Aluminum on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Aluminium (aluminum in
 A free aluminium atom has a
A free aluminium atom has a
 In aqueous solution, Al3+ exists as the hexaaqua cation l(H2O)6sup>3+, which has an approximate Ka of 10−5. Such solutions are acidic as this cation can act as a proton donor and progressively
In aqueous solution, Al3+ exists as the hexaaqua cation l(H2O)6sup>3+, which has an approximate Ka of 10−5. Such solutions are acidic as this cation can act as a proton donor and progressively
 A variety of compounds of empirical formula AlR3 and AlR1.5Cl1.5 exist. The aluminium trialkyls and triaryls are reactive, volatile, and colorless liquids or low-melting solids. They catch fire spontaneously in air and react with water, thus necessitating precautions when handling them. They often form dimers, unlike their boron analogues, but this tendency diminishes for branched-chain alkyls (e.g. Pr''i'', Bu''i'', Me3CCH2); for example, triisobutylaluminium exists as an equilibrium mixture of the monomer and dimer. These dimers, such as trimethylaluminium (Al2Me6), usually feature tetrahedral Al centers formed by dimerization with some alkyl group bridging between both aluminium atoms. They are hard acids and react readily with ligands, forming adducts. In industry, they are mostly used in alkene insertion reactions, as discovered by
A variety of compounds of empirical formula AlR3 and AlR1.5Cl1.5 exist. The aluminium trialkyls and triaryls are reactive, volatile, and colorless liquids or low-melting solids. They catch fire spontaneously in air and react with water, thus necessitating precautions when handling them. They often form dimers, unlike their boron analogues, but this tendency diminishes for branched-chain alkyls (e.g. Pr''i'', Bu''i'', Me3CCH2); for example, triisobutylaluminium exists as an equilibrium mixture of the monomer and dimer. These dimers, such as trimethylaluminium (Al2Me6), usually feature tetrahedral Al centers formed by dimerization with some alkyl group bridging between both aluminium atoms. They are hard acids and react readily with ligands, forming adducts. In industry, they are mostly used in alkene insertion reactions, as discovered by
 Overall, the Earth is about 1.59% aluminium by mass (seventh in abundance by mass).William F McDonoug
Overall, the Earth is about 1.59% aluminium by mass (seventh in abundance by mass).William F McDonoug
The composition of the Earth
quake.mit.edu, archived by the Internet Archive Wayback Machine. Aluminium occurs in greater proportion in the Earth's crust than in the Universe at large, because aluminium easily forms the oxide and becomes bound into rocks and stays in the Earth's crust, while less reactive metals sink to the core. In the Earth's crust, aluminium is the most abundant metallic element (8.23% by mass) and the third most abundant of all elements (after oxygen and silicon). A large number of silicates in the Earth's crust contain aluminium. In contrast, the Earth's
 The history of aluminium has been shaped by usage of alum. The first written record of alum, made by Greek historian
The history of aluminium has been shaped by usage of alum. The first written record of alum, made by Greek historian  As Wöhler's method could not yield great quantities of aluminium, the metal remained rare; its cost exceeded that of gold. The first industrial production of aluminium was established in 1856 by French chemist
As Wöhler's method could not yield great quantities of aluminium, the metal remained rare; its cost exceeded that of gold. The first industrial production of aluminium was established in 1856 by French chemist  Throughout the 20th century, the production of aluminium rose rapidly: while the world production of aluminium in 1900 was 6,800 metric tons, the annual production first exceeded 100,000 metric tons in 1916; 1,000,000 tons in 1941; 10,000,000 tons in 1971. In the 1970s, the increased demand for aluminium made it an exchange commodity; it entered the London Metal Exchange, the oldest industrial metal exchange in the world, in 1978. The output continued to grow: the annual production of aluminium exceeded 50,000,000 metric tons in 2013.
The
Throughout the 20th century, the production of aluminium rose rapidly: while the world production of aluminium in 1900 was 6,800 metric tons, the annual production first exceeded 100,000 metric tons in 1916; 1,000,000 tons in 1941; 10,000,000 tons in 1971. In the 1970s, the increased demand for aluminium made it an exchange commodity; it entered the London Metal Exchange, the oldest industrial metal exchange in the world, in 1978. The output continued to grow: the annual production of aluminium exceeded 50,000,000 metric tons in 2013.
The
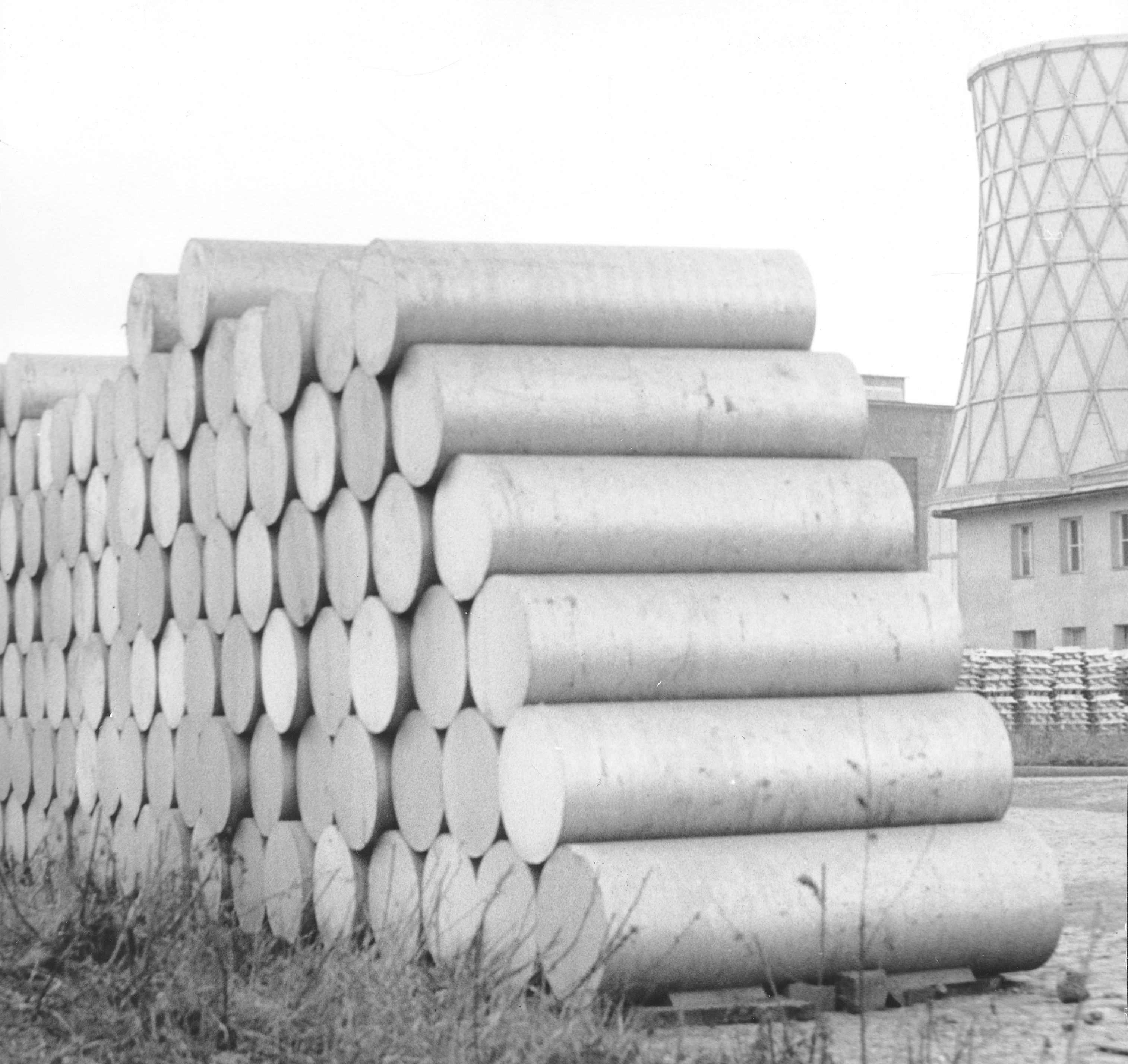
 The conversion of alumina to aluminium metal is achieved by the Hall–Héroult process. In this energy-intensive process, a solution of alumina in a molten () mixture of cryolite (Na3AlF6) with calcium fluoride is electrolyzed to produce metallic aluminium. The liquid aluminium metal sinks to the bottom of the solution and is tapped off, and usually cast into large blocks called aluminium billets for further processing.
Anodes of the electrolysis cell are made of carbon—the most resistant material against fluoride corrosion—and either bake at the process or are prebaked. The former, also called Söderberg anodes, are less power-efficient and fumes released during baking are costly to collect, which is why they are being replaced by prebaked anodes even though they save the power, energy, and labor to prebake the cathodes. Carbon for anodes should be preferably pure so that neither aluminium nor the electrolyte is contaminated with ash. Despite carbon's resistivity against corrosion, it is still consumed at a rate of 0.4–0.5 kg per each kilogram of produced aluminium. Cathodes are made of anthracite; high purity for them is not required because impurities
The conversion of alumina to aluminium metal is achieved by the Hall–Héroult process. In this energy-intensive process, a solution of alumina in a molten () mixture of cryolite (Na3AlF6) with calcium fluoride is electrolyzed to produce metallic aluminium. The liquid aluminium metal sinks to the bottom of the solution and is tapped off, and usually cast into large blocks called aluminium billets for further processing.
Anodes of the electrolysis cell are made of carbon—the most resistant material against fluoride corrosion—and either bake at the process or are prebaked. The former, also called Söderberg anodes, are less power-efficient and fumes released during baking are costly to collect, which is why they are being replaced by prebaked anodes even though they save the power, energy, and labor to prebake the cathodes. Carbon for anodes should be preferably pure so that neither aluminium nor the electrolyte is contaminated with ash. Despite carbon's resistivity against corrosion, it is still consumed at a rate of 0.4–0.5 kg per each kilogram of produced aluminium. Cathodes are made of anthracite; high purity for them is not required because impurities
 Recovery of the metal through
Recovery of the metal through
 The major uses for aluminium metal are in:
* Transportation (
The major uses for aluminium metal are in:
* Transportation (
 Several sulfates of aluminium have industrial and commercial application. Aluminium sulfate (in its hydrate form) is produced on the annual scale of several millions of metric tons. About two-thirds is consumed in water treatment. The next major application is in the manufacture of paper. It is also used as a mordant in dyeing, in pickling seeds, deodorizing of mineral oils, in leather tanning, and in production of other aluminium compounds. Two kinds of alum,
Several sulfates of aluminium have industrial and commercial application. Aluminium sulfate (in its hydrate form) is produced on the annual scale of several millions of metric tons. About two-thirds is consumed in water treatment. The next major application is in the manufacture of paper. It is also used as a mordant in dyeing, in pickling seeds, deodorizing of mineral oils, in leather tanning, and in production of other aluminium compounds. Two kinds of alum,
 Despite its widespread occurrence in the Earth's crust, aluminium has no known function in biology. At pH 6–9 (relevant for most natural waters), aluminium precipitates out of water as the hydroxide and is hence not available; most elements behaving this way have no biological role or are toxic. Aluminium sulfate has an LD50 of 6207 mg/kg (oral, mouse), which corresponds to 435 grams for an person.
Despite its widespread occurrence in the Earth's crust, aluminium has no known function in biology. At pH 6–9 (relevant for most natural waters), aluminium precipitates out of water as the hydroxide and is hence not available; most elements behaving this way have no biological role or are toxic. Aluminium sulfate has an LD50 of 6207 mg/kg (oral, mouse), which corresponds to 435 grams for an person.
 During the 1988 Camelford water pollution incident people in Camelford had their drinking water contaminated with aluminium sulfate for several weeks. A final report into the incident in 2013 concluded it was unlikely that this had caused long-term health problems.
Aluminium has been suspected of being a possible cause of Alzheimer's disease, but research into this for over 40 years has found, , no good evidence of causal effect.
Aluminium increases
During the 1988 Camelford water pollution incident people in Camelford had their drinking water contaminated with aluminium sulfate for several weeks. A final report into the incident in 2013 concluded it was unlikely that this had caused long-term health problems.
Aluminium has been suspected of being a possible cause of Alzheimer's disease, but research into this for over 40 years has found, , no good evidence of causal effect.
