population density of 2000 persons per km2. The total area of the city was . Yaizu is a noted port for commer ...
, Shizuoka Prefecture, Japan (1977)
* L'Aquila, Abruzzo, Italy (1980)
* Valdivia
Valdivia (; Mapuche: Ainil) is a city and commune in southern Chile, administered by the Municipality of Valdivia. The city is named after its founder Pedro de Valdivia and is located at the confluence of the Calle-Calle, Valdivia, and Cau-Cau R ...
, Los Ríos, Chile (1998)
* Xi'an
Xi'an ( , ; ; Chinese: ), frequently spelled as Xian and also known by other names, is the capital of Shaanxi Province. A sub-provincial city on the Guanzhong Plain, the city is the third most populous city in Western China, after Chongqi ...
, Shaanxi
Shaanxi (alternatively Shensi, see § Name) is a landlocked province of China. Officially part of Northwest China, it borders the province-level divisions of Shanxi (NE, E), Henan (E), Hubei (SE), Chongqing (S), Sichuan (SW), Gansu (W), N ...
, China (2015)
* Fuzhou, Fujian
Fujian (; alternately romanized as Fukien or Hokkien) is a province on the southeastern coast of China. Fujian is bordered by Zhejiang to the north, Jiangxi to the west, Guangdong to the south, and the Taiwan Strait to the east. Its cap ...
, China (2017)
* Barile
Barile ( aae, Barilli; Lucano: ) is a town and ''comune'' in the province of Potenza, in the Southern Italian region of Basilicata. It is bounded by the ''comuni'' (municipalities), of Ginestra, Rapolla, Rionero in Vulture, Ripacandida, and ...
, Basilicata, Italy (2009)
See also
* Hobart City CentreNotes
References
Further reading
* *External links
* * * * * {{Authority control 1803 establishments in Australia Australian capital cities Cities in Tasmania Coastal cities in Australia Populated places established in 1803 Southern Tasmania