Aluminium increases
 High levels of aluminium occur near mining sites; small amounts of aluminium are released to the environment at the coal-fired power plants or
High levels of aluminium occur near mining sites; small amounts of aluminium are released to the environment at the coal-fired power plants or
Aluminium
at '' The Periodic Table of Videos'' (University of Nottingham) *
Toxic Substances Portal – Aluminum
' – from the
CDC – NIOSH Pocket Guide to Chemical Hazards – Aluminum
Price history of aluminum, according to the IMF
History of Aluminium
– from the website of the International Aluminium Institute
* {{Authority control Chemical elements Post-transition metals
American
American(s) may refer to:
* American, something of, from, or related to the United States of America, commonly known as the "United States" or "America"
** Americans, citizens and nationals of the United States of America
** American ancestry, pe ...
and Canadian English) is a chemical element
A chemical element is a species of atoms that have a given number of protons in their atomic nucleus, nuclei, including the pure Chemical substance, substance consisting only of that species. Unlike chemical compounds, chemical elements canno ...
with the symbol Al and atomic number
The atomic number or nuclear charge number (symbol ''Z'') of a chemical element is the charge number of an atomic nucleus. For ordinary nuclei, this is equal to the proton number (''n''p) or the number of protons found in the nucleus of ever ...
13. Aluminium has a density lower than those of other common metal
A metal (from ancient Greek, Greek μέταλλον ''métallon'', "mine, quarry, metal") is a material that, when freshly prepared, polished, or fractured, shows a lustrous appearance, and conducts electrical resistivity and conductivity, e ...
s, at approximately one third that of steel
Steel is an alloy made up of iron with added carbon to improve its strength and fracture resistance compared to other forms of iron. Many other elements may be present or added. Stainless steels that are corrosion- and oxidation-resistan ...
. It has a great affinity towards oxygen
Oxygen is the chemical element with the symbol O and atomic number 8. It is a member of the chalcogen group in the periodic table, a highly reactive nonmetal, and an oxidizing agent that readily forms oxides with most elements ...
, and forms a protective layer of oxide on the surface when exposed to air. Aluminium visually resembles silver, both in its color and in its great ability to reflect light. It is soft, non-magnetic and ductile. It has one stable isotope, 27Al; this isotope is very common, making aluminium the twelfth most common element in the Universe. The radioactivity of 26Al is used in radiodating.
Chemically, aluminium is a post-transition metal in the boron group; as is common for the group, aluminium forms compounds primarily in the +3 oxidation state
In chemistry, the oxidation state, or oxidation number, is the hypothetical charge of an atom if all of its bonds to different atoms were fully ionic. It describes the degree of oxidation (loss of electrons) of an atom in a chemical compound. C ...
. The aluminium cation Al3+ is small and highly charged; as such, it is polarizing, and bonds aluminium forms tend towards covalency
A covalent bond is a chemical bond that involves the sharing of electrons to form electron pairs between atoms. These electron pairs are known as shared pairs or bonding pairs. The stable balance of attractive and repulsive forces between atom ...
. The strong affinity towards oxygen leads to aluminium's common association with oxygen in nature in the form of oxides; for this reason, aluminium is found on Earth primarily in rocks in the crust, where it is the third most abundant element after oxygen
Oxygen is the chemical element with the symbol O and atomic number 8. It is a member of the chalcogen group in the periodic table, a highly reactive nonmetal, and an oxidizing agent that readily forms oxides with most elements ...
and silicon
Silicon is a chemical element with the symbol Si and atomic number 14. It is a hard, brittle crystalline solid with a blue-grey metallic luster, and is a tetravalent metalloid and semiconductor. It is a member of group 14 in the periodic ...
, rather than in the mantle
A mantle is a piece of clothing, a type of cloak. Several other meanings are derived from that.
Mantle may refer to:
*Mantle (clothing), a cloak-like garment worn mainly by women as fashionable outerwear
**Mantle (vesture), an Eastern Orthodox ve ...
, and virtually never as the free metal.
The discovery of aluminium was announced in 1825 by Danish physicist Hans Christian Ørsted. The first industrial production of aluminium was initiated by French chemist Henri Étienne Sainte-Claire Deville in 1856. Aluminium became much more available to the public with the Hall–Héroult process developed independently by French engineer Paul Héroult and American engineer Charles Martin Hall in 1886, and the mass production of aluminium led to its extensive use in industry and everyday life. In World Wars I and II, aluminium was a crucial strategic resource for aviation
Aviation includes the activities surrounding mechanical flight and the aircraft industry. ''Aircraft'' includes airplane, fixed-wing and helicopter, rotary-wing types, morphable wings, wing-less lifting bodies, as well as aerostat, lighter- ...
. In 1954, aluminium became the most produced non-ferrous metal, surpassing copper
Copper is a chemical element with the symbol Cu (from la, cuprum) and atomic number 29. It is a soft, malleable, and ductile metal with very high thermal and electrical conductivity. A freshly exposed surface of pure copper has a pink ...
. In the 21st century, most aluminium was consumed in transportation, engineering, construction, and packaging in the United States, Western Europe, and Japan.
Despite its prevalence in the environment, no living organism is known to use aluminium salts metabolically, but aluminium is well tolerated by plants and animals. Because of the abundance of these salts, the potential for a biological role for them is of interest, and studies continue.
Physical characteristics
Isotopes
Of aluminium isotopes, only is stable. This situation is common for elements with an odd atomic number. It is the onlyprimordial
Primordial may refer to:
* Primordial era, an era after the Big Bang. See Chronology of the universe
* Primordial sea (a.k.a. primordial ocean, ooze or soup). See Abiogenesis
* Primordial nuclide, nuclides, a few radioactive, that formed before t ...
aluminium isotope, i.e. the only one that has existed on Earth in its current form since the formation of the planet. Nearly all aluminium on Earth is present as this isotope, which makes it a mononuclidic element and means that its standard atomic weight
The standard atomic weight of a chemical element (symbol ''A''r°(E) for element "E") is the weighted arithmetic mean of the relative isotopic masses of all isotopes of that element weighted by each isotope's abundance on Earth. For example, ...
is virtually the same as that of the isotope. This makes aluminium very useful in nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR), as its single stable isotope has a high NMR sensitivity. The standard atomic weight of aluminium is low in comparison with many other metals.
All other isotopes of aluminium are radioactive
Radioactive decay (also known as nuclear decay, radioactivity, radioactive disintegration, or nuclear disintegration) is the process by which an unstable atomic nucleus loses energy by radiation. A material containing unstable nuclei is consi ...
. The most stable of these is 26Al: while it was present along with stable 27Al in the interstellar medium from which the Solar System formed, having been produced by stellar nucleosynthesis
Stellar nucleosynthesis is the creation (nucleosynthesis) of chemical elements by nuclear fusion reactions within stars. Stellar nucleosynthesis has occurred since the original creation of hydrogen, helium and lithium during the Big Bang. A ...
as well, its half-life
Half-life (symbol ) is the time required for a quantity (of substance) to reduce to half of its initial value. The term is commonly used in nuclear physics to describe how quickly unstable atoms undergo radioactive decay or how long stable ...
is only 717,000 years and therefore a detectable amount has not survived since the formation of the planet. However, minute traces of 26Al are produced from argon
Argon is a chemical element with the symbol Ar and atomic number 18. It is in group 18 of the periodic table and is a noble gas. Argon is the third-most abundant gas in Earth's atmosphere, at 0.934% (9340 ppmv). It is more than twice a ...
in the atmosphere by spallation caused by cosmic ray
Cosmic rays are high-energy particles or clusters of particles (primarily represented by protons or atomic nuclei) that move through space at nearly the speed of light. They originate from the Sun, from outside of the Solar System in our own ...
protons. The ratio of 26Al to 10Be has been used for radiodating of geological processes over 105 to 106 year time scales, in particular transport, deposition, sediment
Sediment is a naturally occurring material that is broken down by processes of weathering and erosion, and is subsequently transported by the action of wind, water, or ice or by the force of gravity acting on the particles. For example, sand ...
storage, burial times, and erosion. Most meteorite scientists believe that the energy released by the decay of 26Al was responsible for the melting and differentiation of some asteroids
An asteroid is a minor planet of the inner Solar System. Sizes and shapes of asteroids vary significantly, ranging from 1-meter rocks to a dwarf planet almost 1000 km in diameter; they are rocky, metallic or icy bodies with no atmosphere. ...
after their formation 4.55 billion years ago.
The remaining isotopes of aluminium, with mass numbers ranging from 22 to 43, all have half-lives well under an hour. Three metastable states are known, all with half-lives under a minute.
Electron shell
An aluminium atom has 13 electrons, arranged in an electron configuration of , with three electrons beyond a stable noble gas configuration. Accordingly, the combined first threeionization energies
Ionization, or Ionisation is the process by which an atom or a molecule acquires a negative or positive charge by gaining or losing electrons, often in conjunction with other chemical changes. The resulting electrically charged atom or molecul ...
of aluminium are far lower than the fourth ionization energy alone. Such an electron configuration is shared with the other well-characterized members of its group, boron, gallium, indium, and thallium; it is also expected for nihonium. Aluminium can relatively easily surrender its three outermost electrons in many chemical reactions (see below
Below may refer to:
*Earth
* Ground (disambiguation)
*Soil
*Floor
* Bottom (disambiguation)
*Less than
*Temperatures below freezing
*Hell or underworld
People with the surname
*Ernst von Below (1863–1955), German World War I general
*Fred Below ...
). The electronegativity of aluminium is 1.61 (Pauling scale).
 A free aluminium atom has a
A free aluminium atom has a radius
In classical geometry, a radius (plural, : radii) of a circle or sphere is any of the line segments from its Centre (geometry), center to its perimeter, and in more modern usage, it is also their length. The name comes from the latin ''radius'', ...
of 143 pm. With the three outermost electrons removed, the radius
In classical geometry, a radius (plural, : radii) of a circle or sphere is any of the line segments from its Centre (geometry), center to its perimeter, and in more modern usage, it is also their length. The name comes from the latin ''radius'', ...
shrinks to 39 pm for a 4-coordinated atom or 53.5 pm for a 6-coordinated atom. At standard temperature and pressure, aluminium atoms (when not affected by atoms of other elements) form a face-centered cubic crystal system bound by metallic bonding provided by atoms' outermost electrons; hence aluminium (at these conditions) is a metal. This crystal system is shared by many other metals, such as lead
Lead is a chemical element with the symbol Pb (from the Latin ) and atomic number 82. It is a heavy metal that is denser than most common materials. Lead is soft and malleable, and also has a relatively low melting point. When freshly cut, ...
and copper
Copper is a chemical element with the symbol Cu (from la, cuprum) and atomic number 29. It is a soft, malleable, and ductile metal with very high thermal and electrical conductivity. A freshly exposed surface of pure copper has a pink ...
; the size of a unit cell of aluminium is comparable to that of those other metals.
The system, however, is not shared by the other members of its group; boron has ionization energies too high to allow metallization, thallium has a hexagonal close-packed structure, and gallium and indium have unusual structures that are not close-packed like those of aluminium and thallium. The few electrons that are available for metallic bonding in aluminium metal are a probable cause for it being soft with a low melting point and low electrical resistivity.Greenwood and Earnshaw, pp. 222–4
Bulk
Aluminium metal has an appearance ranging from silvery white to dull gray, depending on the surface roughness. Aluminium mirrors are the most reflective of all metal mirrors for the nearultraviolet
Ultraviolet (UV) is a form of electromagnetic radiation with wavelength from 10 nm (with a corresponding frequency around 30 PHz) to 400 nm (750 THz), shorter than that of visible light, but longer than X-rays. UV radiation ...
and far infrared
Infrared (IR), sometimes called infrared light, is electromagnetic radiation (EMR) with wavelengths longer than those of Light, visible light. It is therefore invisible to the human eye. IR is generally understood to encompass wavelengths from ...
light, and one of the most reflective in the visible spectrum, nearly on par with silver, and the two therefore look similar. Aluminium is also good at reflecting solar radiation
Solar irradiance is the power per unit area ( surface power density) received from the Sun in the form of electromagnetic radiation in the wavelength range of the measuring instrument.
Solar irradiance is measured in watts per square metre ...
, although prolonged exposure to sunlight in air adds wear to the surface of the metal; this may be prevented if aluminium is anodized
Anodizing is an electrolytic passivation process used to increase the thickness of the natural oxide layer on the surface of metal parts.
The process is called ''anodizing'' because the part to be treated forms the anode electrode of an elect ...
, which adds a protective layer of oxide on the surface.
The density of aluminium is 2.70 g/cm3, about 1/3 that of steel, much lower than other commonly encountered metals, making aluminium parts easily identifiable through their lightness. Aluminium's low density compared to most other metals arises from the fact that its nuclei are much lighter, while difference in the unit cell size does not compensate for this difference. The only lighter metals are the metals of groups 1 and 2, which apart from beryllium
Beryllium is a chemical element with the symbol Be and atomic number 4. It is a steel-gray, strong, lightweight and brittle alkaline earth metal. It is a divalent element that occurs naturally only in combination with other elements to for ...
and magnesium
Magnesium is a chemical element with the symbol Mg and atomic number 12. It is a shiny gray metal having a low density, low melting point and high chemical reactivity. Like the other alkaline earth metals (group 2 of the periodic ...
are too reactive for structural use (and beryllium is very toxic). Aluminium is not as strong or stiff as steel, but the low density makes up for this in the aerospace
Aerospace is a term used to collectively refer to the atmosphere and outer space. Aerospace activity is very diverse, with a multitude of commercial, industrial and military applications. Aerospace engineering consists of aeronautics and ast ...
industry and for many other applications where light weight and relatively high strength are crucial.
Pure aluminium is quite soft and lacking in strength. In most applications various aluminium alloys are used instead because of their higher strength and hardness. The yield strength
In materials science and engineering, the yield point is the point on a stress-strain curve that indicates the limit of elastic behavior and the beginning of plastic behavior. Below the yield point, a material will deform elastically and wi ...
of pure aluminium is 7–11 MPa, while aluminium alloy
An aluminium alloy (or aluminum alloy; see spelling differences) is an alloy in which aluminium (Al) is the predominant metal. The typical alloying elements are copper, magnesium, manganese, silicon, tin, nickel and zinc. There are two pr ...
s have yield strengths ranging from 200 MPa to 600 MPa.
Aluminium is ductile, with a percent elongation of 50-70%,
and malleable allowing it to be easily drawn and extruded. It is also easily machined
Machining is a process in which a material (often metal) is cut to a desired final shape and size by a controlled material-removal process. The processes that have this common theme are collectively called subtractive manufacturing, which utilizes ...
and cast
Cast may refer to:
Music
* Cast (band), an English alternative rock band
* Cast (Mexican band), a progressive Mexican rock band
* The Cast, a Scottish musical duo: Mairi Campbell and Dave Francis
* ''Cast'', a 2012 album by Trespassers William
...
.
Aluminium is an excellent thermal and electrical conductor, having around 60% the conductivity of copper
Copper is a chemical element with the symbol Cu (from la, cuprum) and atomic number 29. It is a soft, malleable, and ductile metal with very high thermal and electrical conductivity. A freshly exposed surface of pure copper has a pink ...
, both thermal and electrical, while having only 30% of copper's density. Aluminium is capable of superconductivity
Superconductivity is a set of physical properties observed in certain materials where electrical resistance vanishes and magnetic flux fields are expelled from the material. Any material exhibiting these properties is a superconductor. Unlike ...
, with a superconducting critical temperature of 1.2 kelvin
The kelvin, symbol K, is the primary unit of temperature in the International System of Units (SI), used alongside its prefixed forms and the degree Celsius. It is named after the Belfast-born and University of Glasgow-based engineer and ...
and a critical magnetic field of about 100 gauss (10 milliteslas). It is paramagnetic and thus essentially unaffected by static magnetic fields. The high electrical conductivity, however, means that it is strongly affected by alternating magnetic fields through the induction of eddy currents.
Chemistry
Aluminium combines characteristics of pre- and post-transition metals. Since it has few available electrons for metallic bonding, like its heaviergroup 13
The Group 13 network ( pl, Trzynastka, Yiddish: ''דאָס דרײַצענטל'') was a Jewish Nazi collaborationist organization in the Warsaw Ghetto during the German occupation of Poland in World War II. The rise and fall of the Group ...
congeners, it has the characteristic physical properties of a post-transition metal, with longer-than-expected interatomic distances. Furthermore, as Al3+ is a small and highly charged cation, it is strongly polarizing and bonding in aluminium compounds tends towards covalency
A covalent bond is a chemical bond that involves the sharing of electrons to form electron pairs between atoms. These electron pairs are known as shared pairs or bonding pairs. The stable balance of attractive and repulsive forces between atom ...
; this behavior is similar to that of beryllium
Beryllium is a chemical element with the symbol Be and atomic number 4. It is a steel-gray, strong, lightweight and brittle alkaline earth metal. It is a divalent element that occurs naturally only in combination with other elements to for ...
(Be2+), and the two display an example of a diagonal relationship.
The underlying core under aluminium's valence shell is that of the preceding noble gas, whereas those of its heavier congeners gallium, indium, thallium, and nihonium also include a filled d-subshell and in some cases a filled f-subshell. Hence, the inner electrons of aluminium shield the valence electrons almost completely, unlike those of aluminium's heavier congeners. As such, aluminium is the most electropositive metal in its group, and its hydroxide is in fact more basic than that of gallium. Aluminium also bears minor similarities to the metalloid boron in the same group: AlX3 compounds are valence isoelectronic to BX3 compounds (they have the same valence electronic structure), and both behave as Lewis acids and readily form adducts. Additionally, one of the main motifs of boron chemistry is regular icosahedral structures, and aluminium forms an important part of many icosahedral quasicrystal alloys, including the Al–Zn–Mg class.
Aluminium has a high chemical affinity to oxygen, which renders it suitable for use as a reducing agent
In chemistry, a reducing agent (also known as a reductant, reducer, or electron donor) is a chemical species that "donates" an electron to an (called the , , , or ).
Examples of substances that are commonly reducing agents include the Earth met ...
in the thermite reaction. A fine powder of aluminium metal reacts explosively on contact with liquid oxygen; under normal conditions, however, aluminium forms a thin oxide layer (~5 nm at room temperature) that protects the metal from further corrosion by oxygen, water, or dilute acid, a process termed passivation.
Because of its general resistance to corrosion, aluminium is one of the few metals that retains silvery reflectance in finely powdered form, making it an important component of silver-colored paints. Aluminium is not attacked by oxidizing acids because of its passivation. This allows aluminium to be used to store reagents such as nitric acid
Nitric acid is the inorganic compound with the formula . It is a highly corrosive mineral acid. The compound is colorless, but older samples tend to be yellow cast due to decomposition into oxides of nitrogen. Most commercially available ni ...
, concentrated sulfuric acid
Sulfuric acid (American spelling and the preferred IUPAC name) or sulphuric acid ( Commonwealth spelling), known in antiquity as oil of vitriol, is a mineral acid composed of the elements sulfur, oxygen and hydrogen, with the molecular fo ...
, and some organic acids.
In hot concentrated hydrochloric acid
Hydrochloric acid, also known as muriatic acid, is an aqueous solution of hydrogen chloride. It is a colorless solution with a distinctive pungent smell. It is classified as a strong acid. It is a component of the gastric acid in the dige ...
, aluminium reacts with water with evolution of hydrogen, and in aqueous sodium hydroxide or potassium hydroxide
Potassium hydroxide is an inorganic compound with the formula K OH, and is commonly called caustic potash.
Along with sodium hydroxide (NaOH), KOH is a prototypical strong base. It has many industrial and niche applications, most of which exp ...
at room temperature to form aluminates—protective passivation under these conditions is negligible. Aqua regia also dissolves aluminium. Aluminium is corroded by dissolved chlorides, such as common sodium chloride, which is why household plumbing is never made from aluminium. The oxide layer on aluminium is also destroyed by contact with mercury due to amalgamation or with salts of some electropositive metals. As such, the strongest aluminium alloys are less corrosion-resistant due to galvanic reactions with alloyed copper
Copper is a chemical element with the symbol Cu (from la, cuprum) and atomic number 29. It is a soft, malleable, and ductile metal with very high thermal and electrical conductivity. A freshly exposed surface of pure copper has a pink ...
, and aluminium's corrosion resistance is greatly reduced by aqueous salts, particularly in the presence of dissimilar metals.
Aluminium reacts with most nonmetals upon heating, forming compounds such as aluminium nitride
Aluminium nitride ( Al N) is a solid nitride of aluminium. It has a high thermal conductivity of up to 321 W/(m·K) and is an electrical insulator. Its wurtzite phase (w-AlN) has a band gap of ~6 eV at room temperature and has a potenti ...
(AlN), aluminium sulfide
Aluminum sulfide or aluminium sulphide is a chemical compound with the formula Al2 S3. This colorless species has an interesting structural chemistry, existing in several forms. The material is sensitive to moisture, hydrolyzing to hydrated alumi ...
(Al2S3), and the aluminium halides (AlX3). It also forms a wide range of intermetallic compounds involving metals from every group on the periodic table.
Inorganic compounds
The vast majority of compounds, including all aluminium-containing minerals and all commercially significant aluminium compounds, feature aluminium in the oxidation state 3+. The coordination number of such compounds varies, but generally Al3+ is either six- or four-coordinate. Almost all compounds of aluminium(III) are colorless. In aqueous solution, Al3+ exists as the hexaaqua cation l(H2O)6sup>3+, which has an approximate Ka of 10−5. Such solutions are acidic as this cation can act as a proton donor and progressively
In aqueous solution, Al3+ exists as the hexaaqua cation l(H2O)6sup>3+, which has an approximate Ka of 10−5. Such solutions are acidic as this cation can act as a proton donor and progressively hydrolyze
Hydrolysis (; ) is any chemical reaction in which a molecule of water breaks one or more chemical bonds. The term is used broadly for substitution, elimination, and solvation reactions in which water is the nucleophile.
Biological hydrolysis i ...
until a precipitate of aluminium hydroxide
Aluminium hydroxide, Al(OH)3, is found in nature as the mineral gibbsite (also known as hydrargillite) and its three much rarer polymorphs: bayerite, doyleite, and nordstrandite. Aluminium hydroxide is amphoteric, i.e., it has both basic ...
, Al(OH)3, forms. This is useful for clarification of water, as the precipitate nucleates on suspended particles in the water, hence removing them. Increasing the pH even further leads to the hydroxide dissolving again as aluminate
In chemistry, an aluminate is a compound containing an oxyanion of aluminium, such as sodium aluminate. In the naming of inorganic compounds, it is a suffix that indicates a polyatomic anion with a central aluminum atom.
Aluminate oxyanions
Alu ...
, l(H2O)2(OH)4sup>−, is formed.
Aluminium hydroxide forms both salts and aluminates and dissolves in acid and alkali, as well as on fusion with acidic and basic oxides. This behavior of Al(OH)3 is termed amphoterism and is characteristic of weakly basic cations that form insoluble hydroxides and whose hydrated species can also donate their protons. One effect of this is that aluminium salts with weak acids are hydrolyzed in water to the aquated hydroxide and the corresponding nonmetal hydride: for example, aluminium sulfide
Aluminum sulfide or aluminium sulphide is a chemical compound with the formula Al2 S3. This colorless species has an interesting structural chemistry, existing in several forms. The material is sensitive to moisture, hydrolyzing to hydrated alumi ...
yields hydrogen sulfide. However, some salts like aluminium carbonate exist in aqueous solution but are unstable as such; and only incomplete hydrolysis takes place for salts with strong acids, such as the halides, nitrate, and sulfate. For similar reasons, anhydrous aluminium salts cannot be made by heating their "hydrates": hydrated aluminium chloride is in fact not AlCl3·6H2O but l(H2O)6l3, and the Al–O bonds are so strong that heating is not sufficient to break them and form Al–Cl bonds instead:
:2 l(H2O)6l3 Al2O3 + 6 HCl + 9 H2O
All four trihalides are well known. Unlike the structures of the three heavier trihalides, aluminium fluoride (AlF3) features six-coordinate aluminium, which explains its involatility and insolubility as well as high heat of formation
In chemistry and thermodynamics, the standard enthalpy of formation or standard heat of formation of a compound is the change of enthalpy during the formation of 1 mole of the substance from its constituent elements in their reference state, w ...
. Each aluminium atom is surrounded by six fluorine atoms in a distorted octahedral arrangement, with each fluorine atom being shared between the corners of two octahedra. Such units also exist in complex fluorides such as cryolite, Na3AlF6. AlF3 melts at and is made by reaction of aluminium oxide with hydrogen fluoride gas at .
With heavier halides, the coordination numbers are lower. The other trihalides are dimeric or polymer
A polymer (; Greek '' poly-'', "many" + '' -mer'', "part")
is a substance or material consisting of very large molecules called macromolecules, composed of many repeating subunits. Due to their broad spectrum of properties, both synthetic a ...
ic with tetrahedral four-coordinate aluminium centers. Aluminium trichloride
Aluminium chloride, also known as aluminium trichloride, is an inorganic compound with the formula . It forms hexahydrate with the formula , containing six water molecules of hydration. Both are colourless crystals, but samples are often contam ...
(AlCl3) has a layered polymeric structure below its melting point of but transforms on melting to Al2Cl6 dimers. At higher temperatures those increasingly dissociate into trigonal planar AlCl3 monomers similar to the structure of BCl3. Aluminium tribromide and aluminium triiodide form Al2X6 dimers in all three phases and hence do not show such significant changes of properties upon phase change. These materials are prepared by treating aluminium metal with the halogen. The aluminium trihalides form many addition compounds or complexes; their Lewis acidic nature makes them useful as catalysts for the Friedel–Crafts reaction
The Friedel–Crafts reactions are a set of reactions developed by Charles Friedel and James Crafts in 1877 to attach substituents to an aromatic ring. Friedel–Crafts reactions are of two main types: alkylation reactions and acylation react ...
s. Aluminium trichloride has major industrial uses involving this reaction, such as in the manufacture of anthraquinones and styrene; it is also often used as the precursor for many other aluminium compounds and as a reagent for converting nonmetal fluorides into the corresponding chlorides (a transhalogenation reaction).
Aluminium forms one stable oxide with the chemical formula
In chemistry, a chemical formula is a way of presenting information about the chemical proportions of atoms that constitute a particular chemical compound or molecule, using chemical element symbols, numbers, and sometimes also other symbols, ...
Al2O3, commonly called alumina. It can be found in nature in the mineral corundum, α-alumina; there is also a γ-alumina phase. Its crystalline form, corundum, is very hard (Mohs hardness
The Mohs scale of mineral hardness () is a qualitative ordinal scale, from 1 to 10, characterizing scratch resistance of various minerals through the ability of harder material to scratch softer material.
The scale was introduced in 1812 by ...
9), has a high melting point of , has very low volatility, is chemically inert, and a good electrical insulator, it is often used in abrasives (such as toothpaste), as a refractory material, and in ceramics, as well as being the starting material for the electrolytic production of aluminium metal. Sapphire and ruby
A ruby is a pinkish red to blood-red colored gemstone, a variety of the mineral corundum ( aluminium oxide). Ruby is one of the most popular traditional jewelry gems and is very durable. Other varieties of gem-quality corundum are called ...
are impure corundum contaminated with trace amounts of other metals. The two main oxide-hydroxides, AlO(OH), are boehmite
Boehmite or böhmite is an aluminium oxide hydroxide (γ-AlO(OH)) mineral, a component of the aluminium ore bauxite. It is dimorphous with diaspore. It crystallizes in the orthorhombic dipyramidal system and is typically massive in habit. It is ...
and diaspore
Diaspore , also known as diasporite, empholite, kayserite, or tanatarite, is an aluminium oxide hydroxide mineral, α-AlO(OH), crystallizing in the orthorhombic system and isomorphous with goethite. It occurs sometimes as flattened crystals, but ...
. There are three main trihydroxides: bayerite, gibbsite, and nordstrandite, which differ in their crystalline structure ( polymorphs). Many other intermediate and related structures are also known. Most are produced from ores by a variety of wet processes using acid and base. Heating the hydroxides leads to formation of corundum. These materials are of central importance to the production of aluminium and are themselves extremely useful. Some mixed oxide phases are also very useful, such as spinel (MgAl2O4), Na-β-alumina (NaAl11O17), and tricalcium aluminate (Ca3Al2O6, an important mineral phase in Portland cement
Portland cement is the most common type of cement in general use around the world as a basic ingredient of concrete, mortar, stucco, and non-specialty grout. It was developed from other types of hydraulic lime in England in the early 19t ...
).
The only stable chalcogenides under normal conditions are aluminium sulfide
Aluminum sulfide or aluminium sulphide is a chemical compound with the formula Al2 S3. This colorless species has an interesting structural chemistry, existing in several forms. The material is sensitive to moisture, hydrolyzing to hydrated alumi ...
(Al2S3), selenide (Al2Se3), and telluride (Al2Te3). All three are prepared by direct reaction of their elements at about and quickly hydrolyze completely in water to yield aluminium hydroxide and the respective hydrogen chalcogenide. As aluminium is a small atom relative to these chalcogens, these have four-coordinate tetrahedral aluminium with various polymorphs having structures related to wurtzite, with two-thirds of the possible metal sites occupied either in an orderly (α) or random (β) fashion; the sulfide also has a γ form related to γ-alumina, and an unusual high-temperature hexagonal form where half the aluminium atoms have tetrahedral four-coordination and the other half have trigonal bipyramidal five-coordination.
Four pnictide
A pnictogen ( or ; from grc, πνῑ́γω "to choke" and -gen, "generator") is any of the chemical elements in group 15 of the periodic table. Group 15 is also known as the nitrogen group or nitrogen family. Group 15 consists of the ele ...
s – aluminium nitride
Aluminium nitride ( Al N) is a solid nitride of aluminium. It has a high thermal conductivity of up to 321 W/(m·K) and is an electrical insulator. Its wurtzite phase (w-AlN) has a band gap of ~6 eV at room temperature and has a potenti ...
(AlN), aluminium phosphide (AlP), aluminium arsenide
Aluminium arsenide () is a semiconductor material with almost the same lattice constant as gallium arsenide and aluminium gallium arsenide and wider band gap than gallium arsenide. (AlAs) can form a superlattice with gallium arsenide ( GaAs) which ...
(AlAs), and aluminium antimonide (AlSb) – are known. They are all III-V semiconductors isoelectronic to silicon
Silicon is a chemical element with the symbol Si and atomic number 14. It is a hard, brittle crystalline solid with a blue-grey metallic luster, and is a tetravalent metalloid and semiconductor. It is a member of group 14 in the periodic ...
and germanium, all of which but AlN have the zinc blende structure. All four can be made by high-temperature (and possibly high-pressure) direct reaction of their component elements.
Aluminium alloys well with most other metals (with the exception of most alkali metals and group 13 metals) and over 150 intermetallics
An intermetallic (also called an intermetallic compound, intermetallic alloy, ordered intermetallic alloy, and a long-range-ordered alloy) is a type of metallic alloy that forms an ordered solid-state compound between two or more metallic eleme ...
with other metals are known. Preparation involves heating fixed metals together in certain proportion, followed by gradual cooling and annealing. Bonding in them is predominantly metallic
Metallic may be a reference to:
*Metal
*Metalloid, metal-like substance
*Metallic bonding, type of chemical bonding
*Metallicity, in astronomy the proportion of elements other than helium and hydrogen in an object
*Metallic color, a color that g ...
and the crystal structure primarily depends on efficiency of packing.
There are few compounds with lower oxidation states. A few aluminium(I) compounds exist: AlF, AlCl, AlBr, and AlI exist in the gaseous phase when the respective trihalide is heated with aluminium, and at cryogenic temperatures. A stable derivative of aluminium monoiodide is the cyclic adduct formed with triethylamine, Al4I4(NEt3)4. Al2O and Al2S also exist but are very unstable. Very simple aluminium(II) compounds are invoked or observed in the reactions of Al metal with oxidants. For example, aluminium monoxide
Aluminium(II) oxide or aluminium monoxide is a compound of aluminium and oxygen with the chemical formula AlO. It has been detected in the gas phase after explosion of aluminized grenades in the upper atmosphere and in stellar absorption spectra. ...
, AlO, has been detected in the gas phase after explosion and in stellar absorption spectra. More thoroughly investigated are compounds of the formula R4Al2 which contain an Al–Al bond and where R is a large organic ligand
In coordination chemistry, a ligand is an ion or molecule (functional group) that binds to a central metal atom to form a coordination complex. The bonding with the metal generally involves formal donation of one or more of the ligand's elect ...
.
Organoaluminium compounds and related hydrides
 A variety of compounds of empirical formula AlR3 and AlR1.5Cl1.5 exist. The aluminium trialkyls and triaryls are reactive, volatile, and colorless liquids or low-melting solids. They catch fire spontaneously in air and react with water, thus necessitating precautions when handling them. They often form dimers, unlike their boron analogues, but this tendency diminishes for branched-chain alkyls (e.g. Pr''i'', Bu''i'', Me3CCH2); for example, triisobutylaluminium exists as an equilibrium mixture of the monomer and dimer. These dimers, such as trimethylaluminium (Al2Me6), usually feature tetrahedral Al centers formed by dimerization with some alkyl group bridging between both aluminium atoms. They are hard acids and react readily with ligands, forming adducts. In industry, they are mostly used in alkene insertion reactions, as discovered by
A variety of compounds of empirical formula AlR3 and AlR1.5Cl1.5 exist. The aluminium trialkyls and triaryls are reactive, volatile, and colorless liquids or low-melting solids. They catch fire spontaneously in air and react with water, thus necessitating precautions when handling them. They often form dimers, unlike their boron analogues, but this tendency diminishes for branched-chain alkyls (e.g. Pr''i'', Bu''i'', Me3CCH2); for example, triisobutylaluminium exists as an equilibrium mixture of the monomer and dimer. These dimers, such as trimethylaluminium (Al2Me6), usually feature tetrahedral Al centers formed by dimerization with some alkyl group bridging between both aluminium atoms. They are hard acids and react readily with ligands, forming adducts. In industry, they are mostly used in alkene insertion reactions, as discovered by Karl Ziegler
Karl Waldemar Ziegler (26 November 1898 – 12 August 1973) was a German chemist who won the Nobel Prize in Chemistry in 1963, with Giulio Natta, for work on polymers. The Nobel Committee recognized his "excellent work on organometallic compound ...
, most importantly in "growth reactions" that form long-chain unbranched primary alkenes and alcohols, and in the low-pressure polymerization of ethene and propene
Propylene, also known as propene, is an unsaturated organic compound with the chemical formula CH3CH=CH2. It has one double bond, and is the second simplest member of the alkene class of hydrocarbons. It is a colorless gas with a faint petrol ...
. There are also some heterocyclic and cluster organoaluminium compounds involving Al–N bonds.
The industrially most important aluminium hydride is lithium aluminium hydride (LiAlH4), which is used in as a reducing agent in organic chemistry
Organic chemistry is a subdiscipline within chemistry involving the scientific study of the structure, properties, and reactions of organic compounds and organic materials, i.e., matter in its various forms that contain carbon atoms.Clayden, J ...
. It can be produced from lithium hydride and aluminium trichloride
Aluminium chloride, also known as aluminium trichloride, is an inorganic compound with the formula . It forms hexahydrate with the formula , containing six water molecules of hydration. Both are colourless crystals, but samples are often contam ...
. The simplest hydride, aluminium hydride
Aluminium hydride (also known as alane and alumane) is an inorganic compound with the formula Al H3. Alane and its derivatives are common reducing (hydride addition) reagents in organic synthesis that are used in solution at both laboratory an ...
or alane, is not as important. It is a polymer with the formula (AlH3)''n'', in contrast to the corresponding boron hydride that is a dimer with the formula (BH3)2.
Natural occurrence
Space
Aluminium's per-particle abundance in the Solar System is 3.15 ppm (parts per million). It is the twelfth most abundant of all elements and third most abundant among the elements that have odd atomic numbers, after hydrogen and nitrogen. The only stable isotope of aluminium, 27Al, is the eighteenth most abundant nucleus in the Universe. It is created almost entirely after fusion of carbon in massive stars that will later becomeType II supernova
A Type II supernova (plural: ''supernovae'' or ''supernovas'') results from the rapid collapse and violent explosion of a massive star. A star must have at least 8 times, but no more than 40 to 50 times, the mass of the Sun () to undergo this ...
s: this fusion creates 26Mg, which, upon capturing free protons and neutrons becomes aluminium. Some smaller quantities of 27Al are created in hydrogen burning
Stellar nucleosynthesis is the creation (nucleosynthesis) of chemical elements by nuclear fusion reactions within stars. Stellar nucleosynthesis has occurred since the original creation of hydrogen, helium and lithium during the Big Bang. As a ...
shells of evolved stars, where 26Mg can capture free protons. Essentially all aluminium now in existence is 27Al. 26Al was present in the early Solar System with abundance of 0.005% relative to 27Al but its half-life of 728,000 years is too short for any original nuclei to survive; 26Al is therefore extinct. Unlike for 27Al, hydrogen burning is the primary source of 26Al, with the nuclide emerging after a nucleus of 25Mg catches a free proton. However, the trace quantities of 26Al that do exist are the most common gamma ray
A gamma ray, also known as gamma radiation (symbol γ or \gamma), is a penetrating form of electromagnetic radiation arising from the radioactive decay of atomic nuclei. It consists of the shortest wavelength electromagnetic waves, typically ...
emitter in the interstellar gas; if the original 26Al were still present, gamma ray maps of the Milky Way would be brighter.
Earth
The composition of the Earth
quake.mit.edu, archived by the Internet Archive Wayback Machine. Aluminium occurs in greater proportion in the Earth's crust than in the Universe at large, because aluminium easily forms the oxide and becomes bound into rocks and stays in the Earth's crust, while less reactive metals sink to the core. In the Earth's crust, aluminium is the most abundant metallic element (8.23% by mass) and the third most abundant of all elements (after oxygen and silicon). A large number of silicates in the Earth's crust contain aluminium. In contrast, the Earth's
mantle
A mantle is a piece of clothing, a type of cloak. Several other meanings are derived from that.
Mantle may refer to:
*Mantle (clothing), a cloak-like garment worn mainly by women as fashionable outerwear
**Mantle (vesture), an Eastern Orthodox ve ...
is only 2.38% aluminium by mass. Aluminium also occurs in seawater at a concentration of 2 μg/kg.
Because of its strong affinity for oxygen, aluminium is almost never found in the elemental state; instead it is found in oxides or silicates. Feldspar
Feldspars are a group of rock-forming aluminium tectosilicate minerals, also containing other cations such as sodium, calcium, potassium, or barium. The most common members of the feldspar group are the ''plagioclase'' (sodium-calcium) felds ...
s, the most common group of minerals in the Earth's crust, are aluminosilicates. Aluminium also occurs in the minerals beryl, cryolite, garnet
Garnets () are a group of silicate minerals that have been used since the Bronze Age as gemstones and abrasives.
All species of garnets possess similar physical properties and crystal forms, but differ in chemical composition. The different ...
, spinel, and turquoise. Impurities in Al2O3, such as chromium and iron
Iron () is a chemical element with symbol Fe (from la, ferrum) and atomic number 26. It is a metal that belongs to the first transition series and group 8 of the periodic table. It is, by mass, the most common element on Earth, right in ...
, yield the gemstones ruby
A ruby is a pinkish red to blood-red colored gemstone, a variety of the mineral corundum ( aluminium oxide). Ruby is one of the most popular traditional jewelry gems and is very durable. Other varieties of gem-quality corundum are called ...
and sapphire, respectively. Native aluminium metal is extremely rare and can only be found as a minor phase in low oxygen fugacity
In chemical thermodynamics, the fugacity of a real gas is an effective partial pressure which replaces the mechanical partial pressure in an accurate computation of the chemical equilibrium constant. It is equal to the pressure of an ideal gas whic ...
environments, such as the interiors of certain volcanoes. Native aluminium has been reported in cold seep
A cold seep (sometimes called a cold vent) is an area of the ocean floor where hydrogen sulfide, methane and other hydrocarbon-rich fluid seepage occurs, often in the form of a brine pool. ''Cold'' does not mean that the temperature of the see ...
s in the northeastern continental slope of the South China Sea
The South China Sea is a marginal sea of the Western Pacific Ocean. It is bounded in the north by the shores of South China (hence the name), in the west by the Indochinese Peninsula, in the east by the islands of Taiwan and northwestern Ph ...
. It is possible that these deposits resulted from bacteria
Bacteria (; singular: bacterium) are ubiquitous, mostly free-living organisms often consisting of one biological cell. They constitute a large domain of prokaryotic microorganisms. Typically a few micrometres in length, bacteria were am ...
l reduction of tetrahydroxoaluminate Al(OH)4−.
Although aluminium is a common and widespread element, not all aluminium minerals are economically viable sources of the metal. Almost all metallic aluminium is produced from the ore bauxite
Bauxite is a sedimentary rock with a relatively high aluminium content. It is the world's main source of aluminium and gallium. Bauxite consists mostly of the aluminium minerals gibbsite (Al(OH)3), boehmite (γ-AlO(OH)) and diaspore (α-AlO ...
(AlO''x''(OH)3–2''x''). Bauxite occurs as a weathering
Weathering is the deterioration of rocks, soils and minerals as well as wood and artificial materials through contact with water, atmospheric gases, and biological organisms. Weathering occurs '' in situ'' (on site, with little or no movement ...
product of low iron and silica bedrock in tropical climatic conditions. In 2017, most bauxite was mined in Australia, China, Guinea, and India.
History
 The history of aluminium has been shaped by usage of alum. The first written record of alum, made by Greek historian
The history of aluminium has been shaped by usage of alum. The first written record of alum, made by Greek historian Herodotus
Herodotus ( ; grc, , }; BC) was an ancient Greek historian and geographer from the Greek city of Halicarnassus, part of the Persian Empire (now Bodrum, Turkey) and a later citizen of Thurii in modern Calabria (Italy). He is known fo ...
, dates back to the 5th century BCE. The ancients are known to have used alum as a dyeing mordant
A mordant or dye fixative is a substance used to set (i.e. bind) dyes on fabrics by forming a coordination complex with the dye, which then attaches to the fabric (or tissue). It may be used for dyeing fabrics or for intensifying stains in ...
and for city defense. After the Crusades
The Crusades were a series of religious wars initiated, supported, and sometimes directed by the Latin Church in the medieval period. The best known of these Crusades are those to the Holy Land in the period between 1095 and 1291 that were ...
, alum, an indispensable good in the European fabric industry, was a subject of international commerce; it was imported to Europe from the eastern Mediterranean until the mid-15th century.
The nature of alum remained unknown. Around 1530, Swiss physician Paracelsus suggested alum was a salt of an earth of alum. In 1595, German doctor and chemist Andreas Libavius experimentally confirmed this. In 1722, German chemist Friedrich Hoffmann announced his belief that the base of alum was a distinct earth. In 1754, German chemist Andreas Sigismund Marggraf
Andreas Sigismund Marggraf (; 3 March 1709 – 7 August 1782) was a German chemist from Berlin, then capital of the Margraviate of Brandenburg, and a pioneer of analytical chemistry. He isolated zinc in 1746 by heating calamine and carbon. Tho ...
synthesized alumina by boiling clay in sulfuric acid and subsequently adding potash
Potash () includes various mined and manufactured salts that contain potassium in water- soluble form.
.
Attempts to produce aluminium metal date back to 1760. The first successful attempt, however, was completed in 1824 by Danish physicist and chemist Hans Christian Ørsted. He reacted anhydrous aluminium chloride with potassium amalgam
Amalgam most commonly refers to:
* Amalgam (chemistry), mercury alloy
* Amalgam (dentistry), material of silver tooth fillings
** Bonded amalgam, used in dentistry
Amalgam may also refer to:
* Amalgam Comics, a publisher
* Amalgam Digital, an in ...
, yielding a lump of metal looking similar to tin. He presented his results and demonstrated a sample of the new metal in 1825. In 1827, German chemist Friedrich Wöhler repeated Ørsted's experiments but did not identify any aluminium. (The reason for this inconsistency was only discovered in 1921.) He conducted a similar experiment in the same year by mixing anhydrous aluminium chloride with potassium and produced a powder of aluminium. In 1845, he was able to produce small pieces of the metal and described some physical properties of this metal. For many years thereafter, Wöhler was credited as the discoverer of aluminium.
 As Wöhler's method could not yield great quantities of aluminium, the metal remained rare; its cost exceeded that of gold. The first industrial production of aluminium was established in 1856 by French chemist
As Wöhler's method could not yield great quantities of aluminium, the metal remained rare; its cost exceeded that of gold. The first industrial production of aluminium was established in 1856 by French chemist Henri Etienne Sainte-Claire Deville
Henri is an Estonian, Finnish, French, German and Luxembourgish form of the masculine given name Henry.
People with this given name
; French noblemen
:'' See the ' List of rulers named Henry' for Kings of France named Henri.''
* Henri I de Mon ...
and companions. Deville had discovered that aluminium trichloride could be reduced by sodium, which was more convenient and less expensive than potassium, which Wöhler had used. Even then, aluminium was still not of great purity and produced aluminium differed in properties by sample. Because of its electricity-conducting capacity, aluminium was used as the cap of the Washington Monument
The Washington Monument is an obelisk shaped building within the National Mall in Washington, D.C., built to commemorate George Washington, once commander-in-chief of the Continental Army (1775–1784) in the American Revolutionary War and ...
, completed in 1885. The tallest building in the world at the time, the non-corroding metal cap was intended to serve as a lightning rod peak.
The first industrial large-scale production method was independently developed in 1886 by French engineer Paul Héroult and American engineer Charles Martin Hall; it is now known as the Hall–Héroult process. The Hall–Héroult process converts alumina into metal. Austrian chemist Carl Joseph Bayer discovered a way of purifying bauxite to yield alumina, now known as the Bayer process
The Bayer process is the principal industrial means of refining bauxite to produce alumina (aluminium oxide) and was developed by Carl Josef Bayer. Bauxite, the most important ore of aluminium, contains only 30–60% aluminium oxide (Al2O3), th ...
, in 1889. Modern production of the aluminium metal is based on the Bayer and Hall–Héroult processes.
Prices of aluminium dropped and aluminium became widely used in jewelry, everyday items, eyeglass frames, optical instruments, tableware, and foil in the 1890s and early 20th century. Aluminium's ability to form hard yet light alloys with other metals provided the metal with many uses at the time. During World War I
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was List of wars and anthropogenic disasters by death toll, one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, ...
, major governments demanded large shipments of aluminium for light strong airframes; during World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the World War II by country, vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great power ...
, demand by major governments for aviation was even higher.
By the mid-20th century, aluminium had become a part of everyday life and an essential component of housewares. In 1954, production of aluminium surpassed that of copper
Copper is a chemical element with the symbol Cu (from la, cuprum) and atomic number 29. It is a soft, malleable, and ductile metal with very high thermal and electrical conductivity. A freshly exposed surface of pure copper has a pink ...
, historically second in production only to iron, making it the most produced non-ferrous metal. During the mid-20th century, aluminium emerged as a civil engineering material, with building applications in both basic construction and interior finish work, and increasingly being used in military engineering, for both airplanes and land armor vehicle engines. Earth's first artificial satellite, launched in 1957, consisted of two separate aluminium semi-spheres joined and all subsequent space vehicles have used aluminium to some extent. The aluminium can
An Aluminum can (British English: Tin can) is a single-use container for packaging made primarily of aluminum.
It is commonly used for food and beverages such as milk and soup but also for products such as oil, chemicals, and other liquids. Globa ...
was invented in 1956 and employed as a storage for drinks in 1958.
real price
In economics, nominal value is measured in terms of money, whereas real value is measured against goods or services. A real value is one which has been adjusted for inflation, enabling comparison of quantities as if the prices of goods had not ...
for aluminium declined from $14,000 per metric ton in 1900 to $2,340 in 1948 (in 1998 United States dollars). Extraction and processing costs were lowered over technological progress and the scale of the economies. However, the need to exploit lower-grade poorer quality deposits and the use of fast increasing input costs (above all, energy) increased the net cost of aluminium; the real price began to grow in the 1970s with the rise of energy cost. Production moved from the industrialized countries to countries where production was cheaper. Production costs in the late 20th century changed because of advances in technology, lower energy prices, exchange rates of the United States dollar, and alumina prices. The BRIC countries' combined share in primary production and primary consumption grew substantially in the first decade of the 21st century. China is accumulating an especially large share of the world's production thanks to an abundance of resources, cheap energy, and governmental stimuli; it also increased its consumption share from 2% in 1972 to 40% in 2010. In the United States, Western Europe, and Japan, most aluminium was consumed in transportation, engineering, construction, and packaging. In 2021, prices for industrial metals such as aluminium have soared to near-record levels as energy shortages in China drive up costs for electricity.
Etymology
The names ''aluminium'' and ''aluminum'' are derived from the word ''alumine'', an obsolete term for ''alumina'', a naturally occurring oxide of aluminium. ''Alumine'' was borrowed from French, which in turn derived it from ''alumen'', the classical Latin name for alum, the mineral from which it was collected. The Latin word ''alumen'' stems from theProto-Indo-European
Proto-Indo-European (PIE) is the reconstructed common ancestor of the Indo-European language family. Its proposed features have been derived by linguistic reconstruction from documented Indo-European languages. No direct record of Proto-Indo ...
root ''*alu-'' meaning "bitter" or "beer".

Origins
British chemistHumphry Davy
Sir Humphry Davy, 1st Baronet, (17 December 177829 May 1829) was a British chemist and inventor who invented the Davy lamp and a very early form of arc lamp. He is also remembered for isolating, by using electricity, several elements for ...
, who performed a number of experiments aimed to isolate the metal, is credited as the person who named the element. The first name proposed for the metal to be isolated from alum was ''alumium'', which Davy suggested in an 1808 article on his electrochemical research, published in Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society. It appeared that the name was created from the English word ''alum'' and the Latin suffix ''-ium''; but it was customary then to give elements names originating in Latin, so that this name was not adopted universally. This name was criticized by contemporary chemists from France, Germany, and Sweden, who insisted the metal should be named for the oxide, alumina, from which it would be isolated. The English name ''alum'' does not come directly from Latin, whereas ''alumine''/''alumina'' obviously comes from the Latin word ''alumen'' (upon declension
In linguistics, declension (verb: ''to decline'') is the changing of the form of a word, generally to express its syntactic function in the sentence, by way of some inflection. Declensions may apply to nouns, pronouns, adjectives, adverbs, and ...
, ''alumen'' changes to ''alumin-'').
One example was ''Essai sur la Nomenclature chimique'' (July 1811), written in French by a Swedish chemist, Jöns Jacob Berzelius, in which the name ''aluminium'' is given to the element that would be synthesized from alum.. (Another article in the same journal issue also gives the name ''aluminium'' to the metal whose oxide is the basis of sapphire.) A January 1811 summary of one of Davy's lectures at the Royal Society
The Royal Society, formally The Royal Society of London for Improving Natural Knowledge, is a learned society and the United Kingdom's national academy of sciences. The society fulfils a number of roles: promoting science and its benefits, re ...
mentioned the name ''aluminium'' as a possibility. The next year, Davy published a chemistry textbook in which he used the spelling ''aluminum''. Both spellings have coexisted since. Their usage is regional: ''aluminum'' dominates in the United States and Canada; ''aluminium'', in the rest of the English-speaking world.
Spelling
In 1812, a British scientist, Thomas Young, wrote an anonymous review of Davy's book, in which he proposed the name ''aluminium'' instead of ''aluminum'', which he thought had a "less classical sound". This name did catch on: although the ' spelling was occasionally used in Britain, the American scientific language used ' from the start. Most scientists throughout the world used ' in the 19th century; and it was entrenched in many other European languages, such asFrench
French (french: français(e), link=no) may refer to:
* Something of, from, or related to France
** French language, which originated in France, and its various dialects and accents
** French people, a nation and ethnic group identified with Franc ...
, German
German(s) may refer to:
* Germany (of or related to)
**Germania (historical use)
* Germans, citizens of Germany, people of German ancestry, or native speakers of the German language
** For citizens of Germany, see also German nationality law
**Ge ...
, and Dutch. In 1828, an American lexicographer, Noah Webster
Noah ''Nukh''; am, ኖህ, ''Noḥ''; ar, نُوح '; grc, Νῶε ''Nôe'' () is the tenth and last of the pre-Flood patriarchs in the traditions of Abrahamic religions. His story appears in the Hebrew Bible ( Book of Genesis, chapters ...
, entered only the ''aluminum'' spelling in his ''American Dictionary of the English Language
''Webster's Dictionary'' is any of the English language dictionaries edited in the early 19th century by American lexicographer Noah Webster (1758–1843), as well as numerous related or unrelated dictionaries that have adopted the Webster's n ...
''. In the 1830s, the ' spelling gained usage in the United States; by the 1860s, it had become the more common spelling there outside science. In 1892, Hall used the ' spelling in his advertising handbill for his new electrolytic method of producing the metal, despite his constant use of the ' spelling in all the patents he filed between 1886 and 1903: it is unknown whether this spelling was introduced by mistake or intentionally; but Hall preferred ''aluminum'' since its introduction because it resembled ''platinum
Platinum is a chemical element with the symbol Pt and atomic number 78. It is a dense, malleable, ductile, highly unreactive, precious, silverish-white transition metal. Its name originates from Spanish , a diminutive of "silver".
Pla ...
'', the name of a prestigious metal. By 1890, both spellings had been common in the United States, the ' spelling being slightly more common; by 1895, the situation had reversed; by 1900, ''aluminum'' had become twice as common as ''aluminium''; in the next decade, the ' spelling dominated American usage. In 1925, the American Chemical Society
The American Chemical Society (ACS) is a scientific society based in the United States that supports scientific inquiry in the field of chemistry. Founded in 1876 at New York University, the ACS currently has more than 155,000 members at all ...
adopted this spelling.
The International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry
The International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC ) is an international federation of National Adhering Organizations working for the advancement of the chemical sciences, especially by developing nomenclature and terminology. It is ...
(IUPAC) adopted ''aluminium'' as the standard international name for the element in 1990. In 1993, they recognized ''aluminum'' as an acceptable variant; the most recent 2005 edition of the IUPAC nomenclature of inorganic chemistry also acknowledges this spelling. IUPAC official publications use the ' spelling as primary, and they list both where it is appropriate.
Production and refinement
The production of aluminium starts with the extraction ofbauxite
Bauxite is a sedimentary rock with a relatively high aluminium content. It is the world's main source of aluminium and gallium. Bauxite consists mostly of the aluminium minerals gibbsite (Al(OH)3), boehmite (γ-AlO(OH)) and diaspore (α-AlO ...
rock from the ground. The bauxite is processed and transformed using the Bayer process
The Bayer process is the principal industrial means of refining bauxite to produce alumina (aluminium oxide) and was developed by Carl Josef Bayer. Bauxite, the most important ore of aluminium, contains only 30–60% aluminium oxide (Al2O3), th ...
into alumina, which is then processed using the Hall–Héroult process, resulting in the final aluminium metal.
Aluminium production is highly energy-consuming, and so the producers tend to locate smelters in places where electric power is both plentiful and inexpensive. As of 2019, the world's largest smelters of aluminium are located in China, India, Russia, Canada, and the United Arab Emirates, while China is by far the top producer of aluminium with a world share of fifty-five percent.
According to the International Resource Panel's Metal Stocks in Society report, the global per capita stock of aluminium in use in society (i.e. in cars, buildings, electronics, etc.) is . Much of this is in more-developed countries ( per capita) rather than less-developed countries ( per capita).
Bayer process
Bauxite
Bauxite is a sedimentary rock with a relatively high aluminium content. It is the world's main source of aluminium and gallium. Bauxite consists mostly of the aluminium minerals gibbsite (Al(OH)3), boehmite (γ-AlO(OH)) and diaspore (α-AlO ...
is converted to alumina by the Bayer process. Bauxite is blended for uniform composition and then is ground. The resulting slurry is mixed with a hot solution of sodium hydroxide; the mixture is then treated in a digester vessel at a pressure well above atmospheric, dissolving the aluminium hydroxide in bauxite while converting impurities into relatively insoluble compounds:
After this reaction, the slurry is at a temperature above its atmospheric boiling point. It is cooled by removing steam as pressure is reduced. The bauxite residue is separated from the solution and discarded. The solution, free of solids, is seeded with small crystals of aluminium hydroxide; this causes decomposition of the l(OH)4sup>− ions to aluminium hydroxide. After about half of aluminium has precipitated, the mixture is sent to classifiers. Small crystals of aluminium hydroxide are collected to serve as seeding agents; coarse particles are converted to alumina by heating; the excess solution is removed by evaporation, (if needed) purified, and recycled.
Hall–Héroult process
 The conversion of alumina to aluminium metal is achieved by the Hall–Héroult process. In this energy-intensive process, a solution of alumina in a molten () mixture of cryolite (Na3AlF6) with calcium fluoride is electrolyzed to produce metallic aluminium. The liquid aluminium metal sinks to the bottom of the solution and is tapped off, and usually cast into large blocks called aluminium billets for further processing.
Anodes of the electrolysis cell are made of carbon—the most resistant material against fluoride corrosion—and either bake at the process or are prebaked. The former, also called Söderberg anodes, are less power-efficient and fumes released during baking are costly to collect, which is why they are being replaced by prebaked anodes even though they save the power, energy, and labor to prebake the cathodes. Carbon for anodes should be preferably pure so that neither aluminium nor the electrolyte is contaminated with ash. Despite carbon's resistivity against corrosion, it is still consumed at a rate of 0.4–0.5 kg per each kilogram of produced aluminium. Cathodes are made of anthracite; high purity for them is not required because impurities
The conversion of alumina to aluminium metal is achieved by the Hall–Héroult process. In this energy-intensive process, a solution of alumina in a molten () mixture of cryolite (Na3AlF6) with calcium fluoride is electrolyzed to produce metallic aluminium. The liquid aluminium metal sinks to the bottom of the solution and is tapped off, and usually cast into large blocks called aluminium billets for further processing.
Anodes of the electrolysis cell are made of carbon—the most resistant material against fluoride corrosion—and either bake at the process or are prebaked. The former, also called Söderberg anodes, are less power-efficient and fumes released during baking are costly to collect, which is why they are being replaced by prebaked anodes even though they save the power, energy, and labor to prebake the cathodes. Carbon for anodes should be preferably pure so that neither aluminium nor the electrolyte is contaminated with ash. Despite carbon's resistivity against corrosion, it is still consumed at a rate of 0.4–0.5 kg per each kilogram of produced aluminium. Cathodes are made of anthracite; high purity for them is not required because impurities leach
Leach may refer to:
* Leach (surname)
* Leach, Oklahoma, an unincorporated community, United States
* Leach, Tennessee, an unincorporated community, United States
* Leach Highway, Western Australia
* Leach orchid
* Leach phenotype, a mutatio ...
only very slowly. The cathode is consumed at a rate of 0.02–0.04 kg per each kilogram of produced aluminium. A cell is usually terminated after 2–6 years following a failure of the cathode.
The Hall–Heroult process produces aluminium with a purity of above 99%. Further purification can be done by the Hoopes process. This process involves the electrolysis of molten aluminium with a sodium, barium, and aluminium fluoride electrolyte. The resulting aluminium has a purity of 99.99%.
Electric power represents about 20 to 40% of the cost of producing aluminium, depending on the location of the smelter. Aluminium production consumes roughly 5% of electricity generated in the United States. Because of this, alternatives to the Hall–Héroult process have been researched, but none has turned out to be economically feasible.
Recycling
 Recovery of the metal through
Recovery of the metal through recycling
Recycling is the process of converting waste materials into new materials and objects. The Energy recycling, recovery of energy from waste materials is often included in this concept. The recyclability of a material depends on its ability t ...
has become an important task of the aluminium industry. Recycling was a low-profile activity until the late 1960s, when the growing use of aluminium beverage can
A drink can (or beverage can) is a metal container designed to hold a fixed portion of liquid such as carbonated soft drinks, alcoholic drinks, fruit juices, teas, herbal teas, energy drinks, etc. Drink cans are made of aluminum (75% ...
s brought it to public awareness. Recycling involves melting the scrap, a process that requires only 5% of the energy used to produce aluminium from ore, though a significant part (up to 15% of the input material) is lost as dross (ash-like oxide). An aluminium stack melter produces significantly less dross, with values reported below 1%.
White dross from primary aluminium production and from secondary recycling operations still contains useful quantities of aluminium that can be extracted industrially. The process produces aluminium billets, together with a highly complex waste material. This waste is difficult to manage. It reacts with water, releasing a mixture of gases (including, among others, hydrogen
Hydrogen is the chemical element with the symbol H and atomic number 1. Hydrogen is the lightest element. At standard conditions hydrogen is a gas of diatomic molecules having the formula . It is colorless, odorless, tasteless, non-to ...
, acetylene, and ammonia
Ammonia is an inorganic compound of nitrogen and hydrogen with the formula . A stable binary hydride, and the simplest pnictogen hydride, ammonia is a colourless gas with a distinct pungent smell. Biologically, it is a common nitrogenous ...
), which spontaneously ignites on contact with air; contact with damp air results in the release of copious quantities of ammonia gas. Despite these difficulties, the waste is used as a filler in asphalt
Asphalt, also known as bitumen (, ), is a sticky, black, highly viscous liquid or semi-solid form of petroleum. It may be found in natural deposits or may be a refined product, and is classed as a pitch. Before the 20th century, the term ...
and concrete
Concrete is a composite material composed of fine and coarse aggregate bonded together with a fluid cement (cement paste) that hardens (cures) over time. Concrete is the second-most-used substance in the world after water, and is the most wid ...
.
Applications

Metal
The global production of aluminium in 2016 was 58.8 million metric tons. It exceeded that of any other metal exceptiron
Iron () is a chemical element with symbol Fe (from la, ferrum) and atomic number 26. It is a metal that belongs to the first transition series and group 8 of the periodic table. It is, by mass, the most common element on Earth, right in ...
(1,231 million metric tons).
Aluminium is almost always alloyed, which markedly improves its mechanical properties, especially when tempered. For example, the common aluminium foil
Aluminium foil (or aluminum foil in North American English; often informally called tin foil) is aluminium prepared in thin metal leaves with a thickness less than ; thinner gauges down to are also commonly used. Standard household foil is typ ...
s and beverage cans are alloys of 92% to 99% aluminium. The main alloying
An alloy is a mixture of chemical elements of which at least one is a metal. Unlike chemical compounds with metallic bases, an alloy will retain all the properties of a metal in the resulting material, such as electrical conductivity, ductility, ...
agents are copper
Copper is a chemical element with the symbol Cu (from la, cuprum) and atomic number 29. It is a soft, malleable, and ductile metal with very high thermal and electrical conductivity. A freshly exposed surface of pure copper has a pink ...
, zinc
Zinc is a chemical element with the symbol Zn and atomic number 30. Zinc is a slightly brittle metal at room temperature and has a shiny-greyish appearance when oxidation is removed. It is the first element in group 12 (IIB) of the periodi ...
, magnesium
Magnesium is a chemical element with the symbol Mg and atomic number 12. It is a shiny gray metal having a low density, low melting point and high chemical reactivity. Like the other alkaline earth metals (group 2 of the periodic ...
, manganese
Manganese is a chemical element with the Symbol (chemistry), symbol Mn and atomic number 25. It is a hard, brittle, silvery metal, often found in minerals in combination with iron. Manganese is a transition metal with a multifaceted array of ...
, and silicon
Silicon is a chemical element with the symbol Si and atomic number 14. It is a hard, brittle crystalline solid with a blue-grey metallic luster, and is a tetravalent metalloid and semiconductor. It is a member of group 14 in the periodic ...
(e.g., duralumin) with the levels of other metals in a few percent by weight. Aluminium, both wrought and cast, has been alloyed with: manganese
Manganese is a chemical element with the Symbol (chemistry), symbol Mn and atomic number 25. It is a hard, brittle, silvery metal, often found in minerals in combination with iron. Manganese is a transition metal with a multifaceted array of ...
, silicon
Silicon is a chemical element with the symbol Si and atomic number 14. It is a hard, brittle crystalline solid with a blue-grey metallic luster, and is a tetravalent metalloid and semiconductor. It is a member of group 14 in the periodic ...
, magnesium
Magnesium is a chemical element with the symbol Mg and atomic number 12. It is a shiny gray metal having a low density, low melting point and high chemical reactivity. Like the other alkaline earth metals (group 2 of the periodic ...
, copper
Copper is a chemical element with the symbol Cu (from la, cuprum) and atomic number 29. It is a soft, malleable, and ductile metal with very high thermal and electrical conductivity. A freshly exposed surface of pure copper has a pink ...
and zinc
Zinc is a chemical element with the symbol Zn and atomic number 30. Zinc is a slightly brittle metal at room temperature and has a shiny-greyish appearance when oxidation is removed. It is the first element in group 12 (IIB) of the periodi ...
among others. For example, the Kynal family of alloys was developed by the British chemical manufacturer Imperial Chemical Industries.
 The major uses for aluminium metal are in:
* Transportation (
The major uses for aluminium metal are in:
* Transportation (automobile
A car or automobile is a motor vehicle with wheels. Most definitions of ''cars'' say that they run primarily on roads, seat one to eight people, have four wheels, and mainly transport people instead of goods.
The year 1886 is regarded ...
s, aircraft, trucks, railway car
A railroad car, railcar (American and Canadian English), railway wagon, railway carriage, railway truck, railwagon, railcarriage or railtruck (British English and UIC), also called a train car, train wagon, train carriage or train truck, is a ...
s, marine vessels, bicycles, spacecraft, ''etc.''). Aluminium is used because of its low density;
* Packaging ( cans, foil, frame, ''etc.''). Aluminium is used because it is non-toxic (see below
Below may refer to:
*Earth
* Ground (disambiguation)
*Soil
*Floor
* Bottom (disambiguation)
*Less than
*Temperatures below freezing
*Hell or underworld
People with the surname
*Ernst von Below (1863–1955), German World War I general
*Fred Below ...
), non- adsorptive, and splinter
A splinter (also known as a sliver) is a fragment of a larger object, or a foreign body that penetrates or is purposely injected into a body. The foreign body must be lodged inside tissue to be considered a splinter. Splinters may cause initia ...
-proof;
* Building and construction ( windows, doors, siding, building wire, sheathing, roofing, ''etc.''). Since steel is cheaper, aluminium is used when lightness, corrosion resistance, or engineering features are important;
* Electricity-related uses (conductor alloys, motors, and generators, transformers, capacitors, ''etc.''). Aluminium is used because it is relatively cheap, highly conductive, has adequate mechanical strength and low density, and resists corrosion;
* A wide range of household
A household consists of two or more persons who live in the same dwelling. It may be of a single family or another type of person group. The household is the basic unit of analysis in many social, microeconomic and government models, and is i ...
items, from cooking utensils to furniture. Low density, good appearance, ease of fabrication, and durability are the key factors of aluminium usage;
* Machinery and equipment (processing equipment, pipes, tools). Aluminium is used because of its corrosion resistance, non- pyrophoricity, and mechanical strength.
* Portable computer cases. Currently rarely used without alloying, but aluminium can be recycled and clean aluminium has residual market value: for example, the used beverage can (UBC) material was used to encase the electronic components of MacBook Air laptop, Pixel 5 smartphone or Summit Lite smartwatch.
Compounds
The great majority (about 90%) of aluminium oxide is converted to metallic aluminium. Being a very hard material (Mohs hardness
The Mohs scale of mineral hardness () is a qualitative ordinal scale, from 1 to 10, characterizing scratch resistance of various minerals through the ability of harder material to scratch softer material.
The scale was introduced in 1812 by ...
9), alumina is widely used as an abrasive; being extraordinarily chemically inert, it is useful in highly reactive environments such as high pressure sodium lamps. Aluminium oxide is commonly used as a catalyst for industrial processes; e.g. the Claus process to convert hydrogen sulfide to sulfur in refineries and to alkylate amine
In chemistry, amines (, ) are compounds and functional groups that contain a basic nitrogen atom with a lone pair. Amines are formally derivatives of ammonia (), wherein one or more hydrogen atoms have been replaced by a substituent ...
s. Many industrial catalysts are supported by alumina, meaning that the expensive catalyst
Catalysis () is the process of increasing the rate of a chemical reaction by adding a substance known as a catalyst (). Catalysts are not consumed in the reaction and remain unchanged after it. If the reaction is rapid and the catalyst recyc ...
material is dispersed over a surface of the inert alumina. Another principal use is as a drying agent or absorbent.
 Several sulfates of aluminium have industrial and commercial application. Aluminium sulfate (in its hydrate form) is produced on the annual scale of several millions of metric tons. About two-thirds is consumed in water treatment. The next major application is in the manufacture of paper. It is also used as a mordant in dyeing, in pickling seeds, deodorizing of mineral oils, in leather tanning, and in production of other aluminium compounds. Two kinds of alum,
Several sulfates of aluminium have industrial and commercial application. Aluminium sulfate (in its hydrate form) is produced on the annual scale of several millions of metric tons. About two-thirds is consumed in water treatment. The next major application is in the manufacture of paper. It is also used as a mordant in dyeing, in pickling seeds, deodorizing of mineral oils, in leather tanning, and in production of other aluminium compounds. Two kinds of alum, ammonium alum
Ammonium aluminium sulfate, also known as ammonium alum or just alum (though there are many different substances also called "alum"), is a white crystalline double sulfate usually encountered as the dodecahydrate, formula (NH4)Al(SO4)2·12H2O. It ...
and potassium alum, were formerly used as mordants and in leather tanning, but their use has significantly declined following availability of high-purity aluminium sulfate. Anhydrous aluminium chloride is used as a catalyst in chemical and petrochemical industries, the dyeing industry, and in synthesis of various inorganic and organic compounds. Aluminium hydroxychlorides are used in purifying water, in the paper industry, and as antiperspirants
A deodorant is a substance applied to the body to prevent or mask body odor due to bacterial breakdown of perspiration or vaginal secretions, for example in the armpits, groin, or feet. A subclass of deodorants, called antiperspirants, prevents ...
. Sodium aluminate is used in treating water and as an accelerator of solidification of cement.
Many aluminium compounds have niche applications, for example:
* Aluminium acetate in solution is used as an astringent.
* Aluminium phosphate is used in the manufacture of glass, ceramic, pulp and paper products, cosmetics
Cosmetics are constituted mixtures of chemical compounds derived from either natural sources, or synthetically created ones. Cosmetics have various purposes. Those designed for personal care and skin care can be used to cleanse or protec ...
, paints, varnishes, and in dental cement
A cement is a binder, a chemical substance used for construction that sets, hardens, and adheres to other materials to bind them together. Cement is seldom used on its own, but rather to bind sand and gravel (aggregate) together. Cement mixe ...
.
* Aluminium hydroxide
Aluminium hydroxide, Al(OH)3, is found in nature as the mineral gibbsite (also known as hydrargillite) and its three much rarer polymorphs: bayerite, doyleite, and nordstrandite. Aluminium hydroxide is amphoteric, i.e., it has both basic ...
is used as an antacid, and mordant; it is used also in water
Water (chemical formula ) is an inorganic, transparent, tasteless, odorless, and nearly colorless chemical substance, which is the main constituent of Earth's hydrosphere and the fluids of all known living organisms (in which it acts as ...
purification, the manufacture of glass and ceramics, and in the waterproofing
Waterproofing is the process of making an object or structure waterproof or water-resistant so that it remains relatively unaffected by water or resisting the ingress of water under specified conditions. Such items may be used in wet environme ...
of fabrics.
* Lithium aluminium hydride is a powerful reducing agent used in organic chemistry
Organic chemistry is a subdiscipline within chemistry involving the scientific study of the structure, properties, and reactions of organic compounds and organic materials, i.e., matter in its various forms that contain carbon atoms.Clayden, J ...
.
* Organoaluminiums are used as Lewis acids and co-catalysts.
* Methylaluminoxane is a co-catalyst for Ziegler–Natta olefin polymerization
In polymer chemistry, polymerization (American English), or polymerisation (British English), is a process of reacting monomer molecules together in a chemical reaction to form polymer chains or three-dimensional networks. There are many f ...
to produce vinyl polymer
In polymer chemistry, vinyl polymers are a group of polymers derived from substituted vinyl () monomers. Their backbone is an extended alkane chain . In popular usage, "vinyl" refers only to polyvinyl chloride (PVC).
Examples
Vinyl polymers ...
s such as polyethene.
* Aqueous aluminium ions (such as aqueous aluminium sulfate) are used to treat against fish parasites such as '' Gyrodactylus salaris''.
* In many vaccines, certain aluminium salts serve as an immune adjuvant In pharmacology, an adjuvant is a drug or other substance, or a combination of substances, that is used to increase the efficacy or potency of certain drugs. Specifically, the term can refer to:
* Adjuvant therapy in cancer management
* Analgesi ...
(immune response booster) to allow the protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, res ...
in the vaccine to achieve sufficient potency as an immune stimulant.
Aluminized substrates
Aluminizing is the process of coating a structure or material with a thin layer of aluminium. It is done to impart specific traits that the underlying substrate lacks, such as a certain chemical or physical property. Aluminized materials include: * Aluminized steel, for corrosion resistance and other properties *Aluminized screen
Aluminized screen may refer to a type of cathode ray tube (CRT) for video display, or to a type of projection screen for showing motion pictures or slides, especially in polarized 3D.
Some cathode ray tubes, e.g., television picture tubes, inclu ...
, for display devices
* Aluminized cloth, to reflect heat
* Aluminized mylar, to reflect heat
Biology
 Despite its widespread occurrence in the Earth's crust, aluminium has no known function in biology. At pH 6–9 (relevant for most natural waters), aluminium precipitates out of water as the hydroxide and is hence not available; most elements behaving this way have no biological role or are toxic. Aluminium sulfate has an LD50 of 6207 mg/kg (oral, mouse), which corresponds to 435 grams for an person.
Despite its widespread occurrence in the Earth's crust, aluminium has no known function in biology. At pH 6–9 (relevant for most natural waters), aluminium precipitates out of water as the hydroxide and is hence not available; most elements behaving this way have no biological role or are toxic. Aluminium sulfate has an LD50 of 6207 mg/kg (oral, mouse), which corresponds to 435 grams for an person.
Toxicity
Aluminium is classified as a non-carcinogen by the United States Department of Health and Human Services. A review published in 1988 said that there was little evidence that normal exposure to aluminium presents a risk to healthy adult, and a 2014 multi-element toxicology review was unable to find deleterious effects of aluminium consumed in amounts not greater than 40 mg/day per kg ofbody mass
Human body weight is a person's mass or weight.
Strictly speaking, body weight is the measurement of weight without items located on the person. Practically though, body weight may be measured with clothes on, but without shoes or heavy accesso ...
. Most aluminium consumed will leave the body in feces; most of the small part of it that enters the bloodstream, will be excreted via urine; nevertheless some aluminium does pass the blood-brain barrier and is lodged preferentially in the brains of Alzheimer's patients.
Evidence published in 1989 indicates that, for Alzheimer's patients, aluminium may act by electrostatically crosslink
In chemistry and biology a cross-link is a bond or a short sequence of bonds that links one polymer chain to another. These links may take the form of covalent bonds or ionic bonds and the polymers can be either synthetic polymers or natural ...
ing proteins, thus down-regulating genes in the superior temporal gyrus
The superior temporal gyrus (STG) is one of three (sometimes two) gyri in the temporal lobe of the human brain, which is located laterally to the head, situated somewhat above the external ear.
The superior temporal gyrus is bounded by:
* the l ...
.
Effects
Aluminium, although rarely, can cause vitamin D-resistant osteomalacia, erythropoietin-resistant microcytic anemia, and central nervous system alterations. People with kidney insufficiency are especially at a risk. Chronic ingestion of hydrated aluminium silicates (for excess gastric acidity control) may result in aluminium binding to intestinal contents and increased elimination of other metals, such asiron
Iron () is a chemical element with symbol Fe (from la, ferrum) and atomic number 26. It is a metal that belongs to the first transition series and group 8 of the periodic table. It is, by mass, the most common element on Earth, right in ...
or zinc
Zinc is a chemical element with the symbol Zn and atomic number 30. Zinc is a slightly brittle metal at room temperature and has a shiny-greyish appearance when oxidation is removed. It is the first element in group 12 (IIB) of the periodi ...
; sufficiently high doses (>50 g/day) can cause anemia.
 During the 1988 Camelford water pollution incident people in Camelford had their drinking water contaminated with aluminium sulfate for several weeks. A final report into the incident in 2013 concluded it was unlikely that this had caused long-term health problems.
Aluminium has been suspected of being a possible cause of Alzheimer's disease, but research into this for over 40 years has found, , no good evidence of causal effect.
Aluminium increases
During the 1988 Camelford water pollution incident people in Camelford had their drinking water contaminated with aluminium sulfate for several weeks. A final report into the incident in 2013 concluded it was unlikely that this had caused long-term health problems.
Aluminium has been suspected of being a possible cause of Alzheimer's disease, but research into this for over 40 years has found, , no good evidence of causal effect.
Aluminium increases estrogen
Estrogen or oestrogen is a category of sex hormone responsible for the development and regulation of the female reproductive system and secondary sex characteristics. There are three major endogenous estrogens that have estrogenic hormonal ac ...
-related gene expression in human breast cancer
Breast cancer is cancer that develops from breast tissue. Signs of breast cancer may include a lump in the breast, a change in breast shape, dimpling of the skin, milk rejection, fluid coming from the nipple, a newly inverted nipple, or ...
cells cultured in the laboratory. In very high doses, aluminium is associated with altered function of the blood–brain barrier. A small percentage of people have contact allergies to aluminium and experience itchy red rashes, headache, muscle pain, joint pain, poor memory, insomnia, depression, asthma, irritable bowel syndrome, or other symptoms upon contact with products containing aluminium.
Exposure to powdered aluminium or aluminium welding fumes can cause pulmonary fibrosis. Fine aluminium powder can ignite or explode, posing another workplace hazard.
Exposure routes
Food is the main source of aluminium. Drinking water contains more aluminium than solid food; however, aluminium in food may be absorbed more than aluminium from water. Major sources of human oral exposure to aluminium include food (due to its use in food additives, food and beverage packaging, and cooking utensils), drinking water (due to its use in municipal water treatment), and aluminium-containing medications (particularly antacid/antiulcer and buffered aspirin formulations). Dietary exposure in Europeans averages to 0.2–1.5 mg/kg/week but can be as high as 2.3 mg/kg/week. Higher exposure levels of aluminium are mostly limited to miners, aluminium production workers, and dialysis patients. Consumption of antacids, antiperspirants, vaccines, and cosmetics provide possible routes of exposure. Consumption of acidic foods or liquids with aluminium enhances aluminium absorption, and maltol has been shown to increase the accumulation of aluminium in nerve and bone tissues.Treatment
In case of suspected sudden intake of a large amount of aluminium, the only treatment is deferoxamine mesylate which may be given to help eliminate aluminium from the body by chelation. However, this should be applied with caution as this reduces not only aluminium body levels, but also those of other metals such as copper or iron.Environmental effects
 High levels of aluminium occur near mining sites; small amounts of aluminium are released to the environment at the coal-fired power plants or
High levels of aluminium occur near mining sites; small amounts of aluminium are released to the environment at the coal-fired power plants or incinerators
Incineration is a waste treatment process that involves the combustion of substances contained in waste materials. Industrial plants for waste incineration are commonly referred to as waste-to-energy facilities. Incineration and other high ...
. Aluminium in the air is washed out by the rain or normally settles down but small particles of aluminium remain in the air for a long time.
Acidic precipitation
In meteorology, precipitation is any product of the condensation of atmospheric water vapor that falls under gravitational pull from clouds. The main forms of precipitation include drizzle, rain, sleet, snow, ice pellets, graupel and hail. ...
is the main natural factor to mobilize aluminium from natural sources and the main reason for the environmental effects of aluminium; however, the main factor of presence of aluminium in salt and freshwater are the industrial processes that also release aluminium into air.
In water, aluminium acts as a toxiс agent on gill
A gill () is a respiratory organ that many aquatic organisms use to extract dissolved oxygen from water and to excrete carbon dioxide. The gills of some species, such as hermit crabs, have adapted to allow respiration on land provided they ar ...
-breathing animals such as fish
Fish are Aquatic animal, aquatic, craniate, gill-bearing animals that lack Limb (anatomy), limbs with Digit (anatomy), digits. Included in this definition are the living hagfish, lampreys, and Chondrichthyes, cartilaginous and bony fish as we ...
when the water is acidic, in which aluminium may precipitate on gills, which causes loss of plasma- and hemolymph
Hemolymph, or haemolymph, is a fluid, analogous to the blood in vertebrates, that circulates in the interior of the arthropod (invertebrate) body, remaining in direct contact with the animal's tissues. It is composed of a fluid plasma in which ...
ions leading to osmoregulatory
Osmoregulation is the active regulation of the osmotic pressure of an organism's body fluids, detected by osmoreceptors, to maintain the homeostasis of the organism's water content; that is, it maintains the fluid balance and the concentration o ...
failure. Organic complexes of aluminium may be easily absorbed and interfere with metabolism in mammals and birds, even though this rarely happens in practice.
Aluminium is primary among the factors that reduce plant growth on acidic soils. Although it is generally harmless to plant growth in pH-neutral soils, in acid soils the concentration of toxic Al3+ cations increases and disturbs root growth and function. Wheat
Wheat is a grass widely cultivated for its seed, a cereal grain that is a worldwide staple food. The many species of wheat together make up the genus ''Triticum'' ; the most widely grown is common wheat (''T. aestivum''). The archaeologi ...
has developed a tolerance to aluminium, releasing organic compound
In chemistry, organic compounds are generally any chemical compounds that contain carbon-hydrogen or carbon-carbon bonds. Due to carbon's ability to catenate (form chains with other carbon atoms), millions of organic compounds are known. Th ...
s that bind to harmful aluminium cations. Sorghum is believed to have the same tolerance mechanism.
Aluminium production possesses its own challenges to the environment on each step of the production process. The major challenge is the greenhouse gas emissions
Greenhouse gas emissions from human activities strengthen the greenhouse effect, contributing to climate change. Most is carbon dioxide from burning fossil fuels: coal, oil, and natural gas. The largest emitters include coal in China and ...
. These gases result from electrical consumption of the smelters and the byproducts of processing. The most potent of these gases are perfluorocarbons from the smelting process. Released sulfur dioxide
Sulfur dioxide (IUPAC-recommended spelling) or sulphur dioxide (traditional Commonwealth English) is the chemical compound with the formula . It is a toxic gas responsible for the odor of burnt matches. It is released naturally by volcanic a ...
is one of the primary precursors of acid rain.
Biodegradation of metallic aluminium is extremely rare; most aluminium-corroding organisms do not directly attack or consume the aluminium, but instead produce corrosive wastes. The fungus ''Geotrichum candidum
''Geotrichum candidum'' is a fungus which is a member of the human microbiome, notably associated with skin, sputum, and faeces where it occurs in 25–30% of specimens. It is common in soil and has been isolated from soil collected around the w ...
'' can consume the aluminium in compact disc
The compact disc (CD) is a digital optical disc data storage format that was co-developed by Philips and Sony to store and play digital audio recordings. In August 1982, the first compact disc was manufactured. It was then released in O ...
s. The bacterium ''Pseudomonas aeruginosa
''Pseudomonas aeruginosa'' is a common encapsulated, gram-negative, aerobic– facultatively anaerobic, rod-shaped bacterium that can cause disease in plants and animals, including humans. A species of considerable medical importance, ''P. a ...
'' and the fungus ''Cladosporium
''Cladosporium'' is a genus of fungi including some of the most common indoor and outdoor molds. Species produce olive-green to brown or black colonies, and have dark-pigmented conidia that are formed in simple or branching chains. Many specie ...
resinae'' are commonly detected in aircraft fuel tanks that use kerosene
Kerosene, paraffin, or lamp oil is a combustible hydrocarbon liquid which is derived from petroleum. It is widely used as a fuel in aviation as well as households. Its name derives from el, κηρός (''keros'') meaning " wax", and was re ...
-based fuels (not avgas), and laboratory cultures can degrade aluminium.
See also
*Aluminium granules
Aluminium granules are fine spherical aggregates of aluminium.
Manufacture
Aluminium granules are manufactured by the melting of primary or secondary aluminium and blown in air or vacuum, or are cast in sand and then sieved off. Other methods i ...
* Aluminium joining
Aluminium alloys are often chosen due to their high strength-to-weight ratio, corrosion resistance, low cost, high thermal and electrical conductivity. There are a variety of techniques to join aluminium including mechanical fasteners, welding, adh ...
* Aluminium–air battery
* Panel edge staining
* Quantum clock
Notes
References
Bibliography
* * * * * * * * *Further reading
* Mimi Sheller, ''Aluminum Dream: The Making of Light Modernity''. Cambridge, Mass.: Massachusetts Institute of Technology Press, 2014.External links
Aluminium
at '' The Periodic Table of Videos'' (University of Nottingham) *
Toxic Substances Portal – Aluminum
' – from the
Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry
The Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry (ATSDR) is a federal public health agency within the United States Department of Health and Human Services. The agency focuses on minimizing human health risks associated with exposure to haz ...
, United States Department of Health and Human Services
CDC – NIOSH Pocket Guide to Chemical Hazards – Aluminum
Price history of aluminum, according to the IMF
History of Aluminium
– from the website of the International Aluminium Institute
* {{Authority control Chemical elements Post-transition metals
Aluminium
Aluminium (aluminum in American and Canadian English) is a chemical element with the symbol Al and atomic number 13. Aluminium has a density lower than those of other common metals, at approximately one third that of steel. It ha ...
Electrical conductors
Pyrotechnic fuels
Airship technology
Reducing agents
E-number additives
Native element minerals
Chemical elements with face-centered cubic structure